2. 潍坊医学院 护理学院, 山东 潍坊 261053;
3. 潍坊医学院 临床医学院, 山东 潍坊 261053;
4. 潍坊医学院 医学研究实验中心, 山东 潍坊 261053
2. College of Nursing, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China;
3. Clinical Medical College, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China;
4. Medicine Research Center, Weifang Medical University, Weifang 261053, China
乳腺癌是一种起源于乳腺组织的恶性肿瘤,是全世界妇女因癌症死亡的最常见原因[1]。侵袭转移是肿瘤细胞重要的生物学行为,与预后不良密切相关,严重威胁着转移患者的健康和生命[2]。因此,深入分析乳腺癌转移机制对改善乳腺癌患者的生存率和预后具有重要意义。
我们对基因如何驱动相应蛋白质改变从而影响表型改变的认识仍有欠缺,因此研究肿瘤组织与正常组织的差异基因从而指导我们更全面的认识肿瘤的发病机制具有重要意义。功能基因组学的进展表明,人类基因组是主动转录的。然而,绝大多数转录本是非编码RNA包括microRNAs(miRNAs)和长链非编码RNA(LncRNA)。MiRNA是一类内源性、进化保守的小非编码RNA分子,可调节靶基因的转录后处理,导致靶mRNA的降解及其翻译抑制[3]。多项研究表明[4-5],miRNA参与细胞上皮间质转化等多种细胞和生理过程,且其异常表达与多种人类肿瘤的进展和转移有关。miRNA发挥作用主要通过与目标mRNA的3'-UTR区结合,导致目标mRNA的降解,从而调控靶蛋白的表达,从而影响人肿瘤的进展。另外,多项研究表明[6-8],与正常组织相比,miR-204在多种人类肿瘤组织中下调,并被认为在多种类型的癌症中具有抑癌作用。核内不均一核糖核蛋白(hnRNPs)参与了包括增殖和凋亡在内的关键肿瘤进展过程,HNRNPA2和HNRNPB1是由HNRNPA2B1基因翻译而来的两个亚型[9],有研究证明HNRNPA2B1在肿瘤发生过程中参与多种重要基因的表达,HNRNPA2B1通过激活Lin28B表达促进卵巢癌的恶性表型并增强其稳定性[10]。
miR-204在乳腺癌中的具体作用仍有待研究,因此,本研究将探讨miR-204是否可以通过靶向调控HNRNPA2B1影响乳腺癌的侵袭和转移,为抑制乳腺癌细胞转移和治疗乳腺癌提供新的靶点。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料与仪器MCF-10A,MDA-MB-231,293T细胞(ATCC),胎牛血清和RPMI 1640培养基(HyClone)。MiRNA上下游引物由生工生物工程有限公司设计合成。8-μm孔径Transwell小室(BD Biosciences)。Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen)。包含HNRNPA2B1 3'-UTR序列的荧光素酶报告基因质粒和含有HNRNPA2B1 3'-UTR突变序列的荧光素酶报告基因质粒均由吉凯公司构建并鉴定。HNRNPA2B1抗体为Rabbit Anti- HNRNPA2B1 antibody(ab31645),β-actin抗体为Rabbit Anti-beta Actin antibody(ab8227),抗体均购自Abcam公司。
1.2 生物信息学数据库GEO数据库:从基因表达谱GEO数据库(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov)中下载两组乳腺癌患者资料。GSE44124数据集为50例乳腺肿瘤组织与30个正常组织miRNA表达谱。GSE38167数据集为31例原发性三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)患者组织(IDC),13例淋巴结转移(LN)患者组织,23例正常乳腺组织(NAT)的miRNA表达谱。Kaplan- Meier Plotter(Kmplot)网站:Kmplot(https://kmplot.com/analysis/)网站能够评估21种癌症类型中54000基因对生存率的影响。最大的数据集包括乳腺癌(6234例)、卵巢癌(2190例)、肺癌(3452例)和胃癌(1440例)。miRNA子系统包括20种不同癌症类型的11 000样本。该系统包括基因芯片和RNA-seq数据源,数据库包括GEO、EGA和TCGA数据库[11]。
