Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1858-1865.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.03
Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinbao ZHAO1,2( ), Yiqin JIA1(
), Yiqin JIA1( ), Handing MAO1, Shijiao WANG3, Fan XU2, Xin LI4, Ye TAO5, Lei XUE6, Shuyuan LIU1(
), Handing MAO1, Shijiao WANG3, Fan XU2, Xin LI4, Ye TAO5, Lei XUE6, Shuyuan LIU1( ), Qing SONG2, Biye ZHOU1(
), Qing SONG2, Biye ZHOU1( )
)
Received:2024-04-02
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Shuyuan LIU, Biye ZHOU
E-mail:zjb130500@163.com;903915664@qq.com;liusydoc@163.com;zhoubiye@qq.com
Jinbao ZHAO, Yiqin JIA, Handing MAO, Shijiao WANG, Fan XU, Xin LI, Ye TAO, Lei XUE, Shuyuan LIU, Qing SONG, Biye ZHOU. Effect of different delayed cooling time on organ injuries in rat models of exertional heat stroke[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1858-1865.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.03
| Group | Weight (g) | Age (week) | Pre-modelling Tc (℃) | Post-modelling Tc (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 251.90±7.29 | 7.0±0.8 | 37.85±0.81 | - |
| EHS | 251.75±6.23 | 6.9±0.8 | 37.97±0.85 | 43.62±0.68 |
| Immediate cooling group | 252.77±9.01 | 7.2±0.5 | 38.07±0.76 | 43.22±0.68 |
| Delayed cooling group A | 250.45±6.36 | 6.8±0.7 | 38.06±0.94 | 43.32±0.99 |
| Delayed cooling group B | 250.29±7.47 | 7.2±0.8 | 37.95±0.83 | 43.52±0.73 |
| Delayed cooling group C | 250.68±6.81 | 7.0±0.9 | 37.68±0.65 | 43.16±0.75 |
Tab.1 Body weight, age, and core temperature (Tc) of the rats before and after modeling in different groups (n=12, Mean±SD)
