南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 245-253.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.05
• • 上一篇
赵亚莉1( ), 李佳怡1, 谷变利1, 陈攀1, 张理1, 张小漫2, 杨平娟1, 石林林1(
), 李佳怡1, 谷变利1, 陈攀1, 张理1, 张小漫2, 杨平娟1, 石林林1( ), 高社干1(
), 高社干1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-10-14
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-03-03
通讯作者:
石林林,高社干
E-mail:676305392@qq.com;celine_shih@ haust.edu.cn;gsg112258@163.com
作者简介:赵亚莉,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 676305392@qq.com
基金资助:
Yali ZHAO1( ), Jiayi LI1, Bianli GU1, Pan CHEN1, Li ZHANG1, Xiaoman ZHANG2, Pingjuan YANG1, Linlin SHI1(
), Jiayi LI1, Bianli GU1, Pan CHEN1, Li ZHANG1, Xiaoman ZHANG2, Pingjuan YANG1, Linlin SHI1( ), Shegan GAO1(
), Shegan GAO1( )
)
Received:2024-10-14
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Linlin SHI, Shegan GAO
E-mail:676305392@qq.com;celine_shih@ haust.edu.cn;gsg112258@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨Ag2Se纳米颗粒清除食管癌胞内牙龈卟啉单胞菌(P. gingivalis)的有效性,并研究清除P. gingivalis后对食管癌恶性进展的影响。 方法 采用化学合成法制备Ag2Se纳米颗粒,通过荧光染色分析和菌落形成实验,评估Ag2Se纳米颗粒对P. gingivalis活性和克隆形成能力的影响;构建P. gingivalis感染的小鼠食管癌皮下荷瘤模型,通过RNAscope原位杂交和定量聚合酶链反应(qPCR)测定治疗后肿瘤组织中P. gingivalis的丰度,并监测荷瘤小鼠肿瘤体积的变化,以评估Ag2Se纳米颗粒清除肿瘤组织中P. gingivalis后对小鼠食管癌恶性进展的影响。通过评估小鼠肝肾功能及主要脏器的病理变化,以评估Ag2Se纳米颗粒的生物安全性。 结果 透射电子显微镜(TEM)的结果显示,本研究制备的Ag2Se为直径50 nm左右的均匀分散球形纳米颗粒。体外实验结果表明Ag2Se纳米颗粒能降低P. gingivalis的活力和克隆增殖能力,且随浓度的增加而逐渐增强(P<0.05)。体内实验结果证实,经Ag2Se纳米颗粒治疗后,小鼠肿瘤组织中P. gingivalis的丰度降低、恶性增殖能力得到抑制(P<0.01)。治疗期间小鼠的肝肾功能和主要脏器未出现明显损伤,提示Ag2Se纳米颗粒具有良好的生物相容性。 结论 Ag2Se纳米颗粒对P. gingivalis具有显著的杀伤和抑制作用,在体内可有效清除胞内P. gingivalis,抑制食管癌的恶性进展,为食管癌的预防和治疗提供新的理论依据。
赵亚莉, 李佳怡, 谷变利, 陈攀, 张理, 张小漫, 杨平娟, 石林林, 高社干. Ag₂Se纳米颗粒通过清除牙龈卟啉单胞菌抑制食管癌恶性进展[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 245-253.
Yali ZHAO, Jiayi LI, Bianli GU, Pan CHEN, Li ZHANG, Xiaoman ZHANG, Pingjuan YANG, Linlin SHI, Shegan GAO. Ag2Se nanoparticles suppress growth of murine esophageal cancer allograft in mice by eliminating Porphyromonas gingivalis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 245-253.
