南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (10): 1985-1994.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.10.17
成思怡1,2,3,4( ), 陈泽锐1,2,3,4, 于长江1,2,3,4, 孙图成1,2,3,4, 朱烁基1,2,3,4(
), 陈泽锐1,2,3,4, 于长江1,2,3,4, 孙图成1,2,3,4, 朱烁基1,2,3,4( ), 刘南波1,2,3,4(
), 刘南波1,2,3,4( ), 朱平1,2,3,4(
), 朱平1,2,3,4( )
)
收稿日期:2024-04-25
出版日期:2024-10-20
发布日期:2024-10-31
通讯作者:
朱烁基,刘南波,朱平
E-mail:debarah17@foxmail.com;zhushuoji@gmail.com;liu.nanbo@163.com;tanganqier@163.com
作者简介:成思怡,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: debarah17@foxmail.com
基金资助:
Siyi CHENG1,2,3,4( ), Zerui CHEN1,2,3,4, Changjiang YU1,2,3,4, Tucheng SUN1,2,3,4, Shuoji ZHU1,2,3,4(
), Zerui CHEN1,2,3,4, Changjiang YU1,2,3,4, Tucheng SUN1,2,3,4, Shuoji ZHU1,2,3,4( ), Nanbo LIU1,2,3,4(
), Nanbo LIU1,2,3,4( ), Ping ZHU1,2,3,4(
), Ping ZHU1,2,3,4( )
)
Received:2024-04-25
Online:2024-10-20
Published:2024-10-31
Contact:
Shuoji ZHU, Nanbo LIU, Ping ZHU
E-mail:debarah17@foxmail.com;zhushuoji@gmail.com;liu.nanbo@163.com;tanganqier@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 高分辨定量剖析生理状态下小鼠心脏电生理本底稳态属性。 方法 随机选取成年C57BL/6小鼠22只(雌雄1∶1),采用无麻醉法固定小鼠四肢,自主呼吸下通过灵敏十二导联电生理采集器(ECGsqa)记录心电波形,包括小鼠特征性P波、R波及ST波,应用LabScribe软件读取与量化心前区V3导联上单一心动周期内高分辨时程参数与振幅参数,使用独立样本t检验比较组间差异,联合皮尔逊相关检验与简单线性回归绘制雌雄心电参数拟合散点图,按相关性强弱区分共享与独特关联对参数,从而揭示定量关联网络概貌。 结果 ECGsqa分析共识别与量化14个特征型心电参数,28.6%的组间差异具有统计学意义。与雄组相比,雌组R波与ST波的振幅与速率均更高(P<0.05)。在初级关联分析所鉴定的51个关联对中,关联阳性群占比为47.1%,其中涵盖雌雄共有(29.2%)、雄特有(29.2%)与雌特有(41.7%)三大关联组。关联对二阶聚类分析发现,雌雄心脏各波形电压的振幅-速率关联对处于普遍稳定强相关水平(P<0.01),而雄组心电特征展现出房-室互联模式,以及雌组心电特征展现独特心房电导系统质量依赖模式。关联群组分布网络特征显示,雌雄各自特有关联参数与共有关联参数之间具有一定程度串联模式。 结论 本研究聚焦雌雄小鼠天然心脏电信号的可被精确识别的数理特征,发现心电波重要特征参数的内在关联网络,揭示心房与心室电传导系统内部联结特征及其性别差异性,可为心血管生理与病理的纵深机制探索提供潜在适用的电稳态制式参照。
成思怡, 陈泽锐, 于长江, 孙图成, 朱烁基, 刘南波, 朱平. 基于特征化定量心电图策略分析小鼠心脏电生理固有稳态制式[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(10): 1985-1994.
Siyi CHENG, Zerui CHEN, Changjiang YU, Tucheng SUN, Shuoji ZHU, Nanbo LIU, Ping ZHU. Intrinsic steady-state pattern of mouse cardiac electrophysiology: analysis using a characterized quantitative electrocardiogram strategy[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(10): 1985-1994.
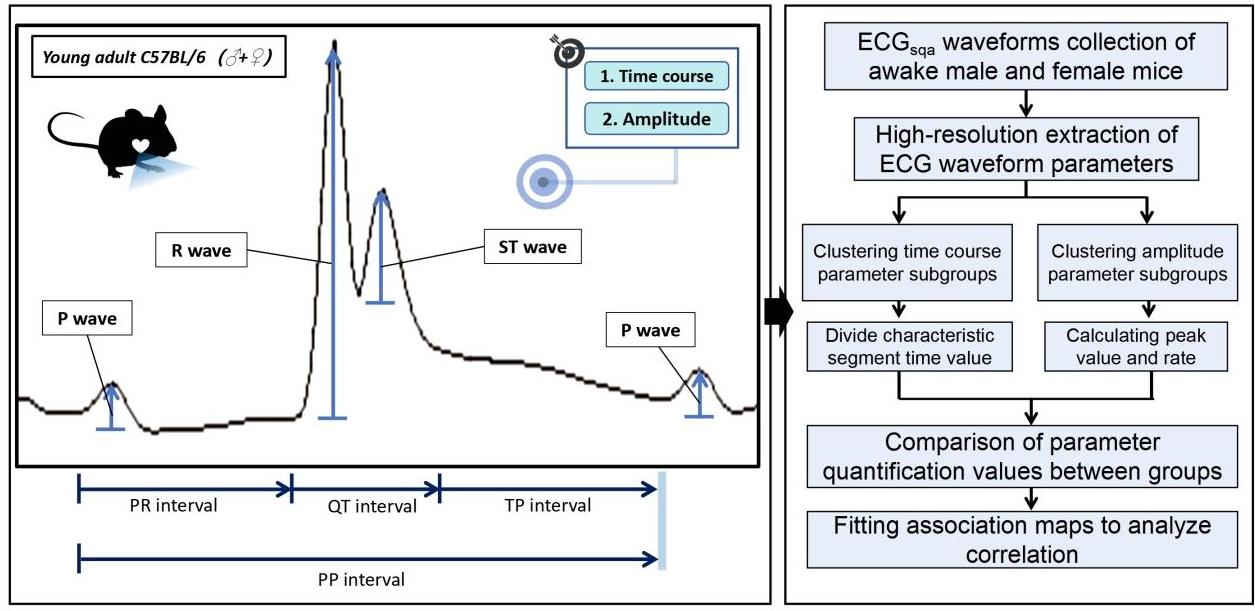
图1 单个心动周期内电生理波段的特征参数与ECGsqa分析路径
Fig.1 Characteristic parameters and mathematical application pathway of ECGsqa parameters within one single cardiac cycle.