1.3 细胞培养与分组细胞培养参考本课题先前已发表文献[12],将MDA-MB-231细胞分组:(1)con组,转入空载慢病毒;(2)miR-204组,转入miR-204过表达慢病毒;(3)miR- 204 + NC组,同时转入miR-204过表达慢病毒和HNRNPA2B1过表达对照质粒;(4)miR-204 + HNRNPA2B1组,同时转入miR-204过表达慢病毒和HNRNPA2B1过表达质粒。
1.4 RT-qPCR实验RNA提取及逆转录过程参考本课题先前已发表文献[13]。PCR条件为95 ℃ 5 s、63 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s进行35个循环。以U6作为内参。MiR-204-5p的上游引物为CGCGTTCCCTTTGTCATCCT,下游引物为AGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATT,茎环结构GTCGTATCCAGTGCAGGGTCCGAGGTATTCGCACTGGATACGACAGGCAT。
1.5 Transwell实验Transwell实验是在Transwell小室中进行的,如文献[3]所述。迁移实验:取对数生长期的MDA-MB-231细胞(2×105)悬浮于200 μL无血清的RPMI 1640培养基中,将细胞悬浮液加至无基质胶Transwell上室中,下室为500 μL胎牛血清。侵袭实验:取对数生长期的MDA-MB-231细胞(2×105)悬浮于200 μL无血清的RPMI 1640培养基中,将细胞悬浮液加至有基质胶Transwell上室中,下室为500 μL胎牛血清。固定染色方法:将细胞培养24 h,用棉签将未通过气孔的细胞除去。用4%多聚甲醛进行细胞固定,姬姆萨(Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, USA)染色。显微镜下随机选取5个视野拍照计数,取穿至下室细胞的平均数为实验结果,实验重复3次。
1.6 双荧光素酶实验293T细胞购自ATCC,细胞培养方式按照ATCC建议。构建pGL3-HNRNPA2B1-3-UTR-MUT和pGL3- HNRNPA2B1-3-UTR-WT质粒,将293T细胞培养于24孔板中,100 ng的pGL3-HNRNPA2B1-3-UTR-MUT和pGL3-HNRNPA2B1-3-UTR-WT使用Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen,12566014)和miRNA对照及过表达载体分别共转染293T细胞。48 h后获得细胞,用双荧光素酶检测系统(Promega)测定荧光素酶活性。
1.7 Western blotWestern blot检测HNRNPA2B1水平,将转染后的细胞提取蛋白。上样,电泳,转膜,封闭,滴加一抗4 ℃过夜,滴加二抗,TBST洗PVDF膜,曝光。β-actin作为内参。
1.8 靶基因预测和Hub基因筛选利用miRTarbase(http://mirtarbase.mbc.nctu.edu. tw/php/index.php)网站、miRWalk(http://mirwalk.umm.uni-heidelberg.de/)网站、Targetscan(http://www.targetscan.org/vert_72/)网站对miR-204进行靶基因预测。利用STRING v11(https://string-db.org/)网站进行PPI分析,STRING v11可构建蛋白质-蛋白质关联网络,支持蛋白质相关信号通路的富集关系,蛋白质或者基因的分子功能,生物过程和细胞组成等的分析[14]。Starbase网站:starBase v2.0(http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn/index.php),可以从大规模CLIP-Seq数据中解码miRNA- ceRNA、miRNA-ncRNA和蛋白-RNA相互作用网络[15]。
1.9 统计学分析采用SPSS 22.0进行统计学处理,实验数据用均数±标准差表示,两组间定量资料采用独立样本t检验,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,以P < 0.05认为差异具有统计学意义。
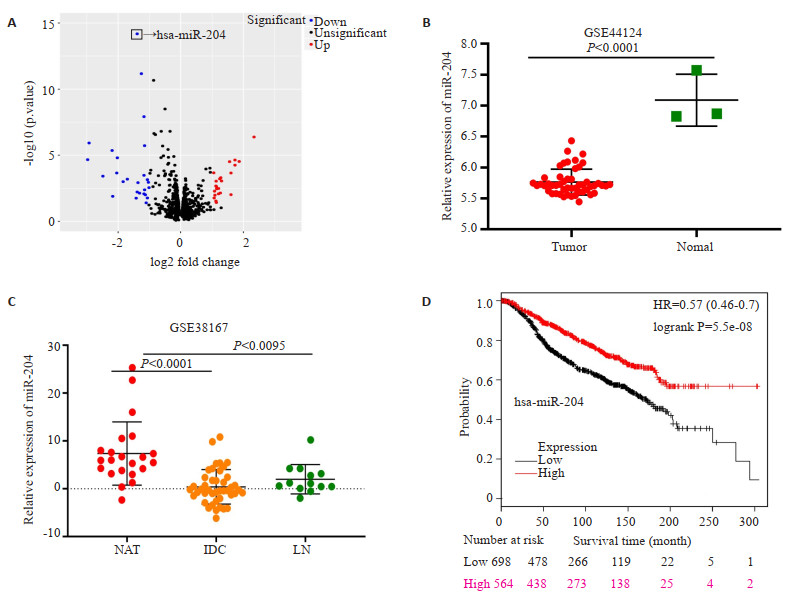
2 结果 2.1 MiR-204在乳腺癌患者组织中的表达情况通过GEO数据库发现miR-204在GSE44124和GSE38167数据集中低表达,通过GEO2R分析发现,miR-204在GSE44124数据集中的表达降低的miRNA中P值最小(图 1A),miR-204在乳腺癌患者组织中的表达较正常乳腺组织降低(图 1B),在GSE38167数据集中,miR-204在浸润性导管癌和有淋巴结转移癌症患者中miR-204的表达水平同样降低(图 1C)。Kmplot数据库对6234例乳腺癌患者的300个月的随访分析结果显示,低表达水平的miR-204与患者不良预后相关,且差异具有显著性(P < 0.05,图 1D)。