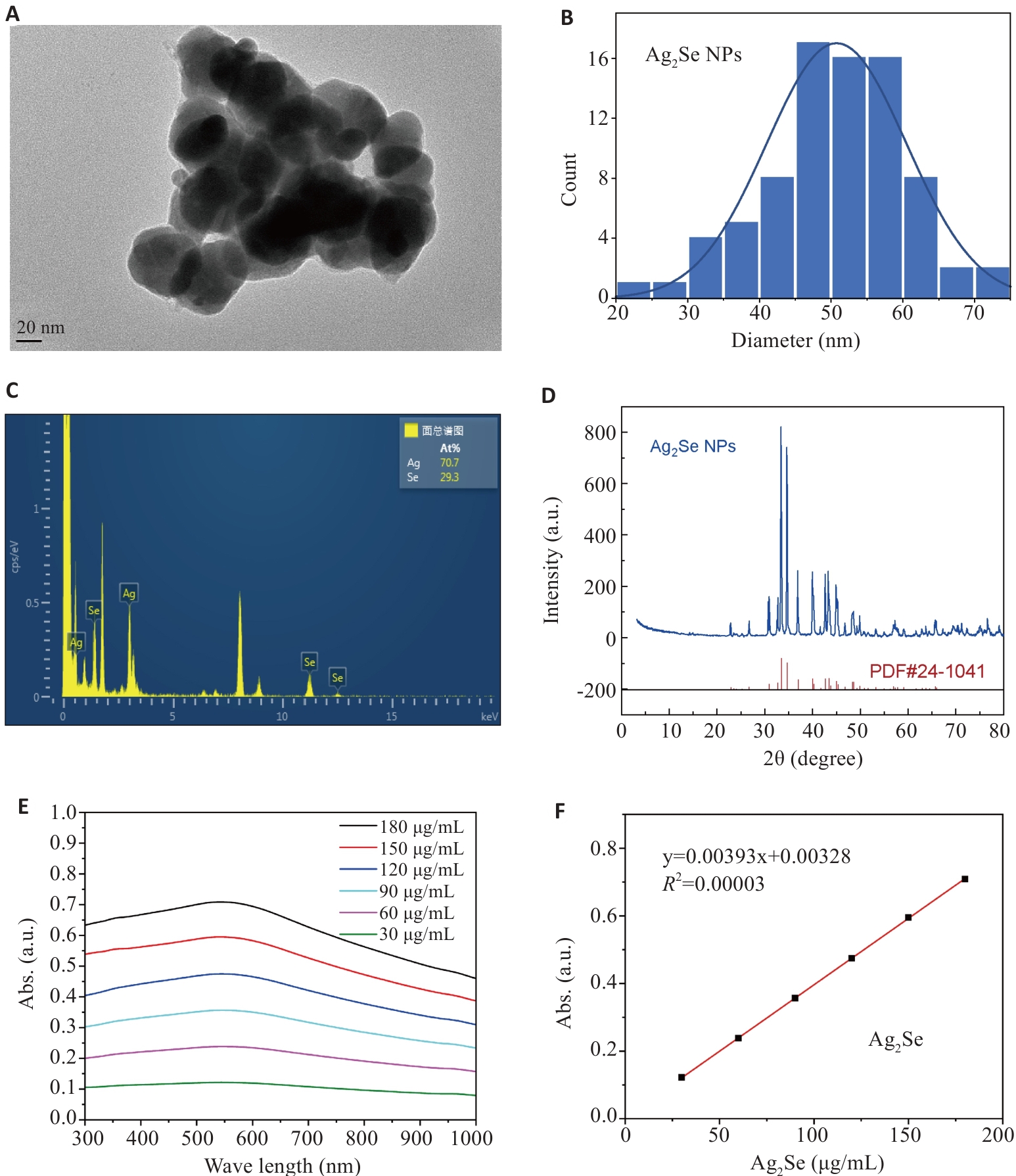
图1 Ag2Se纳米颗粒的表征
Fig.1 Characterization of Ag2Se nanoparticles. A, B: Transmission electron microscopy of Ag2Se nanoparticles and the particle size distribution. C: EDS spectrum of Ag2Se nanoparticles. D: XRD of patterns of Ag2Se nanoparticles. E: Ultraviolet absorption map of Ag2Se nanoparticles at different concentrations. F: Fitting equation of ultraviolet absorption of Ag2Se nanoparticles.