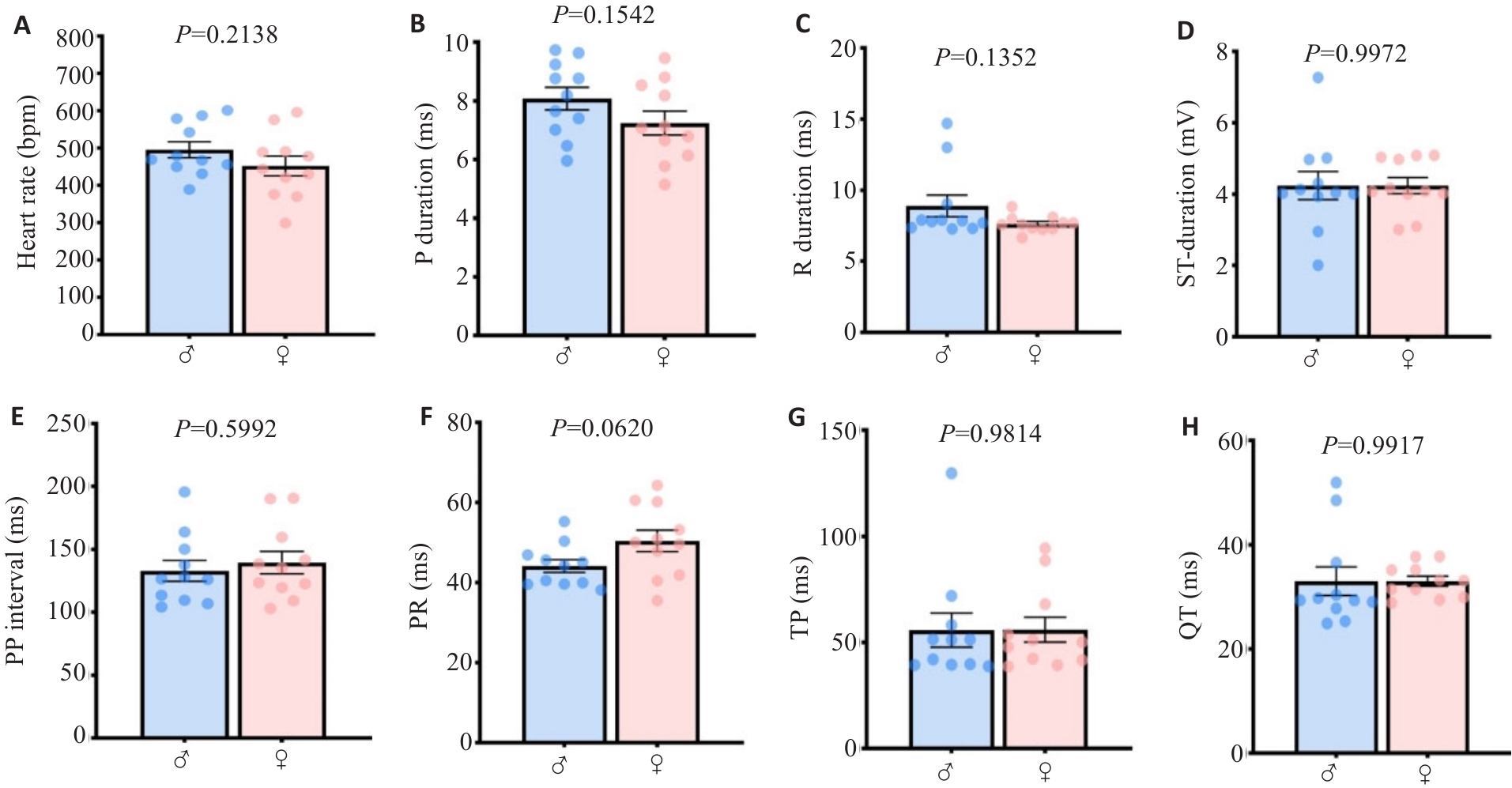
图2 小鼠主要心电时程ECGsqa量化参数具有性别间保守性
Fig. 2 The main quantified ECGsqa time course parameters in mice are conserved between genders. A: Heart rate. B: P wave rising segment duration. C: R wave rising segment duration. D: ST rising segment duration. E: PP interval. F: PR interval. G: P interval. H: QT interval.
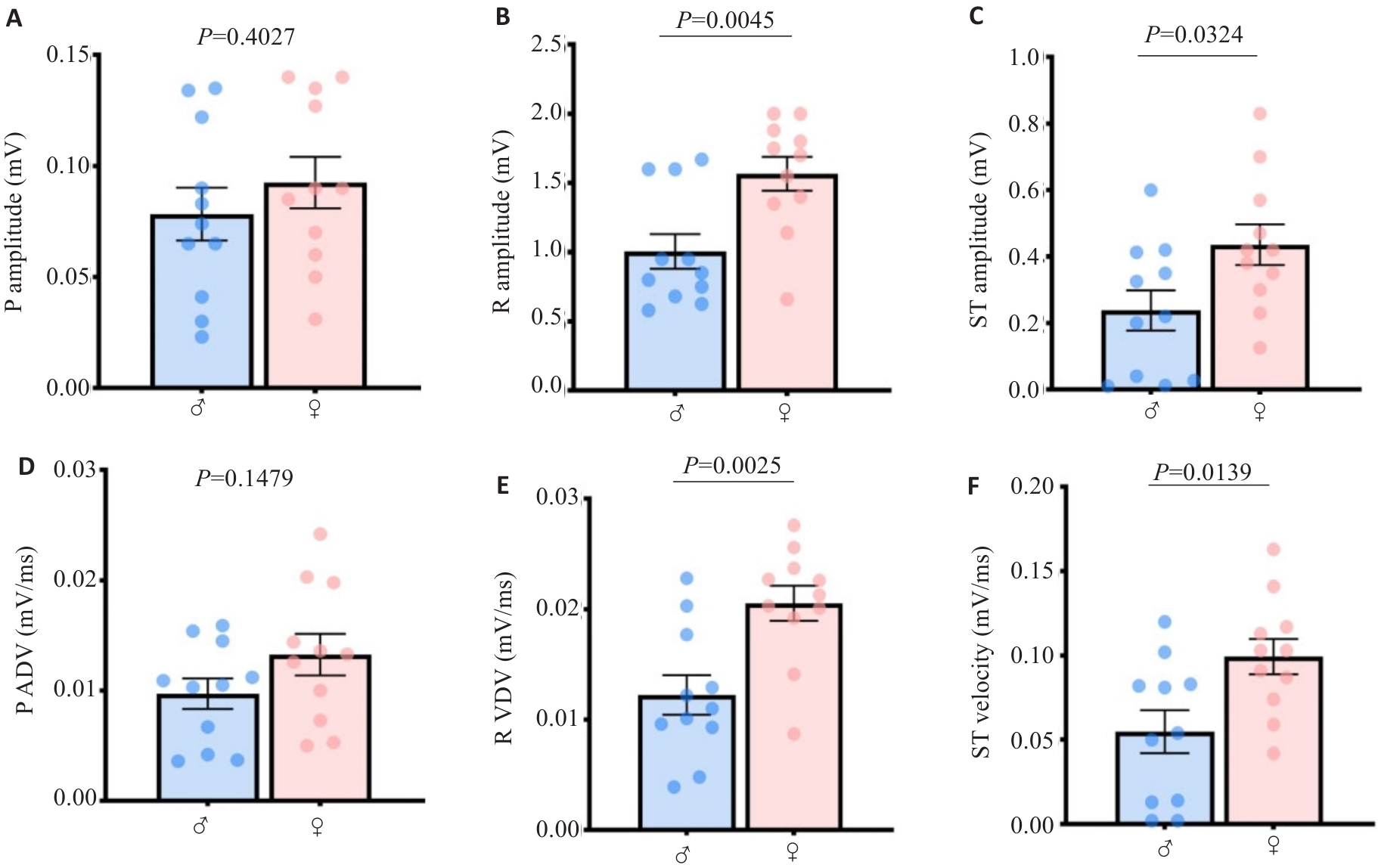
图3 小鼠房室心电波幅与导速的ECGsqa量化值具有性别差异特征
Fig.3 Quantitative values of atrioventricular ECGsqa amplitude and velocity in mice harbor mathematical characteristics of gender differences. A: P wave amplitude. B: R wave amplitude. C: ST segment amplitude. D: P wave velocity. E: R wave velocity. F: ST segment velocity.
