急性呼吸窘迫综合症(ARDS)是由非心源性的各种肺内外致病因素导致的急性、进行性、缺氧性呼吸衰竭,病死率高[1-2]。其发病机制复杂,大量研究表明,肺部过度炎症反应及肺微血管内皮细胞屏障功能受损是ARDS发生、发展的关键因素[2-3]。
内脏脂肪组织来源的丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂,简称Vaspin(serpinA12)是一种新型脂肪细胞因子,属于丝氨酸蛋白酶抑制剂serpin家族成员之一[4]。研究发现Vaspin可调控血管内皮细胞的炎性因子、粘附分子及趋化因子的表达,且能对抗细胞凋亡,对血管内皮具有保护作用[5-6]。然而国内外尚未见Vaspin与ARDS关联及对其影响的相关报道。基于炎症反应爆发和肺泡毛细血管弥漫性损伤是ARDS的主要病理改变[2],我们推测Vaspin可通过其介导的抗炎及血管内皮保护效应对ARDS肺损伤发挥保护性调控。
故此,本研究通过气管内滴注LPS建立小鼠ARDS模型,探究Vaspin对小鼠ARDS的保护作用,并进一步探讨其潜在的调控机制。
1 材料和方法 1.1 实验动物40只SPF级雄性C57BL/6小鼠(6~8周龄,体质量20.0±2.0 g),购自重庆医科大学动物实验中心,并自由饮食、普通光照饲养于重庆医科大学动物实验中心。
1.2 实验试剂脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide, LPS)购自Sigma、PI3K抑制剂渥曼青霉素(wortmannin)购自solarbio公司、Vaspin购自novoprotein公司;RIPA裂解液(RIPA Lysis Buffer)、PMSF及BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒购自碧云天生物科技研究所;酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒购自联科生物科技有限公司;髓过氧化物酶(MPO)测试盒购自南京建成生物工程研究所;SDSPAGE凝胶配制试剂盒购自碧云天生物科技研究所;预染Marker购于Thermo公司;β-肌动蛋白(β-actin)、Akt及p-Akt抗体购自bioworld公司,VCAM-1抗体购自abcam公司,caspase-3、cleaved caspase-3抗体购自万类生物公司;Super Sensitive TM即用型超敏免疫组化二抗试剂盒(鼠/兔)购自南京Bioworld生物科技有限公司,ECL检测试剂盒购自南京凯基生物科技有限公司。
1.3 ARDS小鼠模型建立40只小鼠随机分为对照组、模型组(LPS组)、Vaspin组、渥曼青霉素组(wortmannin组),每组10只。小鼠称重后,腹腔注射4%水合氯醛(0.2 mL/20 g)麻醉小鼠。LPS组、Vaspin组及wortmannin组小鼠通过气管插管按5 mg/kg剂量滴注无菌LPS(10 μg LPS溶于50 μL无菌生理盐水)建立ARDS模型,对照组给予等量无菌生理盐水。Vaspin组及wortmannin组于LPS注射后立即腹腔注射Vaspin(0.1 μg/kg)。wortmannin组分别于LPS注射前、后90 min给予PI3K抑制剂渥曼青霉素(0.06 mg/kg),Vaspin组给予等量无菌生理盐水。
1.4 苏木素-伊红(HE)染色观察小鼠肺组织病理变化24 h后处死小鼠,取右下肺组织,4%多聚甲醛固定,制成5 μm石蜡切片,HE染色,光镜观察。
1.5 小鼠肺组织湿干比(W/D)评估肺水肿取小鼠左下肺组织,放置于事先称重的锡箔纸上称量肺湿重,将样本放置于60 ℃烤箱72 h至恒重后,称量其干重。根据公式计算肺湿干比(W/D)值。
1.6 小鼠支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)检测将1 mL无菌PBS反复灌注小鼠肺组织3次,收集BALF,确保回收率大于90%。并于4 ℃ 12 000 r/min离心30 min,取上清液,按BCA蛋白测定试剂盒说明测定BALF总蛋白含量。
