南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 867-875.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.05.08
聂金蕊1( ), 吴亚慧1, 韩雪梅2, 李亚琪1, 王海宽1(
), 吴亚慧1, 韩雪梅2, 李亚琪1, 王海宽1( ), 张会图1(
), 张会图1( )
)
收稿日期:2023-11-10
出版日期:2024-05-20
发布日期:2024-06-04
通讯作者:
王海宽,张会图
E-mail:nie15128928292@163.com;hkwang@tust.edu.cn;hzhang@tust.edu.cn
作者简介:聂金蕊,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: nie15128928292@163.com
基金资助:
Jinrui NIE1( ), Yahui WU1, Xuemei HAN2, Yaqi LI1, Haikuan WANG1(
), Yahui WU1, Xuemei HAN2, Yaqi LI1, Haikuan WANG1( ), Huitu ZHANG1(
), Huitu ZHANG1( )
)
Received:2023-11-10
Online:2024-05-20
Published:2024-06-04
Contact:
Haikuan WANG, Huitu ZHANG
E-mail:nie15128928292@163.com;hkwang@tust.edu.cn;hzhang@tust.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
目的 对副干酪乳杆菌(L. paracasei TK1501)发酵大豆产物中的后生元进行分离提取和体内外抑菌活性进行研究,评估该后生元在治疗幽门螺旋杆菌(Hp)感染的作用。 方法 L. paracasei TK1501在无氧密闭的环境内以37 ℃、固态发酵参数中料水比1∶1.5,接种量5×107 CFU/mL,培养发酵32 h后,通过大孔树脂XAD-16N吸附法、阳离子交换色谱法、高效液相色谱法分离纯化,对L. paracasei TK1501后生元进行稳定性及抗菌效果分析。将50只C57雄性小鼠随机分为空白组、模型组、阴性对照组、低剂量组(0.02 mL/只)和高剂量组(0.1 mL/只),10只/组,连续灌胃4周。取血清观察胃部炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1β表达水平变化,取小鼠胃组织进行HE染色。 结果 L. paracasei TK1501后生元易被蛋白酶降解,热稳定性好,对酸碱、有机溶剂等不利因素有较好的耐受性(P<0.05);在体外试验中,对金黄色葡萄球菌、Hp等均有较好的杀灭作用;在动物实验中,与模型组相比,L. paracasei TK1501后生元高剂量组明显改善Hp感染(P<0.05),胃部炎症因子TNF-α、IL-1β表达水平变化明显下降(P<0.05)。 结论 L. paracasei TK1501后生元对Hp、金黄色葡萄球菌等具有较好的抑制和杀灭效果,而在相同条件下对肠道中的正常菌群则无明显影响。
聂金蕊, 吴亚慧, 韩雪梅, 李亚琪, 王海宽, 张会图. 副干酪乳杆菌TK1501后生元的制备及对幽门螺旋杆菌的抑制作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 867-875.
Jinrui NIE, Yahui WU, Xuemei HAN, Yaqi LI, Haikuan WANG, Huitu ZHANG. Preparation of Lactobacillus paracei TK1501 postbiotic and its inhibitory effect against Helicobacter pylori infection in mice[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 867-875.
