2. 江西省妇幼保健院肿瘤科,江西 南昌 330006
2. Department of Oncology, Jiangxi Maternal and Children's Health Hospital, Nanchang 330006, China
子痫前期(PE)是引发孕妇和围产期妇女的死亡率升高的关键原因之一[1-2]。研究发现,滋养层细胞浸润不足导致子宫螺旋动脉浸润不足是诱发子痫前期的主要诱因之一[3-4]。另外,PI3K/AKT信号通路已被发现在多种细胞生长迁移和侵袭过程中发挥关键作用,其中包括滋养层细胞[5-6],但是这些机制并未完全阐明。
微小RNA(miR)是一类高度保守的短链的(20~25 nt)非编码RNA,参与多种生理和疾病过程[8]。在PE中,miR可通过调控其靶基因,参与滋养层细胞的增殖、凋亡、侵袭、和迁移[9-10],并在子痫前期的诊断中发挥重要作用[11-12]。最新研究发现miR-34a家族成员miR-34a-5p可调节多种细胞的增殖和侵袭[13]。然而,miR-34a-5p对滋养层细胞的增殖、凋亡、侵袭等作用仍不明确。
细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶(CDK)是一类调节细胞周期的关键蛋白之一,其中,CDK1,CDK2,CDK4已发现参与调节滋养层细胞的增殖和细胞周期[14]。已经发现CDK6是一种关键的细胞周期蛋白,调节G1-S周期进程,与CDK4类似,在人胎盘胎膜早期发育中可与cyclinD1结合形成复合物,参与调节细胞的增殖[15]。在本研究中,我们预测发现miR-34a-5p与CDK6的3'-UTR具有多个结合区域。但是CDK6及miR-34a-5p在滋养层细胞中发挥的作用和二者的调节关系尚不明确,因此本研究主要探讨CDK6及miR-34a-5p在滋养层细胞中发挥的作用和下游机制以及二者的调节关系。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料人绒毛外滋养层细胞系HTR-8/Svneo和人绒毛膜癌细胞系BeWo和JEG-3均购买于美国模式培养物保藏所(ATCC);RPMI 1640培养基、10%胎牛血清(FBS)(Gibco BRL);MTT细胞增殖活性检测试剂盒、caspase 3活性细胞凋亡检测试剂盒、Transwell小室(生工);miR-34a-5p拟似物mimic与其阴性对照mimicNC,miR-34a-5p抑制剂与其阴性对照inhibitor-NC,pcDNA3.1(+)-CDK6过表达质粒和阴性对照(pcDNA)(吉玛);荧光素酶报告基因质粒BCA蛋白分析试剂盒与ECL发光液(碧云天),TRIzol及M-MLV逆转录试剂盒(Invitrogen);miScript逆转录试剂盒(Qiagen);SYBR® Green Master Mi(MedChemExpress);;硝酸纤维膜由Bio-Rad提供;一抗rabbit anti-CDK6、rabbit anti-cleaved-caspase 3、rabbit anti-MMP-9、rabbit antiPI3K、rabbit anti-AKT、rabbit anti-p-AKT、rabbit antiGAPDH,二抗HRP anti-rabbit IgG(Abcam)。DNA酶I(Dnase I)与完全蛋白酶抑制剂(罗氏)。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养人绒毛外滋养层细胞系HTR-8/Svneo和人绒毛膜癌细胞系BeWo和JEG-3均使用RPMI 1640培养基进行培养,含有10%FBS的RPMI 164培养基培养于细胞培养箱(37 ℃,5% CO2)。所有细胞每2~3 d换液1次,待细胞融合率达到80%时按照1:3比例传代。用于miR-34a-5p水平变化的检测。
1.2.2 细胞转染和细胞处理按照生工公司提供的说明书并参考Liu等[16]的研究,分别将miR-34a-5p-mimic(mimic)和miR-34a-5p-mimic-NC(mimic-NC)转染至HTR-8/Svneo细胞中24 h,阴性对照组为mimic-NC。使用pcDNA3.1(+)过表达质粒构建CDK-6过表达载体(pcDNA-CDK6),pcDNA-CDK6与mimic共转染细胞:mimic和pcDNA-CDK6同时转染HTR-8/Svneo细胞24 h(mimic+pcDNA-CDK6)。IGF-1与mimic共处理细胞:mimic转染HTR-8/Svneo细胞24 h继续使用IGF-1处理4 h(mimic+IGF-1)。另外,使用miR-34a-5p-inhibitor(inhibitor)和miR-34a-5p-inhibitor-NC(inhibitor-NC)分别转染HTR-8/Svneo细胞。
