南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1240-1250.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.06.13
杨毓甲1( ), 杨丽芳1,2(
), 杨丽芳1,2( ), 吴雅玲1, 段兆达1, 于春泽1, 吴春云1, 于建云3(
), 吴雅玲1, 段兆达1, 于春泽1, 吴春云1, 于建云3( ), 杨力1(
), 杨力1( )
)
收稿日期:2025-01-03
出版日期:2025-06-20
发布日期:2025-06-27
通讯作者:
于建云,杨力
E-mail:yujiayang1172@163.com;sophiay0717@163.com;jianyunyu@sina.com;yanglikm@163.com
作者简介:杨毓甲,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: yujiayang1172@163.com基金资助:
Yujia YANG1( ), Lifang YANG1,2(
), Lifang YANG1,2( ), Yaling WU1, Zhaoda DUAN1, Chunze YU1, Chunyun WU1, Jianyun YU3(
), Yaling WU1, Zhaoda DUAN1, Chunze YU1, Chunyun WU1, Jianyun YU3( ), Li YANG1(
), Li YANG1( )
)
Received:2025-01-03
Online:2025-06-20
Published:2025-06-27
Contact:
Jianyun YU, Li YANG
E-mail:yujiayang1172@163.com;sophiay0717@163.com;jianyunyu@sina.com;yanglikm@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究大麻二酚(CBD)对多重脑震荡后神经元内质网应激及其介导的神经元凋亡的作用。 方法 将SD大鼠分为假手术组(sham组)、多重脑震荡组(MCC组)、多重脑震荡溶剂组(MCC+TW组,1% tween20)、低剂量CBD-10组(10 mg/kg)和高剂量CBD-40组(40 mg/kg),用金属单摆打击装置制成大鼠MCC模型,给药各组于造模成功后连续腹腔给药2周。采用qRT-PCR、Western blotting和免疫荧光染色检测大鼠脑组织中PERK、eIF2α、ATF4、CHOP、TRIB3、p-AKT、Pro-caspase-3的表达变化。通过网络药理学筛选CBD治疗创伤性脑损伤的核心靶点,经Autodock可视化分析CBD与内质网应激和凋亡相关因子的分子对接情况。 结果 MCC后大脑皮质内质网应激因子PERK、eIF2α、CHOP mRNA表达水平升高(P<0.05)。MCC组大脑皮质中PERK、eIF2α、ATF4、CHOP、TRIB3、p-AKT、Pro-caspase-3蛋白表达水平较sham组升高(P<0.05);CBD治疗后,p-AKT表达水平进一步升高(P<0.05),而其余因子表达水平均降低(P<0.05),且CBD-40组降低更显著。网络药理学分析显示,CBD治疗TBI的核心靶点与内质网应激和脑损伤因子存在蛋白互作关系;分子对接显示CBD,与多个内质网应激和凋亡因子具有较高的结合能。 结论 大鼠多重脑震荡诱发神经元内质网应激和细胞凋亡,CBD可通过抑制内质网应激和抗凋亡发挥神经保护作用,且高剂量CBD的保护作用更明显。
杨毓甲, 杨丽芳, 吴雅玲, 段兆达, 于春泽, 吴春云, 于建云, 杨力. 大麻二酚经PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP通路减轻多重脑震荡大鼠的神经元内质网应激和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250.
Yujia YANG, Lifang YANG, Yaling WU, Zhaoda DUAN, Chunze YU, Chunyun WU, Jianyun YU, Li YANG. Cannabidiol inhibits neuronal endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in rats with multiple concussions by regulating the PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(6): 1240-1250.