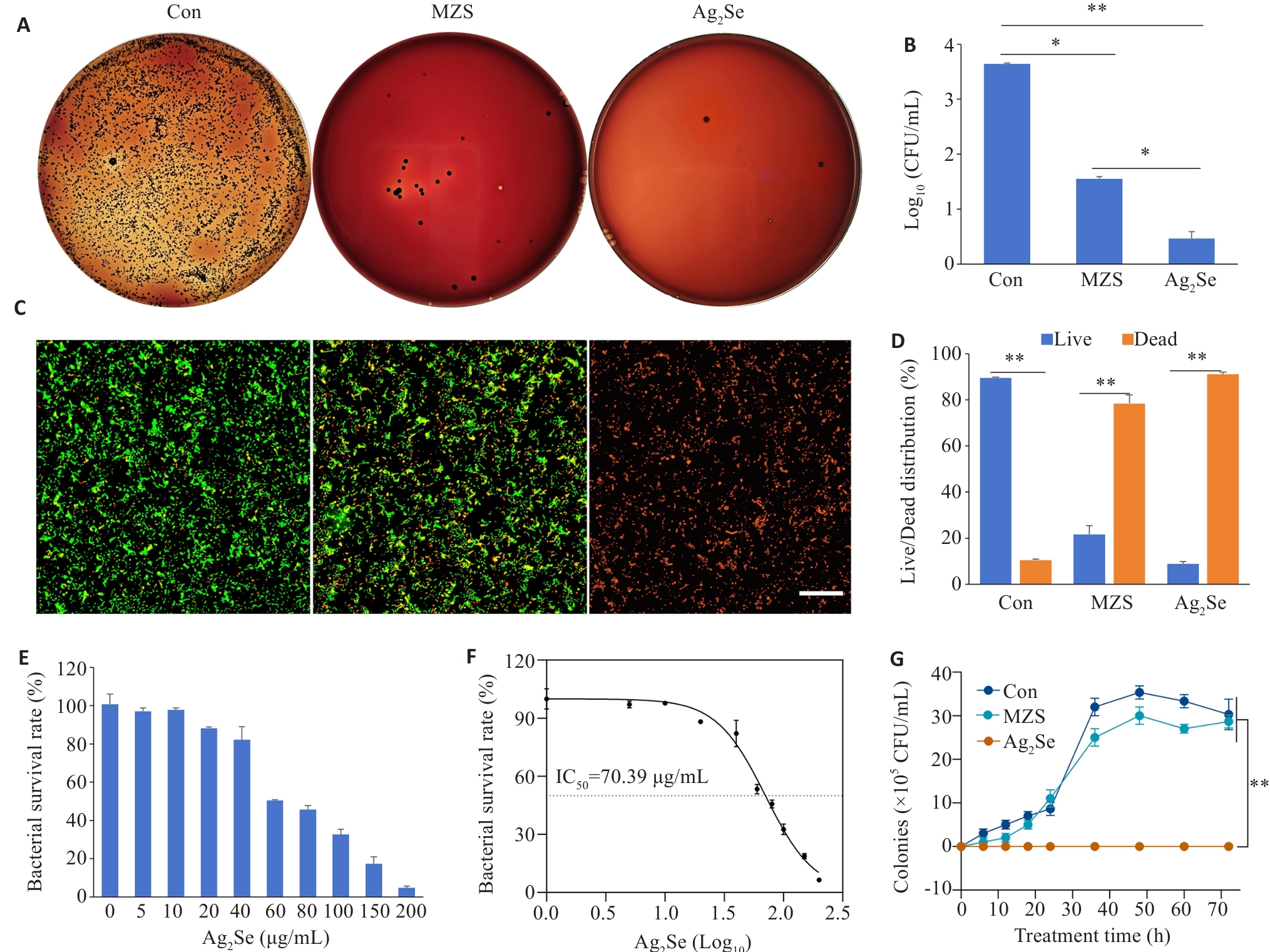
图2 Ag2Se 纳米颗粒体外抗菌性能评价
Fig.2 Antibacterial performance evaluation of Ag2Se nanoparticles in vitro. A: P. gingivalis cultures with different treatments for 6 h and inoculated on solid Columbia blood agar plates at 37 ℃ in a anaerobic chamber for 7 days. B: Quantitative map of colony formation. C: CLSM images of P. gingivalis stained with MycoLight™ Green and PI nucleic acid dye (green and red fluorescence represent live and dead bacteria, respectively), at Ag2Se concentration of 80 μg/mL (scale bar=30 µm). D: Quantitative map of live and dead bacterium. E: Bacterial survival after treatment at different drug concentrations (0, 5, 10, 20, 40, 60, 80, 100, 150, 200 μg/mL). F: Effects of different drug concentrations, expressed as logarithmic values (Log10), on bacterial survival. The IC50 value was 70.39 μg/mL. G: Growth curves of P.gingivalis with different treatments. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
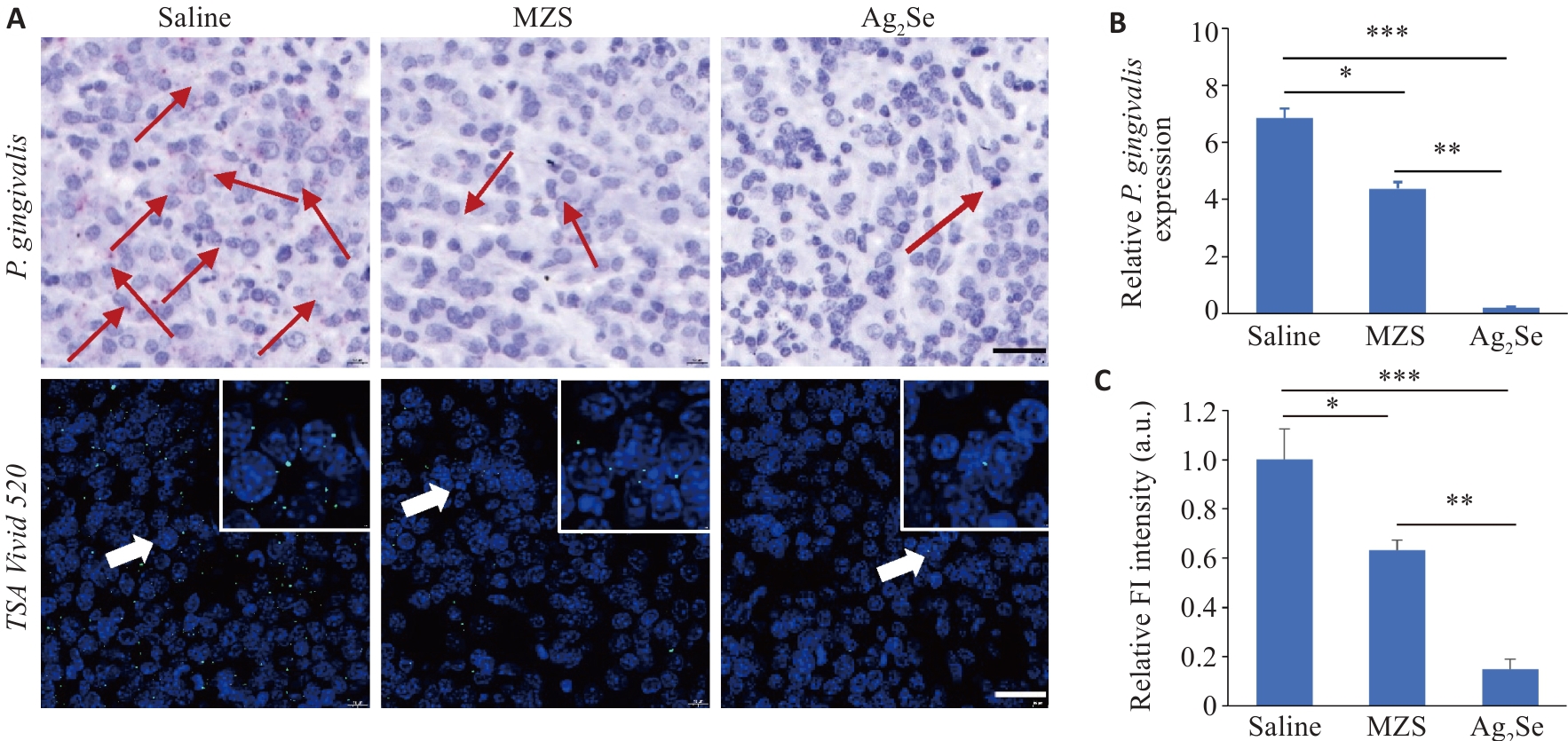
图3 Ag2Se纳米颗粒体内抑菌评估
Fig.3 Antibacterial evaluation of Ag2Se nanoparticles in tumor tissues in tumor-bearing mice. A: RNAscope in situ hybridization to detect the abundance of P. gingivalis in the tumor tissues (scale bar=25 μm). Red and green fluorescence signals both indicate P. gingivalis. B: Quantification of P. gingivalis DNA in the tumor tissue from different treatment groups using qPCR detection. C: Quantitative analysis of fluorescence intensity. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
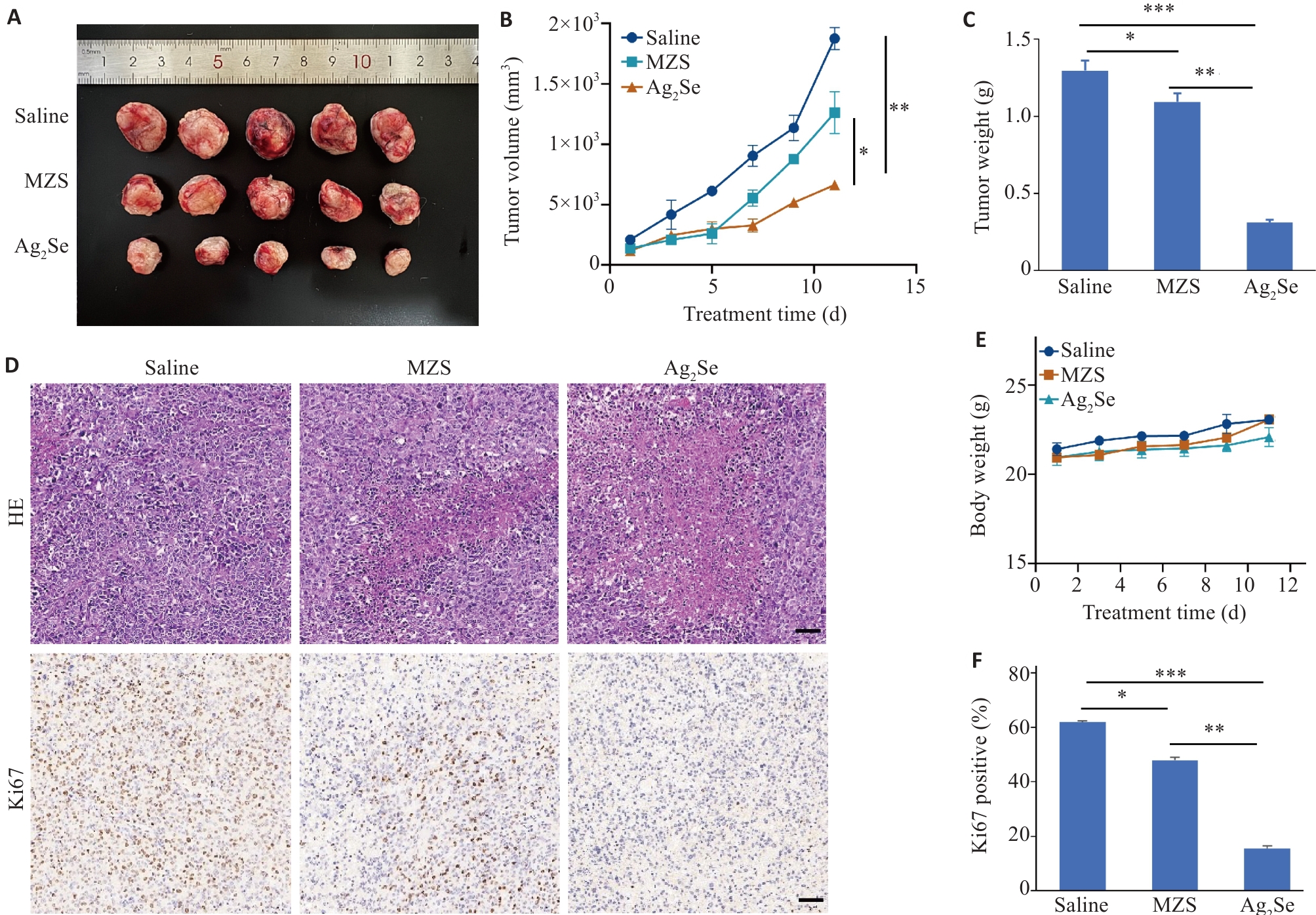
图4 评价Ag2Se纳米颗粒对食管癌细胞生长过程影响
Fig.4 Effect of Ag2Se nanoparticles on growth of esophageal cancer cells in mice. A: Volume of the dissected tumors in each group. B: Tumor volume curves of the mice with different treatments. C: Tumor weight of the mice treated with saline, MZS and Ag2Se nanoparticles. D: HE staining and Ki67 immunohistochemistry of the tumor sections in each group (scale bar=50 μm). E: Body weight curves of C57 mice with different treatments. F: Quantitative analysis of Ki67 staining in different groups. Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=5). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
