2. 宁夏医科大学总医院 临床医学院医学检验系,宁夏 银川 750004
2. Department of Medical Laboratory, College of Clinical Medicine, Ningxia Medical University, Yinchuan 750004, China
肝癌是严重危害我国人民生命健康的疾病,根据全球癌症数据统计,一年有782 500肝癌新发病例,745 500肝癌死亡病例,我国肝癌新发病例及死亡总数占据其中50%[1]。虽然有手术、化疗、肝移植等治疗措施,由于早期诊断的困难,进展迅速和缺乏靶向药物,肝癌的存活率极低[2]。因此,深入研究肝癌转移机制并寻找新的治疗方法尤为重要。整合素作为跨膜蛋白[3],其介导细胞附着于细胞外基质,并且对于细胞信号传导至关重要,参与调节细胞增殖,迁移,分化和存活[4]。近年来,有关整合素与肿瘤侵袭转移的研究越来越多[5-8],但其在肝癌转移中的研究鲜见报道[9]。我们前期在肝癌组织中的研究发现,整合素α5(ITGA5)不仅在肝癌组织中表达增高,且与肝癌的TNM分期和肿瘤转移有关[10]。基于前期研究结果,本项目进一步分析ITGA5与肝癌分级及肝癌患者总体生存率的关系,并利用慢病毒载体研究ITGA5基因沉默后对肝癌细胞增殖、侵袭转移的影响,以及探讨ITGA5在肝癌转移过程中可能存在的分子机制。
1 材料和方法 1.1 细胞与主要试剂人肝癌Bel-7404细胞株(ATCC)。胎牛血清(微科生化);DMEM(Hyclone);兔抗人单克隆抗体TGA5、鼠抗人单克隆抗体(GAPDH)(Abcam);逆转录cDNA合成试剂盒、荧光RT-PCR试剂盒、ECL发光试剂盒(Thermo);50bp DNA Ladder Marker(康为世纪);BD脱脂奶粉(BD);PVDF膜(amresco);蛋白上样缓冲液(SDS-PAGE)(康为世纪);SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒、Matrigel基质胶、puromycin(sigma);结晶紫染色液(索莱宝);Transwell小室(Millipore)。
1.2 主要方法 1.2.1通过UALCAN(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/)在线分析工具[11]分析ITGA5在肝癌和正常组织中的表达情况,并比较肝癌的不同分级之间ITGA5的表达差异。
1.2.2通过GEPIA(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn/)在线分析工具[12]分析ITGA5表达量与肝癌患者生存情况的关系。
1.2.3 细胞系培养采用DMEM培养基加10%胎牛血清、1%青霉素、1%链霉素培养液进行培养ITGA5稳定沉默人肝癌Bel-7404细胞系,培养条件37 ℃、5% CO2。
1.2.4 免疫印记实验培养稳定沉默组及对照组细胞使其对数生长,弃培养基,使用凯基全蛋白提取试剂盒提取总蛋白,BCA法检测其浓度。配制10%聚丙烯酰胺凝胶,取等质量蛋白上样,100 V恒压电泳,300 mA恒流转膜2 h。5%脱脂奶粉室温下封闭1 h,一抗(浓度1:3000)4 ℃过夜。二抗(浓度1:5000)在室温下孵育1 h,PBST洗膜10min × 3次。ECL显影剂曝光,使用Gel- Pro analyzer软件分析蛋白质条带的灰度值。
1.2.5 平板克隆形成实验培养细胞使其呈对数生长,弃培养基,消化,1000 r/min,离心5 min,显微镜下细胞计数,将细胞悬液作梯度倍数稀释。取300、500、700、1000细胞分别接种于细胞培养皿,使细胞分散均匀。37 ℃、5% CO2条件培养2~3周。当培养皿中出现肉眼可见的克隆时,终止培养。弃培养液,4%多聚甲醛固定、甲醇通透、0.1%结晶紫染色、洗涤,自然风干。倒置显微镜下观察克隆并拍照;使用ImageJ软件对各组细胞形成的克隆进行计数。