| Elution time (min) | Flow rate (mL/min) | Mobile phase A% | Mobile phase B% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.8 | 95 | 5 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 80 | 20 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 80 | 20 |
| 20 | 0.8 | 95 | 5 |
表1 流动相洗脱梯度
Tab.1 Mobile phase elution gradients
| Elution time (min) | Flow rate (mL/min) | Mobile phase A% | Mobile phase B% |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.8 | 95 | 5 |
| 5 | 0.5 | 80 | 20 |
| 15 | 0.5 | 80 | 20 |
| 20 | 0.8 | 95 | 5 |
| Protease types | Protease concentration (U/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 50 | |
| Pepsin | 25.1±0.3 | 21.3±0.4 | 19.3±0.1 | 16.7±0.3 | 15.8±0.2 |
| Trypsase | 25.3±0.5 | 19.6±0.3 | 16.8±0.1 | 15.3±0.3 | 13.7±0.3 |
| chymotrypsin | 24.8±0.1 | 21.5±0.5 | 14.7±0.4 | 10.8±0.6 | 10.7±0.4 |
| Proteinase K | 25.2±0.4 | 20.7±0.2 | 12.8±0.5 | 10.7±0.4 | 8.3±0.2 |
| Papain | 25.7±0.2 | 21.3±0.4 | 12.6±0.2 | 11.6±0.2 | 9.6±0.1 |
| Alkaline protease | 25.4±0.4 | 19.7±0.3 | 11.6±0.4 | 9.8±0.1 | 8.2±0.3 |
表2 L. paracasei TK1501后生元对不同蛋白酶的敏感性实验
Tab.2 Sensitivity of L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic to different proteases
| Protease types | Protease concentration (U/mL) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 50 | |
| Pepsin | 25.1±0.3 | 21.3±0.4 | 19.3±0.1 | 16.7±0.3 | 15.8±0.2 |
| Trypsase | 25.3±0.5 | 19.6±0.3 | 16.8±0.1 | 15.3±0.3 | 13.7±0.3 |
| chymotrypsin | 24.8±0.1 | 21.5±0.5 | 14.7±0.4 | 10.8±0.6 | 10.7±0.4 |
| Proteinase K | 25.2±0.4 | 20.7±0.2 | 12.8±0.5 | 10.7±0.4 | 8.3±0.2 |
| Papain | 25.7±0.2 | 21.3±0.4 | 12.6±0.2 | 11.6±0.2 | 9.6±0.1 |
| Alkaline protease | 25.4±0.4 | 19.7±0.3 | 11.6±0.4 | 9.8±0.1 | 8.2±0.3 |
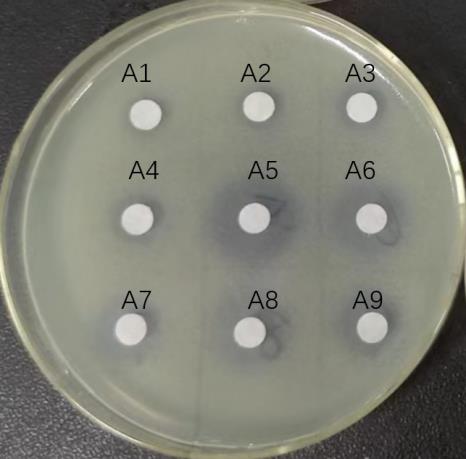
图2 大孔吸附树脂流出液各梯度洗脱液抑菌圈
Fig.2 Bacterial ring for each gradient eluate of the effluent of macroporous adsorbent resin. A1-A3: Effluent of supernatant after large pore adsorption chromatography column; A4-A6: 10%, 20% and 40% ethanol eluent; A7-A9: 60%, 80%, and 100% ethanol eluent.
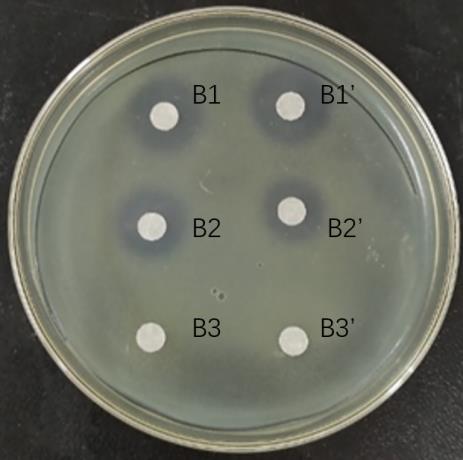
图3 阳离子交换柱各梯度洗脱液抑菌圈
Fig.3 Bacterial inhibition by each gradient eluate of cation exchange columns. B1: Eluent of 20 mmol/L NaOAc+0.2 mol/L NaCl; B2: Eluent of 20 mmol/L NaOAc+0.5 mol/L NaCl; B3: Eluent of 20 mmol/L NaOAc +1.0 mol/L NaCl.

图4 HPLC分析色谱图
Fig.4 HPLC analysis of the ethanol eluents of the macroporous adsorbent resin and cation exchange resin. A: 20% ethanol elution chromatogram. B: 20 mmol/L sodium acetate+0.2 mol/L sodium chloride elution chromatogram of cation exchange resin.
