Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 331-339.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.14
XU Xinzhu1( ), Lina GUO1, Kangdi ZHENG2, Yan MA2, Shuxian LIN1, Yingxi HE1, Wen SHENG1, Suhua XU1, Feng QIU3(
), Lina GUO1, Kangdi ZHENG2, Yan MA2, Shuxian LIN1, Yingxi HE1, Wen SHENG1, Suhua XU1, Feng QIU3( )
)
Received:2024-10-02
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-03-03
Contact:
Feng QIU
E-mail:xuxinzhuxxz@163.com;QFSFL@126.com
XU Xinzhu, Lina GUO, Kangdi ZHENG, Yan MA, Shuxian LIN, Yingxi HE, Wen SHENG, Suhua XU, Feng QIU. Lacticaseibacillus paracasei E6 improves vinorelbine-induced immunosuppression in zebrafish through its metabolites acetic acid and propionic acid[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 331-339.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.02.14
| Gene | Forward (5'—3') | Reverse (5'—3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | TCGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC | CTCGTGGATACCGCAAGATTC |
| IL-2 | AACTCCTACAAGCCCAGCAC | ACACTCGGTCGTCAAACGAA |
| INF-γ | GCCTGGGGAGTATGTTTGCT | CAGGAAGATGGGGTGTGCAT |
Tab.1 Sequences of the primers for qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward (5'—3') | Reverse (5'—3') |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | TCGAGCAGGAGATGGGAACC | CTCGTGGATACCGCAAGATTC |