1.2.6 Transwell侵袭、迁移实验提前将Matrigel基质胶置于4 ℃冰箱中使其融化。将Matrigel基质胶按1:8比例稀释至1 mg/mL,取60 μL铺入Transwell上室。将对数生长期的细胞用胰酶消化,计数,取2×105细胞接种至上室。下室中加入600 μL含30%胎牛血清的培养基。培养48 h后,弃培养液,PBS洗涤,4%多聚甲醛固定,甲醇通透,0.1%结晶紫染色,洗涤。用棉签轻轻擦去小室上层未迁移的细胞,空中气干燥。显微镜下随机选取3个视野观察,拍照;使用ImageJ软件对侵袭转移的细胞进行计数。迁移实验:上室内不铺基质胶,24 h终止实验,其余操作及计数方法同上。
1.2.7 通过Oncomine癌标本数据库[13](https://www.oncomine.org/)分析225例肝癌组织、220例肝组织中ITGA5和PI3K的表达差异。
1.2.8 统计学方法采用SPSS 21.0统计软件进行分析。计量资料以均数±标准差表示。各组之间蛋白质的比较均采用两个独立样本t检验。平板克隆形成实验、细胞侵袭、迁移实验结果的总体均数比较采用单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA)。各组间两两比较采用多重比较的最小显著法(LSD-t)检验。相关性采用Spearman相关性分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 UALCAN分析ITGA5在肝癌中的表达ITGA5在肝癌中的表达显著高于正常组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05,图 1A);而在不同肝癌分级中,Grade 1的ITGA5表达量显著低于Grade 2,且Grade 2的ITGA5表达量显著低于Grade 3,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05,图 1B)。
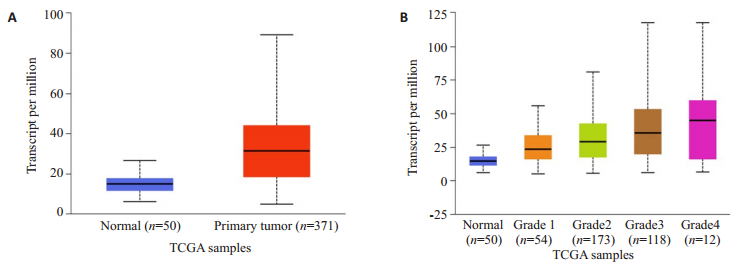
|
图 1 ITGA5在肝癌中的表达情况(UALCAN) Fig.1 ITGA5 expression in liver cancer (UALCAN). A: Expression of ITGA5 in LIHC based on ample types; B Expression of ITGA5 in LIHC based on tumor grade |
ITGA5高表达组的总体生存率(OS)显著低于低表达组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05,图 2)。
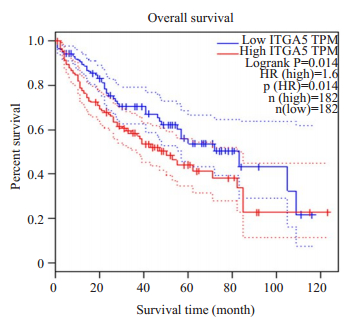
|
图 2 ITGA5的表达与肝癌患者生存情况的关系 Fig.2 Relationship between ITGA5 expression and overall survival of patients with liver cancer (GEPIA) |
ITGA5基因稳定沉默组ITGA5蛋白质表达较空白、阴性对照组明显降低,结果均具有显著性差异(P < 0.05,图 3)。未处理组与阴性对照组的ITGA5蛋白表达无显著性差异(P=0.28)。
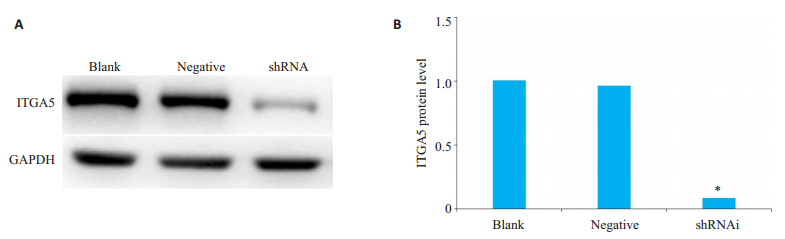
|
图 3 Western blot检测ITGA5蛋白在各组Bel-7404细胞中的表达 Fig.3 ITGA5 protein expression in Bel-7404 cells of each group. A: Protein band; B: Histogram of protein quantification (*P < 0.05 vs negative and Blank) |
平板克隆形成实验结果显示,相比较空白对照组,ITGA5稳定沉默组细胞的克隆形成率明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。而空白对照组和阴性对照组之间的克隆形成率无明显变化(图 4)。