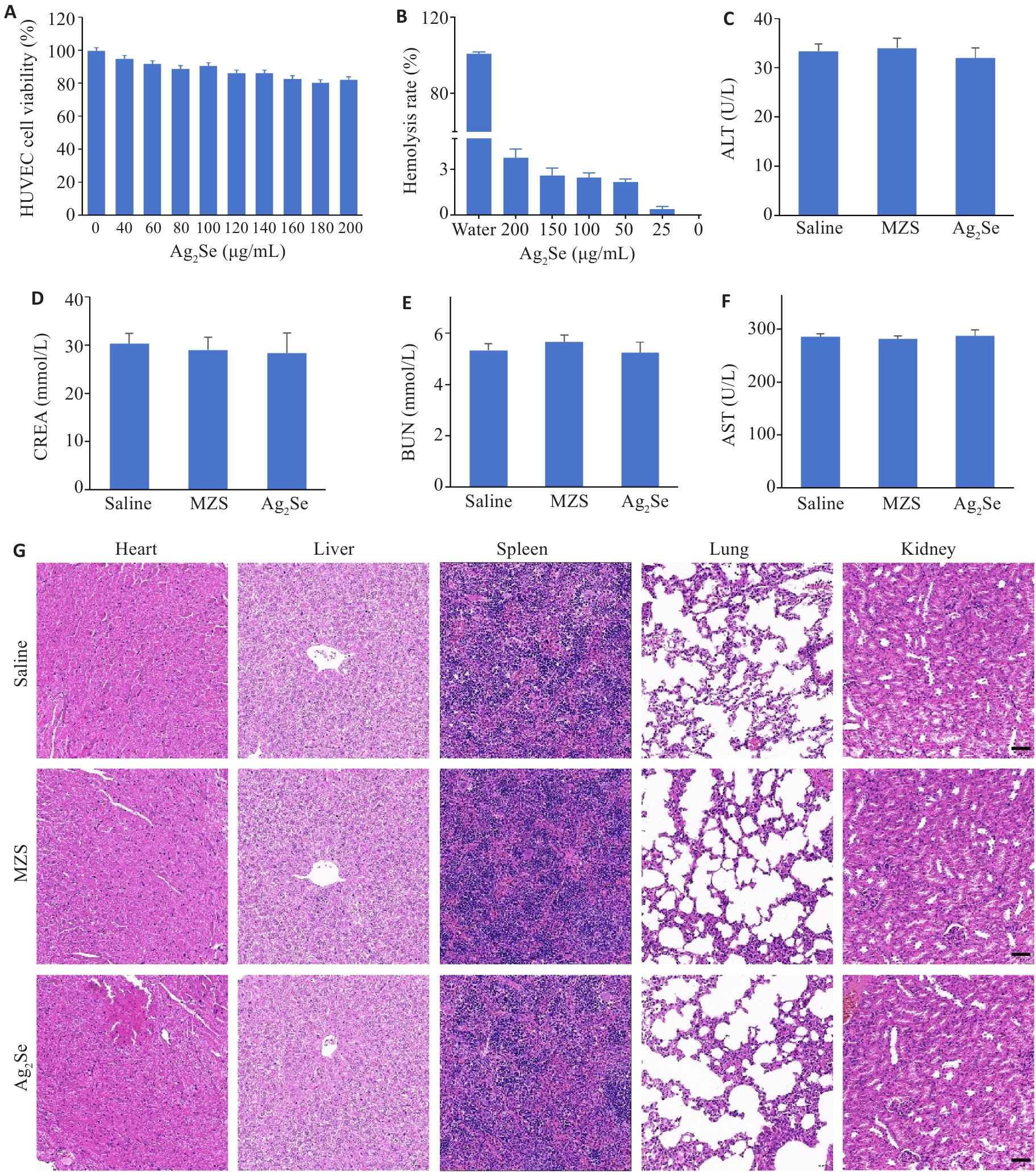
图5 Ag2Se 纳米颗粒生物相容性
Fig.5 Evaluation of biocompatibility of Ag2Se nanoparticles. A: HUVEC viability after incubation with different concentrations of Ag2Se nanoparticles for 24 h. B: Hemolysis assay after different treatments and the hemolysis ratio detected at 540 nm. C-F: ALT, AST, BUN, and CREA of the mice after different treatments. G: HE staining of the heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney tissues in different groups (scale bar=50 μm). Data are presented as Mean±SD (n=3).
| 1 | Fu AK, Yao BQ, Dong TT, et al. Emerging roles of intratumor microbiota in cancer metastasis[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2023, 33(7): 583-93. |
| 2 | Polk DB, Peek RM Jr. Helicobacter pylori: gastric cancer and beyond[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2010, 10(6): 403-14. |
| 3 | Griffith DM, Li HY, Werrett MV, et al. Medicinal chemistry and biomedical applications of bismuth-based compounds and nanoparticles[J]. Chem Soc Rev, 2021, 50(21): 12037-69. |
| 4 | Zhang SK, Xu HF, Zhang LY, et al. Cervical cancer: Epidemiology, risk factors and screening[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2020, 32(6): 720-8. |
| 5 | Ou SW, Chen HP, Wang HF, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum upregulates MMP7 to promote metastasis-related characteristics of colorectal cancer cell via activating MAPK(JNK)-AP1 axis[J]. J Transl Med, 2023, 21(1): 704. |
| 6 | Mima K, Cao Y, Chan AT, et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum in colorectal carcinoma tissue according to tumor location[J]. Clin Transl Gastroenterol, 2016, 7(11): e200. |
