南方医科大学学报 ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (11): 2063-2073.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.11.02
• • 上一篇
银苗朱1( ), 陈奎玉1, 吴丽敏2,3, 江鹏宇1, 籍志慧1, 张念1, 周欢1, 韩辉1(
), 陈奎玉1, 吴丽敏2,3, 江鹏宇1, 籍志慧1, 张念1, 周欢1, 韩辉1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-05-06
出版日期:2024-11-20
发布日期:2024-11-29
通讯作者:
韩辉
E-mail:1492657304@qq.com;hanhuidoctor2022@163.com
作者简介:银苗朱,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 1492657304@qq.com
基金资助:
Miaozhu YIN1( ), Kuiyu CHEN1, Limin WU2,3, Pengyu JIANG1, Zhihui JI1, Nian ZHANG1, Huan ZHOU1, Hui HAN1(
), Kuiyu CHEN1, Limin WU2,3, Pengyu JIANG1, Zhihui JI1, Nian ZHANG1, Huan ZHOU1, Hui HAN1( )
)
Received:2024-05-06
Online:2024-11-20
Published:2024-11-29
Contact:
Hui HAN
E-mail:1492657304@qq.com;hanhuidoctor2022@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探究肝豆补肾汤(GDBSD)影响Wilson病(WD)模型TX雄性小鼠生殖障碍的机制。 方法 以15只正常雄性DL小鼠为对照组,将60只纯合雄性TX小鼠随机分为4组(n=15):WD模型组、青霉胺组、GDBSD组和GDBSD+U0126组(U0126为一种特异性MAPK/ERK激酶抑制剂),其中青霉胺组给予0.09 g/kg青霉胺药液灌胃;GDBSD组给予GDBSD药液灌胃,0.2 mL/(10 g·d);GDBSD+U0126组给予同样GDBSD灌胃另外每日下午同一时间腹腔注射U0126(20 mg/kg)。干预4周后检测各组睾丸组织铜含量;利用HE染色法观察小鼠睾丸与附睾的深层次病理结构及精子构造,通过电子显微镜技术探究睾丸中生精细胞与精子的超微结构特点;TUNEL法标记睾丸组织凋亡细胞;免疫印迹检测B淋巴细胞瘤-2基因(Bcl-2)、细胞色素C(Cytc)、半胱天冬蛋白酶-3(Caspase-3)、细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)和磷酸化激活的细胞外信号调节激酶(p-ERK)蛋白表达;免疫组化标记Brdu阳性细胞;精液质量检测精子密度、活力及畸形率。通过雌鼠的妊娠率和产仔数评估雄性TX小鼠的生育力水平。 结果 与WD模型组相比,青霉胺组、GDBSD组改善了小鼠的睾丸的组织和细胞病理学变化以及精子密度、活力程度和畸形率和生育力水平,并增加了睾丸JOHNSEN评分(P<0.05);Cytc、Caspase-3蛋白表达水平下调,Bcl-2表达上调(P<0.05),GDBSD+U0126组逆转了GDBSD治疗后Bcl-2表达的上调(P<0.05);ERK1/2信号通路研究结果显示,5组之间ERK1/2总蛋白表达水平差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。与对照组相比,WD模型组p-ERK蛋白表达含量明显减少;与WD模型组相比,青霉胺组、GDBSD组p-ERK蛋白表达含量增加;GDBSD+U0126组p-ERK蛋白表达含量低于GDBSD组(P<0.05);在施用U0126后,生精细胞增殖减少,生精细胞凋亡数量增加(P<0.05)。 结论 GDBSD可以改善Wilson病模型TX小鼠异常精子发生和生育力下降,其机制可能通过激活ERK信号通路从而改善生精细胞的增殖和凋亡状况。
银苗朱, 陈奎玉, 吴丽敏, 江鹏宇, 籍志慧, 张念, 周欢, 韩辉. 肝豆补肾汤通过激活ERK信号通路减少Wilson病TX小鼠异常精子生成并促进生精细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(11): 2063-2073.
Miaozhu YIN, Kuiyu CHEN, Limin WU, Pengyu JIANG, Zhihui JI, Nian ZHANG, Huan ZHOU, Hui HAN. Gandou Bushen Decoction improves spermatogenesis and promotes spermatogenic cell proliferation in Wilson disease TX mice by activating testicular ERK signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2063-2073.
| Group | Testicular copper level (μg/g) |
|---|---|
| Control | 2.772±0.306 |
| WD | 9.355±0.425* |
| Penicillamine | 4.129±0.550 # |
| GDBSD | 4.952±0.264 *# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 5.597±0.678# |
表1 小鼠睾丸组织铜含量的比较
Tab.1 Comparison of testicular copper levels among the 5 groups (μg/g, Mean±SD, n=5)
| Group | Testicular copper level (μg/g) |
|---|---|
| Control | 2.772±0.306 |
| WD | 9.355±0.425* |
| Penicillamine | 4.129±0.550 # |
| GDBSD | 4.952±0.264 *# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 5.597±0.678# |
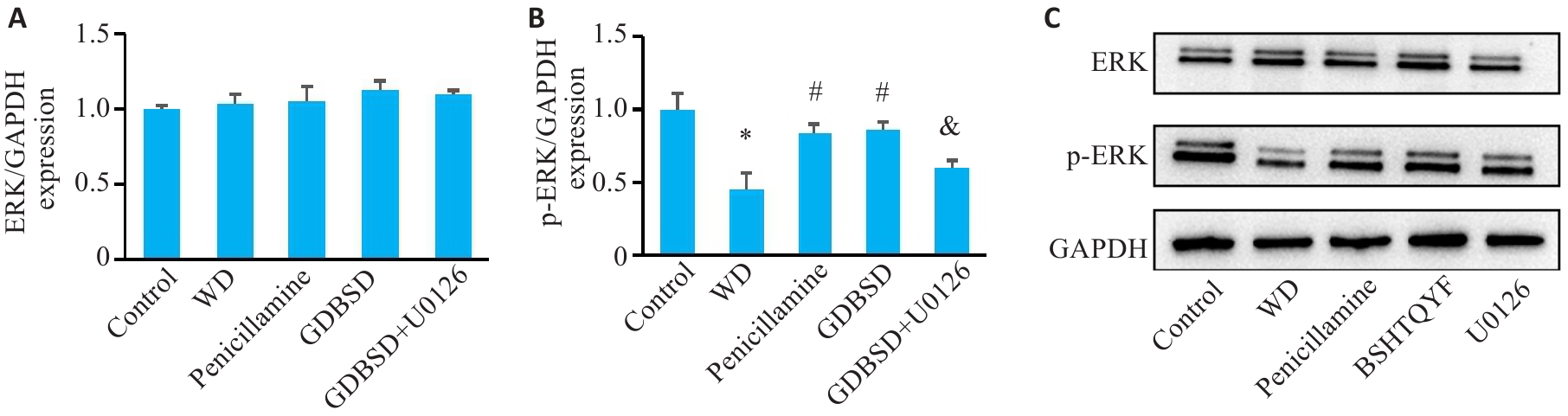
图1 小鼠睾丸组织中ERK、p-ERK蛋白表达
Fig.1 Western blotting for detecting expressions of ERK signaling pathway proteins in mouse testicular tissue. A: ERK. B: p-ERK (Mean±SD, n=5). C: Original protein bands. *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs WD group; &P<0.05 vs GDBSD group.