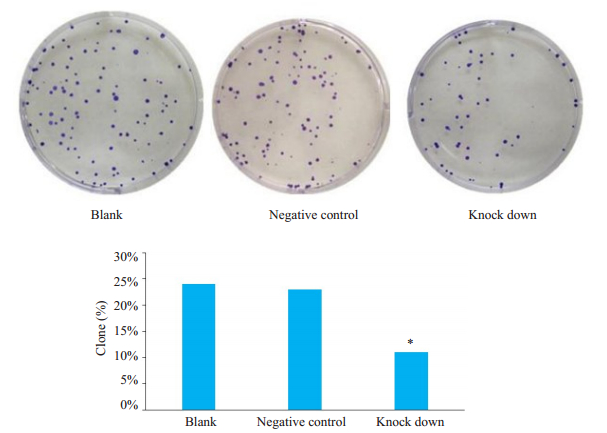
|
图 4 ITGA5对Bel-7404细胞克隆形成的影响 Fig.4 Effect of ITGA5 on the cloning of Bel-7404 cells. A: Figure of clones; B: Histogram of clone formation rate (*P < 0.05 vs Blank and Negative control) |
Transwell侵袭实验检测ITGA5基因沉默后细胞穿膜数目的变化。结果表明ITGA5基因沉默组穿膜细胞数比空白对照及阴性对照组明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。而空白、阴性对照组之间细胞的穿膜数目无明显差异(图 5)。
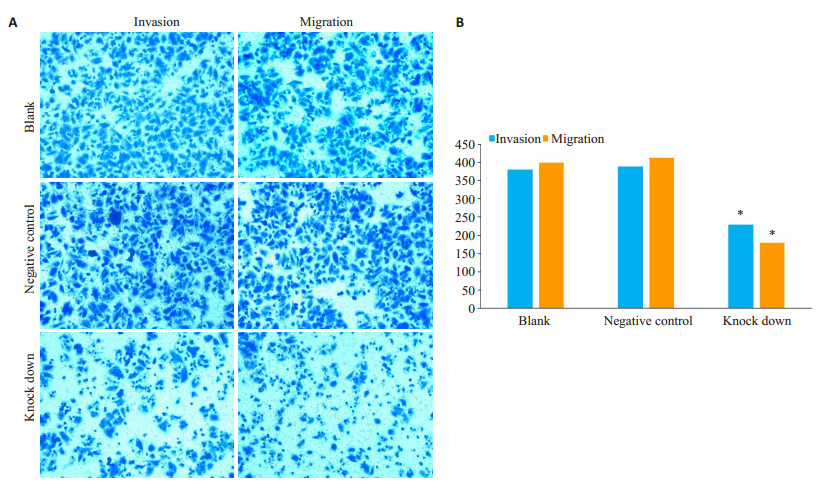
|
图 5 ITGA5对Bel-7404细胞侵袭迁移能力的影响 Fig.5 The effect of ITGA5 on the invasion and migration of Bel-7404 cells. A: Figure of invasion and migration; B: Histogram of invasion and migration of transmembrane cells (*P < 0.05 vs blank and negative control) |
通过Oncomine癌标本数据库对225例肝癌组织、220例肝组织分析发现,相对正常肝组织,ITGA5和PI3K在肝癌组织中高表达,差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)(图 6);分析二者之间相关性结果呈高度正相关(Spearman相关分析:r=1,P < 0.0001)。
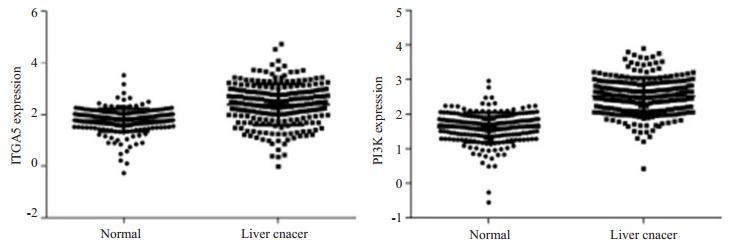
|
图 6 ITGA5与PI3K在肝癌中的表达(Oncomine) Fig.6 Expression of ITGA5 and PI3K in liver cancer (Oncomine). Normal; liver cancer |
整合素是细胞表面粘附分子,其亚基或者二聚体可以调节细胞粘附,细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭迁移和运动等不同生物学功能[14-15],如整合素α5亚基与β1亚基形成二聚体,通过改变二者之间的空间构象影响其与纤连蛋白的粘附能力,进而影响生物学功能[16-17]。近年来,粘附蛋白ITGA5在肿瘤转移中的研究越来越多。我们前期在肝癌中研究发现,ITGA5蛋白及mRNA在肝癌组织中的表达显著高于癌旁组织。分析显示ITGA5的表达与肝癌的TNM分期及肿瘤转移有关[10]。本研究利用UALCAN分析发现ITGA5不仅在肝癌中的表达显著高于正常组而且在不同分级的肝癌组织中表达不同,Grade 1的ITGA5表达量显著低于Grade 2,且Grade 2的ITGA5表达量显著低于Grade 3,分级越高的肝癌组织中ITGA5的表达越高。此外,还利用GEPIA在线分析研究显示ITGA5高表达组的总体生存率(OS)显著低于低表达组。同样在zhang的研究中提示ITGA5在肝癌中表达增高且与肝癌患者预后差相关[18]。最早及最新的研究同样发现ITGA5不仅在肝癌中表达升高,还在乳腺癌、胃癌、结肠癌等恶性肿瘤组织中高表达,且与肿瘤患者预后及生存有关[19-21]。基于以上研究发现,ITGA5与肿瘤的进展及预后密切相关,因此,深入探讨ITGA5在肝癌增殖及侵袭转移中的作用,对肝癌患者临床病情评估及靶向药物的开发等具有重要意义。