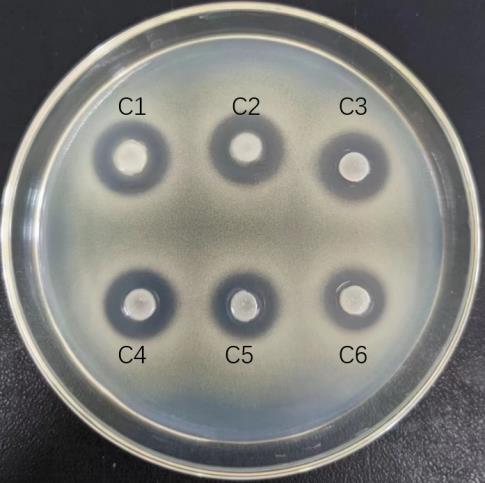
图5 L. paracasei TK1501后生元热稳定性试验
Fig.5 Thermal stability test L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic. C1: Blank control group; C2-C6: Postbiotics heated at 60-100 ℃ for 10 min.
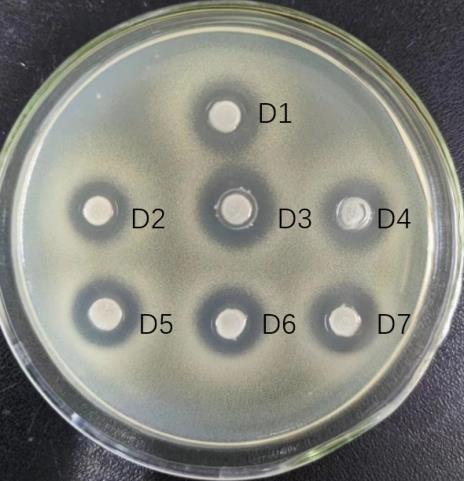
图6 L. paracasei TK1501后生元酸碱耐受性试验
Fig.6 Acid and base tolerance test L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic. D1-D7: Postbiotics at pH3-9 (D3 is the blank control).
| Indicator bacteria | Average number of colonies in the test group (CFU/mL) | Average colony number in control group (CFU/mL) | Sterilizing rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | <10 | 4.5×104 | >99.98* |
| Hp | 2.2×104 | 6.5×104 | 66.10 |
| Salmonella | 2.4×104 | 5.5×104 | 56.40 |
| C. jejuni | 1.6×104 | 2.9×104 | 44.80** |
| C. perfringen | 2.2×104 | 5.8×104 | 63.80** |
| B. subtilis | 5.5×104 | 5.7×104 | 3.50 |
| Bifidobacterium | 4.4×104 | 4.7×104 | 6.40 |
| L. Beijerinck | 5.6×104 | 6.5×104 | 13.80 |
| E. coli | 2.8×104 | 3.1×104 | 9.60 |
| Bacteroides | 3.8×104 | 4.3×104 | 24.30 |
| C. Prazmowski | 4.6×104 | 4.7×104 | 2.00 |
| Proteus | 3.5×104 | 4.1×104 | 14.60 |
| Staphylococcus | 2.1×104 | 4.9×104 | 57.10* |
| Streptococcus | 4.3×104 | 4.8×104 | 10.40 |
表3 L. paracasei TK1501后生元的抗菌谱分析
Tab.3 Analysis of antibacterial spectrum of L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic
| Indicator bacteria | Average number of colonies in the test group (CFU/mL) | Average colony number in control group (CFU/mL) | Sterilizing rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S. aureus | <10 | 4.5×104 | >99.98* |
| Hp | 2.2×104 | 6.5×104 | 66.10 |
| Salmonella | 2.4×104 | 5.5×104 | 56.40 |