1.7 小鼠肺组织MPO活性检测按MPO测试盒要求,测定肺组织匀浆中MPO活性。
1.8 ELISA检测肺组织中炎症因子水平取小鼠右肺组织,冰PBS漂洗后制备肺组织匀浆,按ELISA试剂盒要求测肺组织中IL-1β和TNF-α的含量。
1.9 免疫组织化学法(IHC)观察肺组织中血管细胞间粘附分子(VCAM-1)表达取右上肺组织,4%多聚甲醛固定,常规脱水,石蜡包埋,切片厚度为5 μm,60 ℃烤片1 h后,按Super Sensitive TM免疫组化试剂盒要求操作:石蜡切片二甲苯脱蜡,梯度乙醇水化,枸橼酸盐缓冲液(pH 6.0)微波炉抗原修复,3%过氧化氢阻断内源性过氧化物酶,免疫性动物血清常温封闭,加入抗体VCAM-1(1:500)过夜孵育,37 ℃复温35 min,PBS漂洗,加入一抗放大剂室温孵育30 min,PBS漂洗后滴加辣根过氧化物酶(HRP)聚合物(二抗)室温避光孵育30 min,PBS漂洗后DAB显色,苏木素复染,梯度乙醇脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片,光镜下观察,并记录。
1.10 Western blot法检测肺组织cleaved caspase-3和Akt磷酸化水平使用RIPA裂解液及PMSF提取小鼠肺组织总蛋白,BCA法测定蛋白浓度,蛋白样品-80 ℃保存,并行聚丙烯酰氨凝胶电泳分离蛋白,湿转法转移至聚偏二氟乙烯膜(PVDF膜),5%脱脂奶粉或者5% BSA封闭1 h,分别加入cleaved caspase-3抗体(1:500)、caspase-3抗体(1:500)、p-Akt抗体(1:800)、Akt抗体(1:800)及β-actin抗体(1:5000)4 ℃孵育过夜。TBST洗膜10 min,共3次,加入相应HRP标记的二抗(1: 10 000)37 ℃孵育1 h,再以TBST洗膜10 min,共3次,最后ECL显色,凝胶成像,Quantity One软件分析各条带吸光度值。
1.11 统计学处理采用SPSS18.0统计软件进行统计学处理。计量资料据采用均数±标准差表示,组间比较采用one-way ANOVA分析,各组均数间两两比较采用SNK-q检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
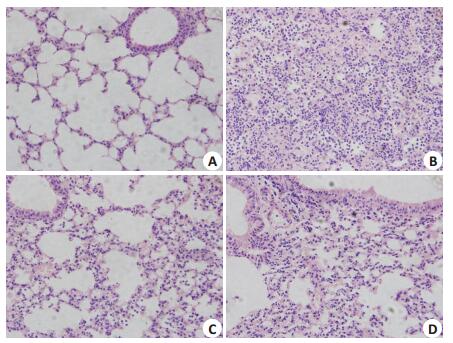
2 结果 2.1 HE染色观察肺组织病理变化对照组肺组织结构清晰,肺泡间隔无增宽,肺泡腔未见炎性细胞及渗出物;LPS组见肺泡间隔增宽,肺泡腔内及间质充血水肿明显伴大量炎性细胞浸润;Vaspin组肺组织损伤明显减轻,间隔轻度增宽,肺泡腔内出血水肿减轻,炎性细胞浸润减轻;wortmannin组病理改变介于LPS组与Vaspin之间(图 1)。
|
图 1 小鼠的肺组织病理改变 Figure 1 Pathological changes in the lung tissues (Original magnification: ×400) |
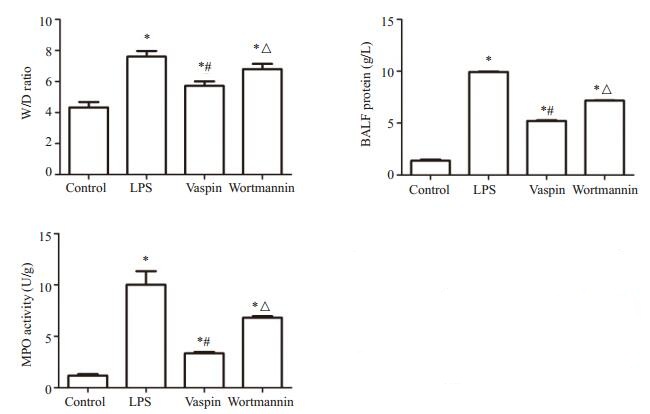
与对照组比较,LPS组、Vaspin组及wortmannin组小鼠肺组织W/D均显著增高(P < 0.05),其中Vaspin组小鼠肺组织W/D值较LPS组及wortmannin组明显减轻(P < 0.05,图 2)。
|
图 2 肺组织湿/干重比、BALF中蛋白含量及肺MPO活性的测定 Figure 2 Lung wet/dry weight (W/D) ratio, total protein level in the BALF and pulmonary MPO activity in different groups (Mean±SD, n=3 or 4). *P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group; △P < 0.05 vs Vaspin group |
与对照组比较,LPS组、Vaspin组及wortmannin组小鼠BALF中总蛋白含量明显增高(P < 0.05),其中Vaspin组BALF中总蛋白含量较LPS组和wortmannin组明显降低(P < 0.05,图 2)。