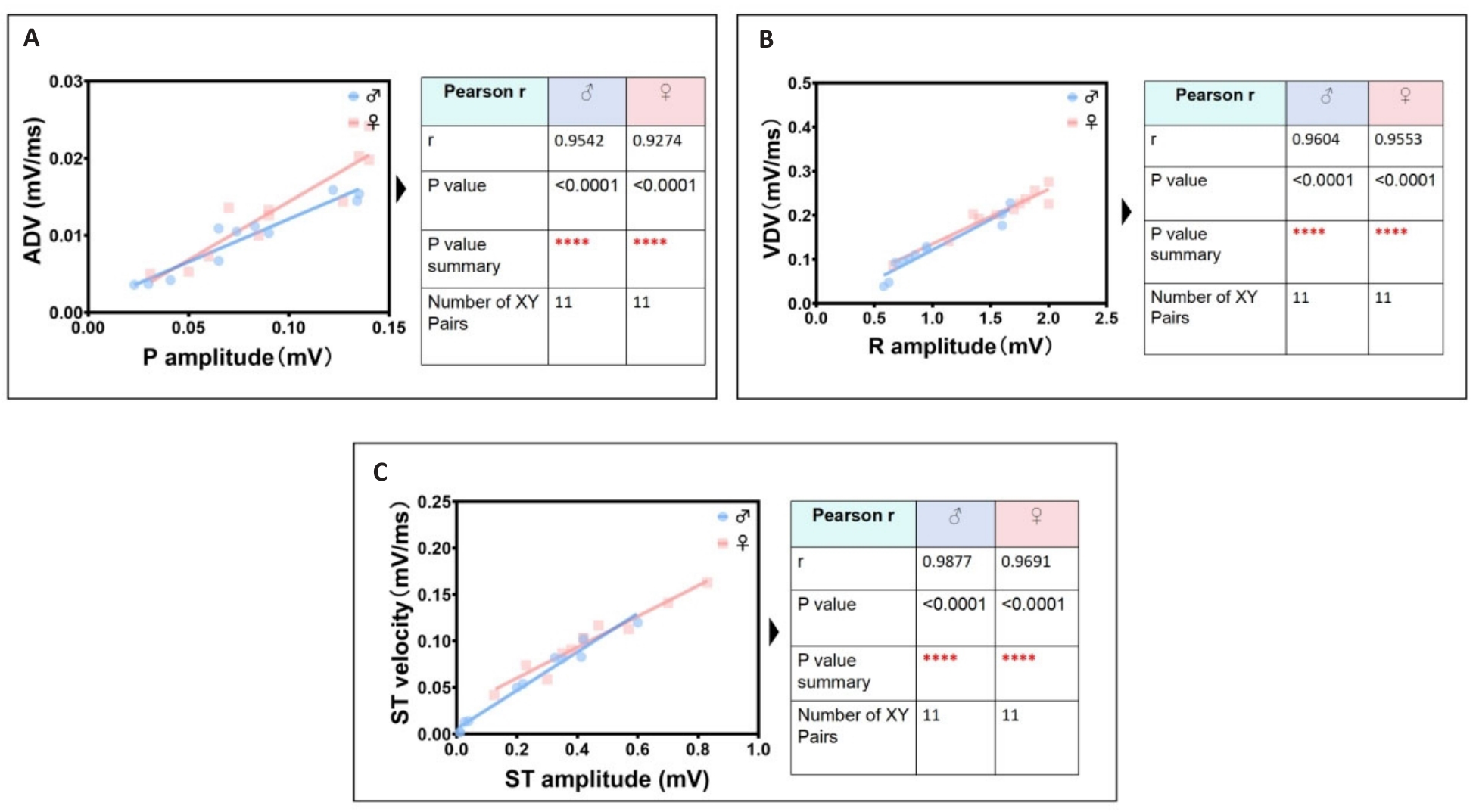
图4 雌雄小鼠心电最显著线性关联参数识别组
Fig.4 Identification group of the most significant linear correlation parameters in ECGsqa of both male and female mice. A: P wave amplitude is positively correlated with atrial depolarization rate (ADV). B: R wave amplitude is positively correlated with ventricular depolarization rate (VDV). C: ST segment amplitude is positively correlated with ventricular ST segment velocity.