| IL-2 | AACTCCTACAAGCCCAGCAC | ACACTCGGTCGTCAAACGAA |
| INF-γ | GCCTGGGGAGTATGTTTGCT | CAGGAAGATGGGGTGTGCAT |
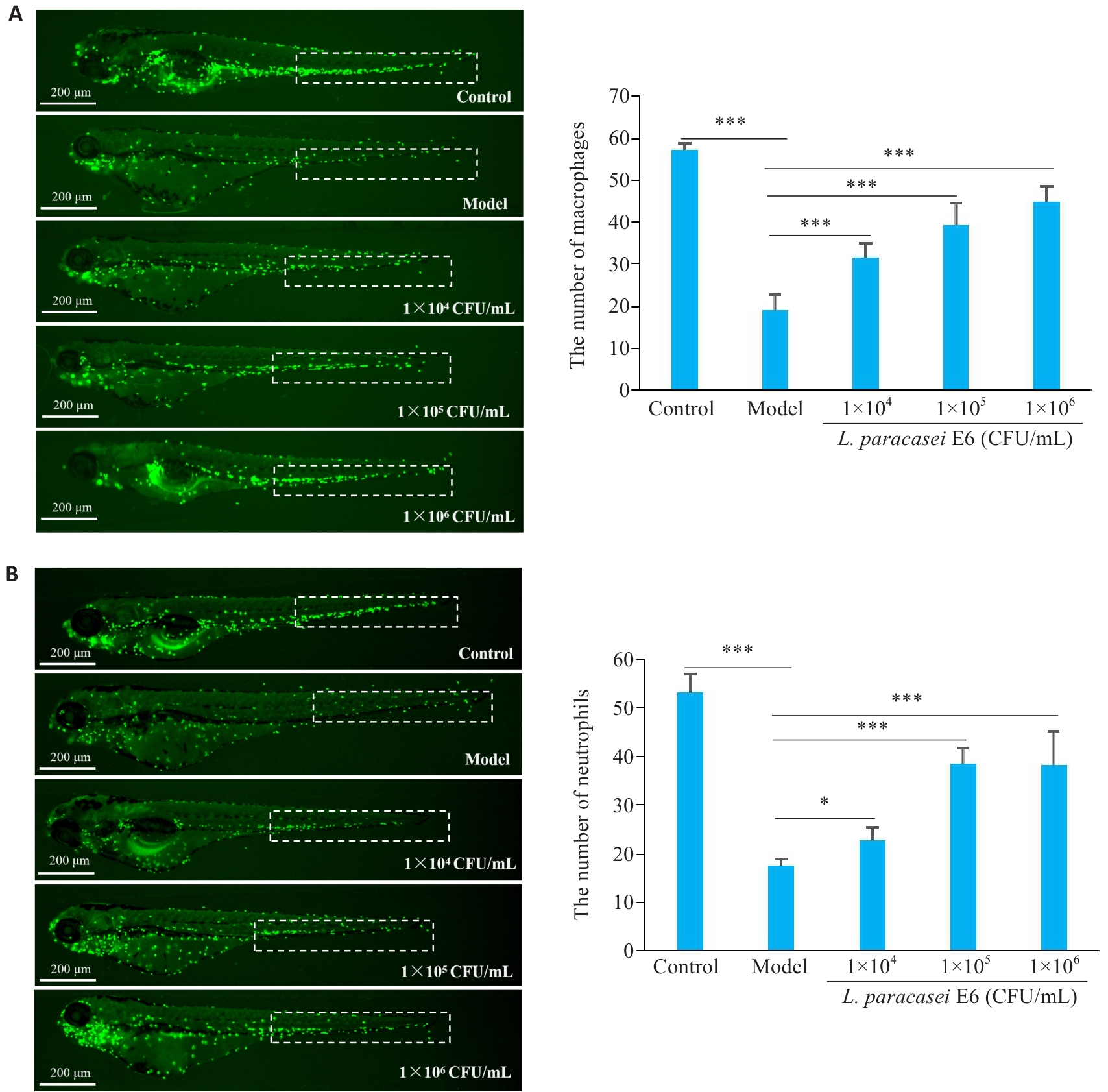
Fig.2 L. paracasei E6 improves vinorelbine-induced immunosuppression in zebrafish. A: L. paracasei E6 inhibits vinorelbine-induced reduction of macrophage count in the caudal hematopoietic tissue (CHT; dashed box) of zebrafish (left). Macrophage counts are shown in the diagram on the right. B: L. paracasei E6 inhibits vinorelbine-induced reduction of neutrophil counts in the CHT (dashed box) in zebrafish. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001.
| SCFAs | Concentration(ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| MRS | Culture supernatant | |
| Acetic acid | 354.70±5.03 | 33576.01±200.71*** |
| Propionic acid | - | 74.65±1.70*** |
| Isobutyric acid | - | - |
| Butyric acid | - | 33.40±2.29*** |
| 2-Methylbutyric acid | - | - |
| Isovaleric acid | - | - |
| Valeric acid | - | - |
| 2, 2-Dimethylbutanoic acid | - | - |
| 2-Ethyl butyric acid | - | - |
| 3, 3-Dimethylbutanoic acid | - | - |
| 2-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| 3-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| 4-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| Caproic acid | - | - |