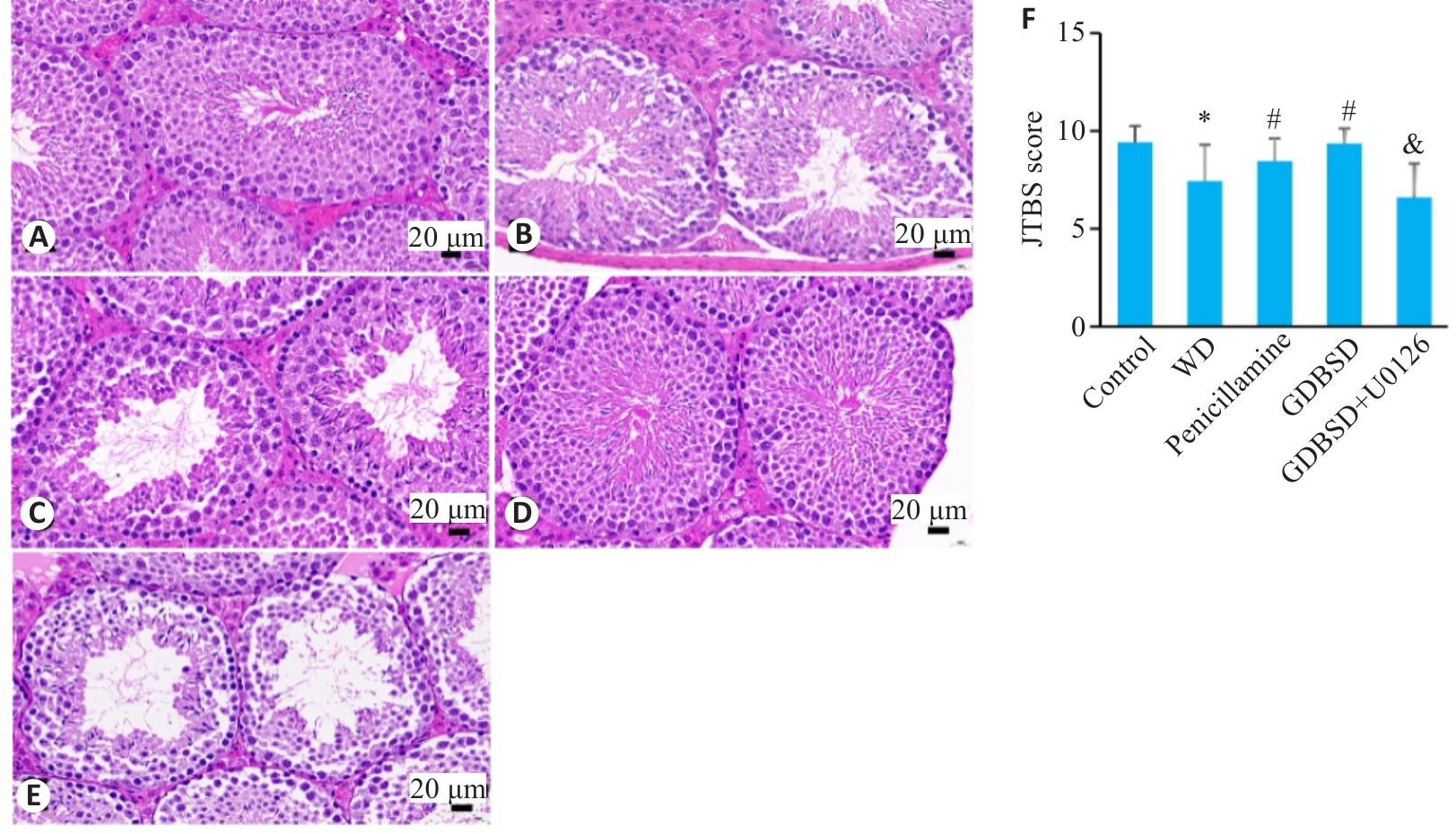
图2 小鼠睾丸组织HE染色结果
Fig.2 HE staining of testicular tissues of the mice. A: Control group. B: WD group. C: Penicillamine group. D: GDBSD group. E: GDBSD+U0126 group. F: Johnsen scores of the germinal tubules in the testicular tissue. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs WD group; &P<0.05 vs GDBSD group.