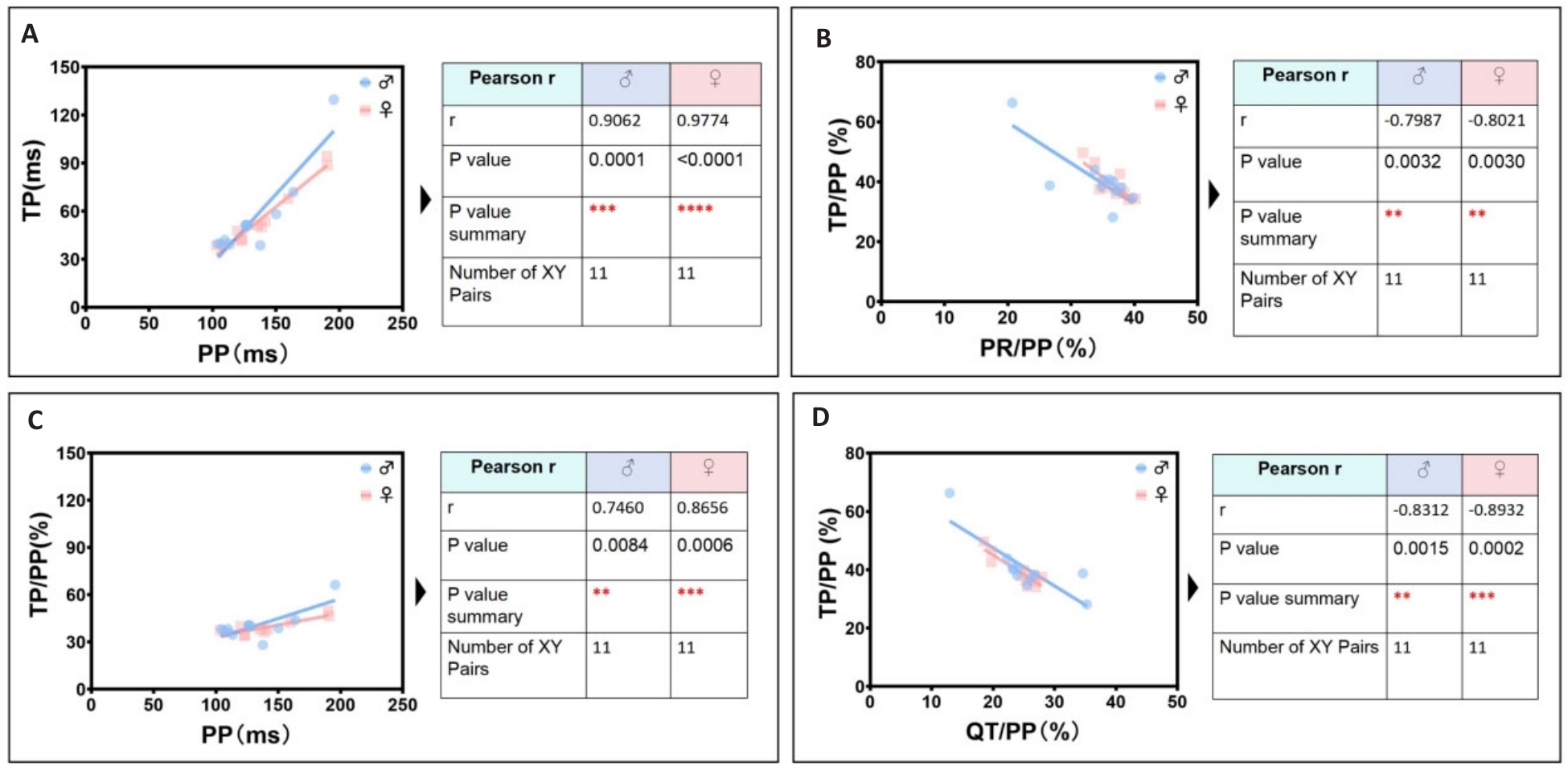
图5 雌雄小鼠心电次显著线性关联参数识别组
Fig.5 Identification group of secondary significant linear correlation parameters in ECGsqa of both male and female mice. A: PP interval is positively correlated with TP interval. B: PR/PP ratio is negatively correlated with TP/PP ratio. C: PP interval is positively correlated with TP/PP ratio. D: QT/PP ratio is negatively correlated with TP/ PP ratio.
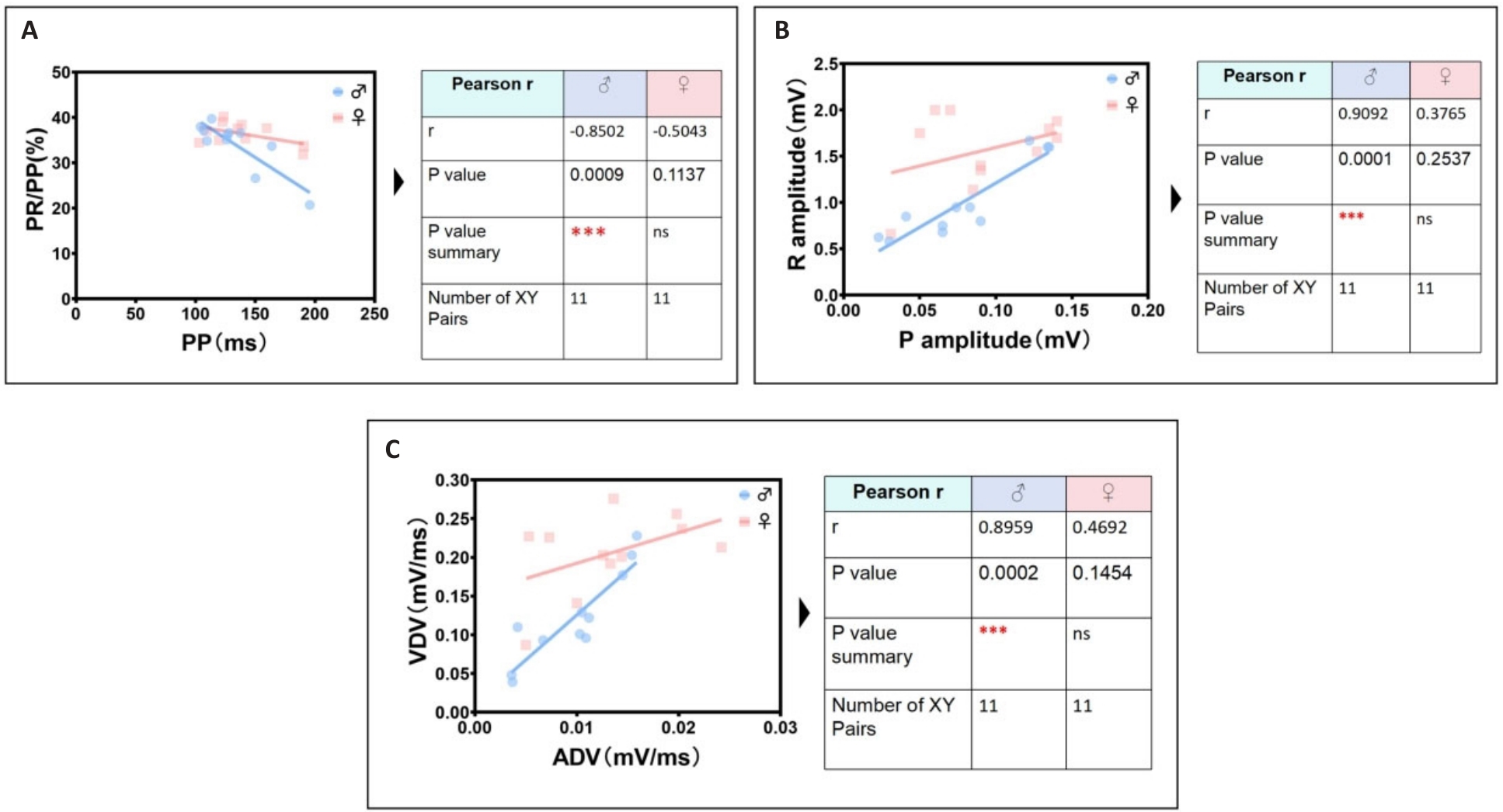
图6 雄鼠最显著独特心电线性相关参数识别组
Fig.6 The most significant unique identification group of ECG linear parameters related to male mice. A: Male PP interval is negatively correlated with male PR/PP ratio. B: Male P wave amplitude is positively correlated with male R wave amplitude. C: Male ADV is positively correlated with male VDV.