1.2.3 实时荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)分别收集HTR-8/ Svneo、BeWo、JEG-3细胞,及HTR-8/Svneo的对照、mimic或mimic-NC处理下的细胞,TRIzol法抽提细胞总RNA,M-MLV逆转录试剂盒合成cDNA,miRNA逆转录使用miScript逆转录试剂盒合成。cDNA特定RNA产物的产量检测使用SYBR® Green Master Mix,RUN6为内参对miR-34a-5p的表达量进行标准化处理。反应体系(20 μL):10 μL SYBR,2.0 ng模板cDNA,正反向引物浓度均为20 μmol/L,体积为0.8 μL,最终使用灭菌蒸馏水加至20 μL。PCR过程:40个循环,94 ℃,1 min;54 ℃,1 min;聚合72 ℃,1 min;延伸72 ℃,7 min。miR-34a-5p的相对表达使用公式2-ΔΔCt计算。miR-34a-5p引物序列:5'-TGGCAGTGTCTTAGCTGGTTGT-3'(上游)和5'-GCGAGCACAGAATTAATACGAC-3(下游);U6引物序列5'-TGCTCGCTTCGGCAGC-3'(上游)和5'-GTATACATGTGCCATGCTGGTG-3′(下游)。
1.2.4 MTT检测细胞增殖活性将待检测各组细胞的密度调整为5×103,并接种于96孔板,MTT(终浓度5mg/mL)37 ℃孵育HTR-8/Svneo细胞4 h,弃上清液后加入DMSO。使用酶标仪检测A490 nm处的吸光度值(A)。计算细胞成活率。细胞存活率=(处理组A-空白对照组A)/(对照组A-空白对照组A)×100%。
1.2.5 Western blot检测细胞加入蛋白裂解液以裂解细胞,BCA法检测蛋白浓度。配制SDS-PAGE凝胶后行蛋白电泳后将凝胶中蛋白转移至PVDF膜,5%脱脂奶粉封闭3.5 h,分别使用相应的一抗CDK-6(1: 1000)、cleaved-caspase 3(1:900)、MMP-9(1:1000)、PI3K(1: 1500)、AKT(1 : 2000)、p-AKT(1 : 800)、GAPDH(1 : 8000)进行孵育,孵育过夜后PBS洗涤3次,每次10 min,随后使用辣根过氧化物酶HRP anti-rabbit IgG(1: 10 000)室温孵育1 h。使用ECL化学发光液进行显色。灰度值使用ImageJ V1.49软件进行分析。
1.2.6 检测细胞的caspase 3活性首先将待检测各组细胞的密度调整为5×103,离心弃掉上清液,使用PBS洗涤2次,加入100 μL裂解缓冲液,冰上放置15 min,涡旋振荡15 s,离心5 min。取10 μL蛋白上清液,加入到90 μL caspase 3活性检测液,加入10 μLAc-LEHD-pNA,避光反应1~2 h后检测结果。
1.2.7 Transwell实验检测细胞浸润能力转染和处理后的各组细胞见浸润能力检测。细胞转染后进行胰酶消化,并用完全培养基终止消化,混合均匀后收集,各组细胞离心并重悬至200 μL加入到transwell小室中,小室中预先包被基质胶并在去血清的培养基中孵育24 h。在放置Transwell小室的24孔板中加入600 μL完全培养基培养24 h后,用棉签小心拭去小室上层未浸润过底膜的上部细胞和基质胶,用甲醇(-20 ℃预冷)固定浸润过Transwell小室底膜的下部细胞10 min,用苏木素染色10 min,蒸馏水浸洗后在200倍显微镜视野下随机挑选9个不同区域的细胞进行计数。
1.2.8 萤光素酶报告基因分析生物信息学预测发现miR-34a-5p序列与CDK6的3'-UTR区具有结合关系。将野生型的CDK6 3'-UTR(Wt-UTR)或突变型的CDK6 3'-UTR(mut-CDK6,已经过点突变)分别插入到pGL3载体的XbaⅠ/FseⅠ位点。荧光素酶活性分析如下,使用双基因转染试剂对细胞共转染mimic、Wt CDK6 3'-UTR或mut-CDK6 3'-UTR,转染时间为48 h。根据制造商的指示,用Dual-Glo荧光素酶检测系统(Promega, Madison, WI)进行荧光素酶活性分析。
1.3 统计学分析本研究实验均独立重复3次,数据采用SPSS.22软件进行分析。结果表示为均数±标准差,多组间使用单因素方差分析比较,组内两两比较采用t检验。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 miR-34a-5p在滋养层细胞中表达下调miRNA的RTqPCR检测结果发现,与两种癌细胞系相比,HTR/Svneo细胞中miR-34a-5p的表达较BeWo和JEG-3细胞降低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 1)。