|
图 1 MiR-204在乳腺癌患者组织中的表达量和miR-204与乳腺癌患者预后的相关性 Fig.1 Expression of miR-204 in breast cancer tissues and its association with the patients' prognosis. A: Volcano plot of GSE44124 showing miRNA expression in breast cancer tissues and normal tissues; B: Expression of miR-204 in GSE44124; C: Expression of miR-204 in GSE38167 (NAT: Normal adjacent tissues, IDC: Invasive ductal carcinoma tissues, LN: Breast cancer tissue with lymph node metastasis); (D) Survival analysis of patients with different expression levels of miR-204 in breast cancer tissues. |
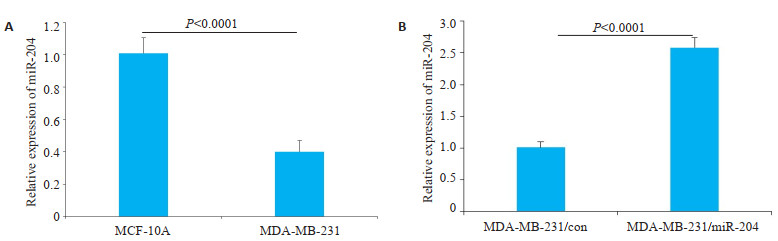
与正常乳腺细胞MCF-10A中miR-204的表达量(1.01±0.10)相比,miR-204在三阴性乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231细胞中表达量(0.40±0.07)低,且差异具有统计学意义(图 2A)。miR-204在MDA-MB-231中的转染效率,相对于MDA-MB-231/con组细胞的miR- 204的表达量(1.01±0.09),miR-204在MDA-MB-231/ miR-204组的表达量(2.58±0.16)升高(图 2B)。
|
图 2 miR-204在各组细胞中的表达量 Fig.2 Expression of miR-204 in different cells. A: The expression of miR-204 in MCF-10A and MDA-MB-231 cells; B: The transfection efficiency of miR-204 in MDA-MB-231 cells. |
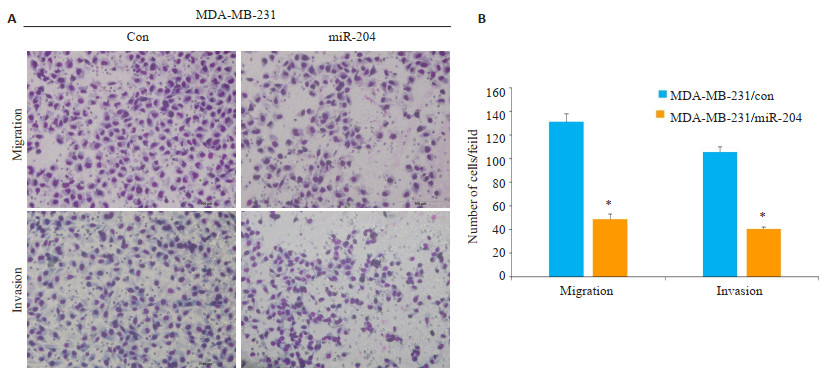
迁移实验显示,MDA-MB-231/miR-204组细胞穿至下室的数量(49.00±4.35)少于MDA-MB-231/con组细胞穿至下室的数量(131.00±7.00),过表达miR-204组侵袭能力降低(P < 0.05);侵袭实验显示,MDA-MB-231/ miR-204组细胞穿过基质胶的细胞数目(40.67±1.53)少于MDA-MB-231/con(105.67±4.04)组细胞穿过基质胶的细胞数目(P < 0.05)(图 3A、B)。
|
图 3 各组MDA-MB-231细胞的侵袭能力 Fig.3 Overexpression of miR-204 inhibits the migration and invasion of breast cancer cells (Giemsa staining, scale bar=100 μm. Mean± SD, n=3, *P < 0.05 vs MDA-MB-231/con group). |
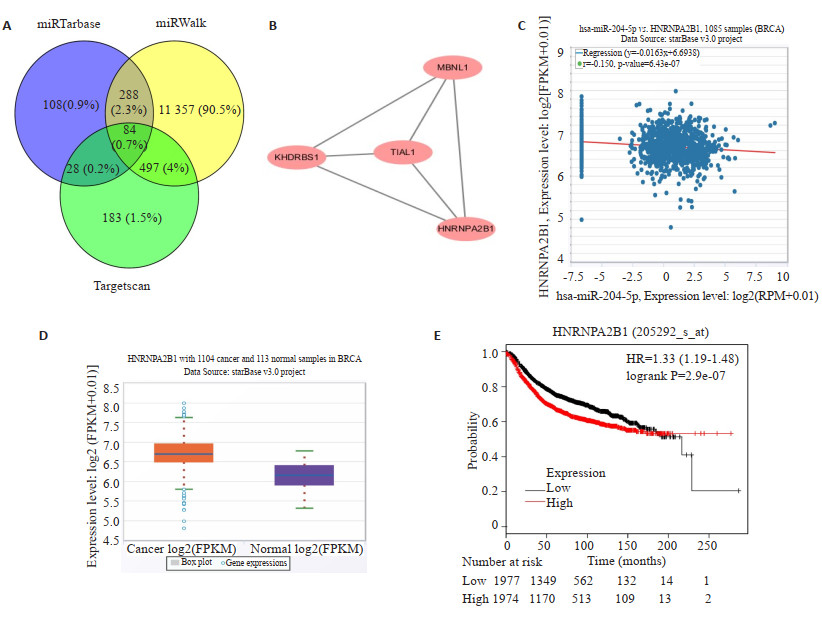
利用靶基因预测软件miRTarbase,miRWalk,TargetScan预测miR-204的靶基因,取交集得84个靶基因(图 4A)。利用此84个靶基因做PPI分析,利用Cytoscape软件的MCODE插件选取连接度超过4的靶基因MBNL1、KHDRBS1、TIAL1、HNRNPA2B1作为我们的Hub基因备选(图 4B)。Starbase网站和Kmplot数据库对HNRNPA2B1进行分析,结果显示,HNRNPA2B1在乳腺癌组织中表达和miR-204-5p的表达呈负相关,且差异具有显著性(图 4C)。与正常乳腺组织相比,HNRNPA2B1在乳腺癌中表达升高,且高表达水平的HNRNPA2B1与患者不良预后相关,且差异具有显著性(P < 0.05,图 4D、E)。
|
