南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2317-2326.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.07
• • 上一篇
林如辉1,2( ), 夏金言2, 马小涵2, 李钻芳1,2(
), 夏金言2, 马小涵2, 李钻芳1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-09
出版日期:2024-12-20
发布日期:2024-12-26
通讯作者:
李钻芳
E-mail:470863153@qq.com;lizuanfang@163.com
作者简介:林如辉,副研究员,E-mail: 470863153@qq.com
Ruhui LIN1,2( ), Jinyan XIA2, Xiaohan MA2, Zuanfang LI1,2(
), Jinyan XIA2, Xiaohan MA2, Zuanfang LI1,2( )
)
Received:2024-04-09
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Zuanfang LI
E-mail:470863153@qq.com;lizuanfang@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨电针百会、神庭对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的神经保护作用机制。 方法 将雄性SD大鼠48只随机分为假手术组、模型组、电针组和非穴组,12只/组。采用Longa法制备局灶性缺血损伤大鼠模型。电针干预大鼠百会、神庭穴7 d。观察大鼠神经功能缺损评分、脑梗死体积变化、学习记忆功能、海马CA1区病理变化、神经元及突触超微结构,并计数突触密度、血清血清γ-氨基丁酸(GABA)、海马组织中GABAARα1、钙调蛋白依赖性蛋白激酶II(CaMKⅡ)、突触素1(SYN1)和突触后致密蛋白-95(PSD-95)蛋白及mRNA表达情况、SYN1和PSD-95表达水平。 结果 与模型组比较,电针组大鼠神经功能缺损评分降低(1.75±0.45 vs 1.50±0.67,P<0.05);脑梗死体积降低(11.25±6.22 vs 3.51±2.21,P<0.05);逃避潜伏期降低下降(62.65±5.12 vs 51.83±6.19,P<0.05)及穿越平台次数增加(1.17±0.75 vs 3.17±0.75,P<0.05);缺血侧海马CA1区神经细胞数量增加;突触间隙宽度相对变小,突触小体相对增加(2.00±0.11 vs 4.00±0.25, P<0.05);血清中GABA含量上升(3.90±0.75 vs 5.54±0.35,P<0.05);海马组织中GABAARα1、SYN1和PSD-95 mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05);CaMKⅡ mRNA表达水平下降(P<0.05)。 