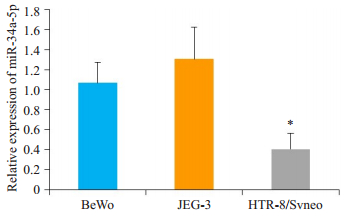
|
图 1 miR-34a-5p体外表达水平miR-34a-5p在培养的人滋养层细胞系HTR-8/Svneo及人绒毛膜癌细胞系BeWo和JEG-3中的表达水平 Fig.1 Expression of miR-34a-5p in cultured human trophoblast cell line HTR-8 /Svneo and human chorionic cancer cell lines BeWo and JEG-3. *P < 0.05 vs BeWo cells. |
为研究miR-34a-5p对HTR-8/Svneo滋养层细胞增殖的影响,使用其拟似物mimic转染HTR-8/Svneo细胞过表达miR-34a-5p(图 2A),结果发现,与对照组相比,mimic组中HTR-8/Svneo细胞的增殖活性降低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 2B),而与对照组相比,mimic-NC组细胞的增殖活性变化无统计学差异(P>0.05,图 2B)。Western blot检测CDK6蛋白表达结果发现,与对照组相比,mimic组中CDK6的表达水平降低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 2C),而mimic-NC组中的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,图 2C)。
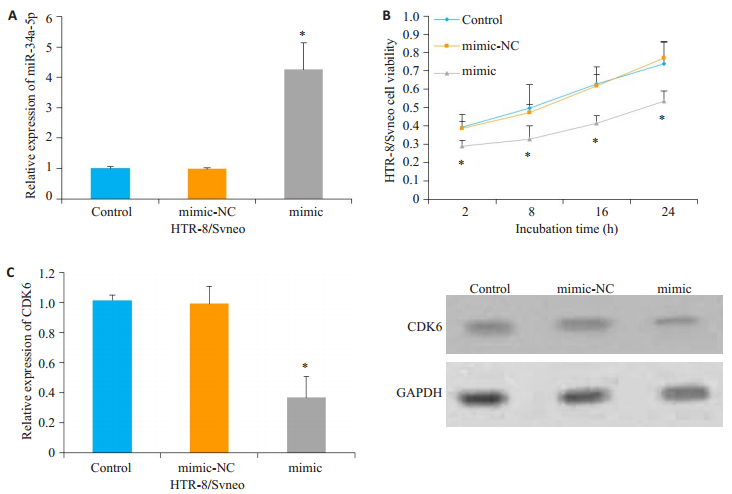
|
图 2 miR-34a-5p对HTR-8/Svneo细胞增殖活性的作用 Fig.2 Effect of transfection with miR-34a-5p mimic on proliferation of HTR-8/Svneo cells. A: The miR-34a-5p mimic was used to induce miR-34a-5p overexpression in HTR-8/Svneo cells; B: Changes in survival rate of HTR-8 /Svneo cells; C: Changes in CDK6 protein expression level in HTR-8/Svneo cells. *P < 0.05 vs control group. |
进一步研究miR-34a-5p对HTR-8/Svneo滋养层细胞凋亡的影响,使用其拟似物mimic转染细胞,与对照组相比,mimic组中HTR-8/Svneo细胞的caspase 3活性增加,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 3A),而与对照相比,mimic-NC组细胞的caspase 3活性变化无统计学差异(P>0.05,图 3A)。检测切割模式的caspase 3(ccaspase 3)表达,结果发现,与对照组相比,mimic组中HTR-8/Svneo细胞中c-caspase 3的表达增加,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 3B),而与对照相比,mimic-NC组细胞中c-caspase 3的表达变化无统计学差异(P>0.05,图 3B)。
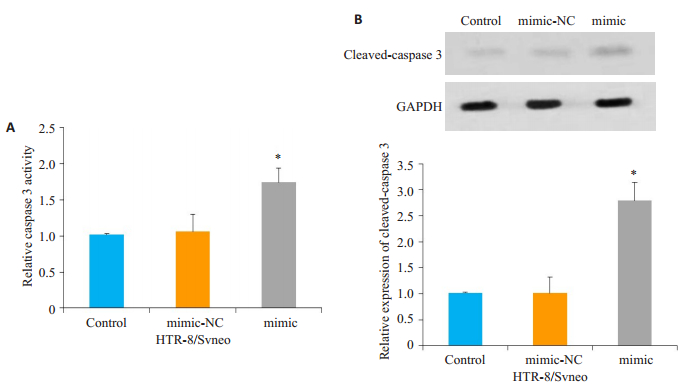
|
图 3 miR-34a-5p对HTR-8/Svneo细胞凋亡的作用 Fig.3 Effect of transfection with miR-34a-5p mimic on apoptosis of HTR-8 /Svneo cells. A: Change in caspase 3 activity in HTR-8/Svneo cells; B: Change in cleaved caspase 3 protein expression levels in HTR-8 /Svneo cells. *P < 0.05 vs control group. |
结果发现,与对照组相比,mimic组中HTR-8/ Svneo细胞的浸润细胞数减少,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 4A),而与对照相比,mimic-NC组浸润细胞数变化无统计学差异(P>0.05,图 4A)。检测MMP-9的表达,结果发现,与对照组相比,mimic组中HTR-8/Svneo细胞中MMP-9的表达水平下调,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 4B),而与对照相比,mimic-NC组细胞中MMP-9的表达变化无统计学差异(P>0.05,图 4B)。