| Group | Weight (g) | Age (week) | Pre-modelling Tc (℃) | Post-modelling Tc (℃) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 251.90±7.29 | 7.0±0.8 | 37.85±0.81 | - |
| EHS | 251.75±6.23 | 6.9±0.8 | 37.97±0.85 | 43.62±0.68 |
| Immediate cooling group | 252.77±9.01 | 7.2±0.5 | 38.07±0.76 | 43.22±0.68 |
| Delayed cooling group A | 250.45±6.36 | 6.8±0.7 | 38.06±0.94 | 43.32±0.99 |
| Delayed cooling group B | 250.29±7.47 | 7.2±0.8 | 37.95±0.83 | 43.52±0.73 |
| Delayed cooling group C | 250.68±6.81 | 7.0±0.9 | 37.68±0.65 | 43.16±0.75 |
| Group | Delay time for cooling (min) | Cooling rate (℃/min) | Number of deaths within 24 h | 24-h mortality rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | - | - | 0 | 0 |
| EHS | - | 0.08±0.05 | 7 | 58.3% |
| Immediate cooling group | 0 | 0.36±0.11* | 1 | 8.3%* |
| Delayed cooling group A | 5 | 0.26±0.07*# | 2 | 16.7%* |
| Delayed cooling group B | 15 | 0.20±0.05*# | 3 | 25.0%* |
| Delayed cooling group C | 30 | 0.16±0.04*#^ | 5 | 41.7%# |
Tab.2 Effect of cooling treatment on 24-h mortality rate of the rat models of EHS (n=12)
| Group | Delay time for cooling (min) | Cooling rate (℃/min) | Number of deaths within 24 h | 24-h mortality rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | - | - | 0 | 0 |
| EHS | - | 0.08±0.05 | 7 | 58.3% |
| Immediate cooling group | 0 | 0.36±0.11* | 1 | 8.3%* |
| Delayed cooling group A | 5 | 0.26±0.07*# | 2 | 16.7%* |
| Delayed cooling group B | 15 | 0.20±0.05*# | 3 | 25.0%* |
| Delayed cooling group C | 30 | 0.16±0.04*#^ | 5 | 41.7%# |