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
PERK eIF2α CHOP | TACAGTGGACGGCGATGATG AAAGCTACTGCTGTGCTGGT CCTCGCTCTCCAGATTCCAG | CTGGGGTCCTCCTTACTGGA GTCGCAATGTAGTGCAGTGT AGCTGTGCCACTTTCCTCTC |
表1 qRT-PCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence of qRT-PCR
| Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
PERK eIF2α CHOP | TACAGTGGACGGCGATGATG AAAGCTACTGCTGTGCTGGT CCTCGCTCTCCAGATTCCAG | CTGGGGTCCTCCTTACTGGA GTCGCAATGTAGTGCAGTGT AGCTGTGCCACTTTCCTCTC |
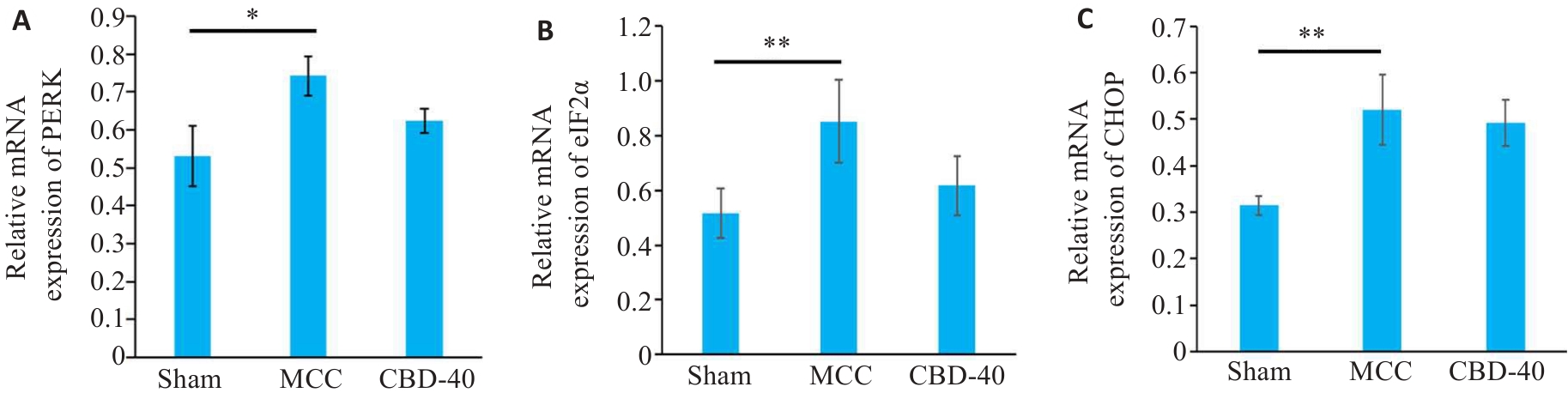
图1 MCC后大鼠大脑皮质PERK、eIF2α和CHOP mRNA的变化
Fig.1 Changes of PERK (A), eIF2α (B) and CHOP (C) mRNA expressions levels in rat cerebral cortex after multiple concussion (MCC). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 (n=3).
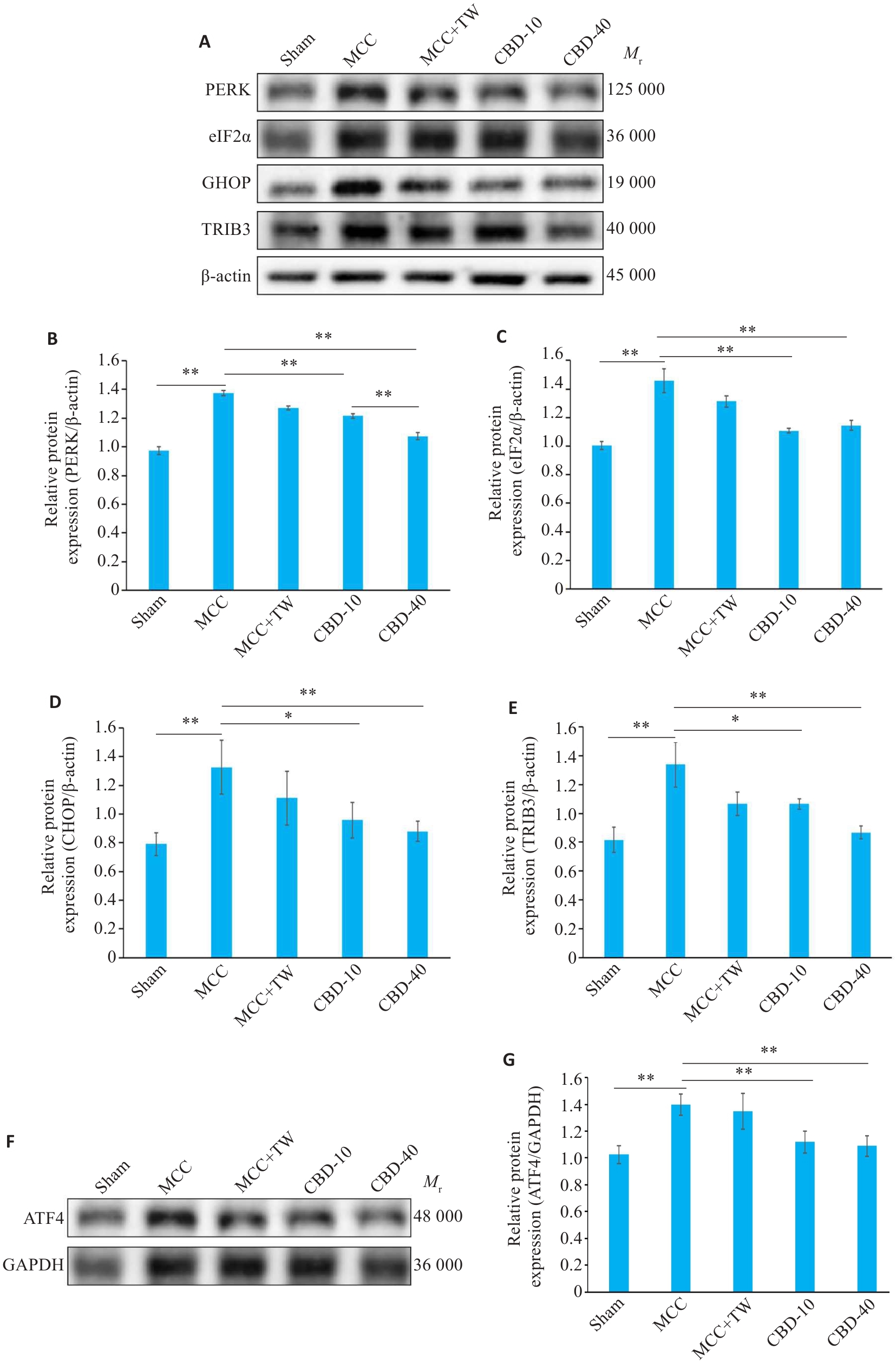