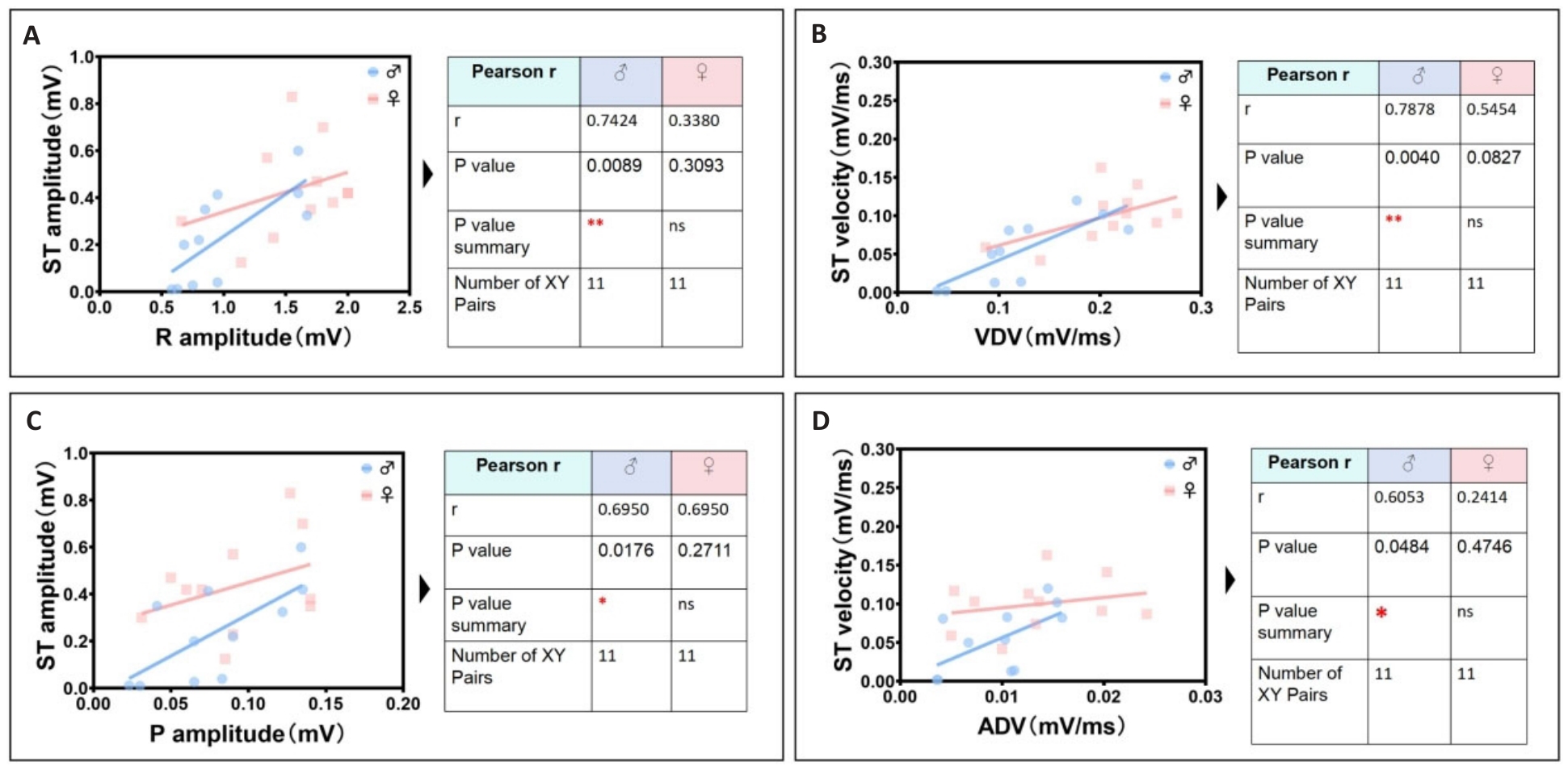
图7 雄鼠次显著独特心电线性相关参数识别组
Fig.7 Identification group of unique cardiac electrical linearity-related parameters in male mice. A: Male R wave amplitude is positively correlated with male ST segment amplitude. B: Male VDV is positively correlated with male ST segment velocity. C: Male P wave amplitude is positively correlated with male ST segment amplitude. D: Male ADV is positively correlated with male ST segment velocity.