结论 电针百会、神庭可改善脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠学习记忆功能,其机制可能通过促进突触再生,上调GABAARα1、SYN1和PSD-95表达,下调CaMKⅡ表达有关。
林如辉, 夏金言, 马小涵, 李钻芳. 电针通过促进突触再生改善脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠的学习记忆功能[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(12): 2317-2326.
Ruhui LIN, Jinyan XIA, Xiaohan MA, Zuanfang LI. Electroacupuncture improves learning and memory function and promotes hippocampal synaptic regeneration in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2317-2326.
| Gene | Primer sequences 5'-3' | Amplified size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| GABAARα1 | F: TGTCTTTGGAGTGACGACCG | 187 |
| R: ATCCCACGCATACCCTCTCT | ||
| CaMKⅡ | F: AAGATGTGCGACCCTGGAAT | 178 |
| R: ACTGAGTGATGCGGATGTAGG | ||
| SYN1 | F: GGTGGATTCTCCGTGGACAT | 142 |
| R: GCAGCCCAATGACCAAACTG | ||
| PSD-95 | F: CAGTGAGACCGACGACATTG | 199 |
| R: GATGATGGGACGAGCATAGTG | ||
| GADPH | F: ACGGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG | 149 |
| R: AAGACGCCAGTAGACTCCACGAC |
表1 引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequences 5'-3' | Amplified size (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| GABAARα1 | F: TGTCTTTGGAGTGACGACCG | 187 |