Tab.2 Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) detected in culture supernatant of L. paracasei E6 (Mean±SD, n=3)
| SCFAs | Concentration(ng/mL) | |
|---|---|---|
| MRS | Culture supernatant | |
| Acetic acid | 354.70±5.03 | 33576.01±200.71*** |
| Propionic acid | - | 74.65±1.70*** |
| Isobutyric acid | - | - |
| Butyric acid | - | 33.40±2.29*** |
| 2-Methylbutyric acid | - | - |
| Isovaleric acid | - | - |
| Valeric acid | - | - |
| 2, 2-Dimethylbutanoic acid | - | - |
| 2-Ethyl butyric acid | - | - |
| 3, 3-Dimethylbutanoic acid | - | - |
| 2-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| 3-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| 4-Methylvaleric acid | - | - |
| Caproic acid | - | - |
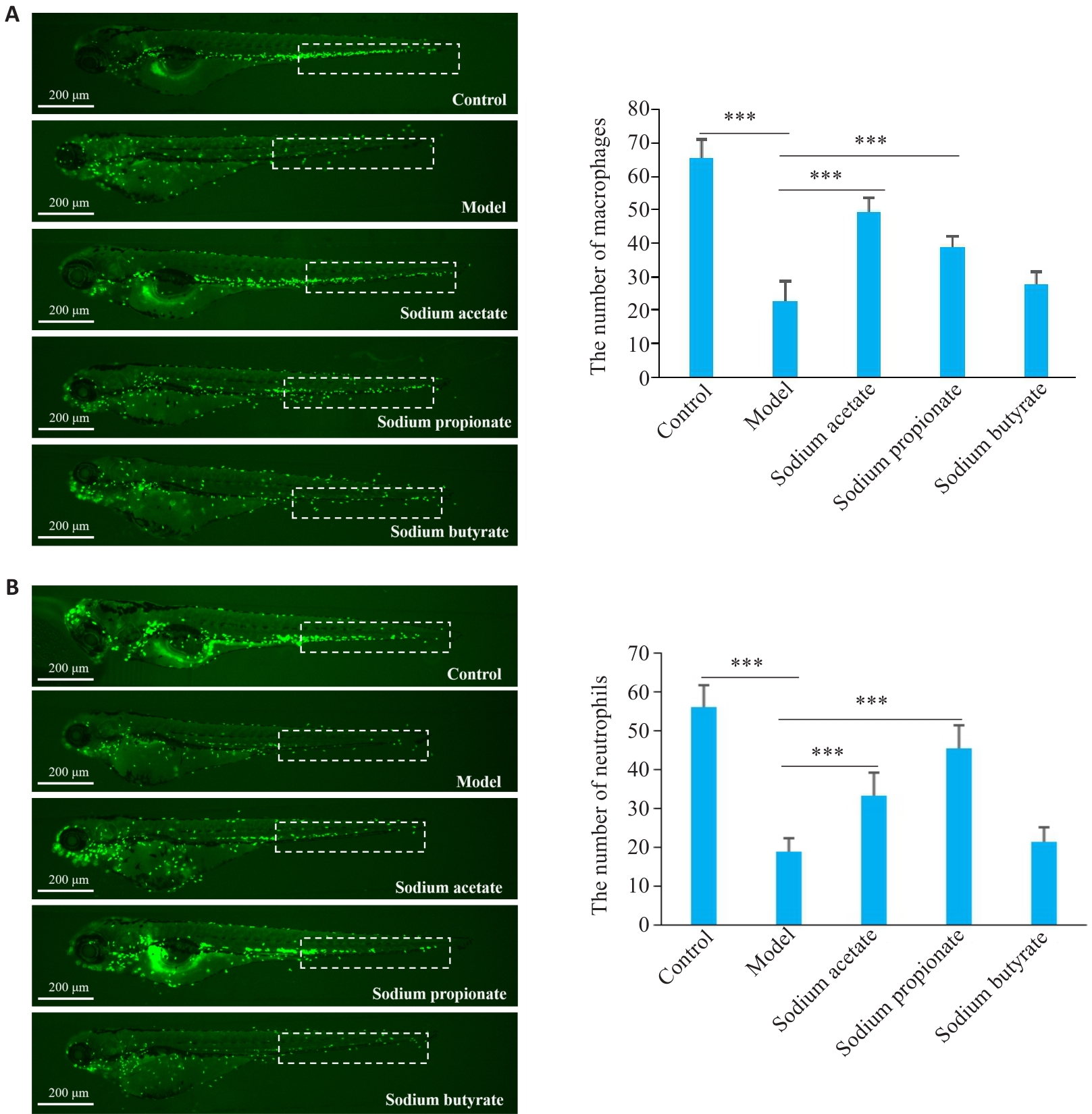
Fig.6 Effects of SCFAs (sodium acetate, sodium propionate, and sodium butyrate) on vinorelbine-induced immunosuppression in zebrafish. A: Effects of sodium acetate, sodium propionate, and sodium butyrate on vinorelbine-induced reduction of macrophage number in the CHT (dashed box) of zebrafish. B: Effects of sodium acetate, sodium propionate, and sodium butyrate on vinorelbine-induced reduction of neutrophil number in the CHT (dashed box) of zebrafish. ***P<0.001.