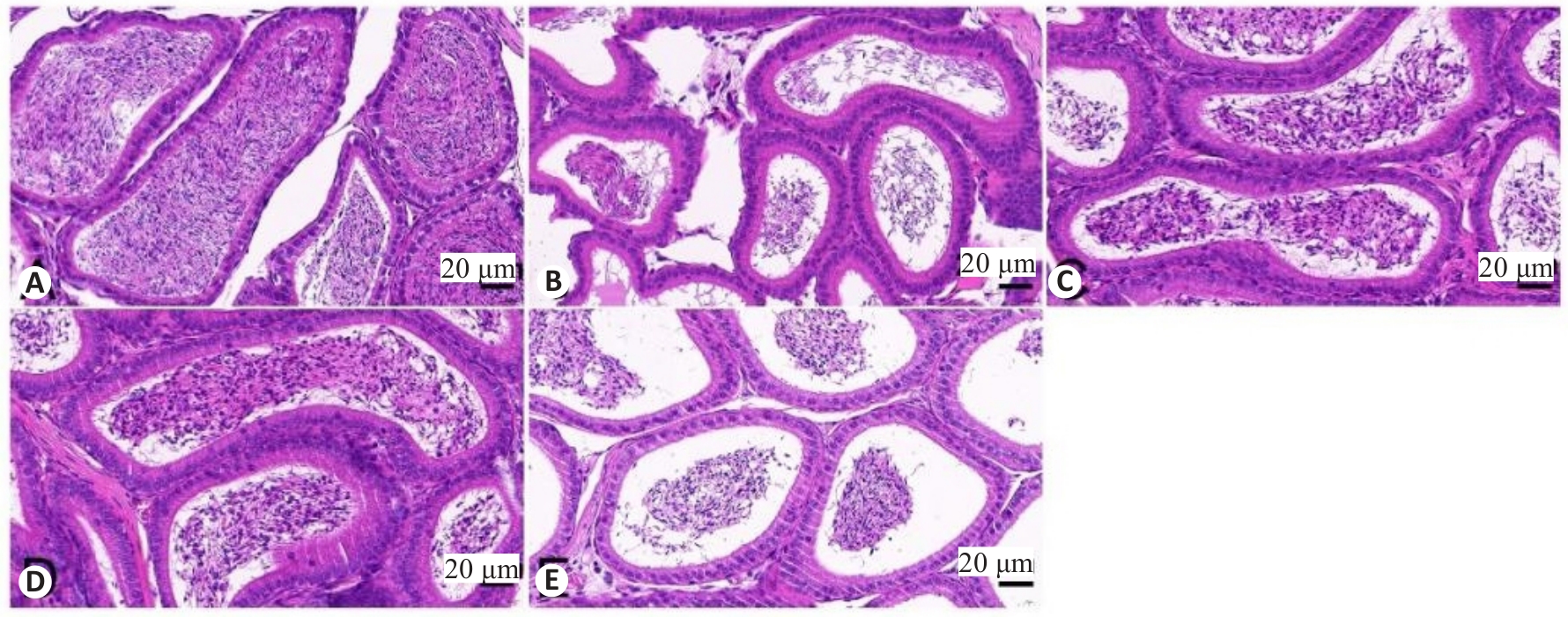
图3 小鼠附睾组织HE染色结果
Fig.3 HE staining of mouse epididymal tissues. A: Control group. B: WD group. C: Penicillamine group. D: GDBSD group. E: GDBSD+U0126 group.
| Group | Sperm density (107/mL) | Sperm survival rate (%) | Sperm malformation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 4.73±0.17 | 71.51±1.65 | 14.97±2.35 |
| WD | 2.20±0.22* | 20.59±1.81* | 79.62±4.44* |
| Penicillamine | 3.50±0.16*# | 61.72±1.12*# | 26.96±3.60*# |
| GDBSD | 3.43±0.50*# | 66.53±1.72*# | 24.84±1.67*# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 2.67±0.12& | 52.50±2.25 & | 77.74±3.39 & |
表2 小鼠精子质量比较
Tab.2 Comparison of sperm quality of the mice (Mean±SD, n=5)
| Group | Sperm density (107/mL) | Sperm survival rate (%) | Sperm malformation rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 4.73±0.17 | 71.51±1.65 | 14.97±2.35 |
| WD | 2.20±0.22* | 20.59±1.81* | 79.62±4.44* |
| Penicillamine | 3.50±0.16*# | 61.72±1.12*# | 26.96±3.60*# |
| GDBSD | 3.43±0.50*# | 66.53±1.72*# | 24.84±1.67*# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 2.67±0.12& | 52.50±2.25 & | 77.74±3.39 & |
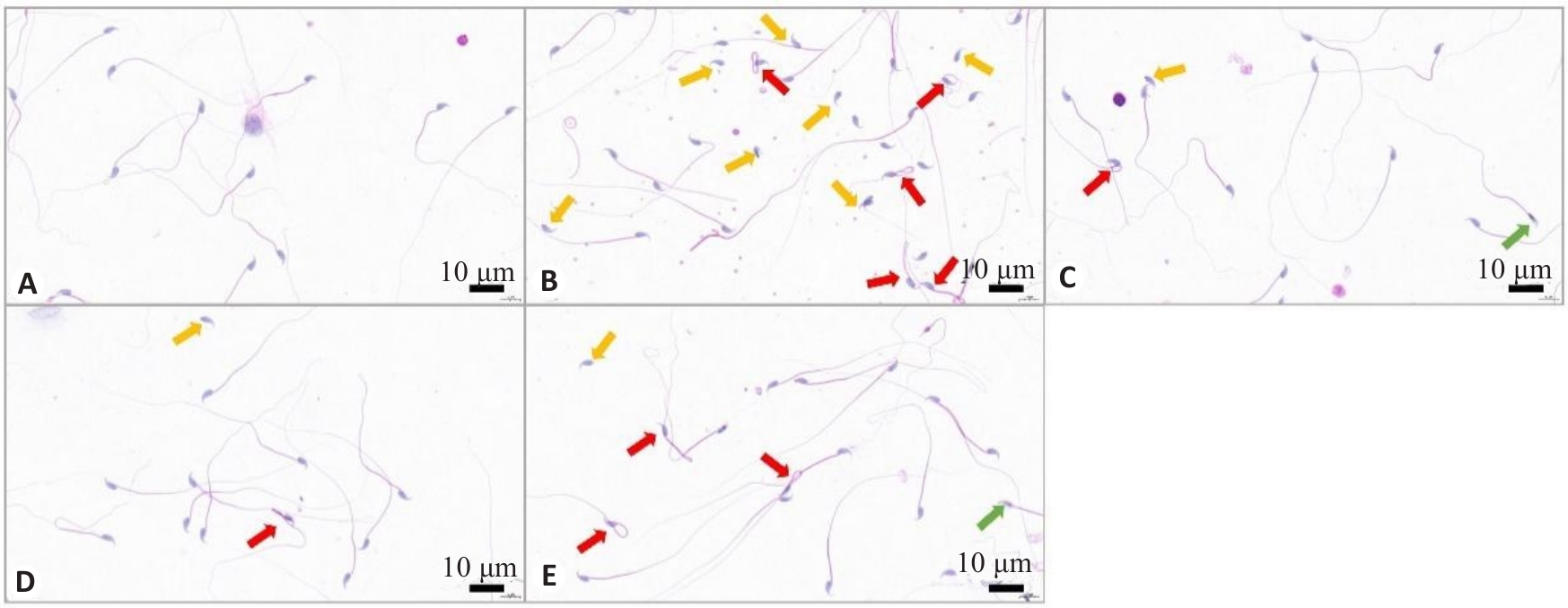
图4 小鼠附睾内精液的HE染色结果
Fig.4 Representative images of HE staining of mouse spermatozoa. A: Control group. B: WD group. C: penicillamine group. D: GDBSD group. E: GDBSD+U0126 group. Red arrows: Sperms with tail curl; Orange arrows: Sperms with a head without a tail; Green arrows: Sperms with head deformity.