| 7 | Fu Y, Li J, Cai WY, et al. The emerging tumor microbe microenvironment: from delineation to multidisciplinary approach-based interventions[J]. Acta Pharm Sin B, 2024, 14(4): 1560-91. |
| 8 | Jiang HX, Li L, Bao YX, et al. Microbiota in tumors: new factor influencing cancer development[J]. Cancer Gene Ther, 2024, 31(12): 1773-85. |
| 9 | Gao SG, Liu YW, Duan XX, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection exacerbates oesophageal cancer and promotes resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy[J]. Br J Cancer, 2021, 125(3): 433-44. |
| 10 | Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2018, 68(6): 394-424. |
| 11 | Zitvogel L, Ayyoub M, Routy B, et al. Microbiome and anticancer immunosurveillance[J]. Cell, 2016, 165(2): 276-87. |
| 12 | Zitvogel L, Daillère R, Roberti MP, et al. Anticancer effects of the microbiome and its products[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(8): 465-78. |
| 13 | Nanayakkara AK, Boucher HW, Fowler VG Jr, et al. Antibiotic resistance in the patient with cancer: escalating challenges and paths forward[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(6): 488-504. |
| 14 | Petrelli F, Ghidini M, Ghidini A, et al. Use of antibiotics and risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies[J]. Cancers, 2019, 11(8): 1174. |
| 15 | Chambers LM, Esakov Rhoades EL, Bharti R, et al. Disruption of the gut microbiota confers cisplatin resistance in epithelial ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2022, 82(24): 4654-69. |
| 16 | Ghanem S, Kim CJ, Dutta D, et al. Antimicrobial therapy during cancer treatment: beyond antibacterial effects[J]. J Intern Med, 2021, 290(1): 40-56. |
| 17 | Liu ZY, Ma YG, Ye JX, et al. Drug delivery systems for enhanced tumour treatment by eliminating intra-tumoral bacteria[J]. J Mater Chem B, 2024, 12(5): 1194-207. |
| 18 | Shi JJ, Kantoff PW, Wooster R, et al. Cancer nanomedicine: progress, challenges and opportunities[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2017, 17(1): 20-37. |