| C. jejuni | 1.6×104 | 2.9×104 | 44.80** |
| C. perfringen | 2.2×104 | 5.8×104 | 63.80** |
| B. subtilis | 5.5×104 | 5.7×104 | 3.50 |
| Bifidobacterium | 4.4×104 | 4.7×104 | 6.40 |
| L. Beijerinck | 5.6×104 | 6.5×104 | 13.80 |
| E. coli | 2.8×104 | 3.1×104 | 9.60 |
| Bacteroides | 3.8×104 | 4.3×104 | 24.30 |
| C. Prazmowski | 4.6×104 | 4.7×104 | 2.00 |
| Proteus | 3.5×104 | 4.1×104 | 14.60 |
| Staphylococcus | 2.1×104 | 4.9×104 | 57.10* |
| Streptococcus | 4.3×104 | 4.8×104 | 10.40 |
| Groups | Feeding time (day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 14 | 21 | 28 | |
| Blank group | 47.07±2.02** | 47.92±2.21** | 50.09±2.09* | 53.53±2.62* |
| Model group | 39.76±1.71 | 42.12±2.26 | 46.23±1.75 | 49.11±1.56 |
| Experiment group 1 | 41.05±1.97 | 43.99±2.35 | 46.95±2.62 | 49.28±2.71 |
| Experiment group 2 | 42.80±2.19 ## | 45.68±2.40 ## | 48.16±3.30 | 49.09±2.79 |
| Experiment group 3 | 42.85±1.80 ## | 45.14±2.50 ## | 47.29±3.45 | 48.08±2.65 |
表4 不同组别小鼠体质量变化
Tab.4 Changes in body weight of the mice in different groups
| Groups | Feeding time (day) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 14 | 21 | 28 | |
| Blank group | 47.07±2.02** | 47.92±2.21** | 50.09±2.09* | 53.53±2.62* |
| Model group | 39.76±1.71 | 42.12±2.26 | 46.23±1.75 | 49.11±1.56 |
| Experiment group 1 | 41.05±1.97 | 43.99±2.35 | 46.95±2.62 | 49.28±2.71 |
| Experiment group 2 | 42.80±2.19 ## | 45.68±2.40 ## | 48.16±3.30 | 49.09±2.79 |
| Experiment group 3 | 42.85±1.80 ## | 45.14±2.50 ## | 47.29±3.45 | 48.08±2.65 |
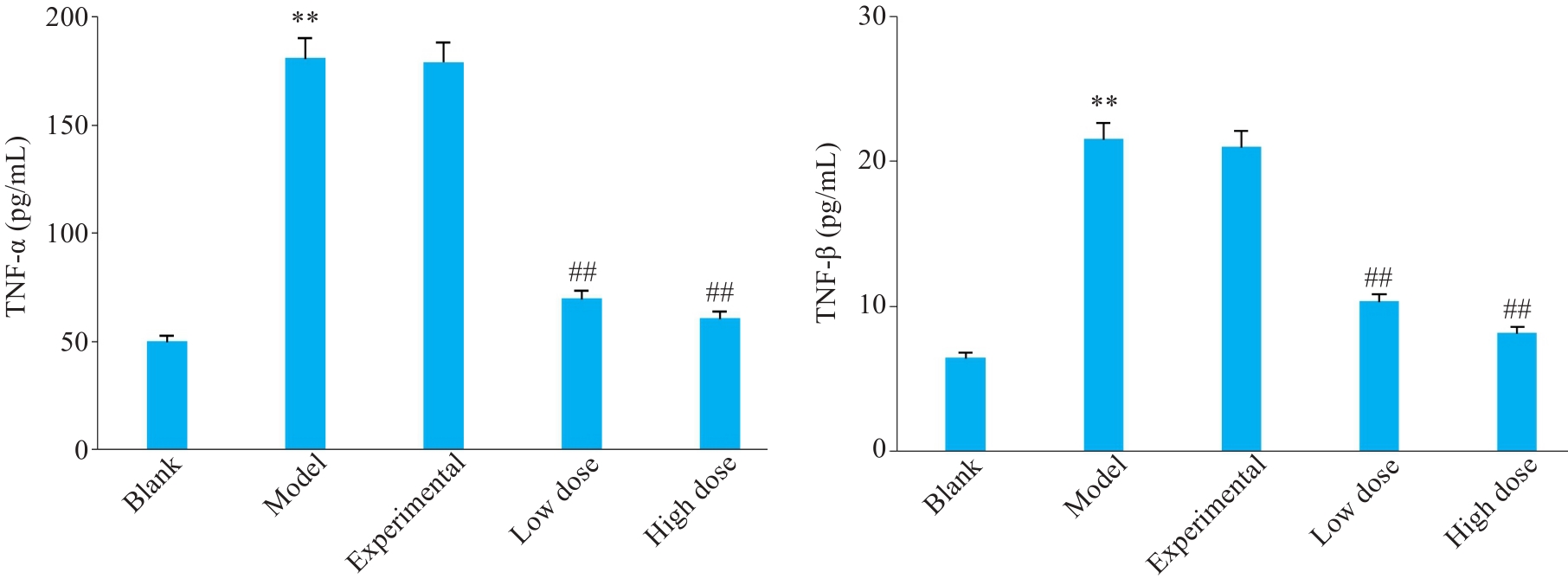
图7 不同组别小鼠胃部炎症因子表达水平变化
Fig.7 Changes of serum levels of gastric inflammatory factors in different groups of mice. **P<0.01 vs blank group; ##P<0.01 vs model group.