| Variables Statistical indicators | Cooling rate | Delay time for cooling | Mortality rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling rate | Pearson correlation coefficient | 1 | -0.912 | -0.961 |
| P | - | 0.088 | 0.009 | |
| Delay time for cooling | Pearson correlation coefficient | -0.912 | 1 | 0.996 |
| P | 0.088 | - | 0.004 | |
| Mortality rate | Pearson correlation coefficient | -0.961 | 0.996 | 1 |
| P | 0.009 | 0.004 | - | |
Tab.3 Correlation analysis of delay time of cooling treatment, cooling rate and 24-h mortality rate of the rat models
| Variables Statistical indicators | Cooling rate | Delay time for cooling | Mortality rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cooling rate | Pearson correlation coefficient | 1 | -0.912 | -0.961 |
| P | - | 0.088 | 0.009 | |
| Delay time for cooling | Pearson correlation coefficient | -0.912 | 1 | 0.996 |
| P | 0.088 | - | 0.004 | |
| Mortality rate | Pearson correlation coefficient | -0.961 | 0.996 | 1 |
| P | 0.009 | 0.004 | - | |

Fig.3 Representative images of rat kidney sections in each group (HE staining, original magnification: ×200). A: Control group. B: EHS group. C: Immediate cooling group. D: Delayed cooling group A. E: Delayed cooling group B. F: Delayed cooling group C.
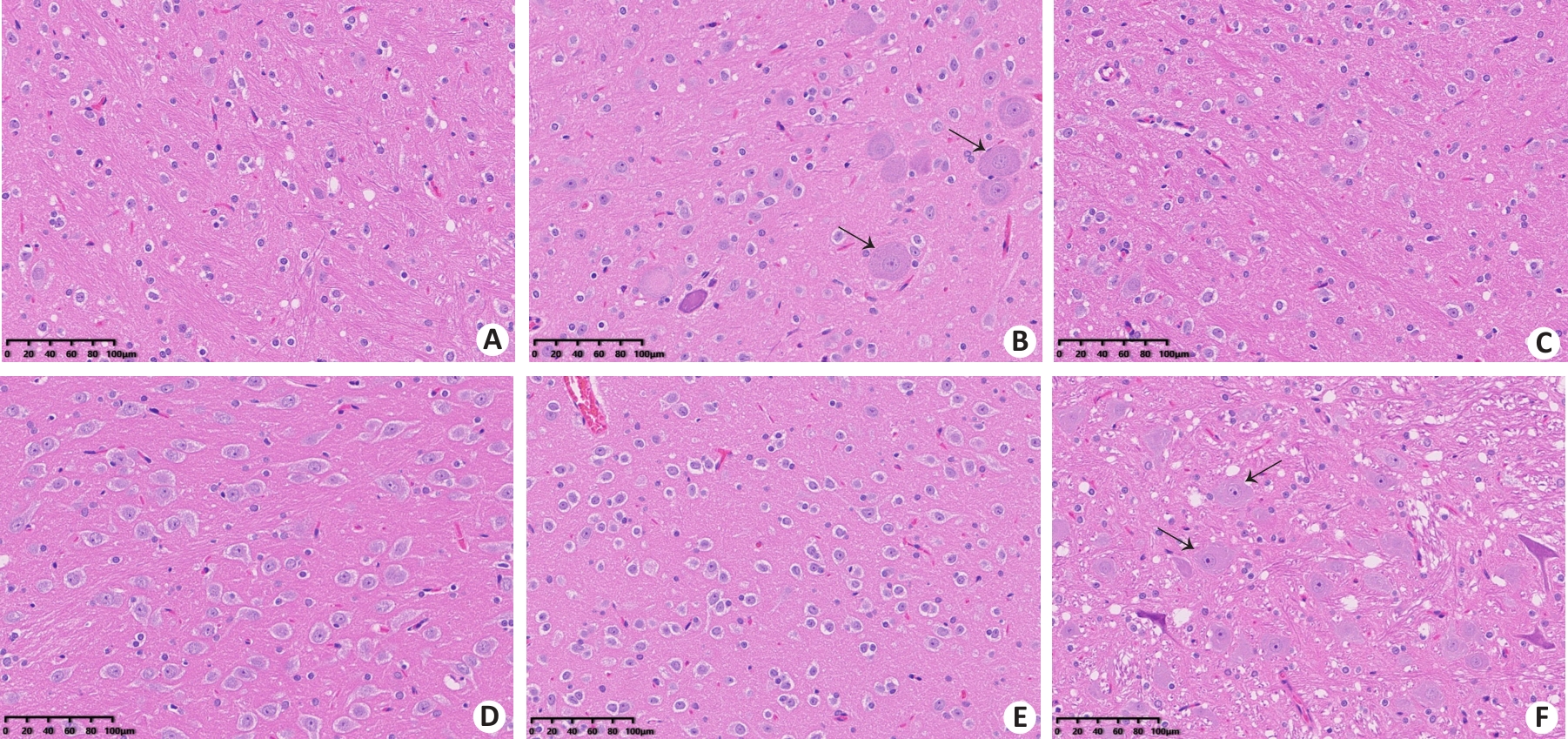
Fig. 4 Representative images of rat brain tissue sections in each group (HE staining, ×200). A: Control group. B: EHS group. C: Immediate cooling group. D: Delayed cooling group A. E: Delayed cooling group B. F: Delayed cooling group C. Black arrows indicate neurons with pyknosis accompanied by collapse and karyolysis of Nissl body.