图 4 miR-204的Hub基因筛选 Fig.4 MBNL1, KHDRBS1, TIAL1, HNRNPA2B1 are Hub genes of miR-204. A: The venny plot of predicted genes; B: The Hub genes of targeted genes made by cytoscape; C: Co-Expression Analysis for hsa-miR-204-5p and HNRNPA2B1; D: The expression of HNRNPA2B1 in breast normal tissues and breast cancer tissues; E: The survival analysis of HNRNPA2B1 in breast cancer patients. |
HNRNPA2B1 mRNA的3'-UTR是miR-204的直接结合位点(P < 0.05,图 5A)。与对照组相比,过表达miR-204组细胞HNRNPA2B1表达水平的平均灰度值(0.50±0.05)比对照组HNRNPA2B1表达水平的平均灰度值(1.00±0.09)低,且差异有统计学意义(图 5B、C)。Transwell迁移实验结果显示,miR-204+HNRNPA2B1组细胞数(122.67±11.06)比miR-204+ NC组细胞穿至下室的细胞数(47.00±3.61)明显增多(P < 0.05);侵袭实验显示,miR-204+HNRNPA2B1组穿过基质胶的细胞数(96.00+2.00)比miR-204+NC组细胞穿过基质胶的细胞数(34.67±2.08)明显增多(P < 0.05,图 5D)。
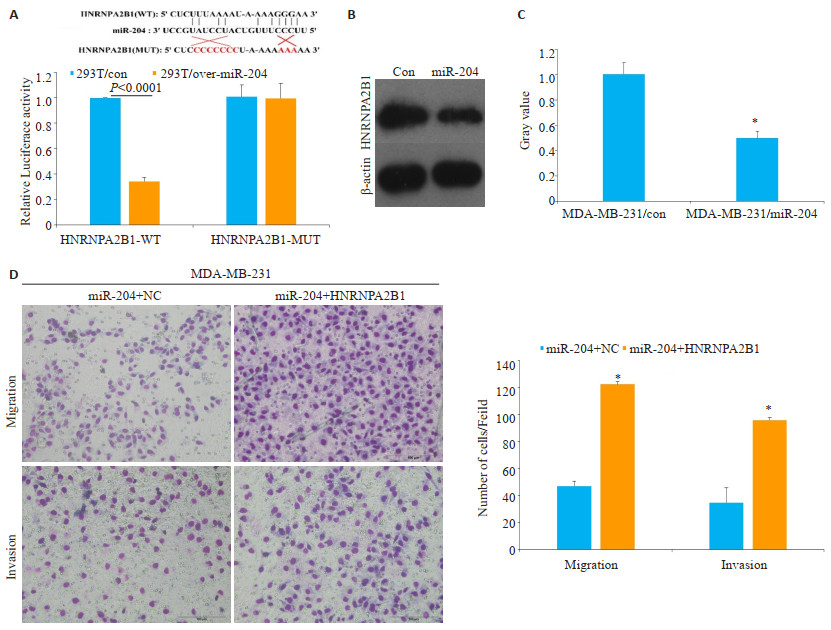
|
图 5 miR-204靶向调控HNRNPA2B1抑制乳腺癌的侵袭和迁移能力 Fig.5 miR-204 inhibits the migration and invasion ability of breast cancer by targeting the regulation of HNRNPA2B1. A: Luciferase activity of cells in different group was detected by luciferase experiment; B & C: The expression of HNRNPA2B1 in transfected cells. *P < 0.05 vs MDA-MB-231/con group; D: The migration and invasion ability in different transfected cells (Giemsa staining, scale bar= 100 μm, Mean±SD, n=3, *P < 0.05 vs miR-204+NC group). |
miRNA是一类21~23 nt的非编码小分子RNA,在多种肿瘤中异常表达,且在转移过程中发挥重要作用,如夏巍等发现miR-671-3p可靶向DEPTOR而抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖与侵袭[19];夏巍等[20]发现miR-152和miR-448靶向于Rictor可抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖。近来多项研究表明miRNA可通过不同方式调控肿瘤发生发展,其中一种重要的调控机制即miRNAs可影响mRNA的稳定性和转译,参与多细胞生物中基因表达的转录后调控,从而影响肿瘤的侵袭增殖能力[21-22]。因此,相较于mRNA,miRNA具有更大的潜力成为治疗乳腺癌的靶点[23-24]。
RNA结合蛋白(RBP)几乎参与了转录后调控层的所有步骤,决定了细胞中每个转录本的命运和功能,并确保细胞内环境的稳定。它们与其他蛋白质、编码RNA和非编码RNA建立高度动态的相互作用,形成称为核糖核蛋白复合物的功能单元[25-26]。作为一个RBP,HNRNPA2B1调节肿瘤发育相关RNA的剪接、稳定性和翻译[27-29]。先前研究揭示了HNRNPA2B1的下调可通过PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制宫颈癌细胞增殖、侵袭和细胞周期,从而引发细胞凋亡[30]。因此,HNRNPA2B1在癌症的发生、发展、基因表达和信号转导中起着直接的作用。