图2 MCC后大鼠脑皮质中PERK、eIF2α、CHOP、TRIB3和ATF4的蛋白表达
Fig.2 Protein expressions of PERK, eIF2α, CHOP, TRIB3 and ATF4 in the cerebral cortex of rats after MCC. A, F: Western blotting for detecting the taget proteins. B, C, D, E, G: Quantitative analysis of the expression levels of PERK, eIF2α, CHOP, TRIB3 and ATF4. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
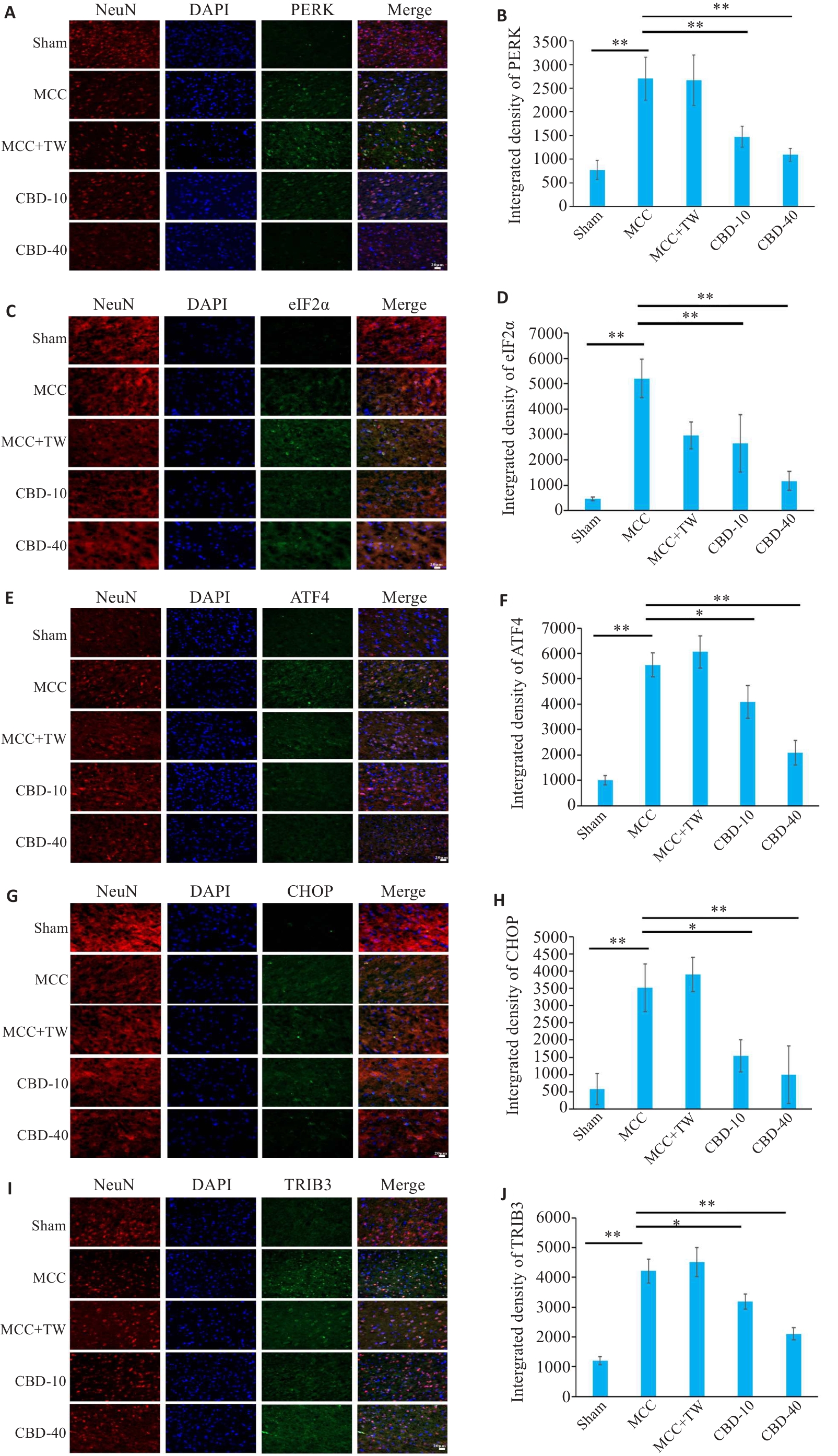
图3 MCC后大鼠脑皮质中PERK、eIF2α、ATF4、CHOP和TRIB3免疫荧光染色
Fig.3 Immunofluorescence staining of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3 in the cerebral cortex of rats after MCC. A, C, E, G, I: Immunofluorescence staining images of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3, respectively (Original magnification: ×400). B, D, F, H, J: Quantitative