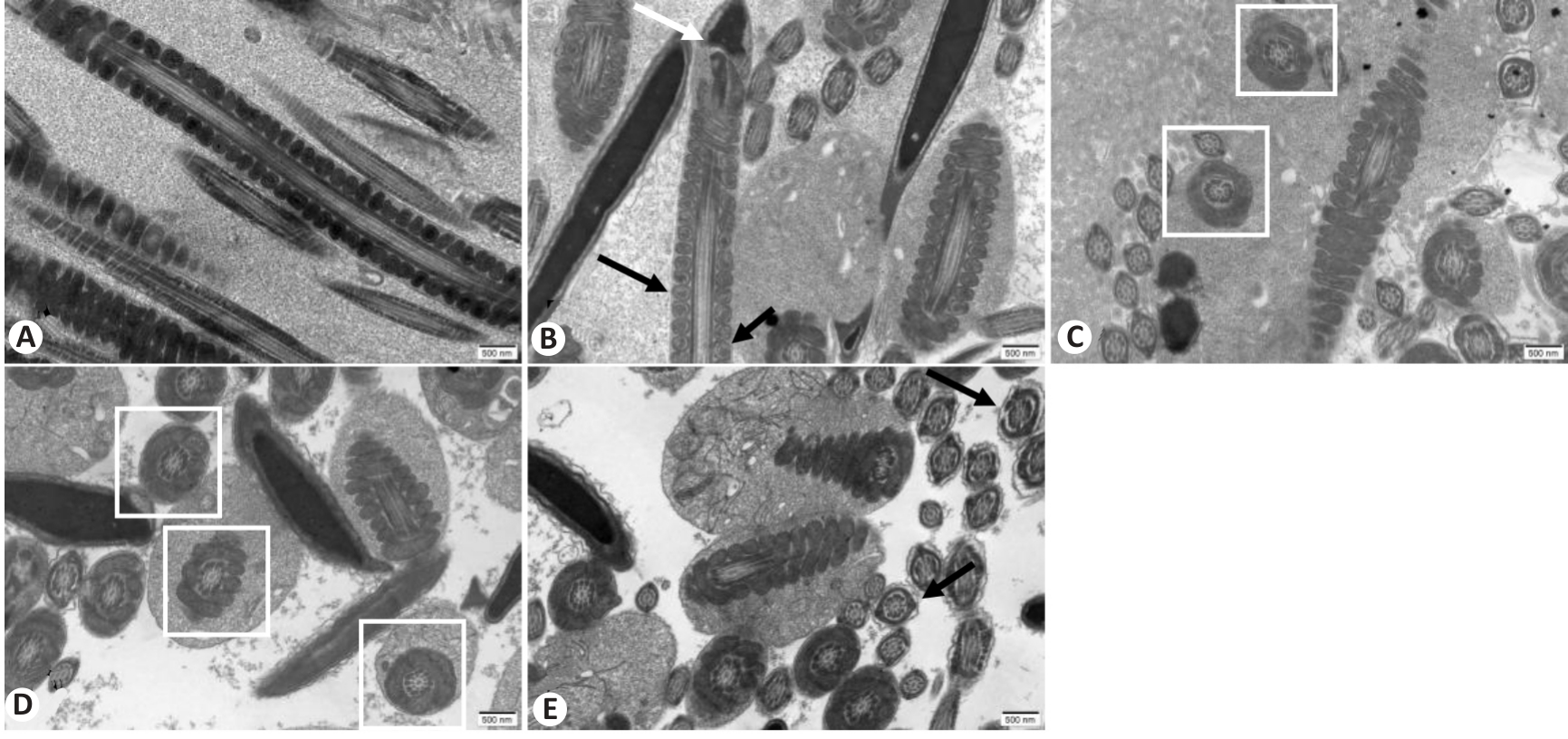
图5 小鼠附睾内精子的超微结构
Fig. 5 Ultrastructural changes of mouse spermatozoa in each group observed with transmission electron microscope (scale bar=500 nm). A: Control group. B: WD group. C: Penicillamine group. D: GDBSD group. E: GDBSD+U0126 group.