本研究通过GEO数据库中的乳腺癌患者相关数据集GSE44124、GSE38167发现miR-204在三阴性乳腺癌患者癌组织中表达降低,在转移性组织里miR-204表达同样降低;生存曲线分析显示低表达miR-204的患者具有更不良的预后。生物信息学数据显示miR-204可能作为抑癌基因在乳腺癌中发挥作用。RT-qPCR结果显示miR-204在乳腺癌细胞中低表达,过表达miR-204发现乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力受抑制,以上结果证实miR-204在人乳腺癌发生发展过程中作为抑癌基因发挥作用。也有研究报道,miR-204在几种人类肿瘤中均有下调表达,miR-204能抑制膀胱癌细胞生长和转移,也能调节宫颈癌细胞的增殖,凋亡和自噬能力[31-32],miR- 204-5p可靶向DSCAM-AS1抑制乳腺癌肿瘤生长[33],miR-204也能可以靶向调控ZEB1抑制乳腺癌的上皮间质转化从而抑制乳腺癌的侵袭和转移[34]。结合我们的结果,miR-204可能作为一个重要的肿瘤抑制因子参与乳腺癌的进程。生物信息学在基础研究中发挥的作用越来越大,我们通过基因预测网站miRTarbase,miRWalk,Targetscan预测可能与miR-204结合的靶基因,三个网站预测的靶基因取交集得84个miR-204的靶基因。通过PPI分析和cytoscape软件的MCODE插件,我们选择这84个靶基因中蛋白与蛋白连接度大于4的作为我们的Hub基因,结果得MBNL1,KHDRBS1,TIAL1,HNRNPA2B1为miR-204的Hub基因。另外,我们发现HNRNPA2B1和miR-204-5p表达呈负相关,在乳腺癌组织中高表达且高表达HNRNPA2B1的乳腺癌患者预后不良,因此选取HNRNPA2B1进一步研究。在此基础上,为了进一步探讨所筛选出来的miR-204对HNRNPA2B1的调控是通过直接结合并作用于其3'- UTR之上,我们构建了野生型(WT)HNRNPA2B1和突变型(MUT)HNRNPA2B1载体,通过双荧光素酶实验证明miR-204可靶向结合HNRNPA2B1。Western blot结果证明,过表达miR-204后,HNRNPA2B1的表达量降低,证实miR- 204可调控HNRNPA2B1的表达,Transwell实验同样证实miR-204对乳腺癌细胞侵袭和迁移能力的抑制作用可被HNRNPA2B1逆转。这些结果表明miR-204可通过抑制HNRNPA2B1的表达从而抑制乳腺癌细胞侵袭转移,从而在乳腺癌中发挥抗肿瘤的作用。
综上所述,miR-204可通过靶向调节HNRNPA2B1抑制乳腺癌的侵袭和转移,有望作为乳腺癌早期诊断以及转移的参考指标,为乳腺癌的诊疗提供新思路。
| [1] |
Yang C, Tabatabaei SN, Ruan XY, et al. The dual regulatory role of MiR-181a in breast cancer[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 44(3): 843-56. DOI:10.1159/000485351 |
| [2] |
Hur K, Toiyama Y, Okugawa Y, et al. Circulating microRNA-203 predicts prognosis and metastasis in human colorectal cancer[J]. Gut, 2017, 66(4): 654-65. |
| [3] |
Li HL, Mou QJ, Li PR, et al. MiR-486-5p inhibits IL-22-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cell by repressing Dock1[J]. J Cancer, 2019, 10(19): 4695-706. DOI:10.7150/jca.30596 |
| [4] |
张国新, 徐新伟, 孟斌, 等. miR-186-5p通过靶向调控PTTG1抑制肺腺癌细胞的上皮-间质转化[J]. 中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2017, 33(4): 380-5. |
| [5] |
Vos PD, Leedman PJ, Filipovska A, et al. Modulation of miRNA function by natural and synthetic RNA-binding proteins in cancer[J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2019, 76(19): 3745-52. |
| [6] |
Zeng J, Wei M, Shi R, et al. MiR-204-5p/Six1 feedback loop promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(2): 2729-35. |
| [7] |