analysis of PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP and TRIB3 expressions, respectively; *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
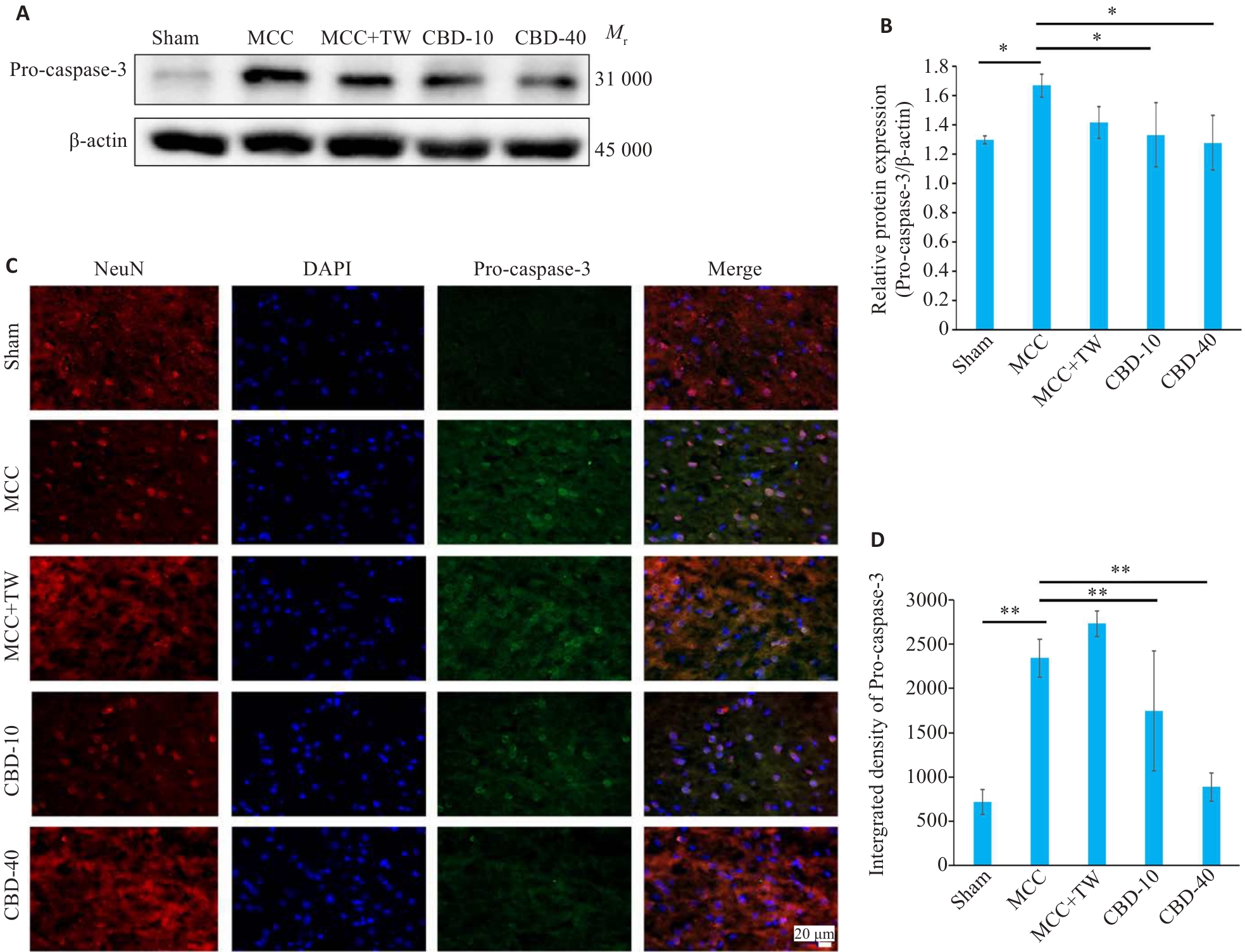
图4 MCC后大鼠脑皮质中Pro-caspase-3表达变化
Fig.4 Expression of pro-caspase-3 in rat brain after MCC. A, B: Western blotting for analyzing pro-caspase-3 expression levels. C, D: Immunofluorescence double-label staining for detecting Pro-caspase-3 expression levels (scale bar=20 µm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图5 MCC后大鼠脑皮质中p-AKT的表达变化
Fig.5 Expression of p-AKT in rat brain after MCC. A, B: Expression of p-AKT detected by Western blotting. C, D: Expression of p-AKT detected by immunofluorescence double-label staining (scale bar=20 µm). *P<0.05, **P<0.01.