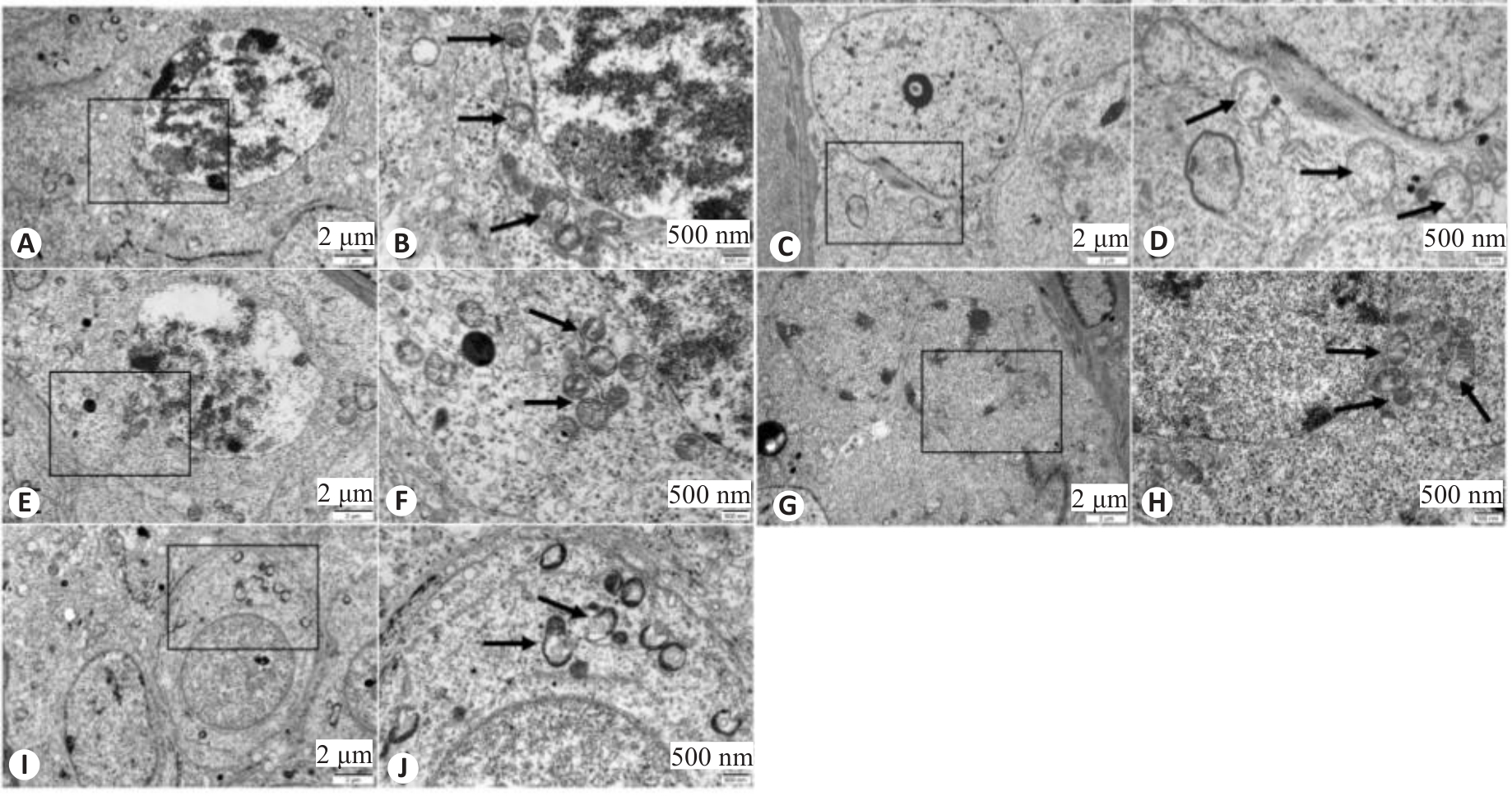
图6 各组小鼠睾丸组织中生精细胞的超微结构
Fig.6 Ultrastructure of mouse spermatocytes in each group observed with transmission electron microscope. A, B: Control group. C, D: WD group. E, F: Penicillamine group. G, H: GDBSD group. I, J: GDBSD+U0126 group. Black arrows indicate mitochondrial structures.
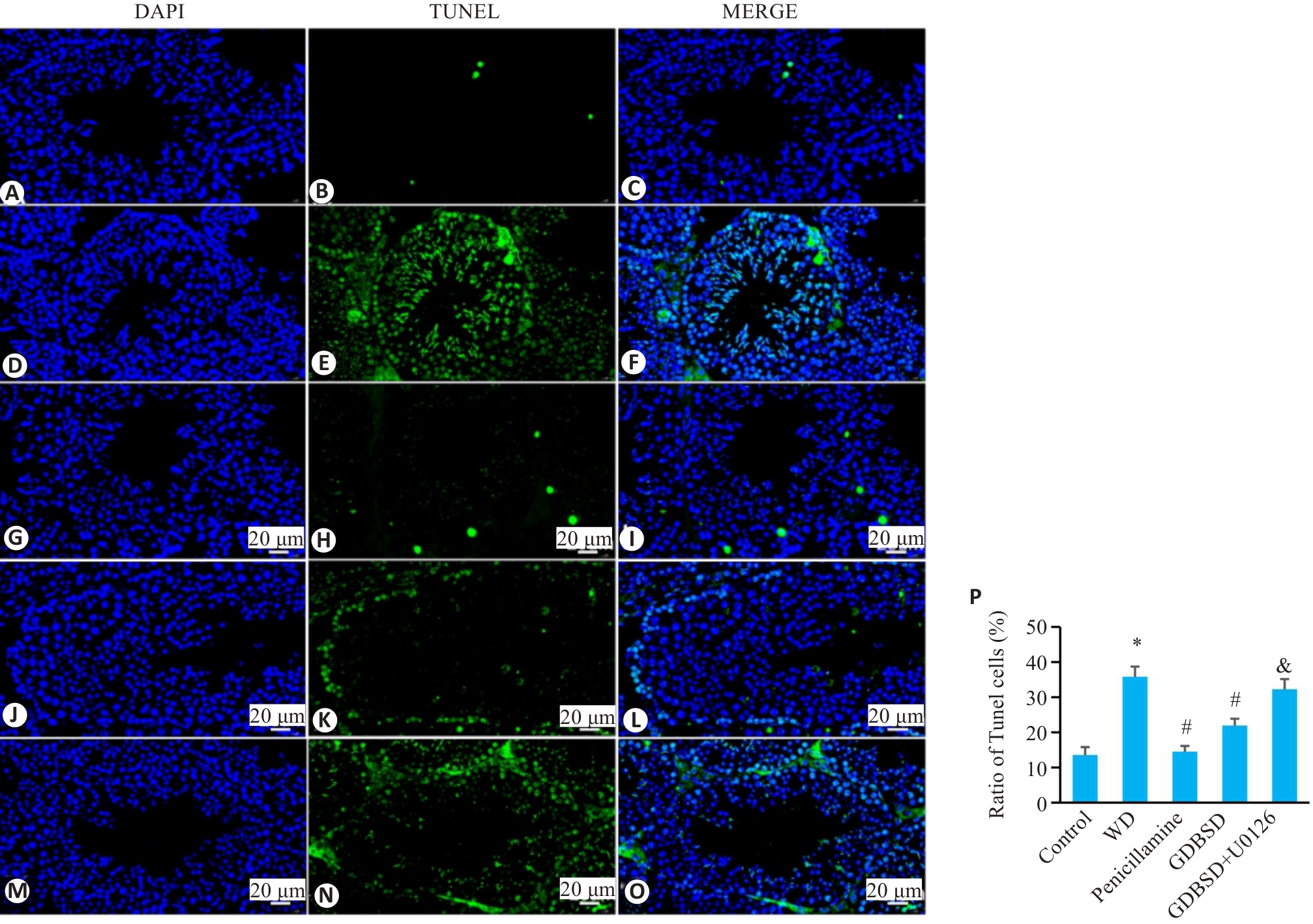
图7 小鼠睾丸组织的 TUNEL 染色结果
Fig. 7 TUNEL staining of mouse testicular tissue. A-C: Control group. D-F: WD group. G-I: Penicillamine group. J-L: GDBSD group. M-O: GDBSD+U0126 group. P: Apoptosis rate of testicular tissue in each group. Apoptotic cells are stained green and nuclei are stained blue (Mean±SD,n=5). *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs WD group; &P<0.05 vs GDBSD group.