为了进一步研究ITGA5对肝癌细胞生物学功能影响,本研究利用前期已构建的ITGA5基因沉默的肝癌细胞模型[22],采用Western blot实验验证ITGA5蛋白低表达。进一步鉴定ITGA5在肝癌细胞中表达下调后其增殖、侵袭迁移能力变化。为研究细胞的体外侵袭能力,运用Matrigel基质胶作为基底膜铺于Transwell上室内,研究发现ITGA5基因沉默组细胞的穿膜能力较对照组下降。同样,在无基质胶的上室膜上,ITGA5基因沉默组穿膜细胞数较对照组明显下降。由此可知,ITGA5表达下降后肝癌细胞Bel-7404侵袭与迁移能力均减弱。此外,本研究利用克隆形成实验研究发现,同等条件下生长的细胞,ITGA5沉默组肝癌细胞比对照组细胞的克隆形成能力明显降低。以上在肝癌细胞中的研究与一些学者在其它肿瘤中的研究相似,如敲低或靶向抑制ITGA5后,食管癌细胞、肾癌细胞、卵巢癌细胞的粘附、侵袭和增殖能力减弱[23-25]。综上所述,结合肝癌组织及细胞研结果究表明,ITGA5是促进肝癌增殖、侵袭转移的重要分子,可作为肝癌转移的重要标志物及治疗靶分子进行深入研究,其具体的分子作用机制还需进一步阐明。
关于整合素参与肿瘤转移的分子机制研究并不多[26-29],近年来,一些相关研究提出,整合素和ECM配体以高亲和力结合后触发信号使其由细胞外基质向细胞内传导[30],以磷酸化的方式激活下游如磷酸肌醇激酶(PI3K)等信号分子,从而影响细胞粘附、转移及存活[21, 31]。本研究通过Oncomine癌标本数据库对225例肝癌组织、220例肝组织分析发现,相对正常肝组织,ITGA5和PI3K在肝癌组织中高表达,且二者之间呈高度正相关。关于ITGA5和PI3K的表达相关性在另一研究中也得到了验证,将ITGA5在基因及蛋白水平过表达或抑制后p-PI3K/PI3K、p-Akt/Akt及其下游蛋白表达水平相应表现为上调或抑制[32]。基于以上研究,可初步推测PI3K是ITGA5下游的潜在靶点,ITGA5通过调控PI3K通路影响肝癌细胞增殖及转移。本研究只是初步探讨了ITGA5调控肝癌转移的分子机制,仍需在肝癌组织中进一步验证、细胞水平及体内实验中动态研究分析ITGA5与PI3K及下游信号分子的表达相关性。从而揭示ITGA5促进肝癌转移分子机制,为肝癌转移治疗提供理论基础及治疗新思路。
总之,ITGA5与肝癌进展及预后有着紧密联系。下调ITGA5可抑制肝癌细胞增殖及侵袭转移能力,提示ITGA5可能促进肝癌生长及转移。因此,深入探讨ITGA5与肝癌发生及进展的作用及其分子机制,将为开发新的肝癌预后靶标提供研究基础,对肝癌患者临床病情评估及靶向药物的开发等具有重要意义。
| [1] |
Lindsey A, Freddie B, Rebecca L, et al. Global Cancer Statistics, 2012[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2015, 65: 87-108. |
| [2] |
Fu J, Wang H. Precision diagnosis and treatment of liver cancer in China[J]. Cancer Lett, 2018, 412: 283-8. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2017.10.008 |
| [3] |
Malgorzata B, Sergio C, Donald G. Integrins[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2010, 11, 339(1): 269-80.
|
| [4] |
Zheng Y, Leftheris K. Insights into Protein-ligand Interactions in Integrin Complexes: Advances in Structure Determinations[J]. J Med Chem, 2020, 2(30): 1010-10. |
| [5] |
