Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (12): 2469-2476.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.24
Jinhong ZHANG1( ), Xin LIU2, Jian LIU2(
), Xin LIU2, Jian LIU2( )
)
Received:2024-08-21
Online:2024-12-20
Published:2024-12-26
Contact:
Jian LIU
E-mail:zyzlj@hebmu.edu.cn;zjh888fff@hebmu.edu.cn
Jinhong ZHANG, Xin LIU, Jian LIU. PHPS1 enhances PD-L1 serine phosphorylation by regulating ROS/SHP-2/AMPK activity to promote apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2469-2476.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.12.24
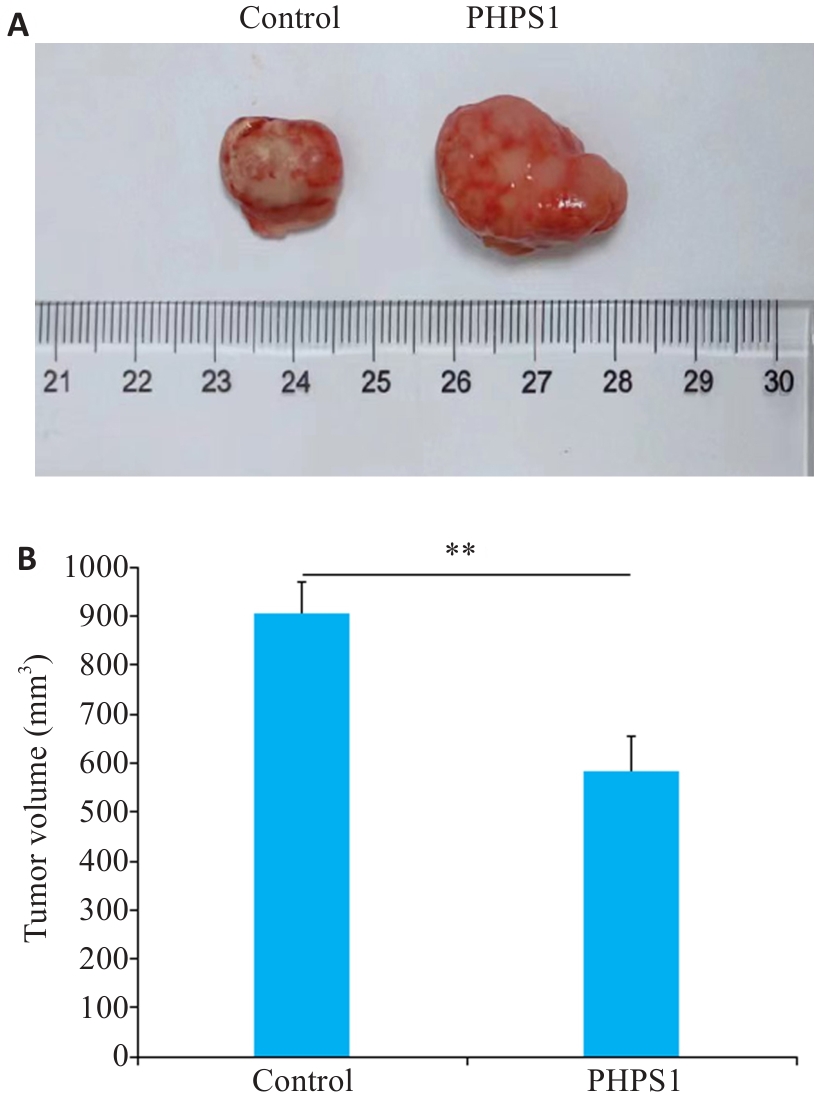
Fig.1 Effect of PHPS1 on tumor growth in nude mice. A: Comparison of tumor growth between the two groups. B: Comparison of tumor volume between the two groups (Mean±SD). **P<0.05.