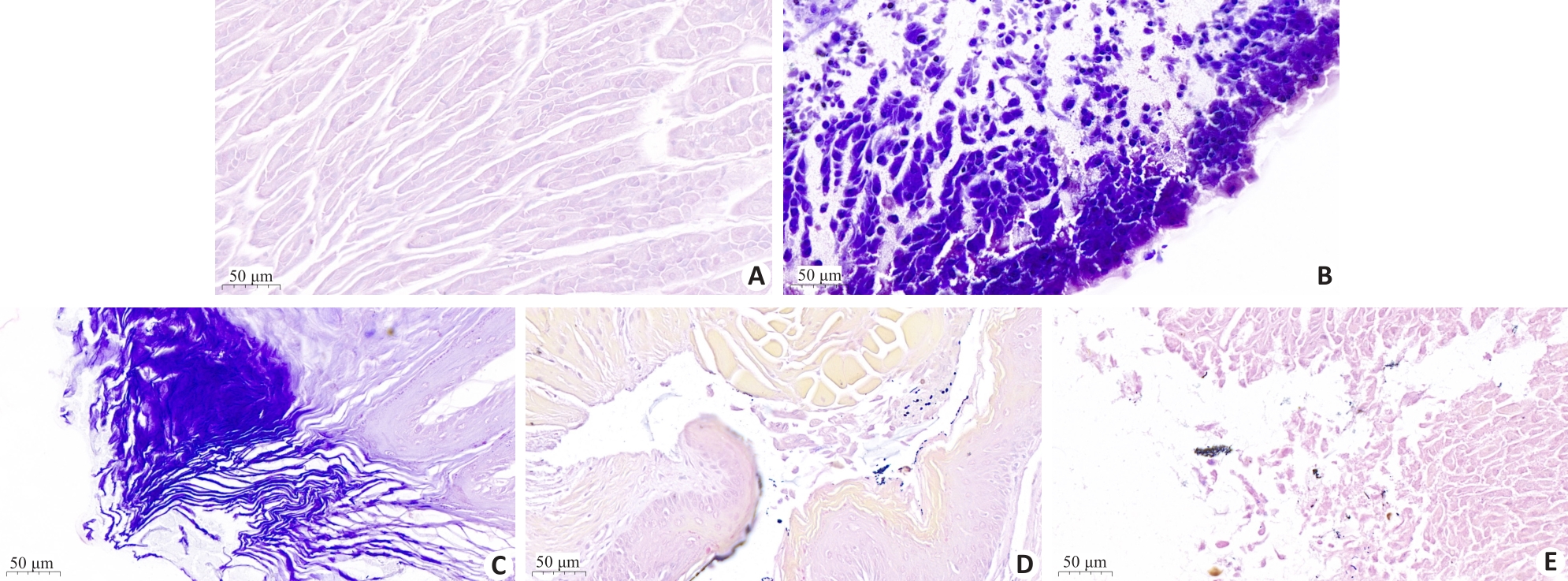
图8 不同组别小鼠胃组织切片HE染色分析
Fig. 8 HE staining of gastric tissues in different groups of mice. A: blank group; B: Hp infection model group; C: L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic control group; D: L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic low dose group; E: L. paracasei TK1501 postbiotic high dose group.