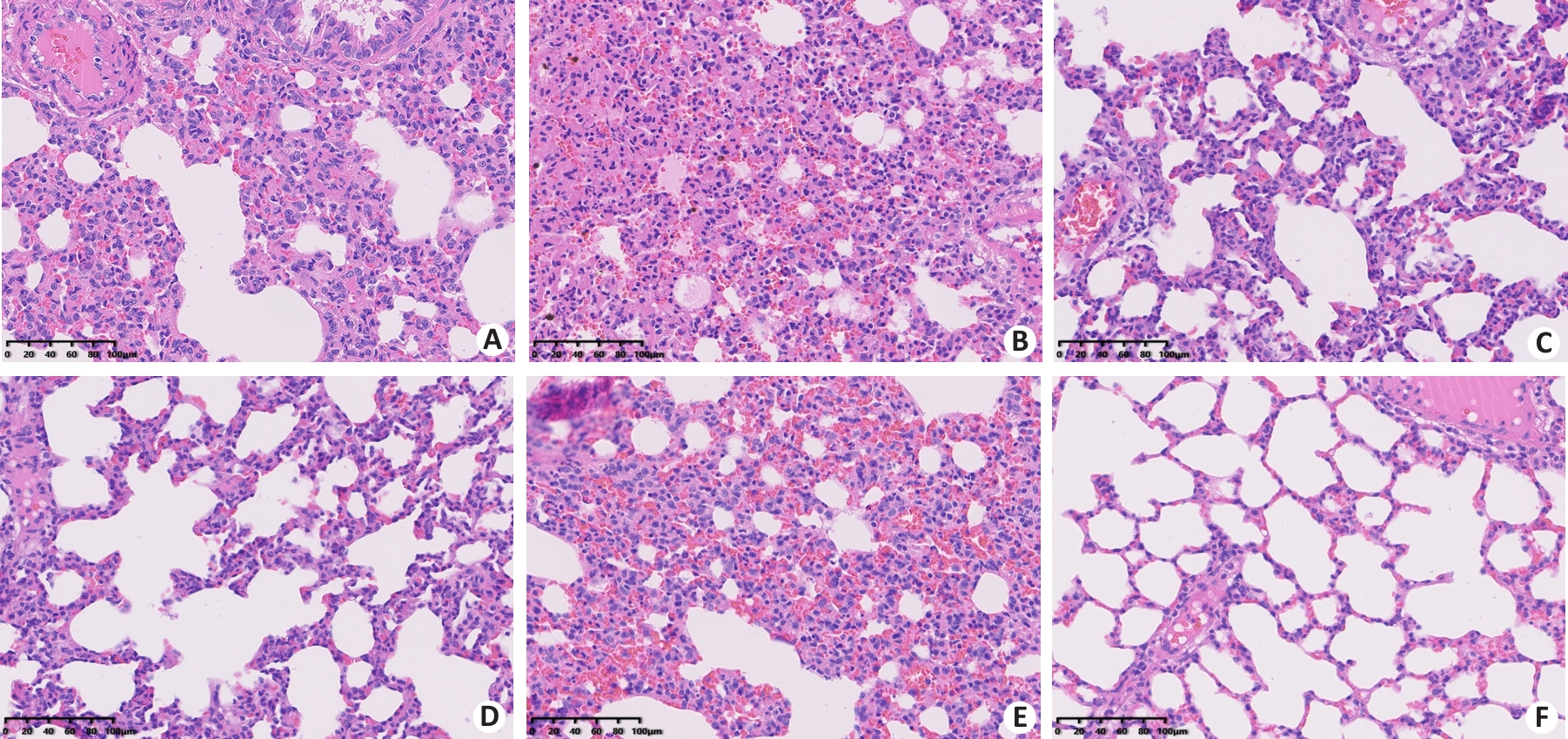
Fig. 5 HE staining of rat lung tissue sections in each group (×200). A: Control group. B: EHS group. C: Immediate cooling group. D: Delayed cooling group A. E: Delayed cooling group B. F: Delayed cooling group C.
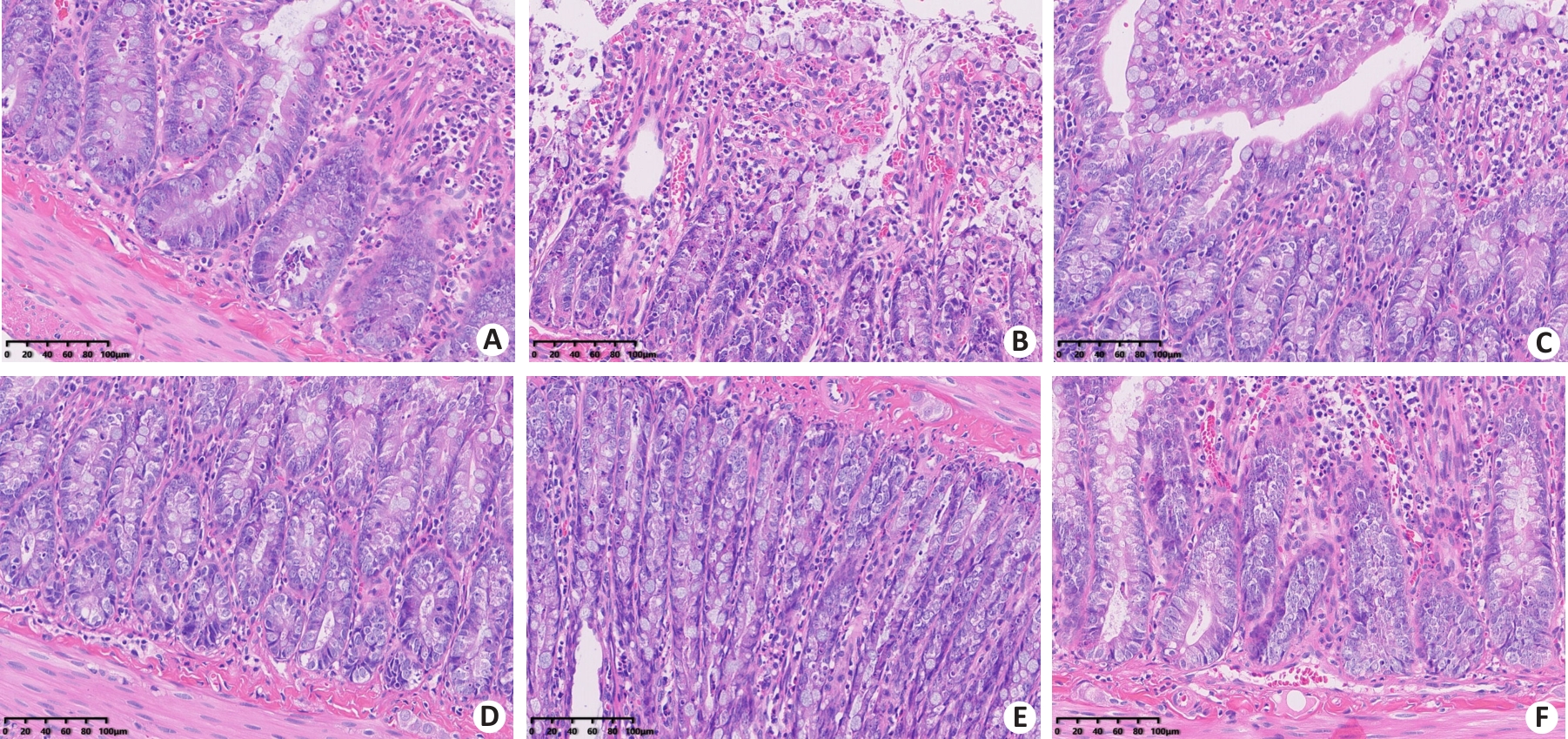
Fig. 6 HE staining of rat small intestine tissues in each group (×200). A: Control group. B: EHS group. C: Immediate cooling group. D: Delayed cooling group A. E: Delayed cooling group B. F: Delayed cooling group C.
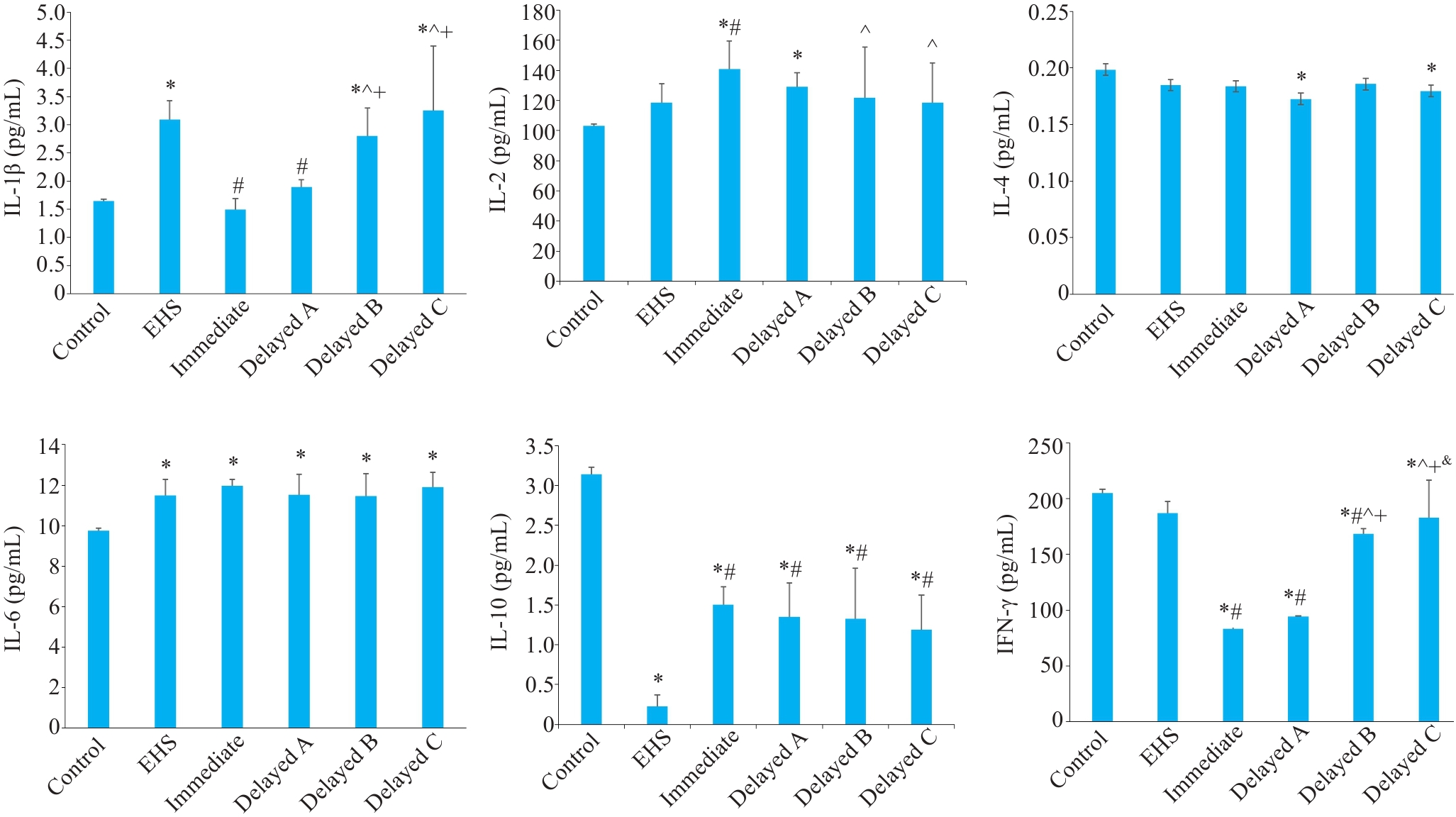
Fig. 7 Comparison of inflammatory factors among the groups. *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs EHS group; ^P<0.05 vs immediate cooling group; + P<0.05 vs delayed cooling group A; &P<0.05 vs delayed cooling group B.
| 1 | 全军热射病防治专家组, 全军重症医学专业委员会. 中国热射病诊断与治疗专家共识[J]. 解放军医学杂志, 2019, 44(3): 181-96. |
| 2 | Liu SY, Song JC, Mao HD, et al. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of heat stroke in China[J]. Mil Med Res, 2020, 7(1): 1. |
| 3 | Katch RK, Scarneo SE, Adams WM, et al. Top 10 research questions related to preventing sudden death in sport and physical activity[J]. Res Q Exerc Sport, 2017, 88(3): 251-68. |
| 4 | Yankelson L, Sadeh B, Gershovitz L, et al. Life-threatening events during endurance sports: is heat stroke more prevalent than arrhythmic death[J]? J Am Coll Cardiol, 2014, 64(5): 463-9. |
| 5 | McGeehin MA, Mirabelli M. The potential impacts of climate variability and change on temperature-related morbidity and mortality in the United States[J]. Environ Health Perspect, 2001, 109(): 185-9. |