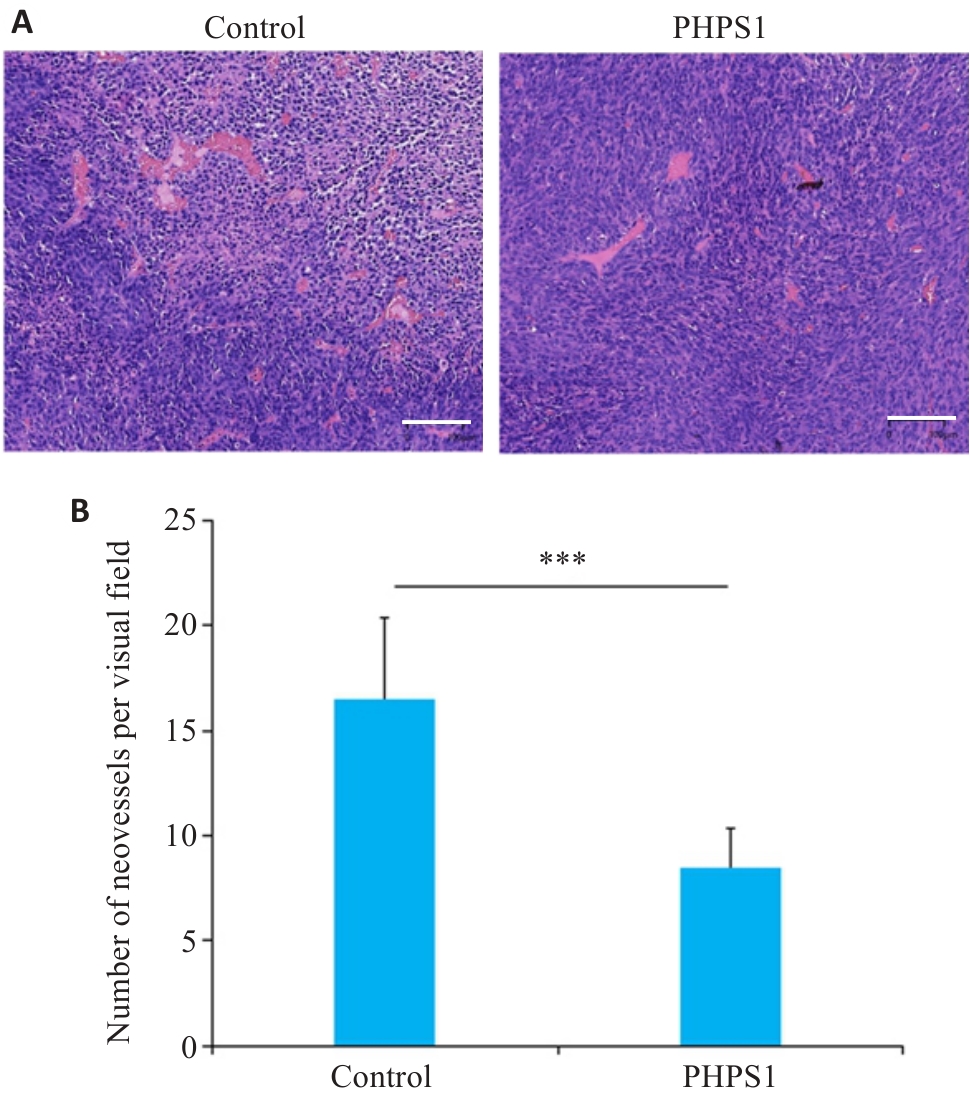
Fig.2 Effect of PHPS1 on angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma xenografts in nude mice in control and PHPS1 groups. A: HE staining of the tumor sections (Scale bar=100 μm). B: Number of neovessels in the two groups (Mean±SD). ***P<0.01.
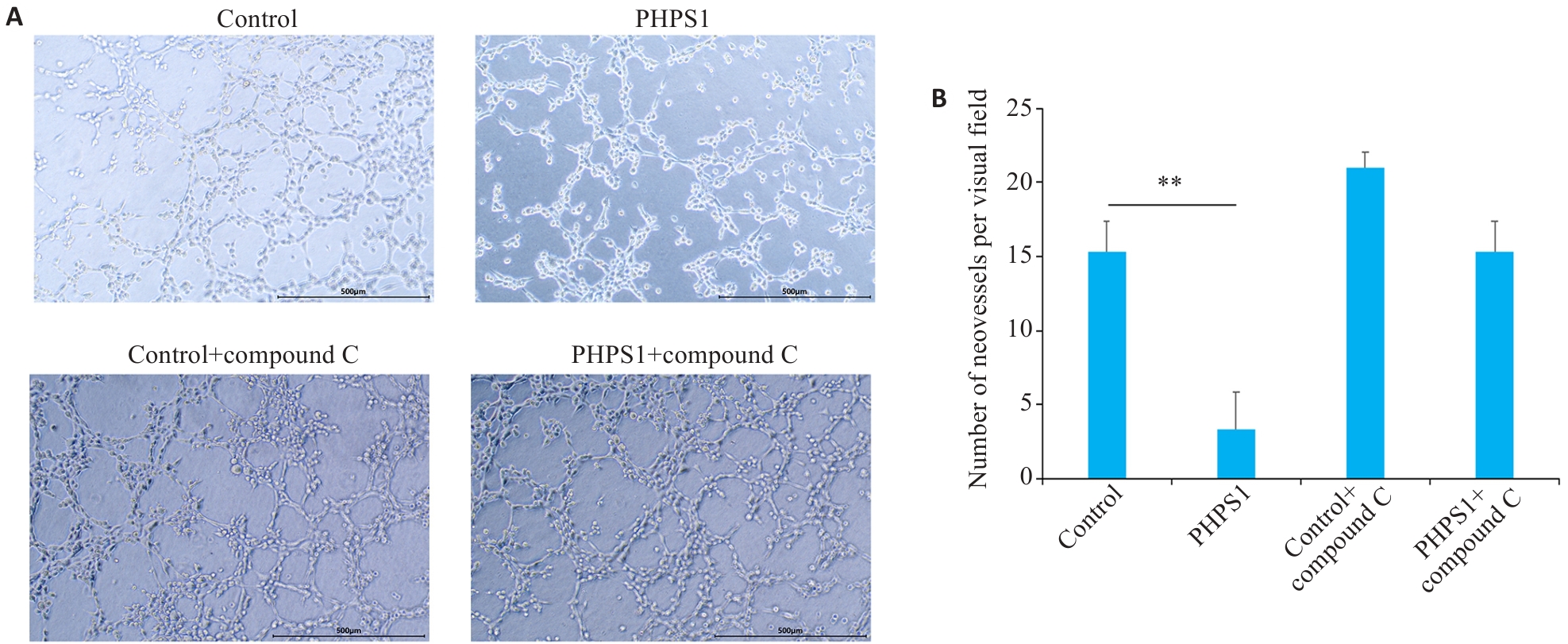
Fig.3 Effect of PHPS1 on angiogenesis in oral squamous cell carcinoma cells. A: Angiogenesis of Ca9-22 cells in different groups assessed by tube formation assay (Scale bar=500 μm). B: Number of neovessels in each group (Mean±SD). **P<0.05.
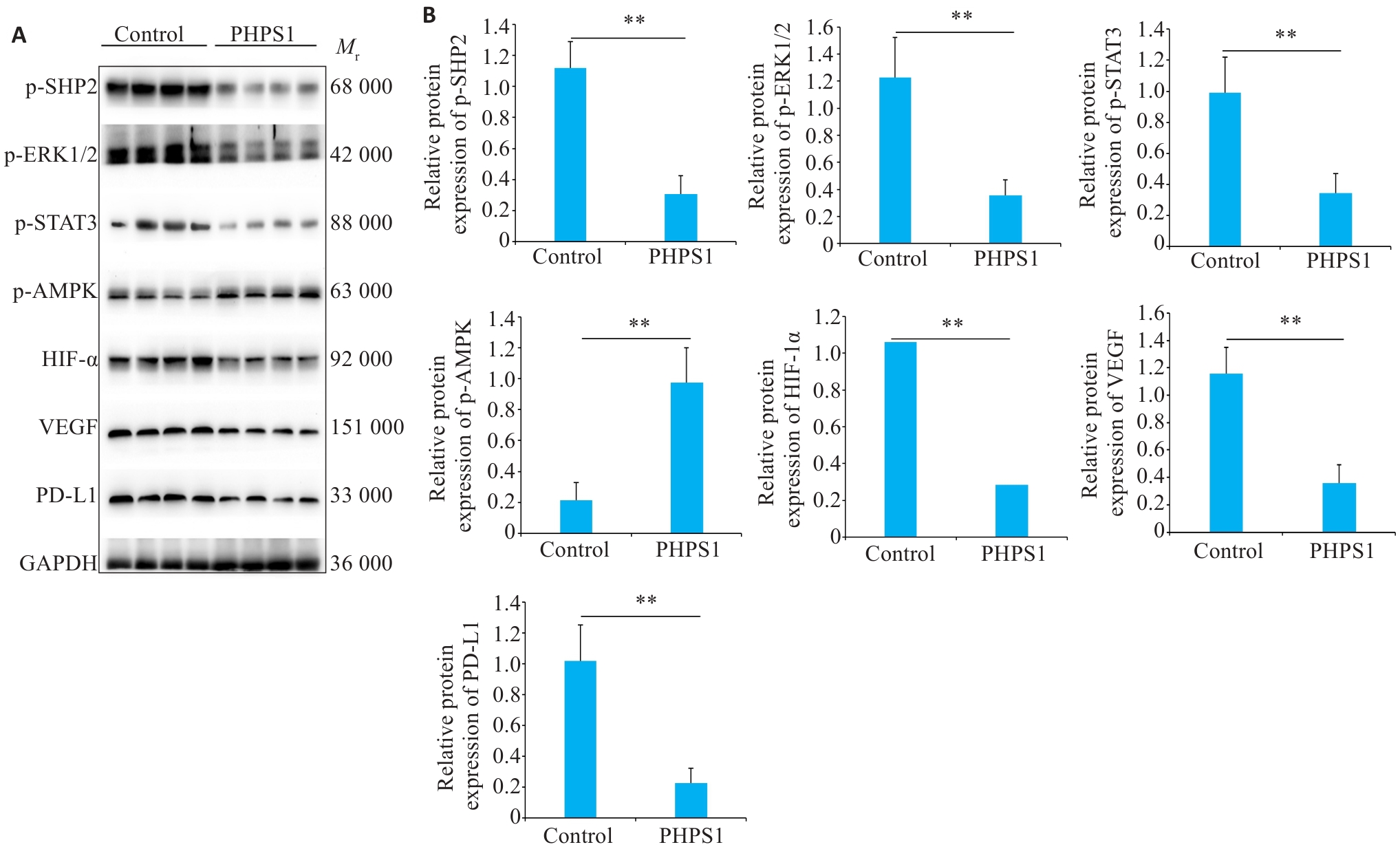
Fig.4 Effect of PHPS1 on expressions of ROS pathway-related proteins in Ca9-22 cells. A: Western blotting of p-SHP-2, p-AMPK, HIF-1α, PD-L1, p-ERK1/2, p-STAT3, and VEGF protein expression in Ca9-22 cells in control and