| R: ATCCCACGCATACCCTCTCT | ||
| CaMKⅡ | F: AAGATGTGCGACCCTGGAAT | 178 |
| R: ACTGAGTGATGCGGATGTAGG | ||
| SYN1 | F: GGTGGATTCTCCGTGGACAT | 142 |
| R: GCAGCCCAATGACCAAACTG | ||
| PSD-95 | F: CAGTGAGACCGACGACATTG | 199 |
| R: GATGATGGGACGAGCATAGTG | ||
| GADPH | F: ACGGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG | 149 |
| R: AAGACGCCAGTAGACTCCACGAC |
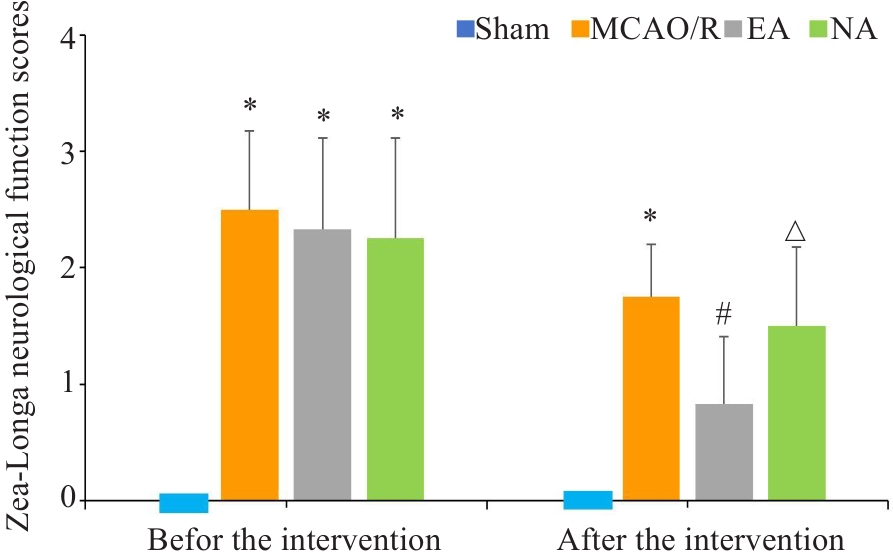
图1 Zea-Longa神经功能评分比较
Fig.1 Comparison of Zea-Longa neurological function scores among the 4 groups before and after the treatment. *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group. EA: Electroacupuncture at acupoints; NA: Electroacupuncture at non-acupoints.
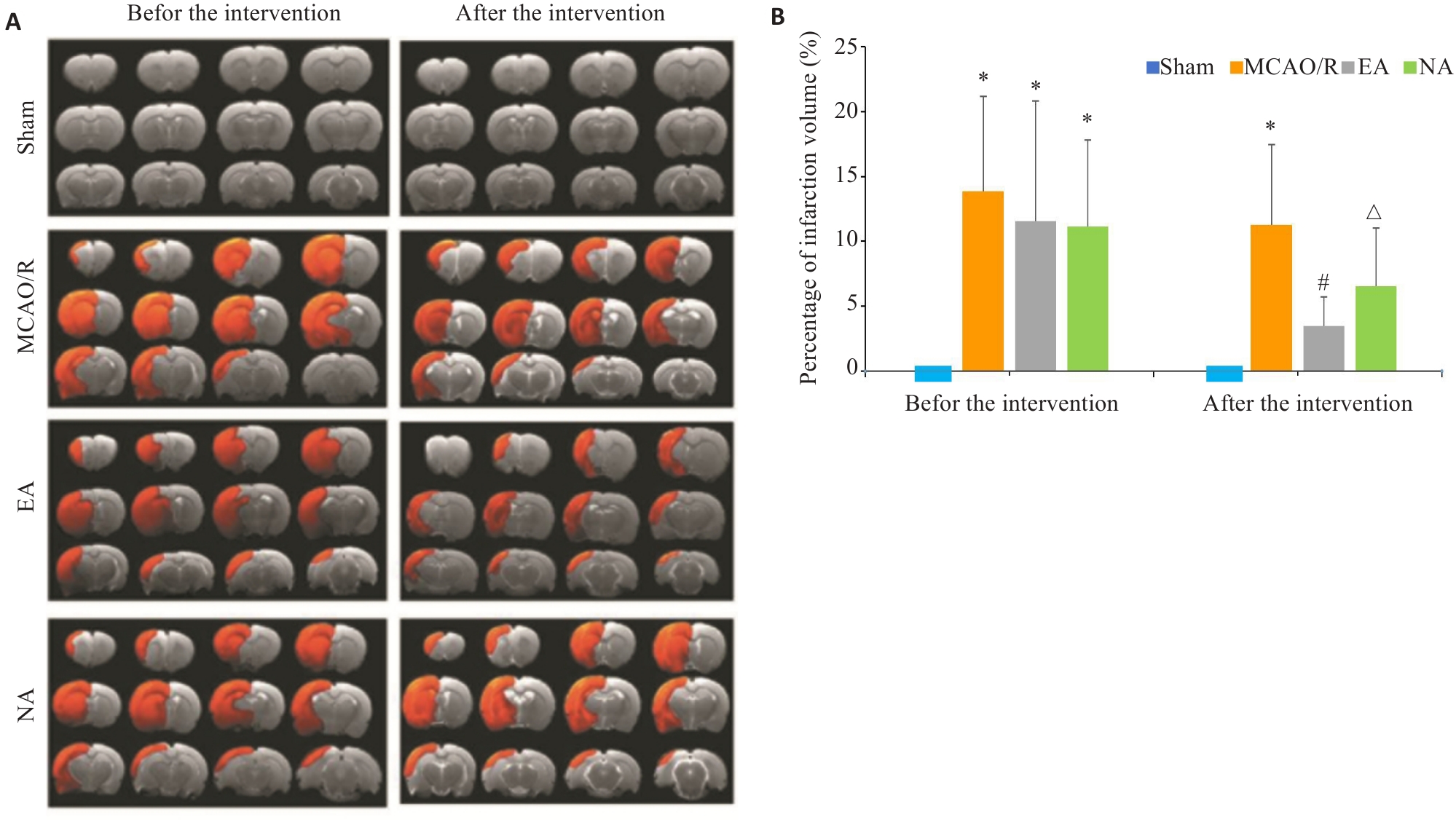
图2 各组大鼠干预前后T2WI图及梗死体积比较
Fig.2 Comparison of T2WI and cerebral infarction volume among the 4 groups before and after the treatment. A: T2WI before and after intervention. Red area indicates cerebral infarction. B: Comparison of cerebral infarction volume.*P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.
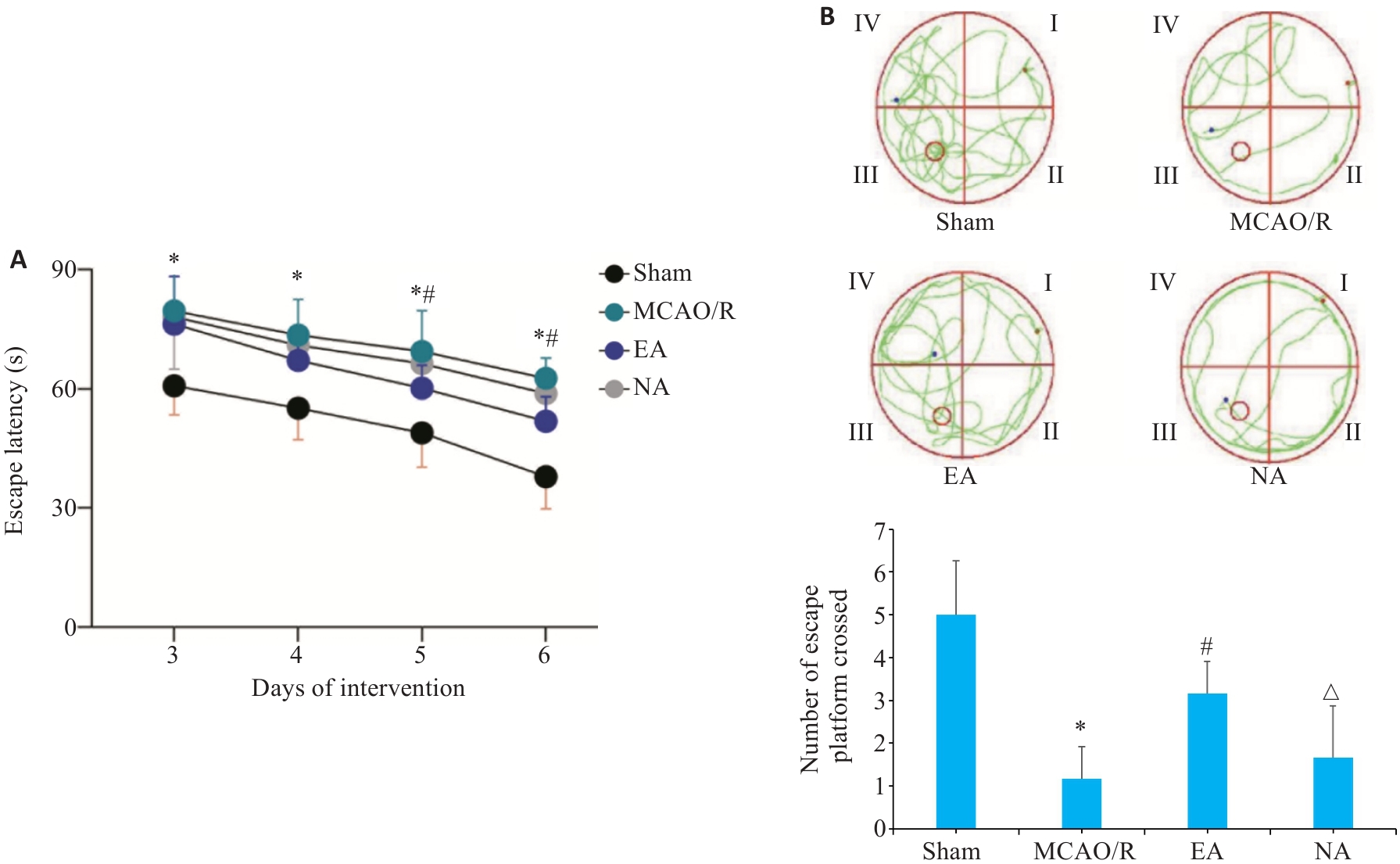
图3 各组大鼠逃避潜伏期和穿越逃生平台次数比较
Fig.3 Comparison of escape latency (A) and number of platform crossings (B) among the 4 groups. *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.