2.4 小鼠肺组织MPO活性比较与对照组比较,LPS组、Vaspin组及wortmannin组小鼠肺组织MPO活性均显著增高(P < 0.05),其中Vaspin组小鼠肺组织MPO活性较LPS组及wortmannin组明显降低(P < 0.05,图 2)。
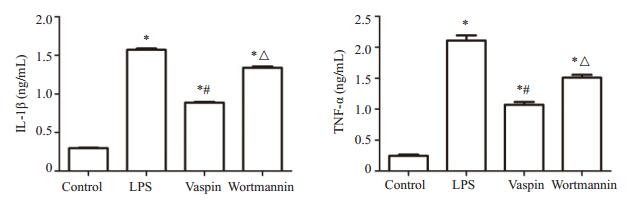
2.5 小鼠肺组织中炎症因子水平比较与对照组比较,LPS组、vaspin组及wortmannin组小鼠肺组织中IL-1β和TNF-α含量均有显著增加(P < 0.05),其中vaspin组肺组织中IL-1β和TNF-α含量较LPS组和wortmannin组均有显著降低(P < 0.05,图 3)。
|
图 3 肺组织中IL-1β含量及TNF-α含量的测定 Figure 3 Levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in the lung tissue in different groups (Mean±SD, n=4). *P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group; △P < 0.05 vs Vaspin group |
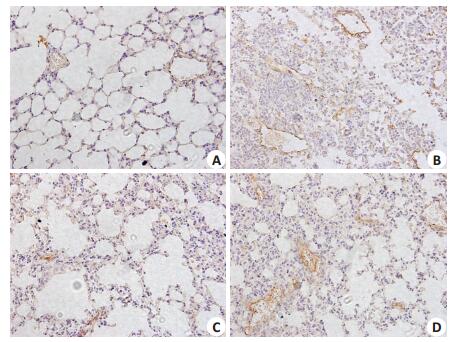
各组小鼠肺组织血管内皮细胞均呈现阳性信号(棕黄色颗粒),即各组小鼠肺组织血管内皮均表达VCAM-1蛋白,其中对照组肺血管内皮细胞染色最浅,LPS组肺血管内皮细胞染色最深,呈深棕黄色,即VCAM-1表达显著升高(P < 0.05),而vaspin干预后,染色明显变淡,即VCAM-1表达显著下调(P < 0.05,图 4)。
|
图 4 肺组织VCAM-1的表达检测 Figure 4 Expression of VCAM-1 in the lung tissue in different group (Immunohistochemical staining, × 400). A: Control group; B: LPSgroup; C: Vaspin group; D: Wortmannin group |
与对照组比较,LPS组cleaved caspase-3蛋白表达明显升高(P < 0.05),vaspin干预后,cleaved caspase-3明显下调(P < 0.05),而wortmannin组较vaspin组表达明显升高(P < 0.05);与对照组、LPS组及wortmannin组相比,vaspin组小鼠肺组织中P-Akt表达水平明显上调(P < 0.05),而LPS组、wortmannin组较对照组表达明显下调(P < 0.05,图 5、6)。
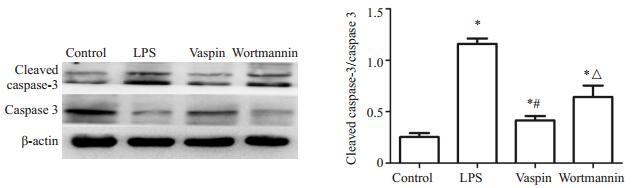
|
图 5 Cleaved caspase-3的蛋白水平检测 Figure 5 Protein level of cleaved caspase-3 in the the lung tissues in different groups determined by Western blotting (Mean ± SD, n=4). *P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group; △ P < 0.05 vs Vaspin group |
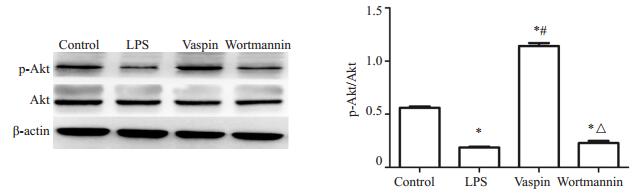
|
图 6 p-Akt的蛋白水平检测 Figure 6 Protein level of p-Akt in the lung tissues in different groups determined by Western blotting (Mean±SD, n=4). *P < 0.05 vs control group; #P < 0.05 vs LPS group; △P < 0.05 vs Vaspin group |