PHPS1 groups. B: Comparison of protein expression levels between control and PHPS1 groups (Mean±SD). **P<0.05.
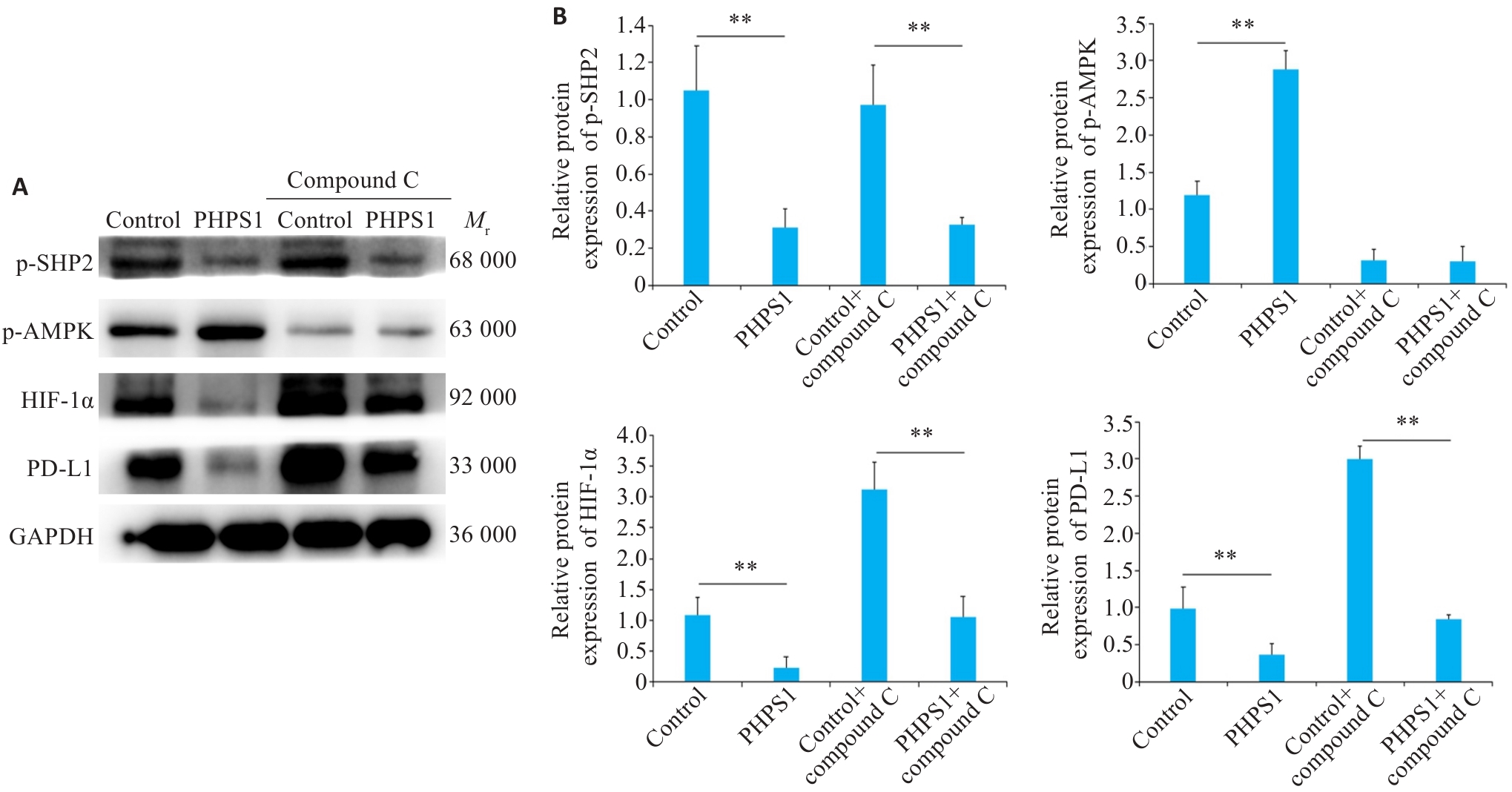
Fig.5 Effect of AMPK inhibitor on expressions of p-SHP-2, p-AMPK, HIF-1α, and PD-L1 proteins. A: Western blotting of p-SHP-2, p-AMPK, HIF-1α, and PD-L1 protein expression in Ca9-22 cells in different groups. B: Comparison of the protein expression levels. **P<0.05.