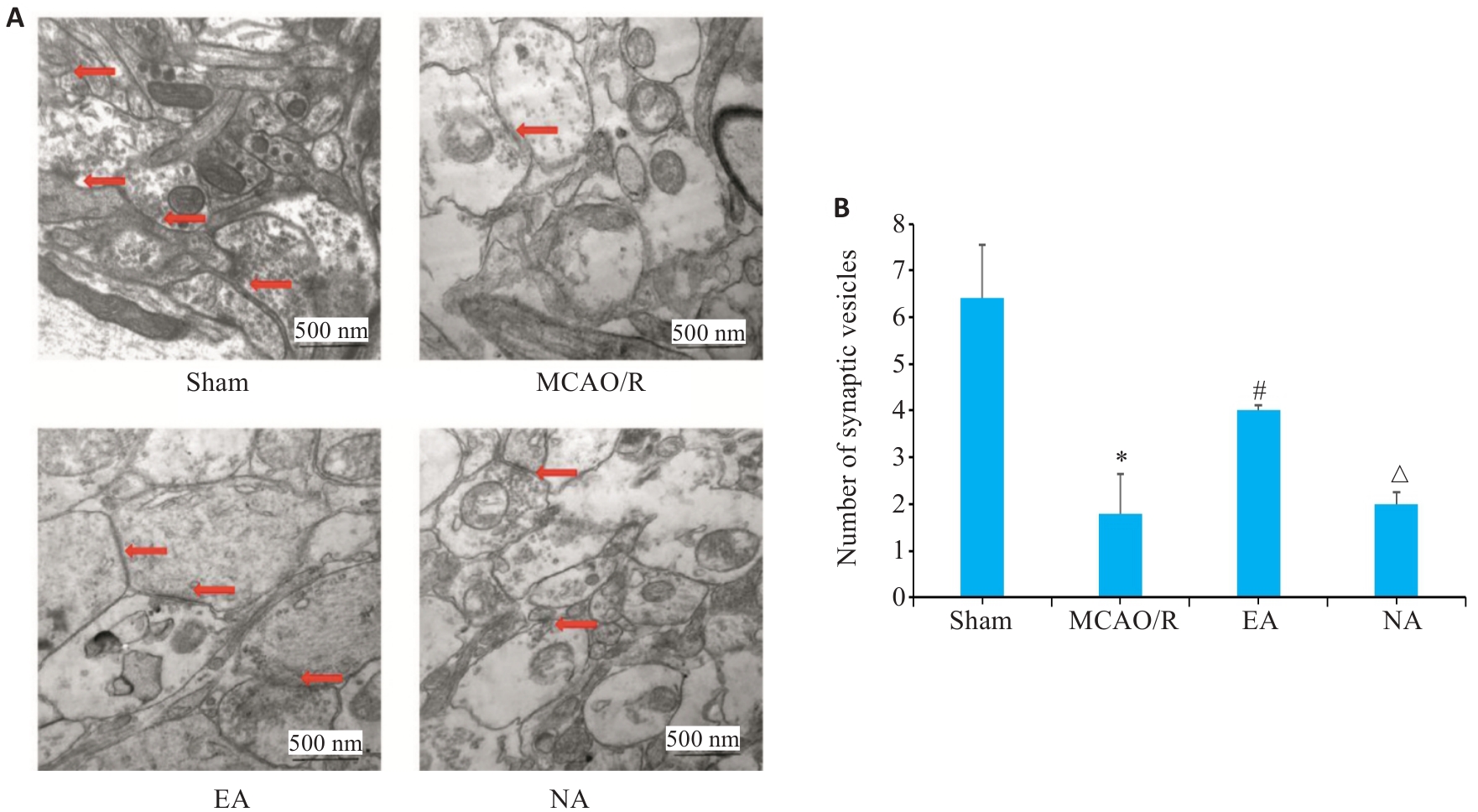
图5 缺血侧海马CA1区突触结构及突触小体数量
Fig.5 Transmission electron microscopy of the synaptic structure and synapsis number in the hippocampal CA1 region on the ischemic side. A: Synaptic ultrastructure of hippocampal CA1 region. Arrows indicate the changed synaptic vesicle. B: Synapsis number in the hippocampal CA1 region on the ischemic side. *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.