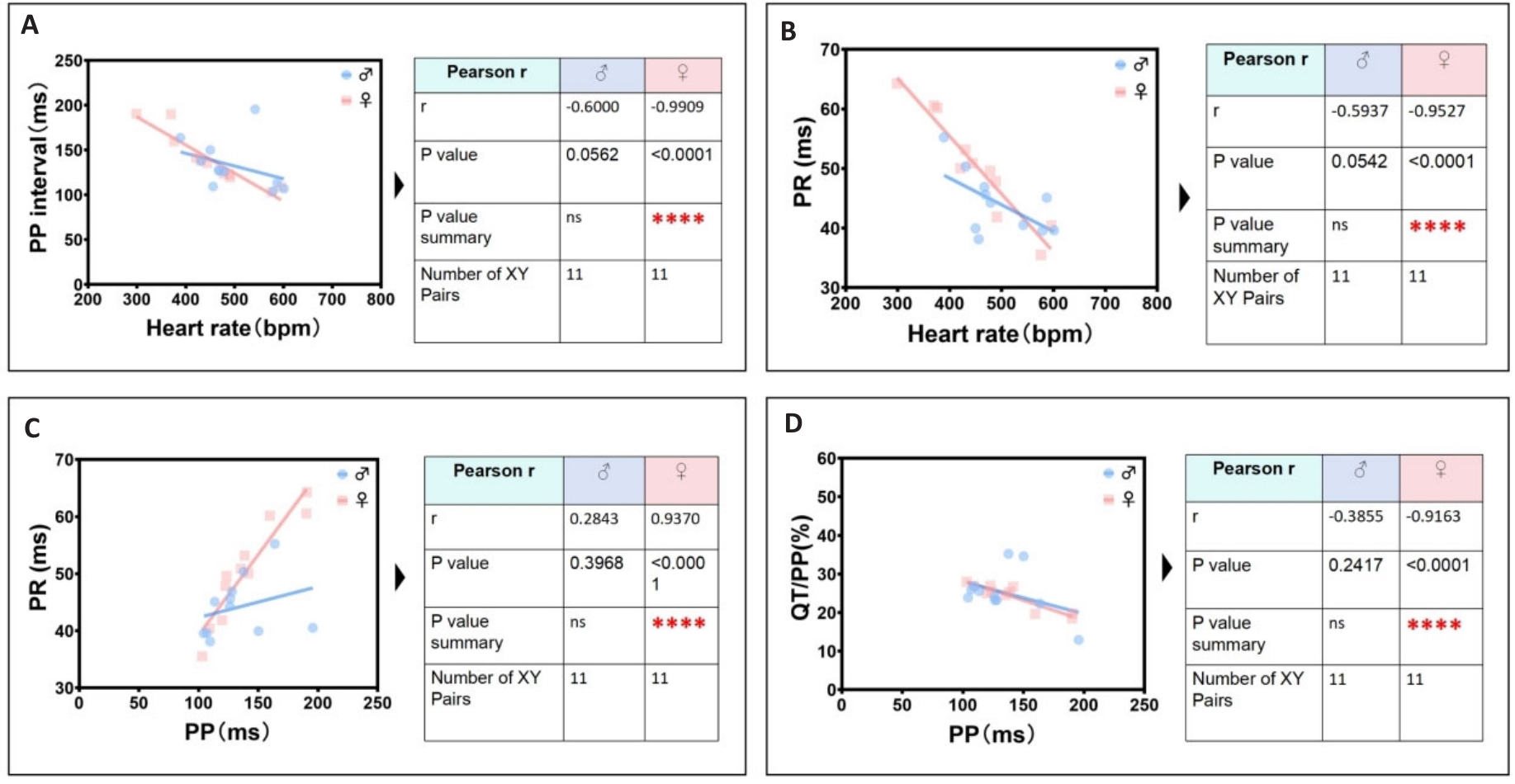
图8 雌鼠最显著独特心电线性相关参数识别组
Fig.8 The most significant unique identification group of ECG linearity-related parameters in female mice. A: Female heart rate is negatively correlated with female PP interval. B: Female heart rate is negatively correlated with female PR interval. C: Female PP interval is positively correlated with female PR interval. D: Female PP interval is negatively correlated with female QT/PP ratio.
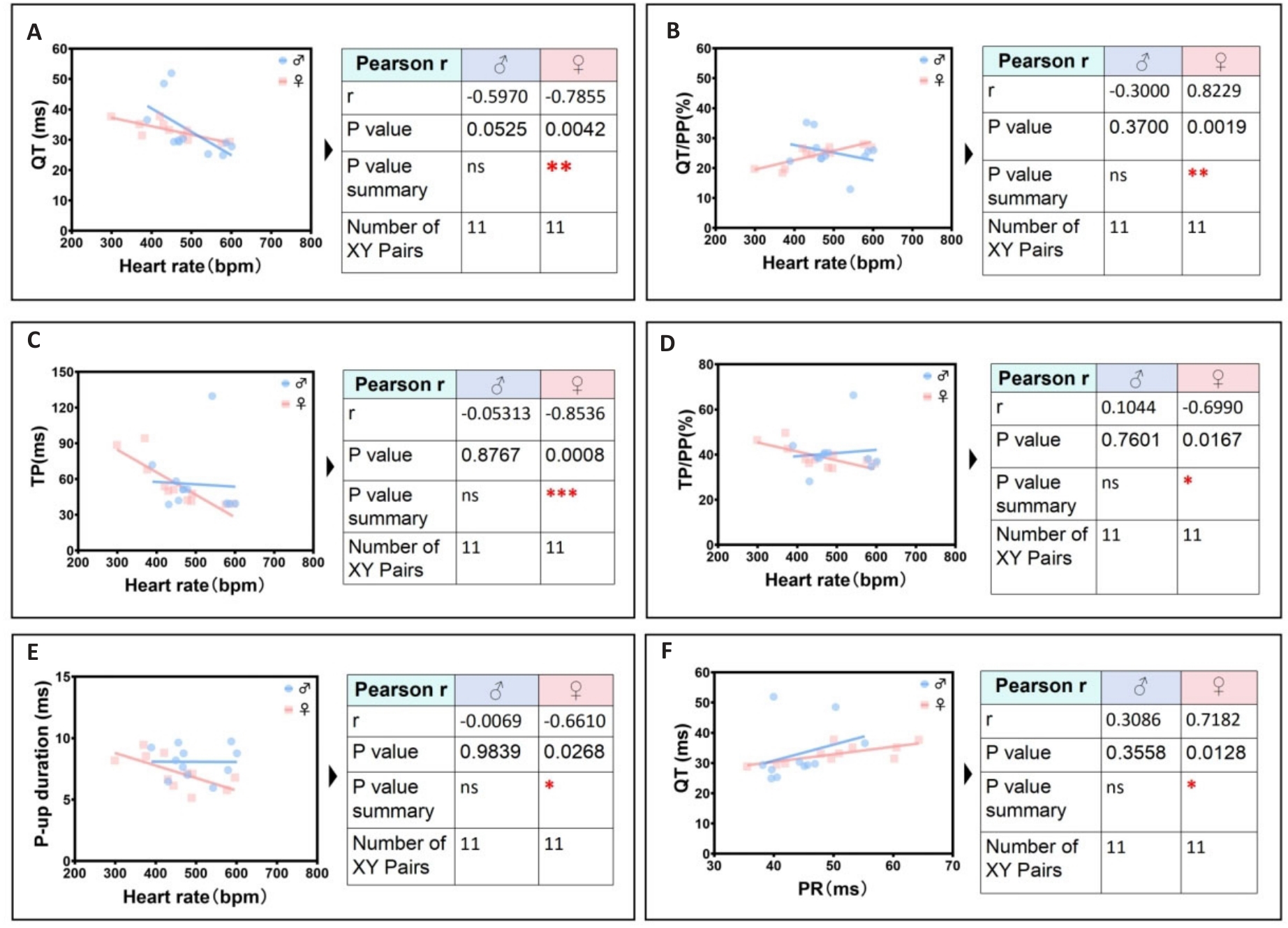
图9 雌鼠次显著独特心电线性相关参数识别组
Fig.9 Secondary significant unique identification group of ECG linearity-related parameters in female mice. A: Female heart rate is negatively correlated with female QT interval. B: Female heart rate is positively correlated with female QT/PP ratio. C: Female heart rate is negatively correlated with female TP ratio. D: Female heart rate is negatively correlated with female TP/PP ratio. E: Heart rate is negatively correlated the peak time of rising P wave in female. F: Female PR interval is positively correlated with female QT interval.