| 19 | Liu JY, Wang ZY, Liu FD, et al. Chemical transformations of nanosilver in biological environments[J]. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(11): 9887-99. |
| 20 | Li W, Ding QH, Li MQ, et al. Stimuli-responsive and targeted nanomaterials: Revolutionizing the treatment of bacterial infections[J]. J Control Release, 2025, 377: 495-523. |
| 21 | Subhan MA, Yalamarty SSK, Filipczak N, et al. Recent advances in tumor targeting via EPR effect for cancer treatment[J]. J Pers Med, 2021, 11(6): 571. |
| 22 | Bruna T, Maldonado-Bravo F, Jara P, et al. Silver nanoparticles and their antibacterial applications[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(13): 7202. |
| 23 | Ren QW, Wang Y, Qian J, et al. Biosynthesis of Ag2Se nanoparticles as a broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent with excellent bioco-mpatibility[J]. J Hazard Mater, 2024, 465: 133201. |
| 24 | Ozdal OG. Green synthesis of Ag, Se, and Ag2Se nanoparticles by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: characterization and their biological and photocatalytic applications[J]. Folia Microbiol, 2024, 69(3): 625-38. |
| 25 | Koul B, Poonia AK, Yadav D, et al. Microbe-mediated biosynthesis of nanoparticles: applications and future prospects[J]. Biomolecules, 2021, 11(6): 886. |
| 26 | Dhanker R, Hussain T, Tyagi P, et al. The emerging trend of bio-engineering approaches for microbial nanomaterial synthesis and its applications[J]. Front Microbiol, 2021, 12: 638003. |
| 27 | El-Khawaga AM, Zidan A, El-Mageed AIAA. Preparation methods of different nanomaterials for various potential applications: a review[J]. J Mol Struct, 2023, 1281: 135148. |
| 28 | Yang XJ, Wang C, Zhang XX, et al. Photothermal and adsorption effects of silver selenide nanoparticles modified by different surfactants in nursing care of cancer patients[J]. Sci Technol Adv Mater, 2020, 21(1): 584-92. |