图7 缺血侧海马GABAARα1、CaMK Ⅱ、SYN1和PSD-95 mRNA相对表达量比较
Fig.7 Comparison of relative expressions of GABAAR1, CaMK II, SYN1 and PSD-95 mRNA in the hippocampus on the ischemic side. *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.
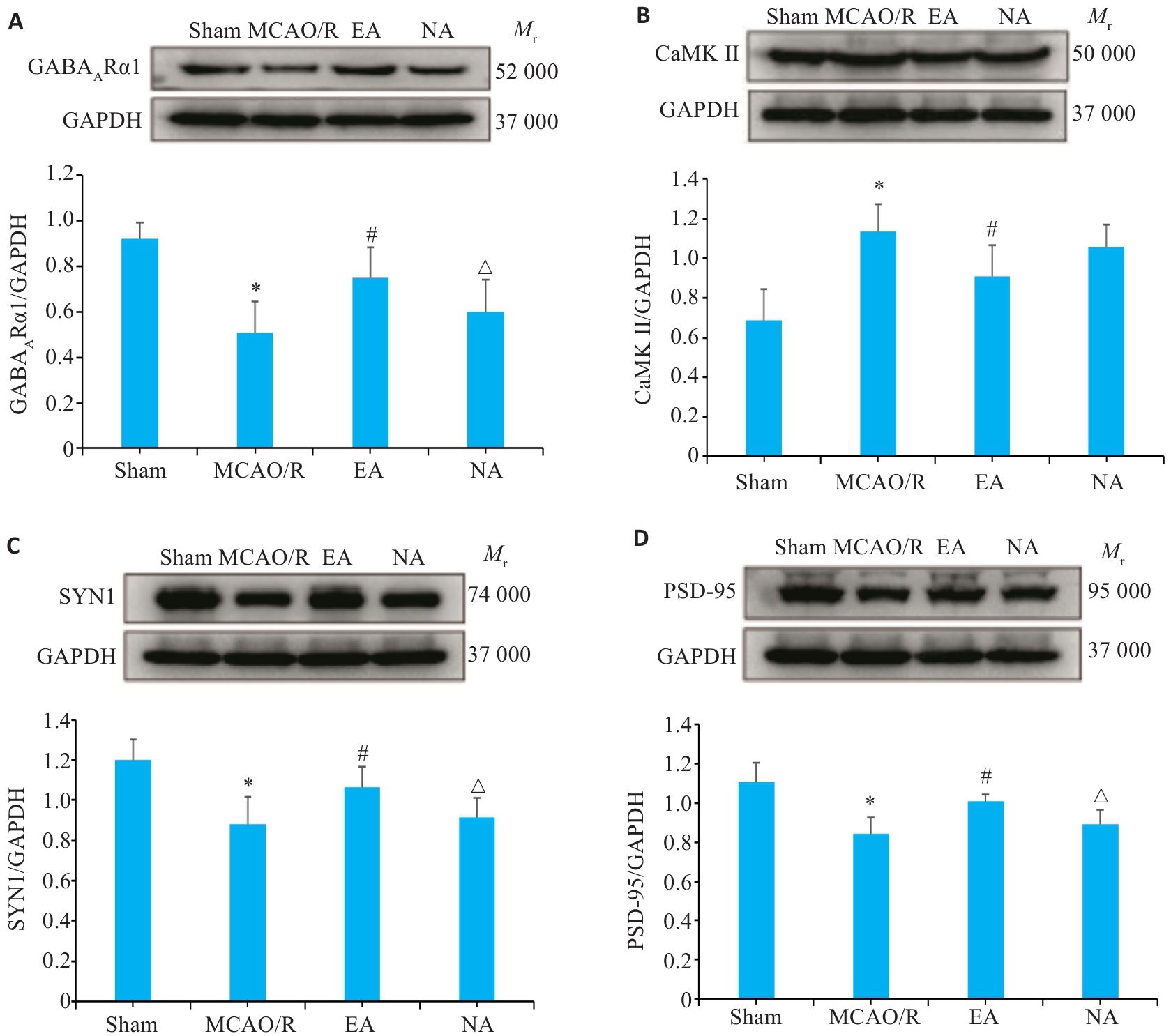
图8 缺血侧海马GABAARα1、CaMK Ⅱ、SYN1和PSD-95蛋白表达比较
Fig.8 Comparison of GABAAR1 (A), CaMK II (B), SYN1 (C) and PSD-95 protein (D) expressions in the hippocampus on the ischemic side detected by Western blotting. *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.