| 6 | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Heat-related deaths: United States, 1999-2003[J]. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep, 2006, 55(29): 796-8. |
| 7 | Maule A. Heat exhaustion and heat stroke among active component members of the U.S. armed forces, 2018-2022[J]. MSMR, 2023, 30(4): 3-7. |
| 8 | Liu CC, Shih MF, Wen YS, et al. Dexamethasone improves heat stroke-induced multiorgan dysfunction and damage in rats[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2014, 15(11): 21299-313. |
| 9 | Wen FL, Xu YJ, Xue LE, et al. Proteomics analyses of acute kidney injury biomarkers in a rat exertional heat stroke model[J]. Front Physiol, 2023, 14: 1176998. |
| 10 | 毛汉丁, 王 娇, 王宇曦, 等. 植入式生物遥测技术在劳力型热射病大鼠实验模型中的应用[J]. 解放军医学院学报, 2021, 42(10): 1068-73, 1088. |
| 11 | 李庆华, 孙荣青, 吕宏迪, 等. 热打击后不同核心温度对大鼠血清炎性细胞因子及MODS的影响[J]. 中华危重病急救医学, 2018, 30(5): 439-43. |
| 12 | 曹 策, 李玲美, 訾明杰, 等. 医学研究中动物实验样本量的确定方法[J]. 中国比较医学杂志, 2023, 33(2): 99-105. |
| 13 | Lin XJ, Lin CH, Liu RX, et al. Myricetin against myocardial injury in rat heat stroke model[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2020, 127: 110194. |
| 14 | He SX, Li R, Peng YM, et al. ACSL4 contributes to ferroptosis-mediated rhabdomyolysis in exertional heat stroke[J]. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle, 2022, 13(3): 1717-30. |
| 15 | Sato A, Ikawa Y, Inoue N, et al. Massive intestinal liquid retention in a case of severe heat stroke[J]. J Paediatr Child Health, 2019, 55(2): 248-9. |