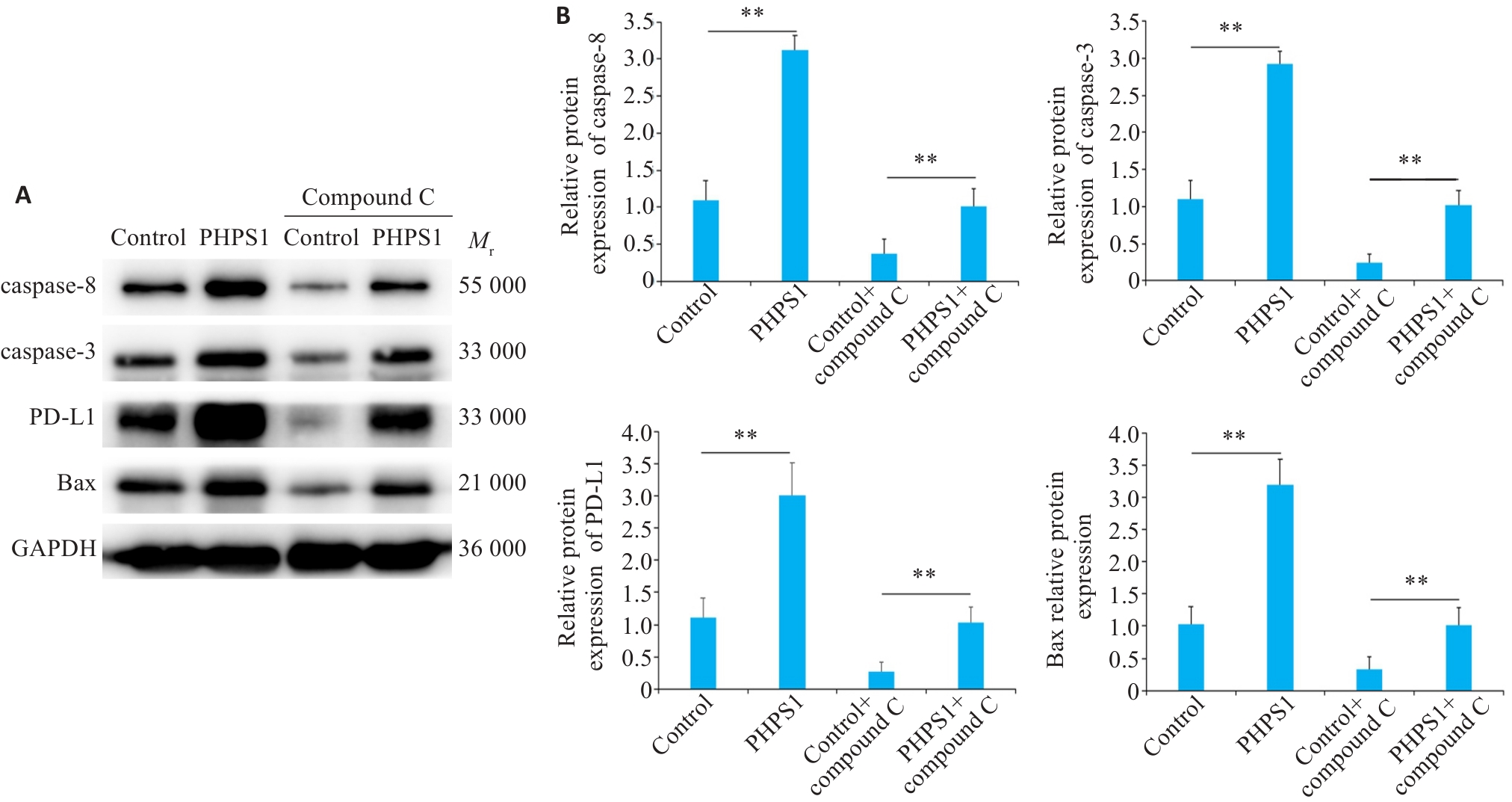
Fig.6 Effect of AMPK inhibitor on expressions of caspase-3, caspase-8, PD-L1, and BAX proteins. A: Western blotting of caspase-3, caspase-8, PD-L1 S195 phosphorylation and Bax protein expressions in Ca9-22 cells in different groups. B: Comparison of the protein expression levels. **P<0.05.