图9 缺血侧海马CA1区SYN1、PSD-95免疫荧光表达比较
Fig.9 Immunofluorescence staining for SYN1 (A) and PSD-95 (B) in the CA1 region of the ischemic hippocampus in the 4 groups (Scale bar=50 μm). *P<0.05 vs Sham group; #P<0.05 vs MCAO/R group; △P<0.05 vs EA group.
| 1 | 《中国脑卒中防治报告》编写组. 《中国脑卒中防治报告2020》概要[J]. 中国脑血管病杂志, 2022, 19(2): 136-44. |
| 2 | Lo JW, Crawford JD, Desmond DW, et al. Profile of and risk factors for poststroke cognitive impairment in diverse ethnoregional groups[J]. Neurology, 2019, 93(24): e2257-e2271. |
| 3 | Gorelick PB, Scuteri A, Black SE, et al. Vascular contributions to cognitive impairment and dementia: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American heart association/american stroke association[J]. Stroke, 2011, 42(9): 2672-713. |
| 4 | Mok VC, Lam BY, Wong A, et al. Early-onset and delayed-onset poststroke dementia-revisiting the mechanisms[J]. Nat Rev Neurol, 2017, 13(3): 148-59. |
| 5 | Bettio LEB, Rajendran L, Gil-Mohapel J. The effects of aging in the hippocampus and cognitive decline[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2017, 79: 66-86. |
| 6 | Preston AR, Eichenbaum H. Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory[J]. Curr Biol, 2013, 23(17): R764-73. |
| 7 | Eichenbaum H. On the integration of space, time, and memory[J]. Neuron, 2017, 95(5): 1007-18. |
| 8 | Yang SL, Ye HC, Huang J, et al. The synergistic effect of acupuncture and computer-based cognitive training on post-stroke cognitive dysfunction: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial of 2×2 factorial design[J]. BMC Complement Altern Med, 2014, 14: 290. |
| 9 | 刘 娇, 冯晓东. 电针百会、神庭穴配合康复训练治疗脑卒中后认知障碍临床研究[J]. 中医学报, 2013, 28(4): 608-10. |
| 10 | 林志诚, 杨珊莉, 薛偕华, 等. 针刺百会穴改善脑卒中患者记忆力的中枢机制[J]. 中国康复理论与实践, 2015, 21(2): 184-8. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9771.2015.02.014 |
| 11 | Chen B, Wang GX, Li WW, et al. Memantine attenuates cell apoptosis by suppressing the calpain-caspase-3 pathway in an experimental model of ischemic stroke[J]. Exp Cell Res, 2017, 351(2): 163-72. |
| 12 | Zhong XY, Chen B, Li ZF, et al. Correction to: electroacupuncture ameliorates cognitive impairment through the inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation by regulating melatonin-mediated mitophagy in stroke rats[J]. Neurochem Res, 2022, 47(7): 1931-3. |
| 13 | Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84-91. |
| 14 | 邓春雷, 殷克敬. 实验针灸学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1998: 147. |
| 15 | George P, Charles W(著), 诸葛启钏(主 译. 大鼠脑立体定位图谱[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005. |
| 16 | Yin CS, Jeong HS, Park HJ, et al. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model[J]. Res Vet Sci, 2008, 84(2): 159-65. |
| 17 | Frick KM, Baxter MG, Markowska AL, et al. Age-related spatial reference and working memory deficits assessed in the water maze[J]. Neurobiol Aging, 1995, 16(2): 149-60. |
| 18 | 郑富盛. 细胞形态立体计量学[M]. 北京: 北京医科大学、中国协和医科大学联合出版社, 1990: 112-113. |
| 19 | 洪文学, 樊凤杰, 宋佳霖. 百会穴研究概况[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2006, 25(2): 42-5. |
| 20 | 刘 芳, 姚立群, 陈金辉. 针刺百会、神庭穴治疗脑卒中后认知功能障碍效果的系统评价[J]. 上海针灸杂志, 2018, 4(1): 104-11. |