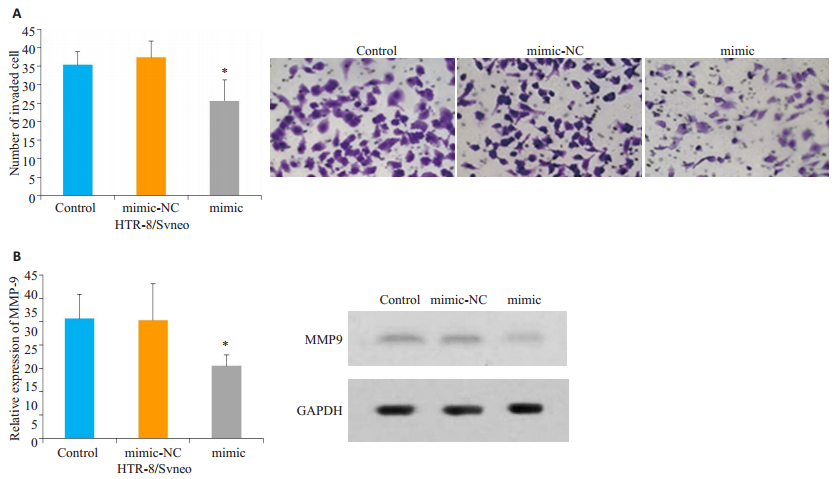
|
图 4 miR-34a-5p对HTR-8/Svneo细胞浸润能力的作用 Fig.4 Effect of transfection with miR-34a-5p mimic on invasion capacity of HTR-8 /Svneo cells. A: Transwell assay to detect the changes in HTR-8/Svneo cell invasion (Original magnification: ×200); B: Changes in MMP-9 protein expression in HTR-8/Svneo cells. *P < 0.05 vs control group. |
经生物信息学分析发现,CDK6 mRNA的3'-UTR中有与miR-34a-5p结合的多个区域,且miR-34a-5p过表达导致CDK6的蛋白表达水平降低(图 2C)。荧光素酶报告基因实验结果发现,miR-34a-5p过表达和pGL3-荧光素酶启动子重组载体共转染细胞24 h后,野生型(Wt)CDK6组中的荧光素酶强度低于CDK6突变组(Mut),差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 5A),因此确定CDK6是miR-34a-5p的靶基因。
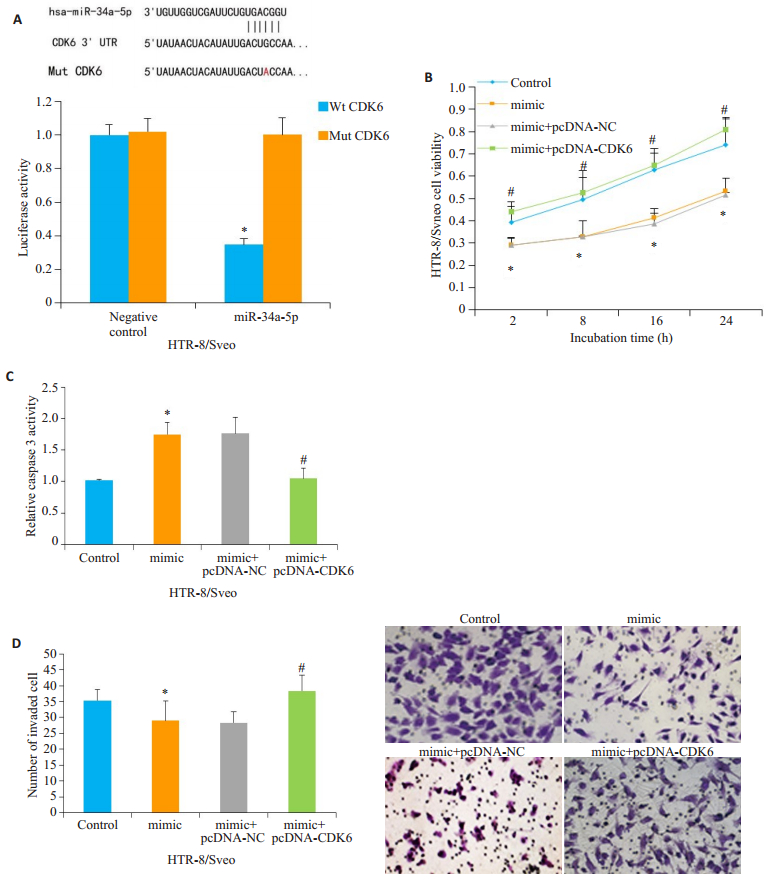
|
图 5 CDK6是miR-34a-5p靶基因之一 Fig.5 CDK6 is one of the target genes of miR-34a-5p. A: Direct interaction between CDK6 and miR-34a-5p detected by luciferase reporter gene assay; B: Changes in survival rate of HTR-8/Svneo cells; C: Changes in caspase-3 activity in HTR-8/Svneo cells; D: Transwell assay to detect the changes in HTR-8/Svneo cell infiltration number (×200). *P < 0.05 vs negative control group or control group; #P < 0.05 vs mimic group. |
另外,对HTR-8/Svneo细胞转染pcDNA-CDK6构建稳定高表达CDK6的细胞,并同时共转染mimic,用以反向证明miR-34a-5p通过控制CDK6对细胞增殖、凋亡、浸润发挥功能。与单独mimic组相比,pcDNA-CDK6+ mimic组中细胞增殖活性和侵袭率均升高、且凋亡率降低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 5B~D)。
2.6 PI3K/AKT信号通路参与调控miR-34a-5p介导的滋养层细胞增殖、凋亡和浸润miR-34a-5p-inhibitor转染细胞后,PI3K/AKT信号蛋白PI3K和p-AKT(ser308)水平都上调(P<0.05,图 6A~E)。使用PI3K/AKT的激动剂IGF-1处理mimic转染的HTR-8/Svneo细胞。结果发现,与单独mimic组相比,IFG-1+mimic组中细胞增殖活性和侵袭率部分升高,且凋亡率降低,差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 6F~H)。
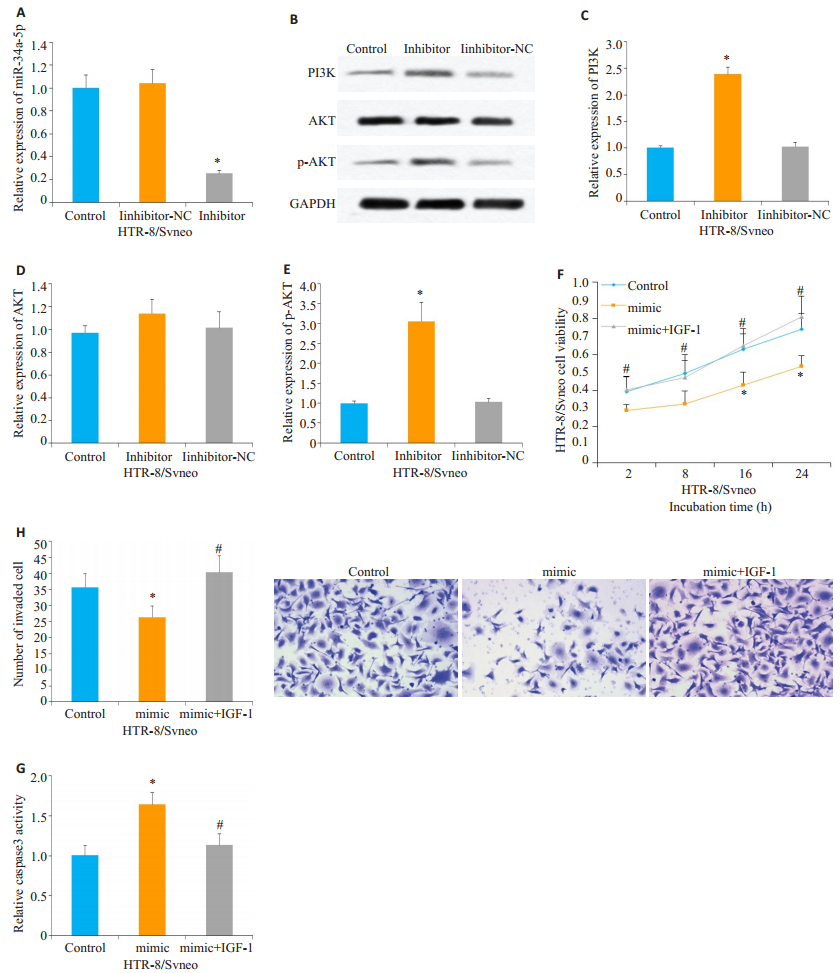
|
图 6 PI3K/AKT是miR-34a-5p发挥作用的关键信号通路 Fig.6 PI3K/AKT is the key signaling pathway for miR-34a-5p to function. A: An inhibitor was used to inhibit miR-34a-5p in HTR-8/Svneo cells (*P < 0.05 vs control group); B-E: PI3K/AKT signal protein expression bands detected by Western blotting (*P < 0.05 vs control group); F: The changes in the survival rate of HTR-8/Svneo cells; G: Changes in caspase 3 activity in HTR-8/Svneo cells; H: Transwell invasion assay for detecting the changes of HTR-8/Svneo cell invasion (×200). F-H: *P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs mimic group. |