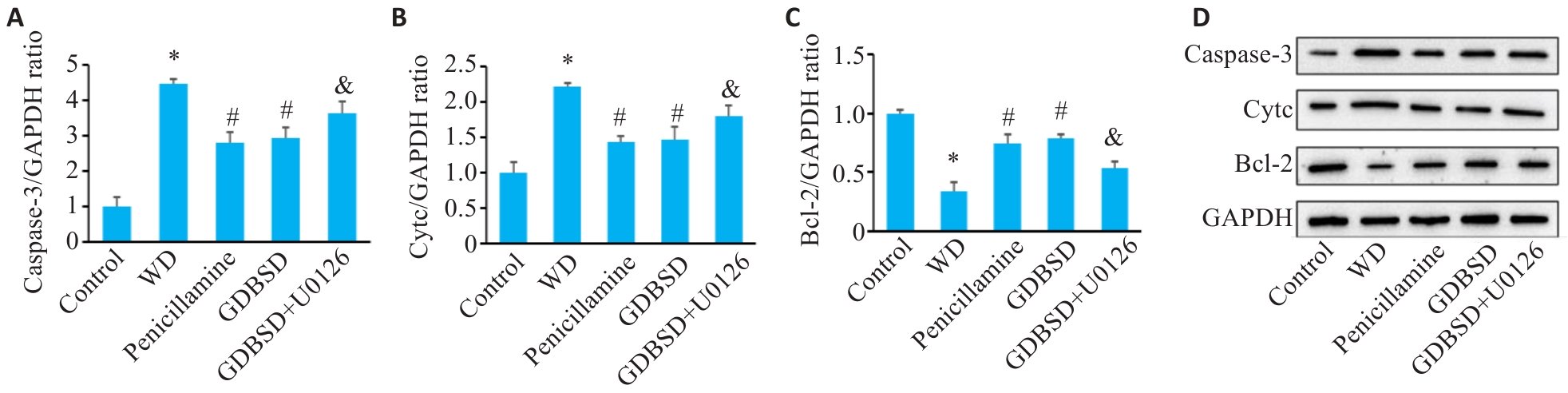
图8 小鼠睾丸组织中Caspase-3、Cytc、Bcl-2的蛋白表达
Fig. 8 Western blotting for detecting expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in mouse testis. A: Caspase-3. B: Cytc. C: Bcl-2. D: Original protein bands. *P<0.05 vs Control group, #P<0.05 vs WD group, &P<0.05 vs GDBSD group.
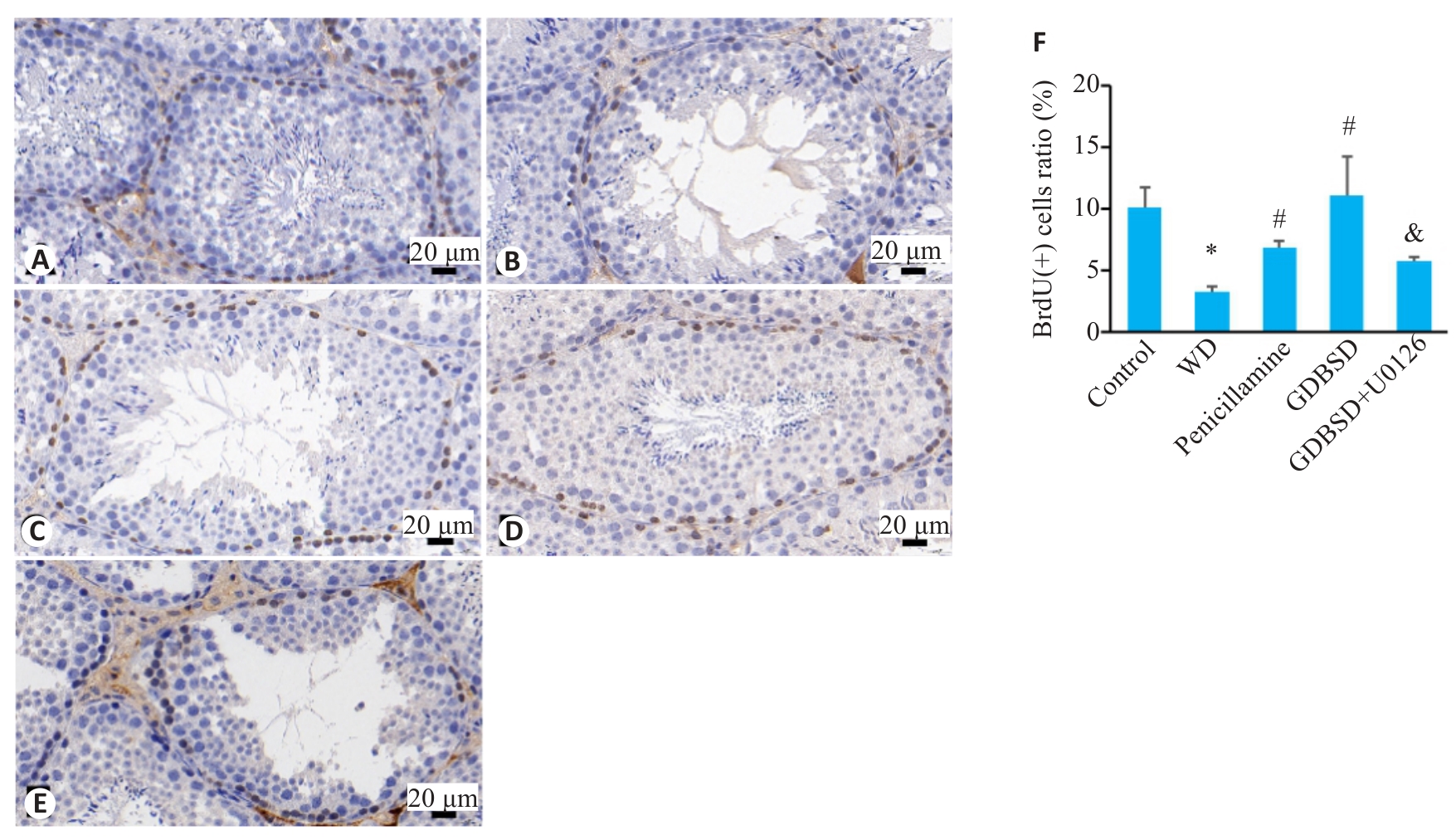
图9 小鼠睾丸组织中免疫组化标记的BrdU
Fig.9 Immunohistochemically labeled BrdU-positive cells in mouse testicular tissue. A: Control group. B: WD group. C: Penicillamine group. D: GDBSD group. E: GDBSD+U0126 group. F: Percentages of BrdU-positive cells in each group. *P<0.05 vs Control group; #P<0.05 vs WD group; &P<0.05 vs GDBSD group.