| 29 | Sepich-Poore GD, Zitvogel L, Straussman R, et al. The microbiome and human cancer[J]. Science, 2021, 371(6536): eabc4552. |
| 30 | Chen MF, Lu MS, Hsieh CC, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis promotes tumor progression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Cell Oncol, 2021, 44(2): 373-84. |
| 31 | Li RY, Huang B, Tian H, et al. Immune evasion in esophageal squamous cell cancer: from the perspective of tumor microenvironment[J]. Front Oncol, 2022, 12: 1096717. |
| 32 | Kolenbrander PE, Palmer RJ Jr, Rickard AH, et al. Bacterial interactions and successions during plaque development[J]. Periodontol 2000, 2006, 42: 47-79. |
| 33 | Rams TE, Sautter JD, van Winkelhoff AJ. Emergence of antibiotic-resistant Porphyromonas gingivalis in United States periodontitis patients[J]. Antibiotics, 2023, 12(11): 1584. |
| 34 | Chen SR, Zou SJ. Porphyromonas gingivalis HmuY and its possible effect on the pathogenesis of periodontitis[J]. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban, 2022, 53(6): 1104-9. |
| 35 | Ndayishimiye J, Kumeria T, Popat A, et al. Nanomaterials: the new antimicrobial magic bullet[J]. ACS Infect Dis, 2022, 8(4): 693-712. |
| 36 | Tang SH, Zheng J. Antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles: structural effects[J]. Adv Healthc Mater, 2018, 7(13): e1701503. |
| 37 | Valdez-Salas B, Beltrán-Partida E, Zlatev R, et al. Structure-activity relationship of diameter controlled Ag@Cu nanoparticles in broad-spectrum antibacterial mechanism[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021, 119: 111501. |
| 38 | Tang H, Yang ST, Yang YF, et al. Blood clearance, distribution, transformation, excretion, and toxicity of near-infrared quantum dots Ag2Se in mice[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2016, 8(28): 17859-69. |
| [1] | 杜越, 张秀森, 周克旭, 金星, 原翔, 高社干. RgpB通过抑制自噬小体与溶酶体融合避免Cx43降解参与食管癌化疗耐药[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1670-1676. |