子痫发生初期,滋养层细胞的浸润能力表现为异常减弱。但滋养层细胞浸润能力的调节分子机制仍不明确。本研究发现在滋养层细胞中处于低水平的miR-34a-5p发挥关键作用。首先,高表达miR-34a-5p后,滋养层细胞的增殖活性和浸润能力均降低,且细胞凋亡率增加。其次,细胞周期蛋白CDK6参与miR-34a-5p对滋养层细胞活性和浸润的调节,而且和PI3K/AKT激活相关。
MiR-34a-5p是一种调节多种细胞的多功能小分子RNA。本研究发现,在具有较高侵袭性的人绒毛膜癌细胞中miR-34a-5p表达水平明显高于滋养层细胞。而且,多项研究发现,miR-34a-5p可抑制癌细胞的迁移和侵袭[13, 17],暗示miR-34a-5p可能与滋养层细胞的浸润有关。为检测miR-34a-5p对滋养层细胞的功能,我们在人滋养层细胞HTR-8/Svneo中通过转染mimic成功高表达miR-34a-5p。有趣的是,高表达miR-34a-5p细胞的浸润能力降低。表明,miR-34a-5p对滋养层细胞浸润具有抑制作用。大量的研究都支持我们的发现,Wang等[18]研究发现miR-34a-5p的减低能促进血管平滑肌细胞的迁移能力,而且miR-34a-5p高表达抑制骨肉瘤细胞的迁移和侵袭能力[13]。另外,多项证据均支持miR-34a-5p的抗细胞增殖与促进凋亡的作用[19],包括肿瘤细胞和非肿瘤细胞[18, 20]。本研究发现miR-34a-5p过表达后,人滋养层细胞HTR-8/Svneo的增殖活性明显降低,而细胞凋亡率增加,我们的结果和以往的研究结果基本一致。因此,本研究结果表明,miR-34a-5p表达增高可抑制滋养层细胞的增殖和浸润,并促进细胞凋亡。
MiRNAs是一大类存在于生物体内具有潜在功能调节作用的“暗物质” [21]。在哺乳动物中,miRNAs发挥功能的机制主要是通过与靶基因mRNA 3'-UTR结合今儿改变或抑制其靶基因的功能或表达水平[22]。在本研究中,经过生物信息学分析,发现细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶CDK6的3'-UTR中具有多个与miR-34a-5p结合区域,我们推测CDK6很有可能是miR-34a-5p的靶基因。蛋白表达检测和荧光素酶报告基因实验均验证CDK6是miR-34a-5p的靶基因。CDK6是一种关键的细胞周期蛋白,调节G1-S周期进程,与CDK4类似,在人胎盘胎膜早期发育中可与cyclinD1结合形成复合物,参与调节细胞的增殖[15, 23]。我们对滋养层细胞进行CDK6高表达联合miR-34a-5p过表达处理,结果发现,联合组中滋养层细胞的增殖率明显上调,凋亡率降低。Wu等[24]研究亦发现miR-129与miR137均可通过下调CDK6的表达抑制癌细胞的增殖。细胞表达显性负性形式的CDK6,可致由NGF剥夺诱导的细胞凋亡被明显延迟[25]。另外Ma等[26]研究发现miR-29a通过靶向调节CDK6抑制雪旺细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭能力,并促进雪旺细胞的凋亡。而且,MiR-29c通过靶向抑制CDK6调控膀胱癌细胞的增殖和侵袭[27]。而本研究过表达CDK6部分恢复因miR-34a-5p过表达所减弱的滋养层细胞的浸润能力。本研究表明,miR-34a-5p通过调控CDK6表达调节滋养层细胞的增殖,浸润和凋亡。
近期,大量的研究均证实PI3K/AKT信号通路在滋养层细胞浸润和增殖中发挥重要作用[28-29]。Xu等[6]研究发现,滋养层细胞的增殖受到PI3K/AKT信号通路的正向调节;在本研究中,我们更加确认了该信号通路对滋养层细胞的增殖活性具有促进作用,miR-34a-5p的mimic对滋养层细胞的抑制作用明显被PI3K/AKT通路的激活剂所逆转。与我们的结果类似的是,Zhang L等[30]研究发现,敲减长链非编码RNA H19通过吸附上调miR-18a-5p对滋养层细胞的增殖和浸润具有抑制功能,而且敲减H19导致的miR-18a-5p上调可以通过抑制PI3K/AKT信号促进滋养层细胞的自噬。与此结果类似的是,在本研究中,我们发现使用PI3K/AKT激活剂IGF-1后恢复了以上结果,这表明PI3K/AKT信号通路可能在miR-34a-5p对滋养层细胞的增殖、浸润和凋亡的调节中发挥核心作用。