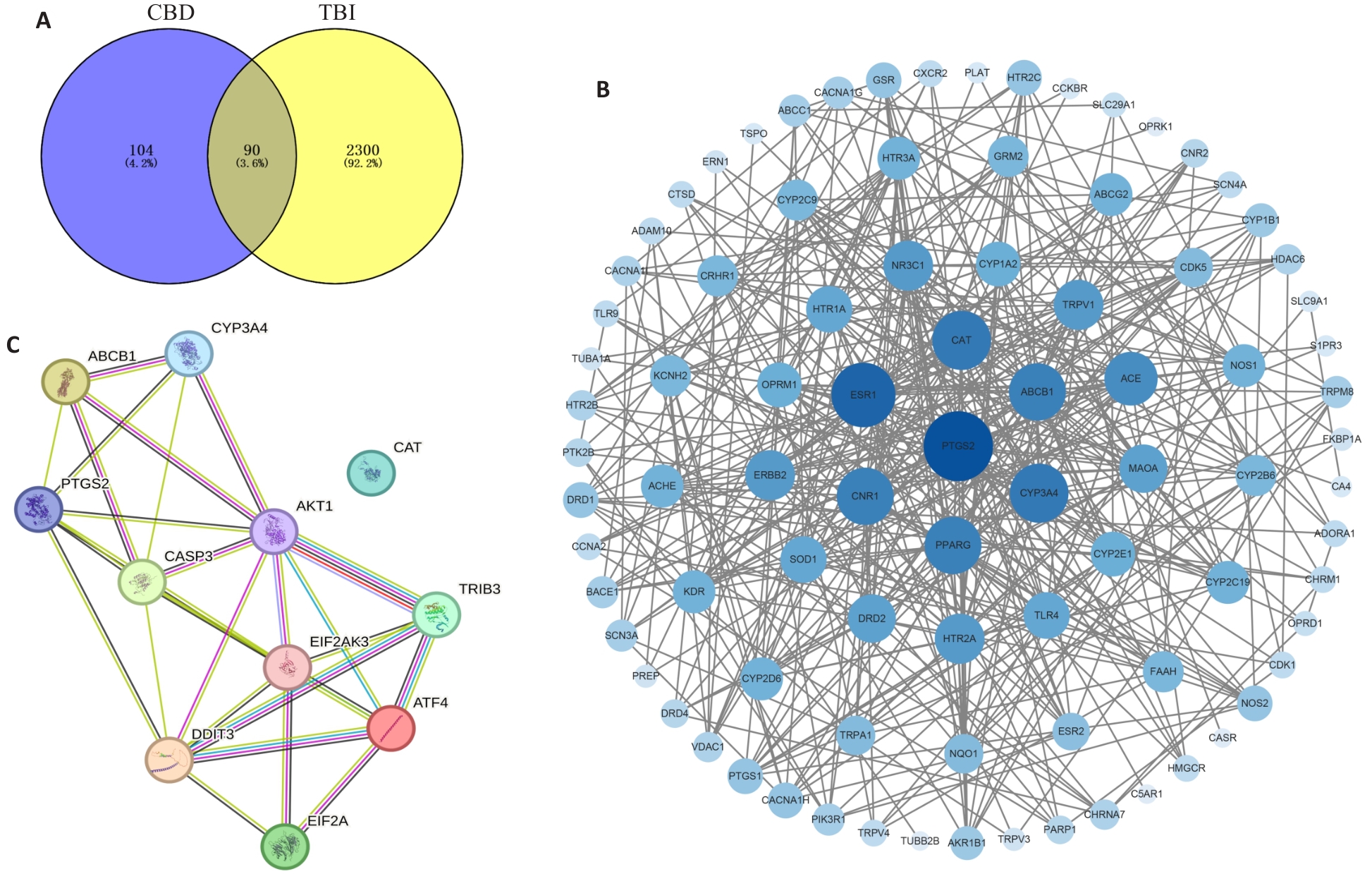
图6 CBD治疗TBI网络药理学分析韦恩图和蛋白互作图
Fig.6 Venn map of network pharmacology analysis of CBD for treatment of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and the protein-protein interaction network. A: Venn diagram of CBD targets and TBI disease targets. B: Visualization of interactions between CBD and TBI intersection target proteins. C: Protein-protein interactions of the core targets of cannabidiol in treatment of TBI diseases with PERK, eIF2α, ATF4, CHOP, TRIB3, AKT, and caspase-3.