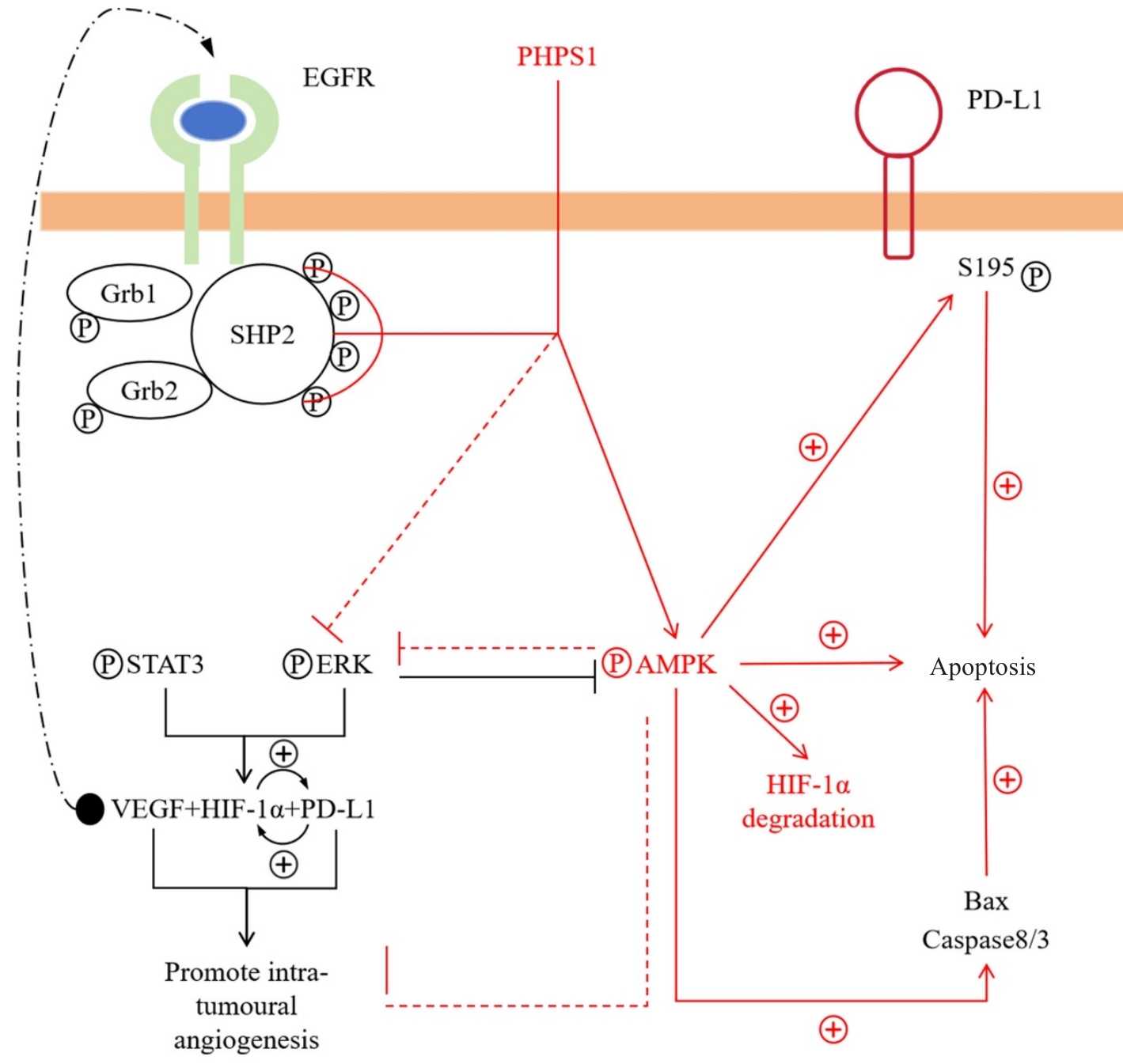
Fig.7 Schematic diagram illustrating the mechanism by which PHPS1 targets the ROS/SHP-2/AMPK pathway, thereby promoting serine phosphorylation of PD-L1 and accelerating tumor apoptosis.