| 1 | Estevinho F, Gomes R, Hasmucrai D, et al. Metronomic oral vinorelbine in a real-world population of advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients[J]. Pulmonology, 2022, 28(5): 368-75. |
| 2 | Wang S, Wei W, Yong H, et al. Synergistic anti-cancer and attenuation effects of thymosin on chemotherapeutic drug vinorelbine in tumor-bearing zebrafish[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 162: 114633. |
| 3 | Boccia R, Glaspy J, Crawford J, et al. Chemotherapy-induced neutropenia and febrile neutropenia in the US: a beast of burden that needs to be tamed[J]? Oncologist, 2022, 27(8): 625-36. |
| 4 | Huang FC, Huang SC. The hazards of probiotics on gut-derived Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis in mice undergoing chemotherapy[J]. Biomedicines, 2024, 12(2): 253. |
| 5 | Thapa D, Kumar V, Naik B, et al. Harnessing probiotic foods: managing cancer through gut health[J]. Food Sci Biotechnol, 2024, 33(9): 2141-60. |
| 6 | Gramajo Lopez A, Gutiérrez F, Saavedra L, et al. Improvement of myelopoiesis in cyclophosphamide-immunosuppressed mice by oral administration of viable or non-viable Lactobacillus strains[J]. Front Immunol, 2021, 12: 647049. |
| 7 | Zhou L, Yin X, Fang B, et al. Effects of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis IU100 on immunomodulation and gut microbiota in immunosuppressed mice[J]. Microorganisms, 2024, 12(3): 493. |
| 8 | Ma W, Li W, Yu S, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of complex probiotics on the immuno-suppressed mice induced by cyclophosphamide[J]. Front Microbiol, 2023, 14: 1055197. |
| 9 | Li SP, Heng X, Guo LY, et al. SCFAs improve disease resistance via modulate gut microbiota, enhance immune response and increase antioxidative capacity in the host[J]. Fish Shellfish Immunol, 2022, 120: 560-8. |
| 10 | Ragavan ML, Hemalatha S. The functional roles of short chain fatty acids as postbiotics in human gut: future perspectives[J]. Food Sci Biotechnol, 2024, 33(2): 275-85. |
| 11 | Li Z, Shi Y, Zhang X, et al. Screening immunoactive compounds of Ganoderma lucidum spores by mass spectrometry molecular networking combined with in vivo zebrafish assays[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2020, 11: 287. |
| 12 | Han L, Kong H, Liu F, et al. Protective effect and mechanisms of new gelatin on chemotherapy-induced hematopoietic injury zebrafish model[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2019, 2019: 8918943. |
| 13 | 王 涛, 戴明珠, 李延川, 等. 复方中药提取物增强免疫力作用及初步机制研究[J]. 中国实验动物学报, 2022, 30(2): 198-207. |
| 14 | 任雪阳, 王 宇, 魏胜利, 等. “保健功能-中药-中药” 关联的石斛保健食品配方规律分析及斑马鱼增强免疫力和缓解体力疲劳功能评价[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(8): 2435-48. |
| 15 | Xia J, Kang Z, Xue Y, et al. A single-cell resolution developmental atlas of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell expansion in zebrafish[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2021, 118(14): e2015748118. |
| 16 | Zhu M, Yang L, Kong S, et al. Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LRa05 alleviates cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppression and intestinal microbiota disorder in mice[J]. J Food Sci, 2024, 89(12): 10003-17. |
| 17 | Rong X, Shu Q. Enhancing immunomodulation in cyclophosphamide-induced immunosuppressed mice through targeted modulation of butyrate-producing gut microbiota via oral administration of Astragalus polysaccharides[J]. Food Sci Nutr, 2024, 12(10): 7683-95. |
| 18 | Huang J, Zhou H, Song T, et al. Fecal microbiota transplantation from sodium alginate-dosed mice and normal mice mitigates intestinal barrier injury and gut dysbiosis induced by antibiotics and cyclophosphamide[J]. Food Funct, 2023, 14(12): 5690-701. |