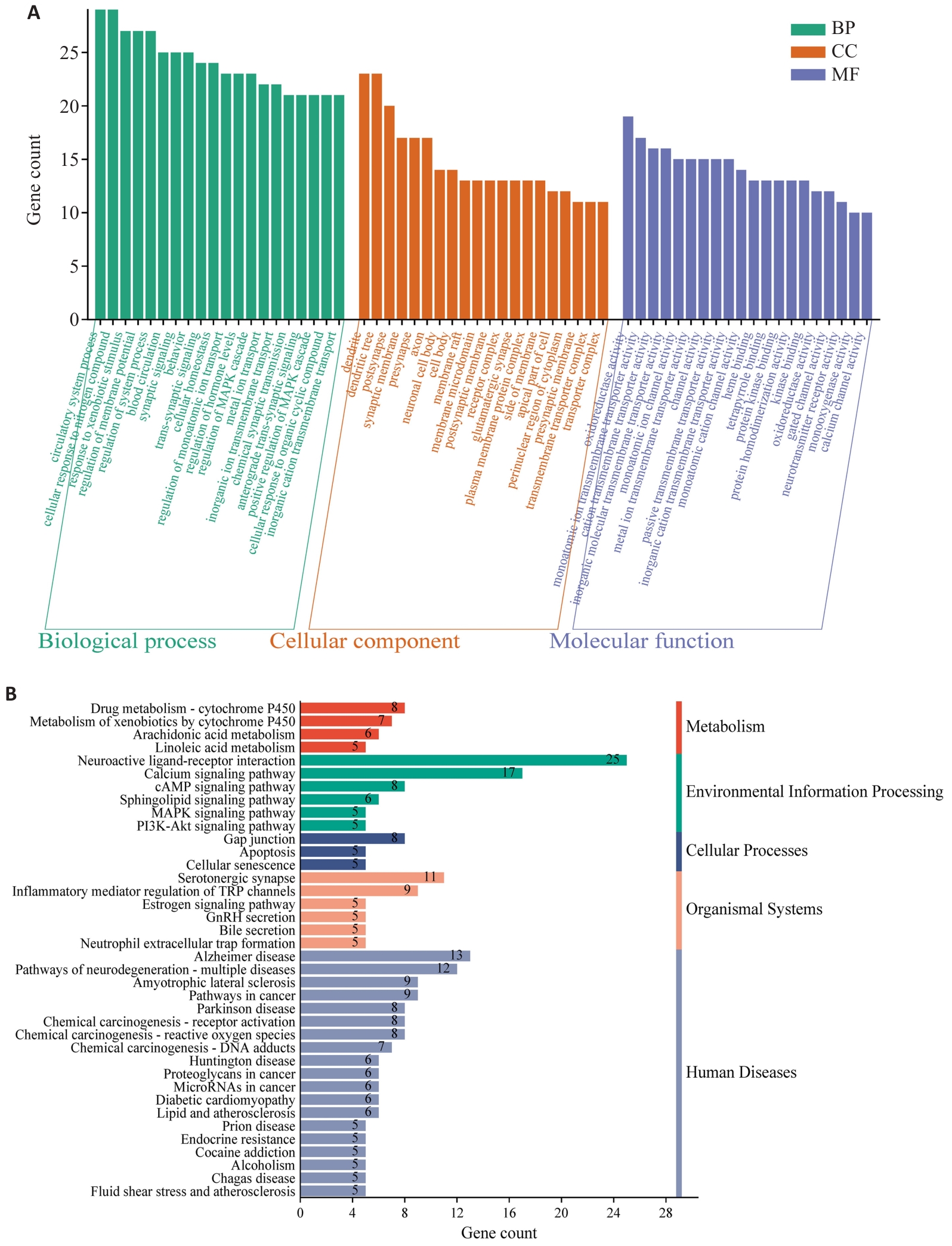
图7 CBD调节TBI潜在靶点GO和KEGG富集分析
Fig.7 GO and KEGG pathway enrichment analyses of the potential targets of CBD in modulating TBI. A: GO enrichment analysis bubble chart. B: KEGG enrichment analysis bar chart.
| Protein | PDB ID | Ligands | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
AKT PERK CHOP eIF2α caspase-3 TRIB3 ATF4 | 3oiw 4g31 2zfy 4v0x 3gjt 3gj0 4ut3 | CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD | -7.1 -6.91 -6.68 -6.2 -5.38 -4.68 -4.46 |
表2 CBD 与内质网应激和凋亡相关蛋白分子对接结合能
Tab.2 Moleculare docking binding energy of CBD with endoplasmic reticulum stress- and apoptosis-related proteins
| Protein | PDB ID | Ligands | Affinity (kcal/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
AKT PERK CHOP eIF2α caspase-3 TRIB3 ATF4 | 3oiw 4g31 2zfy 4v0x 3gjt 3gj0 4ut3 | CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD CBD | -7.1 -6.91 -6.68 -6.2 -5.38 -4.68 -4.46 |

图8 CBD 与ERS和凋亡相关蛋白分子对接
Fig.8 Molecular docking of CBD and endoplasmic reticulum stress- and apoptosis-related proteins AKT (A), PERK (B), CHOP (C), eIF2α (D), caspase-3 (E), TRIB3 (F) and ATF4 (G).