| 16 | Gathiram P, Wells MT, Raidoo D, et al. Changes in lipopolysaccharide concentrations in hepatic portal and systemic arterial plasma during intestinal ischemia in monkeys[J]. Circ Shock, 1989, 27(2): 103-9. |
| 17 | Dokladny K, Moseley PL, Ma TY. Physiologically relevant increase in temperature causes an increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability[J]. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 2006, 290(2): G204-12. |
| 18 | Yang WR, Li BB, Hu Y, et al. Oxidative stress mediates heat-induced changes of tight junction proteins in porcine Sertoli cells via inhibiting CaMKKβ‑AMPK pathway[J]. Theriogenology, 2020, 142: 104-13. |
| 19 | Leon LR, Helwig BG. Heat stroke: role of the systemic inflammatory response[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2010, 109(6): 1980-8. |
| 20 | 刘树元, 汪 茜, 邢 令, 等. 劳力型热射病器官损伤机制与救治策略[J]. 武警医学, 2020, 31(5): 450-4. |
| 21 | Hu J, Kang HJ, Liu C, et al. Response of regulatory T cells to classic heat stroke in mice[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(6): 4609-15. |
| 22 | Ganesan S, Volodina O, Pearce SC, et al. Acute heat stress activated inflammatory signaling in porcine oxidative skeletal muscle[J]. Physiol Rep, 2017, 5(16): e13397. |
| 23 | 徐向迎, 宗 晶, 王小洁. 重症劳力性热射病患者的胃肠道屏障破坏及对策探讨[J]. 海军医学杂志, 2023, 44(4): 414-6. |
| 24 | Lim CL. Heat sepsis precedes heat toxicity in the pathophysiology of heat stroke-a new paradigm on an ancient disease[J]. Antioxidants, 2018, 7(11): 149. |
| 25 | Bouchama A, Knochel JP. Heat stroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2002, 346(25): 1978-88. |