Nithikoon A, Pithi C. Integrin as a Molecular Target for Anti-cancer Approaches in Lung Cancer[J]. Anticancer Res, 2019, 39(2): 541-8. DOI:10.21873/anticanres.13146 |
| [6] |
Jian JX, Jin CG, Zhi YW. Integrin α5 promotes tumor progression and is an independent unfavorable prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J]. Human Pathology, 2016, 48: 69-75. DOI:10.1016/j.humpath.2015.09.029 |
| [7] |
Kirat KG, Sekhar P, Shuvojit M. Integrins and Metastasis[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2013, 7(3): 251-61. DOI:10.4161/cam.23840 |
| [8] |
Laetitia S, Jay D, Sara W. Integrins and Cancer: Regulators of Cancer Stemness, Metastasis, and Drug Resistance[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2015, 25(4): 234-40. DOI:10.1016/j.tcb.2014.12.006 |
| [9] |
Shihong S, Yun Z, Ting M, et al. Targeting High Expressed α 5 β 1 Integrin in Liver Metastatic Lesions To Resist Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer by RPM Peptide-Modified Chitosan-Stearic Micelles[J]. Mol Pharm, 2018, 2, 15(4): 1653-63.
|
| [10] |
何彩霞, 王亚婷, 李鹏, 等. 整合素α5和含半胱氨酸的天冬氨酸蛋白水解酶3在肝细胞癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华消化杂志, 2017, 37(1): 45-8. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-1432.2017.01.013 |
| [11] |
Darshan S, Chandrashekar, Bhuwan B, et al. UALCAN: A Portal for Facilitating Tumor Subgroup Gene Expression and Survival Analyses[J]. Neoplasia, 2017, 8, 19(8): 649-58.
|
| [12] |
Zefang T, Chenwei L, Boxi K, et al. GEPIA: A Web Server for Cancer and Normal Gene Expression Profiling and Interactive Analyses. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 3, 45(W1): W98-W102.
|
| [13] |
Daniel R R, Jianjun Y, Shanker K, et al. ONCOMINE: A Cancer Microarray Database and Integrated Data-Mining Platform[J]. Neoplasia, 2004, 1, 6(1): 1-6.