| 19 | Song YL, Sun MY, Ma FL, et al. Lactiplantibacillus plantarum DLPT4 protects against cyclophosphamide-induced immuno-suppression in mice by regulating immune response and intestinal flora[J]. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins, 2024, 16(2): 321-33. |
| 20 | Min FF, Hu JL, Huang T, et al. Effects of Lactobacillus casei NCU011054 on immune response and gut microbiota of cyclophosphamide induced immunosuppression mice[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2023, 174: 113662. |
| 21 | Ahmadnia A, Mohammadi S, Yamchi A, et al. Augmenting the antitumor efficacy of natural killer cells via SynNotch receptor engineering for targeted IL-12 secretion[J]. Curr Issues Mol Biol, 2024, 46(4): 2931-45. |
| 22 | Fang HT, Li HZ, Chen Y, et al. Bifidobacterium breve CCFM1310 enhances immunity in immunosuppressed mice via modulating immune response and gut microbiota[J]. Food Biosci, 2024, 59: 104058. |
| 23 | Son MY, Cho HS. Anticancer effects of gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids in cancers[J]. J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2023, 33(7): 849-56. |
| 24 | Li XY, He MZ, Yi XR, et al. Short-chain fatty acids in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: New prospects for short-chain fatty acids as therapeutic targets[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(5): e26991. |
| 25 | Zhu Z, Luo Y, Lin L, et al. Modulating effects of turmeric polysaccharides on immune response and gut microbiota in cyclophosphamide-treated mice[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2024, 72(7): 3469-82. |
| 26 | Al-Qadami GH, Secombe KR, Subramaniam CB, et al. Gut microbiota-derived short-chain fatty acids: impact on cancer treatment response and toxicities[J]. Microorganisms, 2022, 10(10): 2048. |
| 27 | Cazzaniga M, Cardinali M, Di Pierro F, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids, particularly butyrate, in oncological immunotherapy with checkpoint inhibitors: the effectiveness of complementary treatment with Clostridium butyricum 588[J]. Microorganisms, 2024, 12(6): 1235. |
| 28 | Mann ER, Lam YK, Uhlig HH. Short-chain fatty acids: linking diet, the microbiome and immunity[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2024, 24: 577-95. |
| 29 | Kalyanaraman B, Cheng G, Hardy M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in cancer prevention and cancer treatment[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2024, 761: 110172. |
| 30 | Antunes KH, Singanayagam A, Williams L, et al. Airway-delivered short-chain fatty acid acetate boosts antiviral immunity during rhinovirus infection[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 151(2): 447-57. e5. |
| 31 | Antunes KH, Fachi JL, de Paula R, et al. Microbiota-derived acetate protects against respiratory syncytial virus infection through a GPR43-type 1 interferon response[J]. Nat Commun, 2019, 10: 3273. |
| [1] | . Investigating the causal relationship between human blood metabolites and coronary artery disease using two-sample Mendelian randomization [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(2): 272-278. |
| [2] | . Characteristics of BK polymavirus infection in kidney transplant recipients [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2019, 39(01): 120-. |
| [3] | . Primary lung cancer in Chinese renal transplant recipients: a single-center analysis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(06): 715-. |
| [4] | HUANG Xue-shan, CHEN Dao-zhong, CHEN Liang-wan, LI Zeng-qi, LIAO Chong-xian. Immunosuppression induction with daclizumab and antithymocyte globulin in cardiac transplantation: clinical experience with 8 cases [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(02): 126-128,147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||