| 1 | Renu K, Vinayagam S, Veeraraghavan VP, et al. Molecular crosstalk between the immunological mechanism of the tumor microenvironment and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in oral cancer[J]. Vaccines, 2022, 10(9): 1490. |
| 2 | Grégoire V, Grau C, Lapeyre M, et al. Target volume selection and delineation (T and N) for primary radiation treatment of oral cavity, oropharyngeal, hypopharyngeal and laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 87: 131-7. |
| 3 | Porceddu SV, Daniels C, Yom SS, et al. Head and neck cancer international group (HNCIG) consensus guidelines for the delivery of postoperative radiation therapy in complex cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck (cSCCHN)[J]. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, 2020, 107(4): 641-51. |
| 4 | Woo SB. Oral epithelial dysplasia and premalignancy[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2019, 13(3): 423-39. |
| 5 | Bai YC, Boath J, White GR, et al. The balance between differentiation and terminal differentiation maintains oral epithelial homeostasis[J]. Cancers, 2021, 13(20): 5123. |
| 6 | Niogret C, Birchmeier W, Guarda G. SHP-2 in lymphocytes' cytokine and inhibitory receptor signaling[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 2468. |
| 7 | Wu XL, Guan SY, Lu YG, et al. Macrophage-derived SHP-2 inhibits the metastasis of colorectal cancer via Tie2-PI3K signals[J]. Oncol Res, 2023, 31(2): 125-39. |
| 8 | Feng GS. Shp2-mediated molecular signaling in control of embryonic stem cell self-renewal and differentiation[J]. Cell Res, 2007, 17(1): 37-41. |
| 9 | Spaulding HR, Yan Z. AMPK and the adaptation to exercise[J]. Annu Rev Physiol, 2022, 84: 209-27. |
| 10 | Ciccarese F, Zulato E, Indraccolo S. LKB1/AMPK pathway and drug response in cancer: a therapeutic perspective[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2019, 2019: 8730816. |
| 11 | Hsu CC, Peng DN, Cai Z, et al. AMPK signaling and its targeting in cancer progression and treatment[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2022, 85: 52-68. |
| 12 | Karampitsakos T, Galaris A, Barbayianni I, et al. SH2 domain-containing phosphatase-SHP2 attenuates fibrotic responses through negative regulation of mitochondrial metabolism in lung fibroblasts[J]. Diagnostics, 2023, 13(6): 1166. |
| 13 | Jiang JH, Hu BJ, Chung CS, et al. SHP2 inhibitor PHPS1 ameliorates acute kidney injury by Erk1/2-STAT3 signaling in a combined murine hemorrhage followed by septic challenge model[J]. Mol Med, 2020, 26(1): 89. |
| 14 | Salem IH, Plante S, Gounni AS, et al. A shift in the IL-6/STAT3 signalling pathway imbalance towards the SHP2 pathway in severe asthma results in reduced proliferation process[J]. Cell Signal, 2018, 43: 47-54. |
| 15 | Tan SZ, Li DP, Zhu X. Cancer immunotherapy: pros, cons and beyond[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2020, 124: 109821. |
| 16 | Sobierajska K, Ciszewski WM, Sacewicz-Hofman I, et al. Endothelial cells in the tumor microenvironment[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2020, 1234: 71-86. |
| 17 | Xu ZY, Guo CY, Ye QL, et al. Endothelial deletion of SHP2 suppresses tumor angiogenesis and promotes vascular normalization[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 6310. |
| 18 | Chen H, Cresswell GM, Libring S, et al. Tumor cell-autonomous SHP2 contributes to immune suppression in metastatic breast cancer[J]. Cancer Res Commun, 2022, 2(10): 1104-18. |
| 19 | Zhao H, Ren XJ, Kong RY, et al. Auxilin regulates intestinal stem cell proliferation through EGFR[J]. Stem Cell Reports, 2022, 17(5): 1120-37. |
| 20 | Herzig S, Shaw RJ. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2018, 19(2): 121-35. |
| 21 | Chun Y, Kim J. AMPK-mTOR signaling and cellular adaptations in hypoxia[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(18): 9765. |
| 22 | Cha JH, Yang WH, Xia WY, et al. Metformin promotes antitumor immunity via endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation of PD-L1[J]. Mol Cell, 2018, 71(4): 606-20. e7. |
| 23 | Cha JH, Chan LC, Li CW, et al. Mechanisms controlling PD-L1 expression in cancer[J]. Mol Cell, 2019, 76(3): 359-70. |
| 24 | Chen DS, Mellman I. Elements of cancer immunity and the cancer-immune set point[J]. Nature, 2017, 541(7637): 321-30. |