| Group | Fertility rate (%) | Pups per litter |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 80.00 | 10.11±1.73 |
| WD | 37.50 | 4.00±0.82* |
| Penicillamine | 62.50 | 7.40±1.04# |
| GDBSD | 66.67 | 8.14±1.55# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 42.86 | 5.00±0.81& |
表3 5组雄性小鼠生育能力比较
Tab.3 Comparison of fertility of male mice among the 5 groups (Mean±SD, n=5)
| Group | Fertility rate (%) | Pups per litter |
|---|---|---|
| Control | 80.00 | 10.11±1.73 |
| WD | 37.50 | 4.00±0.82* |
| Penicillamine | 62.50 | 7.40±1.04# |
| GDBSD | 66.67 | 8.14±1.55# |
| GDBSD+U0126 | 42.86 | 5.00±0.81& |
| 1 | Favata MF, Horiuchi KY, Manos EJ, et al. Identification of a novel inhibitor of mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase[J]. J Biolog Chem, 1998, 273(29): 18623-32. |
| 2 | Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, et al. Wilson's disease[J]. Lancet, 2007, 369(9559): 397-408. |
| 3 | Sandahl TD, Laursen TL, Munk DE, et al. The prevalence of Wilson's disease: an update[J]. Hepatology, 2020, 71(2): 722-32. |
| 4 | Litwin T, Bembenek J, Antos A, et al. The maternal and fetal outcomes of pregnancy in Wilson's disease: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(9): 2072. |
| 5 | Pfeiffenberger J, Beinhardt S, Gotthardt DN, et al. Pregnancy in Wilson's disease: management and outcome[J]. Hepatology, 2018, 67(4): 1261-9. |
| 6 | Tarnacka B, Rodo M, Cichy S, et al. Procreation ability in Wilson's disease[J]. Acta Neurol Scand, 2000, 101(6): 395-8. |
| 7 | Zhang H, Zhang WW, Mo CY, et al. Production of functional sperm from in vitro-cultured premeiotic spermatogonia in a marine fish[J]. Zool Res, 2022, 43(4): 537-51. |
| 8 | 韩 辉, 郑明翠, 吴丽敏, 等. 补肾化痰祛瘀法治疗肝豆状核变性少弱精子症临床研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2018, 29(10): 2421-3. |
| 9 | Herman S, Lipiński P, Ogórek M, et al. Molecular regulation of copper homeostasis in the male gonad during the process of spermatogenesis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(23): 9053. |
| 10 | Chen HL, Wang YY, Luo J, et al. Autophagy and apoptosis mediated nano-copper-induced testicular damage[J]. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf, 2022, 229: 113039. |
| 11 | Guo HR, Ouyang YJ, Yin H, et al. Induction of autophagy via the ROS-dependent AMPK-mTOR pathway protects copper-induced spermatogenesis disorder[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 49: 102227. |
| 12 | Litwin T, Dušek P, Członkowska A. Symptomatic treatment of neurologic symptoms in Wilson disease[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2017, 142: 211-23. |
| 13 | Lee EJ, Woo MH, Moon JS, et al. Efficacy and safety of D-penicillamine, trientine, and zinc in pediatric Wilson disease patients[J]. Orphanet J Rare Dis, 2024, 19(1): 261. |
| 14 | Weiss KH, Stremmel W. Clinical considerations for an effective medical therapy in Wilson's disease[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2014, 1315: 81-5. |
| 15 | European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson's disease[J]. J Hepatol, 2012, 56(3): 671-85. |
| 16 | 韩 辉, 杨文明, 张 娟, 等. 肝豆状核变性的中医证候特征[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2014, 26(1): 16-9. |
| 17 | Dong T, Wu MC, Tang LL, et al. GanDouLing promotes proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells in the mouse model of Wilson's disease[J]. Biosci Rep, 2021, 41(1): BSR20202717. |
| 18 | 何望生, 杨文明, 汪 瀚, 等. 肝豆灵汤改善痰瘀互结型Wilson病患者肝脏功能的临床观察[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2020, 26(8): 105-11. |
| 19 | Cheng CL, Wang Q, Huang YR, et al. Gandouling inhibits hepatic fibrosis in Wilson's disease through Wnt-1/β‑catenin signaling pathway[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 311: 116445. |
| 20 | 奚亚明, 韩 辉, 吴丽敏, 等. 男性肝豆状核变性合并生殖功能损害的中医证候特征[J]. 中医药通报, 2018, 17(5): 56-8. |
| 21 | 陈秋莹. 补肾化痰祛瘀方对女性Wilson病合并生殖系统损害患者的临床观察及对雌性TX小鼠下丘脑-垂体-卵巢轴的作用研究[D]. 安徽中医药大学, 2023. |
| 22 | 王婷婷. 补肾化痰祛瘀方对男性Wilson病伴生殖系统损害的临床观察及对下丘脑-垂体-睾丸轴的实验研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽中医药大学, 2022. |
| 23 | 奚亚明. 男性肝豆状核变性合并生殖损害的中医证候特征及中医药治疗临床研究[D]. 安徽中医药大学, 2020. |
| 24 | 王路瑶, 韩 辉, 赵 丹, 等. 韩辉运用肝豆补肾汤辨治男性肝豆状核变性合并生殖系统损害经验[J]. 中医药通报, 2024, 23(2): 16-9. |
| 25 | 赵 丹, 韩 辉, 房新如, 等. 肝豆补肾汤治疗男性肝豆状核变性合并生殖损害的理想点法综合疗效评价研究[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2024, 36(4): 720-6. |
| 26 | Chen J, Aguilera G. Vasopressin protects hippocampal neurones in culture against nutrient deprivation or glutamate-induced apoptosis[J]. J Neuroendocrinol, 2010, 22(10): 1072-81. |
| 27 | Pan HC, Jiang Q, Yu Y, et al. Quercetin promotes cell apoptosis and inhibits the expression of MMP-9 and fibronectin via the AKT and ERK signalling pathways in human glioma cells[J]. Neurochem Int, 2015, 80: 60-71. |