Zhang LH, Wang XQ, Chen PS. MiR-204 down regulates SIRT1 and reverts SIRT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition, anoikis resistance and invasion in gastric cancer cells[J]. BMC Cancer, 2013, 13: 290. |
| [8] |
Zhu XL, Shen HL, Yin XM, et al. IL-6R/STAT3/miR-204 feedback loop contributes to cisplatin resistance of epithelial ovarian cancer cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(24): 39154-66. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.16610 |
| [9] |
Yu YH, Wang YS, Xiao XY, et al. MiR-204 inhibits hepatocellular cancer drug resistance and metastasis through targeting NUAK1[J]. Biochimie Et Biol Cell, 2019, 97(5): 563-70. DOI:10.1139/bcb-2018-0354 |
| [10] |
Wu ZY, Wang SM, Chen ZH, et al. MiR-204 regulates HMGA2 expression and inhibits cell proliferation in human thyroid cancer[J]. Cancer Biomark, 2015, 15(5): 535-42. DOI:10.3233/CBM-150492 |
| [11] |
Dangli A, Plomaritoglou A, Boutou E, et al. Recognition of subsets of the mammalian A/B-type core heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptides by novel autoantibodies[J]. Biochem J, 1996, 320(Pt 3): 761-7. |
| [12] |
Yang Y, Wei Q, Tang YL, et al. Loss of hnRNPA2B1 inhibits malignant capability and promotes apoptosis via down-regulating Lin28B expression in ovarian cancer[J]. Cancer Lett, 2020, 475: 43-52. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.029 |
| [13] |
Nagy á, Lánczky A, Menyhárt O, et al. Validation of miRNA prognostic power in hepatocellular carcinoma using expression data of independent datasets[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 9227. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-27521-y |
| [14] |
Li HL, Zhang BG, Liu YQ, et al. EBP50 inhibits the migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells via LIMK/cofilin and the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/MMP signaling pathway[J]. Med Oncol, 2014, 31(9): 162. |
| [15] |