| 26 | Bouchama A, Roberts G, Al Mohanna F, et al. Inflammatory, hemostatic, and clinical changes in a baboon experimental model for heatstroke[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2005, 98(2): 697-705. |
| 27 | Epstein Y, Yanovich R. Heatstroke[J]. N Engl J Med, 2019, 380(25): 2449-59. |
| 28 | Leon LR, Helwig BG. Role of endotoxin and cytokines in the systemic inflammatory response to heat injury[J]. Front Biosci, 2010, 2(3): 916-38. |
| 29 | Bouchama A, Kunzelmann C, Dehbi M, et al. Recombinant activated protein C attenuates endothelial injury and inhibits procoagulant microparticles release in baboon heatstroke[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2008, 28(7): 1318-25. |
| 30 | Li Y, Palmer A, Lupu L, et al. Inflammatory response to the ischaemia-reperfusion insult in the liver after major tissue trauma[J]. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg, 2022, 48(6): 4431-44. |
| 31 | Cannon JG. Inflammatory cytokines in nonpathological states[J]. News Physiol Sci, 2000, 15: 298-303. |
| 32 | Christman JW, Sadikot RT, Blackwell TS. The role of nuclear factor-kappa B in pulmonary diseases[J]. Chest, 2000, 117(5): 1482-7. |
| 33 | Schwarze J, Cieslewicz G, Joetham A, et al. Critical roles for interleukin-4 and interleukin-5 during respiratory syncytial virus infection in the development of airway hyperresponsiveness after airway sensitization[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000, 162(2 Pt 1): 380-6. |
| 34 | Shanley TP, Schmal H, Friedl HP, et al. Regulatory effects of intrinsic IL-10 in IgG immune complex-induced lung injury[J]. J Immunol, 1995, 154(7): 3454-60. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||