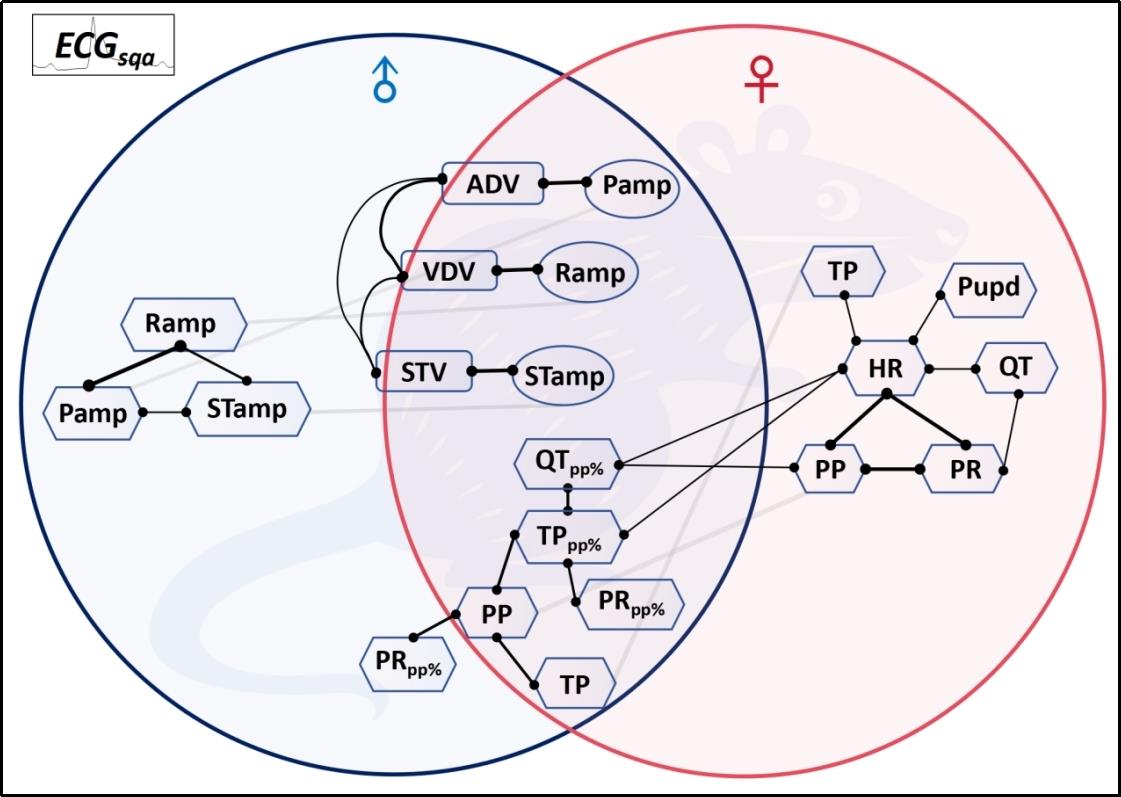
图10 定量心电关联参数网探识小鼠心脏电传导系统固有生理稳态模式
Fig.10 Quantitative ECG correlation parameter network characterizes the intrinsic physiological homeostasis pattern of the mouse cardiac electrical conduction system.
| 1 | Martin SS, Aday AW, Almarzooq ZI, et al. 2024 heart disease and stroke statistics: a report of US and global data from the American heart association[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(8): e347-60. |
| 2 | Goette A, Auricchio A, Boriani G, et al. EHRA White Paper: knowledge gaps in arrhythmia management-status 2019[J]. Europace, 2019, 21(7): 993-4. |
| 3 | Thomas RJ. Cardiac rehabilitation-challenges, advances, and the road ahead[J]. N Engl J Med, 2024, 390(9): 830-41. |
| 4 | Kowey PR, Naccarelli GV. Antiarrhythmic drug therapy: where do we go from here?[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(11): 801-3. |
| 5 | Nogami A, Kurita T, Abe H, et al. JCS/JHRS 2019 guideline on non-pharmacotherapy of cardiac arrhythmias[J]. J Arrhythm, 2021, 37(4): 709-870. |
| 6 | Kingma J, Simard C, Drolet B. Overview of cardiac arrhythmias and treatment strategies[J]. Pharmaceuticals, 2023, 16(6): 844. |
| 7 | Fye WB. A history of the origin, evolution, and impact of electrocardiography [J]. Am J Cardiol, 1994, 73(13):937-49. |
| 8 | Jahmunah V, Oh SL, Wei JKE, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of congestive heart failure using ECG signals‑A review[J]. Phys Med, 2019, 62: 95-104. |
| 9 | Oestereicher MA, Wotton JM, Ayabe S, et al. Comprehensive ECG reference intervals in C57BL/6N substrains provide a generalizable guide for cardiac electrophysiology studies in mice[J]. Mamm Genome, 2023, 34(2): 180-99. |
| 10 | Obergassel J, O'Reilly M, Sommerfeld LC, et al. Effects of genetic background, sex, and age on murine atrial electrophysiology[J]. Europace, 2021, 23(6): 958-69. |
| 11 | Haq KT, Cooper BL, Berk F, et al. The effect of sex and age on ex vivo cardiac electrophysiology: insight from a guinea pig model[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2023, 324(1): H141-54. |
| 12 | Ahmadi P, Afzalian A, Jalali A, et al. Age and gender differences of basic electrocardiographic values and abnormalities in the general adult population; Tehran Cohort Study[J]. BMC Cardiovasc Disord, 2023, 23(1): 303. |
| 13 | Xie M, Zhu SJ, Liu G, et al. A novel quantitative electrocardiography strategy reveals the electroinhibitory effect of tamoxifen on the mouse heart[J]. J Cardiovasc Transl Res, 2023, 16(5): 1232-48. |
| 14 | Jia BZ, Qi YT, Wong-Campos JD, et al. A bioelectrical phase transition patterns the first vertebrate heartbeats[J]. Nature, 2023, 622(7981): 149-55. |
| 15 | Levin M. Bioelectric signaling: Reprogrammable circuits underlying embryogenesis, regeneration, and cancer[J]. Cell, 2021, 184(8): 1971-89. |
| 16 | Gajendragadkar PR, von Ende A, Ibrahim M, et al. Assessment of the causal relevance of ECG parameters for risk of atrial fibrillation: a Mendelian randomisation study[J]. PLoS Med, 2021, 18(5): e1003572. |
| 17 | Amuzescu B, Airini R, Epureanu FB, et al. Evolution of mathematical models of cardiomyocyte electrophysiology[J]. Math Biosci, 2021, 334: 108567. |
| 18 | Lawson BAJ, Drovandi CC, Cusimano N, et al. Unlocking data sets by calibrating populations of models to data density: a study in atrial electrophysiology[J]. Sci Adv, 2018, 4(1): e1701676. |
| 19 | Morotti S, Liu C, Hegyi B, et al. Quantitative cross-species translators of cardiac myocyte electrophysiology: model training, experimental validation, and applications[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(47): eabg0927. |
| 20 | Mazhar F, Bartolucci C, Regazzoni F, et al. A detailed mathematical model of the human atrial cardiomyocyte: integration of electrophysiology and cardiomechanics[J]. J Physiol, 2024, 602(18): 4543-83. |
| 21 | Ntalla I, Weng LC, Cartwright JH, et al. Multi-ancestry GWAS of the electrocardiographic PR interval identifies 202 loci underlying cardiac conduction[J]. Nat Commun, 2020, 11(1): 2542. |
| 22 | van Duijvenboden S, Ramírez J, Young WJ, et al. Genomic and pleiotropic analyses of resting QT interval identifies novel loci and overlap with atrial electrical disorders[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2021, 30(24): 2513-23. |
| 23 | Liu G, Iden JB, Kovithavongs K, et al. In vivo temporal and spatial distribution of depolarization and repolarization and the illusive murine T wave[J]. J Physiol, 2004, 555(Pt 1): 267-79. |
| 24 | Rodrigues JC, McIntyre B, Dastidar AG, et al. The effect of obesity on electrocardiographic detection of hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy: recalibration against cardiac magnetic resonance[J]. J Hum Hypertens, 2016, 30(3): 197-203. |