| 21 | Ning WH, Li L, Wang RQ, et al. Electroacupuncture pretreatment enhances the calcium efflux activity of Na+/Ca2+ exchanger to attenuate cerebral injury by PI3K/Akt-mediated NCX1 upregulation after focal cerebral ischaemia[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(12): e33265. |
| 22 | 许能贵, 易 玮, 赖新生, 等. 电针对局灶性脑缺血大鼠NO、NOS和ET-1的影响[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2002, 19(1): 63-4. |
| 23 | 曹娅军, 王思诺, 余 燕, 等. 电针 “百会” “神庭” 穴对血管性认知障碍大鼠海马泛素化修饰蛋白质组学的影响[J]. 中国康复医学杂志, 2023, 38(8): 1025-34. |
| 24 | Chen YL, Ouyang L, Meng LL, et al. Electroacupuncture ameliorates blood-brain barrier disruption after ischemic stroke through histone acetylation regulation at the matrix metalloproteinase 9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 2 genes[J]. Chung I Tsa Chih Ying Wen Pan, 2024, 44(4): 734-44. |
| 25 | 李章晗, 黎华茂, 艾年年. 通督调神针刺法联合康复运动治疗脑卒中恢复期偏瘫肢体运动功能障碍的临床观察[J]. 广州中医药大学学报, 2021, 38(7): 1401-6. |
| 26 | 詹 杰, 潘锐焕, 郭友华, 等. 针刺百会、神庭联合基础治疗和常规康复训练治疗脑卒中后认知障碍: 随机对照研究[J]. 中国针灸, 2016, 36(8): 803-6. |
| 27 | 杜坤锐, 刘 畅, 陈潇煜, 等. 电针对血管性痴呆大鼠海马微血管结构和相关蛋白表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2023, 48(11): 1079-87. |
| 28 | 陈 磊, 焦 鹏, 李方辉. 针刺百会、神庭穴联合康复训练治疗卒中后认知功能障碍[J]. 中国老年保健医学, 2020, 18(2): 11-3. |
| 29 | 屈媛媛, 冯楚文, 孙忠人, 等. 电针对慢性疲劳综合征大鼠行为学及海马炎性因子的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2024, 49(3): 274-82. |
| 30 | 杨 燕, 孙忠人, 李超然, 等. 电针干预对慢性疲劳综合征大鼠海马组织蛋白质磷酸化表达的影响[J]. 针刺研究, 2024, 49(6): 594-603. |
| 31 | Liu WL, Wang X, Yang SL, et al. Electroacupunctre improves motor impairment via inhibition of microglia-mediated neuroinflammation in the sensorimotor cortex after ischemic stroke[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 151: 313-22. |
| 32 | Huang YC, Tzeng WS, Wang CC, et al. Neuroprotective effect of agmatine in rats with transient cerebral ischemia using MR imaging and histopathologic evaluation[J]. Magn Reson Imaging, 2013, 31(7): 1174-81. |
| 33 | 孔营楠, 詹松华, 龚志刚, 等. 从TLR4信号通路探讨电针减轻小鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤的炎症反应机制[J]. 中国中西医结合影像学杂志, 2020, 18(6): 568-71, 581. |
| 34 | Ovadia-Caro S, Margulies DS, Villringer A. The value of resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging in stroke[J]. Stroke, 2014, 45(9): 2818-24. |
| 35 | Sweatt JD. Neural plasticity and behavior-sixty years of conceptual advances[J]. J Neurochem, 2016, 139(): 179-99. |
| 36 | Forner S, Baglietto-Vargas D, Martini AC, et al. Synaptic impairment in Alzheimer's disease: a dysregulated symphony[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2017, 40(6): 347-57. |
| 37 | Barberis A. Postsynaptic plasticity of GABAergic synapses[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2020, 169: 107643. |
| 38 | Sente A, Desai R, Naydenova K, et al. Differential assembly diversifies GABAA receptor structures and signalling[J]. Nature, 2022, 604(7904): 190-4. |
| 39 | Rudolph U, Crestani F, Möhler H. GABA(A) receptor subtypes: dissecting their pharmacological functions[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2001, 22(4): 188-94. |
| 40 | Xu YF, Lian YJ, Li J, et al. KangPiLao decoction modulates cognitive and emotional disorders in rats with central fatigue through the GABA/Glu pathway[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2022, 13: 939169. |