| Groups | Clump counts (CFU/mL) | Urease reagent detection |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 3.40×10-1 | -- |
| Model | 2.57×10-3** | ++ |
| Experimental control | 2.39×10-3 | ++ |
| Low dose | 1.38×10-2 ## | - |
| High dose | 3.60×10-1## | - - |
表5 不同组别小鼠胃黏膜中Hp生长情况
Tab.5 Quantitative analysis of Hp in gastric mucosa of the mice in different groups
| Groups | Clump counts (CFU/mL) | Urease reagent detection |
|---|---|---|
| Blank | 3.40×10-1 | -- |
| Model | 2.57×10-3** | ++ |
| Experimental control | 2.39×10-3 | ++ |
| Low dose | 1.38×10-2 ## | - |
| High dose | 3.60×10-1## | - - |
| 1 | Lim SM. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of antimicrobial substances produced by lactic acid bacteria isolated from Baikkimchi[J]. J Korean Soc Appl Biol Chem, 2014, 57(5): 621-30. DOI: 10.1007/s13765-014-4198-6 |
| 2 | Li YL, Li XY, Tan ZJ. An overview of traditional Chinese medicine therapy for Helicobacter pylori-related gastritis[J]. Helicobacter, 2021, 26(3): e12799. DOI: 10.1111/hel.12799 |
| 3 | Shi YY, Yang ZW, Zhang T, et al. SIRT1-targeted miR-543 autophagy inhibition and epithelial-mesenchymal transition promotion in Helicobacter pylori CagA-associated gastric cancer[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2019, 10(9): 625-33. DOI: 10.1038/s41419-019-1859-8 |
| 4 | Han TT, Jing XH, Bao JY, et al. H. pylori infection alters repair of DNA double-strand breaks via SNHG17[J]. J Clin Invest, 2020, 130(7): 3901-18. DOI: 10.1172/jci125581 |
| 5 | Feige MH, Vieth M, Sokolova O, et al. Helicobacter pylori induces direct activation of the lymphotoxin beta receptor and non-canonical nuclear factor-kappa B signaling[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res, 2018, 1865(4): 545-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.01.006 |
| 6 | Aiba, Umeda K, Rahman S, et al. Synergistic effect of anti-Helicobacter pylori urease immunoglobulin Y from egg yolk of immunized hens and Lactobacillus johnsonii No.1088 to inhibit the growth of Helicobacter pylori in vitro and in vivo [J]. Vaccine, 2019, 37(23): 3106-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.04.045 |
| 7 | Watanabe Y, Oikawa R, Kodaka Y, et al. Cancer-related genetic variants of Helicobacter pylori strains determined using gastric wash-based whole-genome analysis with single-molecule real-time technology[J]. Int J Cancer, 2021, 148(1): 178-92. DOI: 10.1002/ijc.33257 |
| 8 | 黎文鸿, 李紫薇, 汪 娜, 等. 中国儿童幽门螺杆菌感染现状及其影响因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国全科医学, 2022, 25(28): 3569-78. |
| 9 | Resende C, Thiel A, Machado JC, et al. Gastric cancer: basic aspects[J]. Helicobacter, 2011, 16(): 38-44. DOI: 10.1111/j.1523-5378.2011.00879.x |
| 10 | 董奇灵, 赵慧慧, 李雪莹, 等. 中医药抗幽门螺杆菌感染的研究进展[J]. 中医药学报, 2023, 51(4): 108-11. |
| 11 | Ren S, Cai PP, Liu YQ, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in China: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 2022, 37(3): 464-70. DOI: 10.1111/jgh.15751 |
| 12 | 鞠俊杰. 含铋剂四联疗法与传统三联疗法治疗幽门螺杆菌(H.pylori)阳性小儿胃炎的临床疗效[J]. 中西医结合心血管病电子杂志, 2018, 6(9): 193-8. |
| 13 | Hu Y, Zhang M, Lu B, et al. Helicobacter pylori and antibiotic resistance, A continuing and intractable problem[J]. Helicobacter, 2016, 21(5): 349-63. DOI: 10.1111/hel.12299 |
| 14 | Gough EK. The impact of mass drug administration of antibiotics on the gut microbiota of target populations[J]. Infect Dis Poverty, 2022, 11(1): 76-83. DOI: 10.1186/s40249-022-00999-5 |
| 15 | Alava J, Altuğ G, Davies J, et al. Antibiotics as CECs: an overview of the hazards posed by antibiotics and antibiotic resistance[J]. Frontiers Marine Sci, 2016,3:102. DOI: 10.3389/fmars.2016.00024 |