Zhang GX, Li HL, Sun RM, et al. Long non-coding RNA ZEB2-AS1 promotes the proliferation, metastasis and epithelial mesenchymal transition in triple-negative breast cancer by epigenetically activating ZEB2[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2019, 23(5): 3271-9. DOI:10.1111/jcmm.14213 |
| [16] |
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, et al. STRING v11: protein-protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2019, 47(D1): D607-D613. DOI:10.1093/nar/gky1131 |
| [17] |
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, et al. starBase v2.0: decoding miRNAceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2014, 42(Database issue): D92-7. |
| [18] |
Wu JN, Zheng CX, Wang X, et al. MicroRNA-30 family members regulate calcium/calcineurin signaling in podocytes[J]. J Clin Invest, 2015, 125(11): 4091-106. |
| [19] |
Yu L, Wu D, Gao H, et al. Clinical utility of a STAT3-regulated miRNA-200 family signature with prognostic potential in early gastric cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2018, 24(6): 1459-72. |
| [20] |
夏巍, 龚德贵, 秦晓平, 等. MiR-671-3p靶向DEPTOR而抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖与侵袭[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(1): 42-8. |
| [21] |
张杰, 韩增胜, 董立新, 等. miR-152和miR-448靶向于Rictor并抑制结直肠癌细胞增殖[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2019, 39(5): 533-9. |
| [22] |
Croset M, Pantano F, Kan CWS, et al. miRNA-30 family members inhibit breast cancer invasion, osteomimicry, and bone destruction by directly targeting multiple bone metastasis-associated genes[J]. Cancer Res, 2018, 78(18): 5259-73. |
| [23] |
Ma L. MicroRNA and Metastasis[J]. Adv Cancer Res, 2016(132): 165-207. |
| [24] |
Orangi E, Motovali-Bashi M. Evaluation of miRNA-9 and miRNA- 34a as potential biomarkers for diagnosis of breast cancer in Iranian women[J]. Gene, 2019, 687: 272-9. |
| [25] |
Yerukala Sathipati S, Ho SY. Identifying a miRNA signature for predicting the stage of breast cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 16138. DOI:10.1038/s41598-018-34604-3 |
| [26] |
Pereira B, Billaud M, Almeida R. RNA-binding proteins in cancer: old players and new actors[J]. Trends Cancer, 2017, 3(7): 506-28. DOI:10.1016/j.trecan.2017.05.003 |