| 41 | Govindpani K, Calvo-Flores Guzmán B, Vinnakota C, et al. Towards a better understanding of GABAergic remodeling in Alzheimer's disease[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2017, 18(8): 1813. |
| 42 | Hell JW. CaMKII: claiming center stage in postsynaptic function and organization[J]. Neuron, 2014, 81(2): 249-65. |
| 43 | Dittmer PJ, Wild AR, Dell’Acqua ML, et al. STIM1 Ca2+ sensor control of L-type Ca2+-channel-dependent dendritic spine structural plasticity and nuclear signaling[J]. Cell Rep, 2017, 19(2): 321-34. |
| 44 | Fels JA, Manfredi G. Sex differences in ischemia/reperfusion injury: the role of mitochondrial permeability transition[J]. Neurochem Res, 2019, 44(10): 2336-45. |
| 45 | 姚路路, 杜 鑫, 付渊博, 等. 针灸调控神经可塑性作用机制初探[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2022, 38(10): 1-5. |
| 46 | 程 洁, 李忠仁, 朱 毅, 等. 电针对脑缺血再灌注大鼠海马钙调蛋白表达的影响[J]. 中国针灸, 2011, 31(11): 1015-9. |
| 47 | Forte N, Binda F, Contestabile A, et al. Synapsin I synchronizes GABA release in distinct interneuron subpopulations[J]. Cereb Cortex, 2020, 30(3): 1393-406. |
| 48 | Habif M, Do Carmo S, Báez MV, et al. Early long-term memory impairment and changes in the expression of synaptic plasticity-associated genes, in the McGill-R-Thy1-APP rat model of alzheimer's-like brain amyloidosis[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2020, 12: 585873. |
| 49 | Xiao LY, Wang XR, Yang Y, et al. Applications of acupuncture therapy in modulating plasticity of central nervous system[J]. Neuromodulation, 2018, 21(8): 762-76. |
| [1] | 李明明, 何梁超, 李天雨, 鲍岩, 徐祥, 陈光. 小鼠顶叶皮层反复轻度创伤性脑损伤抑制延髓NLG-1和PSD-95的表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 960-966. |
| [2] | 孙秀颀, 蔡静, 张安邦, 庞博, 陈春艳, 查琪琪, 全菲, 叶涛. 电针预处理通过抑制NF-kB/NLRP3信号通路介导炎症和凋亡改善大鼠脑卒中后痉挛[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2102-2109. |
| [3] | 郑 祥, 高颂爱, 尤 浩, 王浩琦, 高彦平, 王金丽, 李 嘉, 李 玲. 电针可改善骨关节炎大鼠的关节炎症和运动功能:基于调控Wnt-7B/β-catenin信号通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(4): 590-596. |
| [4] | 葛鑫宇, 郭 芳, 范 俊, 陈宝田, 于 林, 任 静, 李纪强, 卢成林, 莫嘉文, 李树基, 袁乐欣, 胡号应, 刘 赟, 周 晓, 崔 娟, 朱志敏, 曹 雄. 柴胡桂枝汤通过sirt1-p53信号通路产生抗抑郁作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 399-405. |
| [5] | 谢璨灿, 吴双华, 李峥嵘, 黄 冰, 曾维忠. 电针刺激通过JAK1/STAT3通路减轻脓毒症大鼠的急性肺损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(11): 1662-1667. |
| [6] | 宋文秀, 韩晓实, 李克雷, 陈 超, 王华军, 郑小飞. 电针干预促进大鼠肩袖损伤修复和运动功能康复[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(10): 1513-1517. |
| [7] | 张建杏,王研,郭远波,纪雪霞,王晟. 电针足三里穴对大鼠手术后T淋巴细胞免疫功能的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1384-. |
| [8] | 刘菲,李学智,付妮妮,席小芳,任毅,杨晓光,张愉. 短刺法对兔膝骨关节炎软骨细胞Sox9、VEGF和ColⅩ表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(07): 997-. |
| [9] | 张超男,黄学宽,骆言,蒋娟,万磊,王玲. 电针对急性痛风性关节炎大鼠踝关节髓样细胞表达激发受体表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(01): 133-. |
| [10] | 陈晓琳,唐成林,谢辉,唐念珍,郜婕,刘仁建. 电针对非酒精性脂肪性肝病大鼠肝TLR4、NF-κB表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1584-. |
| [11] | 姜雪梅;黄泳;卓鹰;高彦平;. 头电针治疗帕金森病的疗效观察[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(01): 114-116. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||