| 25 | de Coster M, Demolder A, de Meyer V, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of R-wave detection by insertable cardiac monitors[J]. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol, 2020, 43(5): 511-7. |
| 26 | Ramírez J, van Duijvenboden S, Young WJ, et al. Common genetic variants modulate the electrocardiographic tpeak-to-tend interval[J]. Am J Hum Genet, 2020, 106(6): 764-78. |
| 27 | Yogasundaram H, Zheng YG, Ly E, et al. Relationship between baseline electrocardiographic measurements and outcomes in patients with high-risk heart failure: insights from the VerICiguaT Global Study in Subjects with Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction (VICTORIA) trial[J]. Eur J Heart Fail, 2023, 25(10): 1822-30. |
| 28 | Mayourian J, la Cava WG, Vaid A, et al. Pediatric ECG-based deep learning to predict left ventricular dysfunction and remodeling[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(12): 917-31. |
| 29 | Ardissino M, Patel KHK, Rayes B, et al. Multiple anthropometric measures and proarrhythmic 12-lead ECG indices: a Mendelian randomization study[J]. PLoS Med, 2023, 20(8): e1004275. |
| 30 | Chen LY, Ribeiro ALP, Platonov PG, et al. P wave parameters and indices: a critical appraisal of clinical utility, challenges, and future research-a consensus document endorsed by the international so-ciety of electrocardiology and the international society for holter and noninvasive electrocardiology[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2022, 15(4): e010435. |
| 31 | Young WJ, Lahrouchi N, Isaacs A, et al. Genetic analyses of the electrocardiographic QT interval and its components identify additional loci and pathways[J]. Nat Commun, 2022, 13(1): 5144. |
| 32 | Broman MT, Nadadur RD, Perez-Cervantes C, et al. A genomic link from heart failure to atrial fibrillation risk: FOG2 modulates a TBX5/GATA4-dependent atrial gene regulatory network[J]. Circulation, 2024, 149(15): 1205-30. |
| 33 | Frimodt-M ller EK, Soliman EZ, Kizer JR, et al. Lifestyle habits associated with cardiac conduction disease[J]. Eur Heart J, 2023, 44(12): 1058-66. |
| 34 | Gottlieb LA, Larsen K, Halade GV, et al. Prolonged QT intervals in mice with cardiomyocyte-specific deficiency of the molecular clock[J]. Acta Physiol, 2021, 233(1): e13707. |
| 35 | Calò L, Crescenzi C, Martino A, et al. The diagnostic value of the 12-LeadECGin arrhythmogenic LeftVentricularCardiomyopathy: novel ECG signs[J]. JACC Clin Electrophysiol, 2023, 9(12): 2615-27. |
| 36 | Nam JM, Lim JE, Ha TW, et al. Cardiac-specific inactivation of Prdm16 effects cardiac conduction abnormalities and cardiomyopathy-associated phenotypes[J]. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2020, 318(4): H764-77. |
| 37 | Karakayali M, Artac I, Omar T, et al. Assessment of the efficacy of the electrocardiographic P-wave peak time in predicting atrial high rate episode in patients with cardiac implantable electronic devices[J]. J Electrocardiol, 2023, 80: 40-4. |
| 38 | Hennis K, Rötzer RD, Rilling J, et al. In vivo and ex vivo electrophysiological study of the mouse heart to characterize the cardiac conduction system, including atrial and ventricular vulnerability[J]. Nat Protoc, 2022, 17(5): 1189-222. |
| 39 | Litviňuková M, Talavera-López C, Maatz H, et al. Cells of the adult human heart[J]. Nature, 2020, 588(7838): 466-72. |
| 40 | Li Q, Lin ZW, Liu R, et al. Multimodal charting of molecular and functional cell states via in situ electro-sequencing[J]. Cell, 2023, 186(9): 2002-17. e21. |
| 41 | Jagannatha GNP, Antara IMPS, Kosasih AM, et al. P-wave peak time and P-wave dispersion in surface electrocardiography as initial predictors of new-onset atrial fibrillation in early-onset hypertension[J]. Hypertens Res, 2024, 47(1): 137-48. |
| 42 | Feeny AK, Rickard J, Trulock KM, et al. Machine learning of 12-lead QRS waveforms to identify cardiac resynchronization therapy patients with differential outcomes[J]. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2020, 13(7): e008210. |
| 43 | Hnatkova K, Andršová I, Novotný T, et al. QRS micro-fragmentation as a mortality predictor[J]. Eur Heart J, 2022, 43(40): 4177-91. |
| 44 | Chen N, Wang L, Jiao JC, et al. RV1+RV3 index to differentiate idiopathic ventricular arrhythmias arising from right ventricular outflow tract and aortic sinus of Valsalva: a multicenter study[J]. J Am Heart Assoc, 2024, 13(7): e033779. |
| 45 | Wallet J, Kimura Y, Blom NA, et al. The R″ wave in V1 and the negative terminal QRS vector in aVF combine to a novel 12-lead ECG algorithm to identify slow conducting anatomical isthmus 3 in patients with tetralogy of Fallot[J]. Europace, 2023, 25(6): euad139. |
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||