| 1 | Howell DR, Southard J. The molecular pathophysiology of concussion[J]. Clin Sports Med, 2021, 40(1): 39-51. doi:10.1016/j.csm.2020.08.001 |
| 2 | McGuire JL, Ngwenya LB, McCullumsmith RE. Neurotransmitter changes after traumatic brain injury: an update for new treatment strategies[J]. Mol Psychiatry, 2019, 24(7): 995-1012. doi:10.1038/s41380-018-0239-6 |
| 3 | Galgano M, Toshkezi G, Qiu XC, et al. Traumatic brain injury: current treatment strategies and future endeavors[J]. Cell Transplant, 2017, 26(7): 1118-30. doi:10.1177/0963689717714102 |
| 4 | Kang X, Wang J, Yan LY. Endoplasmic reticulum in oocytes: spatiotemporal distribution and function[J]. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2023, 40(6): 1255-63. doi:10.1007/s10815-023-02782-3 |
| 5 | Ajoolabady A, Kaplowitz N, Lebeaupin C, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases[J]. Hepatology, 2023, 77(2): 619-39. doi:10.1002/hep.32562 |
| 6 | Di Conza G, Ho PC. ER stress responses: an emerging modulator for innate immunity[J]. Cells, 2020, 9(3): 695. doi:10.3390/cells9030695 |
| 7 | Chen S, Li X, Zhang XW, et al. PCV2 and PRV coinfection induces endoplasmic reticulum stress via PERK-eIF2α-ATF4-CHOP and IRE1-XBP1-EDEM pathways[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2022, 23(9): 4479. doi:10.3390/ijms23094479 |
| 8 | Xia SH, Wu JW, Zhou WD, et al. HRC promotes anoikis resistance and metastasis by suppressing endoplasmic reticulum stress in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Int J Med Sci, 2021, 18(14): 3112-24. doi:10.7150/ijms.60610 |
| 9 | Paccosi E, Balzerano A, Proietti-De-Santis L. Interfering with the ubiquitin-mediated regulation of Akt as a strategy for cancer treatment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2023, 24(3): 2809. doi:10.3390/ijms24032809 |
| 10 | Khezri MR, Ghasemnejad-Berenji M, Moloodsouri D. The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway and Caspase-3 in alzheimer's disease: Which one Is the beginner[J]? J Alzheimers Dis, 2023, 92(2): 391-3. doi:10.3233/jad-221157 |
| 11 | 曹珍珍, 于建云, 李娟娟, 等. 一重和三重脑震荡大鼠脑固缩的神经细胞定量变化研究[J]. 昆明医科大学学报, 2013, 34(7): 12-6. |
| 12 | Zhang H, Zhang ZG, Wang Z, et al. Research on the changes in balance motion behavior and learning, as well as memory abilities of rats with multiple cerebral concussion-induced chronic traumatic encephalopathy and the underlying mechanism[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2018, 16(3): 2295-302. doi:10.3892/etm.2018.6474 |
| 13 | Wang L, Wu XH, Yang G, et al. Cannabidiol alleviates the damage to dopaminergic neurons in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydro-pyridine-induced Parkinson's disease mice via regulating neuronal apoptosis and neuroinflammation[J]. Neuroscience, 2022, 498: 64-72. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2022.06.036 |
| 14 | Castillo-Arellano J, Canseco-Alba A, Cutler SJ, et al. The polypharmacological effects of cannabidiol[J]. Molecules, 2023, 28(7): 3271. doi:10.3390/molecules28073271 |
| 15 | Song H, Xu LC, Zhang RP, et al. Rosemary extract improves cognitive deficits in a rats model of repetitive mild traumatic brain injury associated with reduction of astrocytosis and neuronal degeneration in hippocampus[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2016, 622: 95-101. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2016.04.048 |
| 16 | Sun DD, Wang JH, Liu XL, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and improves neuronal function after traumatic brain injury in mice[J]. Brain Res, 2020, 1732: 146682. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146682 |
| 17 | Ruan Z, Lu Q, Wang JE, et al. MIF promotes neurodegeneration and cell death via its nuclease activity following traumatic brain injury[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2021, 79(1): 39. doi:10.1007/s00018-021-04037-9 |
| 18 | Yang YY, Lu DF, Wang MH, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response: emerging regulators in progression of traumatic brain injury[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2024, 15(2): 156. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06515-x |
| 19 | Davis CK, Bathula S, Hsu M, et al. An antioxidant and anti-ER stress combo therapy decreases inflammation, secondary brain damage and promotes neurological recovery following traumatic brain injury in mice[J]. J Neurosci, 2022, 42(35): 6810-21. doi:10.1523/jneurosci.0212-22.2022 |