综上所述,我们的研究表明miR-34a-5p通过调控CDK6表达和PI3K/AKT信号通路激活调节滋养层细胞的增殖,浸润和凋亡。本研究为子痫前期相关疾病的早期发现和治疗提供了新的靶点,为滋养层细胞凋亡和浸润等作用和机制的进一步研究提供了重要的理论和实践基础。
| [1] |
Xu RH, Chen X, Li DS, et al. BMP4 initiates human embryonic stem cell differentiation to trophoblast[J]. Nat Biotechnol, 2002, 20(12): 1261. DOI:10.1038/nbt761 |
| [2] |
Mol BW, Roberts CT, Thangaratinam S, et al. Pre-eclampsia[J]. The Lancet, 2016, 387(10022): 999-1011. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00070-7 |
| [3] |
Myatt L. Role of placenta in preeclampsia[J]. Endocrine, 2002, 19(1): 103-11. DOI:10.1385/ENDO:19:1:103 |
| [4] |
Chen YY, Chuang PY, Chen CP, et al. Functional antagonism between high-temperature requirement protein A (HtrA) family members regulates trophoblast invasion[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 576744. |
| [5] |
Li H, Cao G, Zhang N, et al. RBP4 regulates trophoblastic cell proliferation and invasion via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(3): 2873-9. |
| [6] |
Xu J, Xia Y, Zhang H, et al. Overexpression of long non-coding RNA H19 promotes invasion and autophagy via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in trophoblast cells[J]. Biomed Pharmaco Ther, 2018, 101: 691-7. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2018.02.134 |
| [7] |
Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs[J]. Nature, 2004, 431(7006): 350. DOI:10.1038/nature02871 |
| [8] |
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function[J]. Cell, 2004, 116(2): 281-97. |
| [9] |
Shi Z, She K, Li H, et al. MicroRNA-454 contributes to sustaining the proliferation and invasion of trophoblast cells through inhibiting Nodal/ALK7 signaling in pre-eclampsia[J]. Chem-Biol Interac, 2019, 298: 8-14. DOI:10.1016/j.cbi.2018.10.012 |
| [10] |
Yang X, Meng T. MicroRNA-431 affects trophoblast migration and invasion by targeting ZEB1 in preeclampsia[J]. Gene, 2019, 683: 225-32. DOI:10.1016/j.gene.2018.10.015 |
| [11] |