| 16 | Bendjeddou K, Fons M, Strocker P, et al. Characterization and purification of a bacteriocin from Lactobacillus paracasei subsp. paracasei BMK2005, an intestinal isolate active against multidrug-resistant pathogens[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2012, 28(4): 1543-52. DOI: 10.1007/s11274-011-0958-1 |
| 17 | Kumar SB, Arnipalli SR, Ziouzenkova O. Antibiotics in food chain: the consequences for antibiotic resistance[J]. Antibiotics, 2020, 9(10): 688-96. DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics9100688 |
| 18 | Bengoa AA, Errea AJ, Rumbo M, et al. Modulatory properties of Lactobacillus paracasei fermented milks on gastric inflammatory conditions[J]. Int Dairy J, 2020, 111: 104839-45. DOI: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2020.104839 |
| 19 | Das D, Sarkar S, Borsingh Wann S, et al. Current perspectives on the anti-inflammatory potential of fermented soy foods[J]. Food Res Int, 2022, 152: 110922-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110922 |
| 20 | Ali Mousavi Jam S, Talebi M, Alipour B, et al. The therapeutic effect of potentially probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei on dimethylhydrazine induced colorectal cancer in rats[J]. Food Biosci, 2021, 41: 101097. DOI: 10.1016/j.fbio.2021.101097 |
| 21 | Lv XC, Chen M, Huang ZR, et al. Potential mechanisms underlying the ameliorative effect of Lactobacillus paracasei FZU103 on the lipid metabolism in hyperlipidemic mice fed a high-fat diet[J]. Food Res Int, 2021, 139: 109956-63. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109956 |
| 22 | Xie Y, Guo QS, Wang GS. Preparative separation and purification of the total flavonoids in Scorzonera austriaca with macroporous resins[J]. Molecules, 2016, 21(6): 768-83. DOI: 10.3390/molecules21060768 |
| 23 | Friedrich V, Gerhard M. Vaccination against Helicobacter pylori-An approach for cancer prevention?[J]. Mol Aspects Med, 2023, 92: 101183. DOI: 10.1016/j.mam.2023.101183 |
| 24 | Berger H, Marques MS, Zietlow R, et al. Gastric cancer pathogenesis[J]. Helicobacter, 2016, 21(): 34-8. DOI: 10.1111/hel.12338 |
| 25 | 张 乐, 丁一珍, 潘媛娜, 等. 产细菌素乳酸菌的筛选及其益生性能评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2023, 49(22): 19-26. |
| 26 | Cruz POD, Matos CJ, Nascimento YM, et al. Efficacy of potentially probiotic fruit-derived Lactobacillus fermentum, L. paracasei and L. plantarum to remove aflatoxin M1 in vitro [J]. Toxins, 2020, 13(1): 4-12. DOI: 10.3390/toxins13010004 |
| 27 | Lv XR, Ma HH, Sun MT, et al. A novel bacteriocin DY4-2 produced by Lactobacillus plantarum from cutlassfish and its application as bio-preservative for the control of Pseudomonas fluorescens in fresh turbot (Scophthalmus maximus) fillets[J]. Food Contr, 2018, 89: 22-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.02.002 |
| 28 | Miao JY, Liao WW, Pan ZY, et al. Isolation and identification of iron-chelating peptides from casein hydrolysates[J]. Food Funct, 2019, 10(5): 2372-81. DOI: 10.1039/c8fo02414f |
| 29 | Gomaa EZ. Synergistic antibacterial efficiency of bacteriocin and silver nanoparticles produced by probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei against multidrug resistant bacteria[J]. Int J Pept Res Ther, 2019, 25(3): 1113-25. DOI: 10.1007/s10989-018-9759-9 |
| 30 | 韩雪冰, 元香南, 方 俊, 等. 乳酸菌维持动物肠道健康的研究进展[J]. 中国科学: 生命科学, 2023, 53(4): 464-79. |
| 31 | 单春乔, 刘艳, 刘秋晨, 等. 嗜酸乳杆菌产细菌素生物学特性与临床应用的研究[C]// 第八届全国畜牧兽医青年科技工作者学术研讨会论文集. 绍兴, 2016: 440. |