| 28 | Chen ZH, Liu MJ, Hu JH, et al. Substance P restores spermatogenesis in busulfan-treated mice: a new strategy for male infertility therapy[J]. Biomedecine Pharmacother, 2021, 133: 110868. |
| 29 | Xu BF, Washington AM, Hinton BT. PTEN signaling through RAF1 proto-oncogene serine/threonine kinase (RAF1)/ERK in the epididymis is essential for male fertility[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2014, 111(52): 18643-8. |
| 30 | Zhang ZW, Zhi-GangTan, Qiao N, et al. Copper-induced spermatozoa head malformation is related to oxidative damage to testes in CD-1 mice[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2016, 173(2): 427-32. |
| 31 | Wang TT, Wu LM, Chen QY, et al. Copper deposition in Wilson's disease causes male fertility decline by impairing reproductive hormone release through inducing apoptosis and inhibiting ERK signal in hypothalamic-pituitary of mice[J]. Front Endocrinol, 2022, 13: 961748. |
| 32 | Klee JG. Undiagnosed Wilson's disease as cause of unexplained miscarriage[J]. Lancet, 1979, 2(8139): 423. |
| 33 | 奚亚明, 韩 辉. 男性肝豆状核变性生殖激素水平临床观察[J]. 中医药临床杂志, 2019, 31(2): 208-10. |
| 34 | Aydemir B, Kiziler AR, Onaran I, et al. Impact of Cu and Fe concentrations on oxidative damage in male infertility[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res, 2006, 112(3): 193-203. |
| 35 | Sharma P, Kaushal N, Saleth LR, et al. Oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and autophagy: balancing the contrary forces in spermatogenesis[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis, 2023, 1869(6): 166742. |
| 36 | Almog T, Lazar S, Reiss N, et al. Identification of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 and p38 MAPK as regulators of human sperm motility and acrosome reaction and as predictors of poor spermatozoan quality[J]. J Biol Chem, 2008, 283(21): 14479-89. |
| 37 | Brown JL, Xie JJ, Brieño-Enriquez MA, et al. Sex- and age-specific impact of ERK loss within the pituitary gonadotrope in mice[J]. Endocrinology, 2018, 159(3): 1264-76. |
| 38 | Xu A, Li X, Li K, et al. Linoleic acid promotes testosterone production by activating Leydig cell GPR120/ERK pathway and restores BPA-impaired testicular toxicity[J]. Steroids, 2020, 163: 108677. |
| 39 | Wu PK, Becker A, Park JI. Growth inhibitory signaling of the raf/MEK/ERK pathway[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2020, 21(15): 5436. |
| 40 | Suzuki C, Tanigawa M, Tanaka H, et al. Effect of D-serine on spermatogenesis and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase (ERK) phosphorylation in the testis of the silkworm, Bombyx mori [J]. J Insect Physiol, 2014, 67: 97-104. |
| 41 | Sun PB, Wang YY, Gao T, et al. Hsp90 modulates human sperm capacitation via the Erk1/2 and p38 MAPK signaling pathways[J]. Reprod Biol Endocrinol, 2021, 19(1): 39. |
| 42 | Grimaldi P, Orlando P, Di Siena S, et al. The endocannabinoid system and pivotal role of the CB2 receptor in mouse spermatogenesis[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2009, 106(27): 11131-6. |
| 43 | Zhang CH, Wang Y, Sun QQ, et al. Copper nanoparticles show obvious in vitro and in vivo reproductive toxicity via ERK mediated signaling pathway in female mice[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2018, 14(13): 1834-44. |
| 44 | Yang Y, Zhang XJ, Cui HY, et al. Apelin-13 protects the brain against ischemia/reperfusion injury through activating PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways[J]. Neurosci Lett, 2014, 568: 44-9. |
| 45 | 徐乐文, 董健健, 高曼莉, 等. 肝豆汤联合青霉胺对Wilson病模型肝脏铜死亡抑制作用[J]. 中国中西医结合杂志, 2024, 44(3): 331-8. |
| [1] | 张笑颜, 王 谢, 王 杰, 邵 楠, 蔡 标, 谢道俊. 黄蒲通窍胶囊改善Wilson病铜负荷大鼠的认知损害:基于抑制内质网应激介导的凋亡途径[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(3): 447-454. |
| [2] | 赵晨玲, 董 婷, 孙伦燕, 胡慧冰, 王 琼, 田丽伟, 江张胜. Wilson病脂代谢异常患者发生肝纤维化的列线图预测模型的建立与验证[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1720-1725. |
| [3] | 陈文邦, 朱 潇, 周 少, 杏福宝, 唐 震, 李小军, 张 雷. 敲低galectin-1可抑制肺腺癌细胞的增殖、迁移和侵袭并促进其凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1628-1637. |
| [4] | 袁巍巍, 孙 辉, 于 丽, 王京波. 莪术醇通过蛋白激酶信号通路抑制瘢痕疙瘩成纤维细胞的增殖和胶原合成[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(5): 687-693. |
| [5] | 张梦颖, 杨玉有, 刘 敏, 梁 利, 罗 瑞, 尹丹旸, 郭风劲. 雌二醇通过ERβ调控ERK磷酸化影响细胞增殖和凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(3): 336-343. |
| [6] | 刘敏,谢巍伟,郑维,尹丹旸,罗瑞,郭风劲. 雌二醇与ESR1靶向结合通过ERK信号通路调控软骨细胞的增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(02): 134-. |
| [7] | 殷亮,王荩,黄凤昌,张云飞,许宁,文政琦,李文亮,董坚. 甲磺酸阿帕替尼对结肠癌HCT-116 细胞增殖的抑制作用及其机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(03): 367-. |
| [8] | 杨梦月,熊紫薇,李维娜,贾苗苗,刘刚. 小鼠DNAJB13与HK1 的相互作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(12): 1684-. |
| [9] | 朱莉,刘刚. 小鼠生精相关基因pQE/Dnajb13重组载体的构建和蛋白表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(12): 1757-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||