Motawi TM, Sabry D, Maurice NW, et al. Role of mesenchymal stem cells exosomes derived microRNAs; miR-136, miR-494 and miR- 495 in pre-eclampsia diagnosis and evaluation[J]. Arch Biochem Biophys, 2018, 659: 13-21. DOI:10.1016/j.abb.2018.09.023 |
| [12] |
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, et al. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation[J]. Nat Cell Biol, 2009, 11(3): 228. DOI:10.1038/ncb0309-228 |
| [13] |
Jia D, Niu Y, Li D, et al. LncRNA C2dat1 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion by targeting miR-34a-5p in osteosarcoma cells[J]. Oncol Res, 2018, 26(5): 753-64. DOI:10.3727/096504017X15024946480113 |
| [14] |
Li J, Li R, Gao Y, et al. LncRNA CCAT1 promotes the progression of preeclampsia by regulating CDK4[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22: 1216-23. |
| [15] |
De Falco M, Fedele V, Cobellis L, et al. Pattern of expression of cyclin D1/CDK4 complex in human placenta during gestation[J]. Cell Tissue Res, 2004, 317(2): 187-94. |
| [16] |
Liu Q, Yu W, Zhu S, et al. Long noncoding RNA GAS5 regulates the proliferation, migration, and invasion of glioma cells by negatively regulating miR-18a-5p[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2018, 234(1): 757-68. |
| [17] |
Gao J, Li N, Dong Y, et al. miR-34a-5p suppresses colorectal cancer metastasis and predicts recurrence in patients with stage Ⅱ/Ⅲ colorectal cancer[J]. Oncogene, 2015, 34(31): 4142. DOI:10.1038/onc.2014.348 |
| [18] |
Wang H, Jin Z, Pei T, et al. LncRNA C2dat1 enhances vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by targeting miR- 34a-5p[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(3): 3001-8. DOI:10.1002/jcb.27070 |
| [19] |
Wang X, Xie Y, Wang J. Overexpression of microRNA-34a-5p inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells by downregulation of Bcl-2[J]. Oncol Res, 2018, 26(6): 977-85. DOI:10.3727/096504017X15037506066252 |
| [20] |
Xiao X, Gu Y, Wang G, et al. c-Myc, RMRP, and miR-34a-5p form a positive-feedback loop to regulate cell proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2019, 122: 526-37. DOI:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.10.207 |