| 32 | 柳 青. 乳酸杆菌产细菌素对金黄色葡萄球菌和肺炎链球菌临床株的体外抑菌效果研究[J]. 中国实用医药, 2022, 17(20): 192-4. |
| 33 | Techo S, Visessanguan W, Vilaichone RK, et al. Characterization and antibacterial activity against Helicobacter pylori of lactic acid bacteria isolated from Thai fermented rice noodle[J]. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 2019, 11(1): 92-102. DOI: 10.1007/s12602-018-9385-z |
| 34 | Pei JJ, Yuan YH, Yue YL. Primary characterization of bacteriocin paracin C-a novel bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus paracasei .[J]. Food Control, 2013, 34(1): 168-76. DOI: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2013.03.040 |
| 35 | Mendiola AS, Cardona AE. The IL-1β phenomena in neuroinflammatory diseases[J]. J Neural Transm, 2018, 125(5): 781-95. DOI: 10.1007/s00702-017-1732-9 |
| 36 | Wang YJ, Che MX, Xin JG, et al. The role of IL-1β and TNF‑α in intervertebral disc degeneration[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 131: 110660. DOI: 10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110660 |
| 37 | Sato Y, Okamoto K, Kida Y, et al. Overview of chemotherapy for gastric cancer[J]. J Clin Med, 2023, 12(4): 1336-45. DOI: 10.3390/jcm12041336 |
| 38 | Shi YY, Wang P, Guo YL, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced DNA damage is a potential driver for human gastric cancer AGS cells[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2019, 38(3): 272-80. DOI: 10.1089/dna.2018.4487 |
| 39 | Ren ZJ, Li JY, Du XH, et al. Helicobacter pylori-induced progranulin promotes the progression of the gastric epithelial cell cycle by regulating CDK4[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2022, 32(7): 844-54. DOI: 10.4014/jmb.2203.03053 |
| [1] | 蔡子萌, 易佩伟, 陶 泉, 冯衍秋. 1H-MRS、Dixon水脂分离与Z谱成像技术在大鼠棕色脂肪上的量化比较[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 783-788. |
| [2] | 苏炳森, 操龙斌, 郑介婷, 张 琳, 张子康, 邱 峰. 健康妇女生殖道内格氏乳杆菌的分离鉴定与安全性评价[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(12): 1809-1815. |
| [3] | 陈贤华,潘炜伦,李 博,郑 磊. 外泌体双膜蛋白共表达检测平台:基于磁性分离和催化发夹组装[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(12): 1453-1460. |
| [4] | 江茜茜,朱云程,季卫东. 精神分析疗法治疗儿童睡行症1 例报告[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(05): 505-. |
| [5] | 赖杰伟,陈韵岱,韩宝石,季磊,石亚君,黄志聪,阳维,冯前进. 基于DenseNet的心电数据自动诊断算法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(01): 69-. |
| [6] | 刘镖水,张晶,程军营,华佳,冯衍秋. 基于多分辨率和区域增长的两点Dixon水脂分离技术[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(02): 245-. |
| [7] | 杨诚,郭文彬,张万松,卞军,杨建昆,亓涛,王春艳,刘存东. 基于PEG6000富集精液来源外泌体的提取及鉴定[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(11): 1531-. |
| [8] | 祝旭龙,颜谭,姚维杰,王永恒,程冲,向俊西,吕毅,高庆东,李建辉. 大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的分离与培养方法优化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1621-. |
| [9] | 孔艺,刘媛,李国锋,谢海辉. 大戟根的化学成分分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(12): 1748-. |
| [10] | 汪艳丽,刘如秀,刘宇,李泱. 用于膜片钳研究的乳鼠窦房结细胞的分离与鉴定[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(03): 397-. |
| [11] | 胡国栋,陈英华,刘爱华,周国红,康静,蔡绍曦. 一种改良的肺微血管内皮细胞培养方法[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2012, 32(08): 1151-. |
| [12] | 陈静,邹玉平. 内窥镜在原发性闭角型青光眼房角分离术中的临床价值[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2012, 32(07): 1056-. |
| [13] | 刘军; 安靓; 陈金拳; . 胎鼠肝nestin阳性细胞的分离培养和诱导分化研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(12): 1757-1759. |
| [14] | 陆东风; 吴昊; 黄璟; 李妍;. 新生SD大鼠心肌干细胞的体外分离培养与鉴定[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(11): 1629-1632. |
| [15] | 吕本强; 邢学锋; 罗佳波;. 注射用双黄连冻干粉化学成分的分离与鉴别[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(10): 1471-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||