| [2] | 杨泽, 张秀森, 张旭东, 柳颖, 张嘉诚, 原翔. 基于YTHDF2介导凋亡相关因子降解途径研究牙龈卟啉单胞菌协助食管癌免疫逃逸[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1159-1165. |
| [3] | 刘 溪, 胡 欢, 房 静, 黄 璐, 程向阳. 红景天注射液降低食管癌根治术患者单肺通气期间肺内分流及血清炎症介质:46例随机对照试验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(4): 706-711. |
| [4] | 林晓丰, 黄马养, 陈君千, 周 逊, 钟卓丹, 陆文聪, 黄显莹, 刘添文. 锰基纳米材料用于胃肠道恶性肿瘤的化学动力治疗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(8): 1432-1439. |
| [5] | 申刘青, 张顶彧, 高社干. 牙龈卟啉单胞菌感染对食管癌细胞内IFNGR1棕榈酰化位点突变的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(7): 1155-1163. |
| [6] | 曾 娇, 李心竹, 殷琳莹, 陈 婷, 侯 晋. 牙龈卟啉单胞菌在体外可破坏脐静脉内皮屏障功能:基于下调ZO-1、occludin和VE-cadherin的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 287-293. |
| [7] | 罗 钞, 王高明, 胡力文, 强 勇, 郑 超, 申 翼. 食管癌患者术后预测模型的构建和验证:基于SEER数据库[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(6): 794-804. |
| [8] | 孙巧玉, 刘 佳, 樊筱玓, 周咏春, 王效静, 崔 珍. 血浆SEPTIN9甲基化水平检测有助于食管癌诊断和放疗敏感性预测[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1214-1219. |
| [9] | 黄 强, 卢 笛, 韩继钧, 于洪峰, 董 文, 蔡开灿, 余学飞. 基于开端同轴探头技术的人体正常食管和食管癌介电特性比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(11): 1741-1746. |
| [10] | 杏福宝, 张 雷, 唐 震, 李小军, 贡会源, 王 彪, 胡雁南. 胸腹腔镜食管癌根治术对患者术后免疫功能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 146-150. |
| [11] | 龚 拯, 龙小毛, 韦慧君, 唐 莹, 栗 俊, 马 利, 余 军. 右美托咪定联合肺保护性通气策略可减轻单肺通气食管癌根治术患者的肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(07): 1013-1017. |
| [12] | 姚文柱,路 宁,崔曼莉,王 佳,杜召召,张明鑫. 阳性淋巴结比率≥0.16是影响食管癌患者预后的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(06): 837-842. |
| [13] | 吴宇翔,辛道,刘灿,王峰. SIRT1通过调控Snail表达参与食管癌EC-9706和Eca-109细胞的上皮间质转化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1325-. |
| [14] | 曹赛,程梅容,刘素娥,段晓乐,李梅. 食管癌组织中TAK1 和TAB1 的表达及与临床预后的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(07): 895-. |
| [15] | 郭鑫,吴源周,贾龙飞,李雅玲,闫玉生,陈群清. 微创和开放食管癌切除术对食管癌患者循环肿瘤细胞的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(03): 318-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||