| 20 | Ghemrawi R, Khair M. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in neurodegenerative diseases[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(17): 6127. doi:10.3390/ijms21176127 |
| 21 | 陈乃洁, 林 瑶, 许 茜, 等. 基于PERK-eIF2α通路探讨苁蓉舒痉颗粒对帕金森病模型大鼠黑质纹状体内质网应激的调节作用 [J]. 福建中医药, 2023, 54(8): 18-22. |
| 22 | Jiang W, Dong W, Li M, et al. Nitric oxide induces immunogenic cell death and potentiates cancer immunotherapy[J]. ACS Nano, 2022, 16(3): 3881-94. doi:10.1021/acsnano.1c09048 |
| 23 | 费慧芝. CTRP1改善脑缺血再灌注致神经元损伤及机制研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆医科大学, 2021. |
| 24 | Meng Y, Xu XJ, Niu D, et al. Organophosphate flame retardants induce oxidative stress and Chop/Caspase 3-related apoptosis via Sod1/p53/Map3k6/Fkbp5 in NCI-1975 cells[J]. Sci Total Environ, 2022, 819: 153160. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153160 |
| 25 | 刘殿雷, 龙景培, 卜贺启, 等. 冬凌草甲素通过内质网应激诱导胰腺癌细胞凋亡的研究[J]. 中草药, 2022, 53(15): 4773-80. |
| 26 | 朱 宝, 李 国, 王兰清. 米索前列醇抑制内质网应激减轻脊髓损伤小鼠神经细胞凋亡[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2023, 29(4): 337-40. |
| 27 | Song MQ, Bode AM, Dong ZG, et al. AKT as a therapeutic target for cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2019, 79(6): 1019-31. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-2738 |
| 28 | Fan J, Du JX, Zhang ZW, et al. The protective effects of hydrogen sulfide new donor methyl S-(4-fluorobenzyl)- N-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxybenzoyl)-l-cysteinate on the ischemic stroke[J]. Molecules, 2022, 27(5): 1554. doi:10.3390/molecules27051554 |
| 29 | Zhao Y, Han Y, Bu DF, et al. Reduced AKT phosphorylation contributes to endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated hippocampal neuronal apoptosis in rat recurrent febrile seizure[J]. Life Sci, 2016, 153: 153-62. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2016.04.008 |
| 30 | Blaskovich MAT, Kavanagh AM, Elliott AG, et al. The antimicrobial potential of cannabidiol[J]. Commun Biol, 2021, 4(1): 7. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-01530-y |
| 31 | Patel V, Abu-Hijleh F, Rigg N, et al. Cannabidiol protects striatal neurons by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress[J]. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res, 2023, 8(2): 299-308. |
| 32 | 杨丽芳, 于春泽, 张先俊, 等. 大麻二酚对大鼠多重脑震荡炎症反应的抑制作用 [J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志, 2024, 42(3): 278-83. |
| [1] | 吴新顺, 李劲草, 刘影, 邱仁洪, 王恒林, 薛瑞, 张扬, 李硕, 范琼尹, 董华进, 张有志, 曹江北. 大麻二酚通过调节昼夜节律改善大鼠全麻术后的睡眠障碍[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(4): 744-750. |
| [2] | 鲁玲君, 杨小迪, 张华平, 梁媛, 石秀兰, 周鑫. 重组日本血吸虫半胱氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂对急性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(6): 1126-1134. |
| [3] | 周伟, 聂军, 胡佳, 蒋艺枝, 张大发. 内质网应激相关基因在主动脉夹层疾病中的差异性表达及与免疫浸润的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 859-866. |
| [4] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 邵 楠, 蔡 标, 谢道俊. 黄蒲通窍胶囊改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠的认知损害:基于抑制内质网应激介导的凋亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [5] | 邱建国, 邱一桐, 李国荣, 张林生, 郑雪, 姚泳江, 王熙丹, 黄海阳, 张凤敏, 苏冀彦, 郑学宝, 黄晓其. 黄芩汤通过调控内质网应激减轻小鼠溃疡性结肠炎[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2172-2183. |
| [6] | 张文婧, 胡兆霆. 降糖三黄片抑制糖尿病小鼠胰岛细胞的内质网应激和自噬[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(9): 1317-1323. |
| [7] | 罗 兰, 佟家祺, 李 璐, 金 沐. 氙气后处理对大鼠脊髓缺血再灌注损伤起保护作用:基于下调mTOR通路和抑制内质网应激介导的神经元凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(8): 1256-1262. |
| [8] | 卓灵剑, 王烁辰, 刘 星, 陈保安, 李 想. 雌二醇通过上调IRE1α-XBP1信号轴抑制小鼠腹腔巨噬细胞的分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 432-437. |
| [9] | 黄浩华, 乔妤婕, 黄 奕, 董航明. HSP90α通过调控气道上皮细胞内质网应激加重屋尘螨诱导的哮喘气道炎症[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 347-353. |
| [10] | 高经华, 刘亚伟, 吉晶晶, 刘志锋. 热打击可通过调控内质网应激通路促进神经细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 702-709. |
| [11] | 张梦颖, 杨玉有, 刘 敏, 梁 利, 罗 瑞, 尹丹旸, 郭风劲. 雌二醇通过ERβ调控ERK磷酸化影响细胞增殖和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 336-343. |
| [12] | 杨妙婷,陈芝娟,肖淳欣,唐外姣,周本杰. 护肝清脂片药物血清对非酒精性脂肪肝细胞模型内质网应激的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(11): 1277-. |
| [13] | 徐文明,林建聪,陈美姬,张常然,李延兵. 糖原合酶激酶-3β与内质网应激相互作用参与高糖引起的人脐静脉内皮细胞损伤[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(05): 612-. |
| [14] | 王海臻,蔡丹纯,廖丹丹,钟梅,高云飞,盛超. 内质网应激介导滋养细胞凋亡在妊娠期肝内胆汁淤积症中的作用及机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2018, 38(05): 572-. |
| [15] | 黄丽丽,祝小林,邓伟谦,段娜,梁秀洁,王悦,郭婷婷,束双双,向晓红,姜婷婷,汤珣,章俊. p38 MAPK信号通路介导晚期氧化蛋白产物诱导的肾小管上皮细胞间充质转分化[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(09): 1209-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||