| 25 | Yao H, Lan J, Li CS, et al. Inhibiting PD-L1 palmitoylation enhances T-cell immune responses against tumours[J]. Nat Biomed Eng, 2019, 3(4): 306-17. |
| 26 | Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation[J]. Cell, 2011, 144(5): 646-74. |
| 27 | Mabeta P, Steenkamp V. The VEGF/VEGFR axis revisited: implications for cancer therapy[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(24): 15585. |
| 28 | Wang ZQ, Zhao P, Tian KH, et al. TMEM9 promotes lung adenocarcinoma progression via activating the MEK/ERK/STAT3 pathway to induce VEGF expression[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15(4): 295. |
| 29 | Lee SH, Golinska M, Griffiths JR. HIF-1-independent mechanisms regulating metabolic adaptation in hypoxic cancer cells[J]. Cells, 2021, 10(9): 2371. |
| 30 | Ma S, Lu CC, Yang LY, et al. ANXA2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by activating MYC-HIF1A-VEGF axis[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 37(1): 183. |
| [1] | CHEN Shoufeng, ZHANG Shuchao, FAN Weilin, SUN Wei, LIU Beibei, LIU Jianmin, GUO Yuanyuan. Efficacy of combined treatment with pirfenidone and PD-L1 inhibitor in mice bearing ectopic bladder cancer xenograft [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(2): 210-216. |
| [2] | LIU Tongjia, WANG Wanlun, ZHANG Ting, LIU Shuang, BIAN Yanchao, ZHANG Chuanling, XIAO Rui. Expression of TUBB4B in mouse primary spermatocyte GC-2 cells and its regulatory effect on NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2023, 43(6): 1002-1009. |
| [3] | YANG Shuluan, ZHAO Wenqu, PENG Xianru, LAN Zihan, HUANG Junwen, HAN Huishan, CHEN Ying, CAI Shaoxi, ZHAO Haijin. Inhibition of TAK1 aggravates airway inflammation by increasing RIPK1 activity and promoting macrophage death in a mouse model of toluene diisocyanate-induced asthma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(2): 181-189. |
| [4] | ZHAO Aiyue, SU Yunxia, FU Deqiang. MiR-4772 modulates tumor immune microenvironment by regulating immune-related genes in ovarian cancer [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2022, 42(11): 1638-1645. |
| [5] | . Fuxinfang improves hypoxia-induced injury of human aortic endothelial cells by regulating c-Fos-NR4A1-p38 pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2021, 41(2): 200-209. |
| [6] | . Exogenous agmatine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation and dysfunction of human umbilical vein endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2018, 38(06): 652-. |
| [7] | . Salidroside protects PC12 cells from H2O2-induced apoptosis via suppressing NOX2-ROS-MAPKs signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2017, 37(02): 178-. |
| [8] |
.
Effect of curcumin on expressions of mitogen-activated protein kinases and matrix metalloproteinases in Jurkat cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2013, 33(12): 1792-. |
| [9] | YANG Li-ping,LIU Zhi-feng,LI Yong-ming,LI Zhi-jie,JIANG Yong Department of Pathophysiology and Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Functional Proteomics,Southern Medical University,Guangzhou 510515,China. Cell-penetrating peptide-based functional study of p38 MAPK [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2006, 26(05): 553-557. |
| [10] | HUANG Qi-jin, XU Ru-xiang, KE Yi-quan. Changes of brain p38 MAPK in rabbits with craniocerebral gunshot injury in hot and humid environment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2005, 25(09): 1155-1157. |
| [11] | LIU Hui1, OUYANG Ping2, LIU Zhen-hua1, LAI Wen-yan2, XU Ding-li2. Aspirin inhibits proliferation and expression of p44/42 MAPK phosphorylation in vascular endothelial cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(09): 1013-1015. |
| [12] | OUYANG Ping1, PENG Wen-lie2, LAI Wen-yan1, XU An-long2. Green tea polyphenols inhibit low-density lipoprotein-induced proliferation of rat vascular smooth muscle cells [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(09): 975-979. |
| [13] | OUYANG Ping1, PENG Wen-lie2, XU Ding-li1, LAI Wen-yan1, XU An-long2. Green tea polyphenols inhibit advanced glycation end product-induced rat vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2004, 24(03): 247-251. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||