| [27] |
Brinegar AE, Cooper TA. Roles for RNA-binding proteins in development and disease[J]. Brain Res, 2016, 1647: 1-8. DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.02.050 |
| [28] |
Hutchison S, LeBel C, Blanchette M, et al. Distinct sets of adjacent heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (HNRNP) A1/A2 binding sites control 5' splice site selection in the HNRNP A1 mRNA precursor[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(33): 29745-52. |
| [29] |
Villarroya BC, Gutiérrez VC, Sánchez CF, et al. Sumoylated hnRNPA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs[J]. Nat Commun, 2013, 4: 2980. |
| [30] |
Fähling M, Mrowka R, Steege A, et al. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein-A2/B1 modulate collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase, alpha (I) mRNA stability[J]. J Biol Chem, 2006, 281(14): 9279-86. |
| [31] |
Shi X, Ran L, Liu Y, et al. Knockdown of HNRNP A2/B1 inhibits cell proliferation, invasion and cell cycle triggering apoptosis in cervical cancer via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Oncol Rep, 2018, 39(3): 939-50. |
| [32] |
Li Y, Chen R, Li Z, et al. miR-204 negatively regulates cell growth and metastasis by targeting ROBO4 in human bladder cancer[J]. Onco Targets Ther, 2019, 12: 8515-24. DOI:10.2147/OTT.S205023 |
| [33] |
Li N, Guo XR, Liu L, et al. Molecular mechanism of miR-204 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and autophagy of cervical cancer cells by targeting ATF2[J]. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol, 2019, 47(1): 2529-35. |
| [34] |
Liang WH, Li N, Yuan ZQ, et al. DSCAM-AS1 promotes tumor growth of breast cancer by reducing miR-204-5p and up-regulating RRM2[J]. Mol Carcinog, 2019, 58(4): 461-73. DOI:10.1002/mc.22941 |
| [35] |
Wang YZ, Zhou YJ, Yang ZC, et al. MiR-204/ZEB2 Axis functions as key mediator for MALAT1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer[J]. Tumour Biol, 2017, 39(7): 1010428317690998. DOI:10.1177/1010428317690998 |
 2020, Vol. 40
2020, Vol. 40