|
| [14] |
Avander F, Sonnenberg A. Function and Interactions of Integrins[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2001, 305(3): 285-98. DOI:10.1007/s004410100417 |
| [15] |
Zhao HL, You Z, You XD, et al. Roles of Integrin in Tumor Development and the Target Inhibitors[J]. Chin J Nat Med, 2019, 17(4): 241-51. |
| [16] |
Yang S, Wei X, Jing L, et al. Relating Conformation to Function in Integrin α5β1[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2016, 113(27): E3872-81. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1605074113 |
| [17] |
Iain DC, Martin JH. Integrin Structure, Activation, and Interactions [J]. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 2011, 1, 3(3): a004994.
|
| [18] |
Zhang X, Cheng SL, Bian K, et al. MicroRNA-26a promotesanoikis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting alpha5 integrin[J]. Oncotarget, 2015, 6: 2277-89. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.2956 |
| [19] |
Julia AJ, Inês G, Chae Y, el at. Hypoxia Selectively Enhances Integrin α 5 β 1 Receptor Expression in Breast Cancer to Promote Metastasis[J]. Mol Cancer Res, 2017, 15(6): 723-34. DOI:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-16-0338 |
| [20] |
Xue-Bin Zhang, Lei Song, Hong-Juan Wen, et al. Upregulation of microRNA-31 Targeting Integrin α5 Suppresses Tumor Cell Invasion and Metastasis by Indirectly Regulating PI3K/AKT Pathway in Human Gastric Cancer SGC7901 Cells[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(6): 8317-25. DOI:10.1007/s13277-015-4511-y |
| [21] |
Ling L, Ruting X, Rong W, Chunmiao C. Integrin α5 subunit is required for the tumor supportive role of fibroblasts in colorectal adenocarcinoma and serves as a potential stroma prognostic marker[J]. Molecular Oncology, 2019, 3: 1-28. |
| [22] |
郭亚妹, 孙昊, 何彩霞, 等. ITGA5慢病毒shRNA表达载体及Bel- 7404稳定细胞系的构建[J]. 宁夏医科大学学报, 2018, 3(1): 2-8. |
| [23] |
Sicong H, Weiguo J, Weiming X. Integrin α5 promotes migration and cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(12): 2774-88. |
| [24] |
Breuksch I, Prosinger F, Baehr F. Integrin α5 triggers the metastatic potential in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(64): 107530-42. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.22501 |
| [25] |
Ohyagi HC, Sawada K, Kamiura S, et al. miR-92a Inhibits Peritoneal Dissemination of Ovarian Cancer Cells by Inhibiting Integrin a5 Expression[J]. Am J Pathol, 2013, 182(5): 1876-89. DOI:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.01.039 |
| [26] |
Qin L, Chen X, Wu Y, et al. Steroid receptor coactivator-1 upregulates integrin alpha(5)expression to promote breast cancer cell adhesion and migration[J]. Cancer Res, 2011, 71: 1742-51. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3453 |
| [27] |
Huang C, Verhulst S, Shen Y, et al. AKR1B10promotes breast cancer metastasis through integrin alpha5/delta-catenin mediated FAK/Src/ Rac1 signaling pathway[J]. Oncotarget, 2016, 7: 43779-91. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.9672 |
| [28] |
Chen Q, Kinch MS, Lin TH, et al. Integrin-mediated cell adhesion activates mitogen-activated protein kinases[J]. Biol Chem, 1994, 269: 26602-5. |
| [29] |
Khwaja A, Rodriguez VP, Wennstrom S, et al. Matrix adhesion and Ras transformation both activate a phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and protein kinase B/Akt cellular survival pathway[J]. EMBO J, 1997, 16: 2783-93. DOI:10.1093/emboj/16.10.2783 |
| [30] |
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E. Integrin Signaling. Science[J]. 1999, 13, 285(5430): 1028-32.
|
| [31] |
Qing CF, Hua T, Yan W, el at. Integrin-α5 Promoted the Progression of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Modulated PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway[J]. Arch Oral Biol, 2019, 101: 85-91. DOI:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.03.007 |
| [32] |
Zhang CZ, Wang XD, Wang HW, et al. Sorafenib inhibits liver cancer growth by decreasing mTOR, AKT, and PI3K expression[J]. J BUON, 2015, 20(1): 218-22. |
 2020, Vol. 40
2020, Vol. 40