| [21] |
de Ronde MWJ, Ruijter JM, Moerland PD, et al. Study design and qPCR data analysis guidelines for reliable circulating miRNA biomarker experiments: a review[J]. Clin Chem, 2018, 64(9): 1308-18. DOI:10.1373/clinchem.2017.285288 |
| [22] |
Enomoto Y, Takagi R, Naito Y, et al. Identification of the novel 3' UTR sequences of human IL-21 mRNA as potential targets of miRNAs[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 7780. |
| [23] |
Palazon L, Davies T, Gardner R. Translational inhibition of cyclin B1 and appearance of cyclin D1 very early in the differentiation of mouse trophoblast giant cells[J]. Mol Hum Reprod, 1998, 4(11): 1013-20. DOI:10.1093/molehr/4.11.1013 |
| [24] |
Wu J, Qian J, Li C, et al. miR-129 regulates cell proliferation by downregulating Cdk6 expression[J]. Cell Cycle, 2010, 9(9): 1809-18. DOI:10.4161/cc.9.9.11535 |
| [25] |
Borgne A, Golsteyn R M. The role of cyclin-dependent kinases in apoptosis[J]. Prog Cell Cycle Res, 2003, 5: 453-9. |
| [26] |
Ma J, Li T, Yuan H, et al. MicroRNA-29a inhibits proliferation and motility of schwannoma cells by targeting CDK6[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2018, 119(3): 2617-26. DOI:10.1002/jcb.26426 |
| [27] |
Zhao X, Li J, Huang S, et al. MiRNA-29c regulates cell growth and invasion by targeting CDK6 in bladder cancer[J]. Am J Transl Res, 2015, 7(8): 1382. |
| [28] |
Xu Y, Sui L, Qiu B, et al. ANXA4 promotes trophoblast invasion via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in preeclampsia[J]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2019, 316(4): C481-91. DOI:10.1152/ajpcell.00404.2018 |
| [29] |
Li H, Cao G, Zhang N, et al. RBP4 regulates trophoblastic cell proliferation and invasion via the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(3): 2873-9. |
| [30] |
Zhang L, Deng X, Shi X, et al. Silencing H19 regulated proliferation, invasion, and autophagy in the placenta by targeting miR-18a-5p[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(6): 9006-15. DOI:10.1002/jcb.28172 |
 2020, Vol. 40
2020, Vol. 40