ARDS病死率高,治疗效果欠佳[7],虽不是典型的血管性疾病,但研究表明,肺血管内皮细胞屏障及功能障碍是ARDS的重要发病机制[8]。近年来,大量研究证实多种脂肪因子(如Adiponectin、Omentin等)对ARDS发挥保护性调控[9-10],其中新近发现的脂肪因子Vaspin因其抗炎、抗凋亡及抗氧化应激等作用对血管内皮有保护性作用[5-6, 11-12]。因此,我们通过气管插管滴注LPS建立肺内源性ARDS小鼠模型,探讨Vaspin对小鼠ARDS的保护作用。结果发现,Vaspin预处理能显著改善小鼠肺组织病理改变,并明显减轻肺水肿及降低BALF蛋白含量,说明Vaspin可减轻ARDS肺损伤并改善肺微血管通透性。MPO是中性粒细胞(PMN)聚集及活化的标志[13],研究证实PMN活化后释放多种炎症介质,包括TNF-α、IL-1β等,可引发炎症级联,诱导炎症细胞浸润,增加肺微血管通透性,最终导致肺损伤[14-15]。本实验中,Vaspin干预后肺组织MPO活性,肺组织匀浆中IL-1β和TNF-α水平均明显降低,表明Vaspin对ARDS具有抗炎保护作用。另一方面,血管细胞间粘附分子(VCAM-1)主要由血管内皮细胞表达。正常生理条件下,肺血管内皮细胞不表达或者仅少量表达VCAM-1,内毒素、促炎因子等刺激致粘附分子大量表达,介导炎性细胞与肺血管内皮细胞粘附,损伤肺内皮细胞导致内皮细胞通透性增加,进一步导致肺组织的损伤[16-17]。经Vaspin干预后,VCAM-1的表达显著降低,表明Vaspin可以直接降低粘附分子的表达,减少炎性细胞与肺内皮细胞粘附聚集,从而减轻急性肺损伤。
肺内皮细胞过度凋亡将导致肺微血管屏障完整性缺失,在ARDS发生发展过程中起重要作用[18],细胞凋亡作为细胞程序性死亡,受半胱氨酸蛋白酶(Caspase)家族的调节,其中caspase 3是多条凋亡通路的汇聚点,剪切型caspase 3(cleaved caspase-3)活化将导致细胞凋亡的发生,提示凋亡已进入不可逆阶段,检测cleaved caspase-3可间接发现细胞凋亡情况[19-20]。本实验通过对cleaved caspase-3蛋白的测定证实,vaspin干预后小鼠的cleaved caspase-3蛋白表达显著降低,提示vaspin可能对LPS致小鼠ARDS肺组织有抗凋亡保护作用。
磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)及其靶蛋白-蛋白激酶B是细胞内重要的信号传导通路,可通过影响其下游多种效应分子的活性,对细胞凋亡、增殖等发挥重要作用[21],近年来,大量体内外实验证实,PI3K/Akt信号通路在LPS诱导的急性炎症反应中发挥重要的负向调节作用[22-23],而本课题组前期实验证实上调PI3K/Akt信号通路对ARDS有保护作用[9, 24]。研究发现,vaspin可上调PI3K/ Akt信号通路对游离脂肪酸诱导的内皮细胞起抗凋亡作用[6]以及激活PI3K/Akt/eNOS信号通路缓解高糖诱导的内皮祖细胞功能紊乱[25]。因此,我们大胆假设,vaspin可通过激活PI3K/Akt通路对ARDS发挥保护性调控,本实验中LPS组p-Akt蛋白水平降低,vaspin干预可明显上调肺组织p-Akt的表达。而PI3K抑制剂渥曼青霉素能阻断vaspin的保护效应及其引起的Akt磷酸化,表明vaspin可能至少部分通过上调PI3K/Akt信号通路改善肺微血管通透性,抑制肺部炎症及肺内皮细胞凋亡,从而对肺内皮细胞起保护作用,但其具体分子机制还需进一步研究。
综上所述,Vaspin可通过其介导的抗炎及血管内皮保护效应,对ARDS肺损伤发挥保护性调控,其可能机制为激活了PI3K/Akt信号通路,为ARDS的防治提供了新思路。
| [1] |
Ranieri VM, Rubenfeld GD, Thompson B, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome the Berlin definition[J].
JAMA, 2012, 307(23): 2526-33.
|
| [2] |
Bijli KM, Fazal F, Slavin SA, et al. Phospholipase C-ε signaling mediates endothelial cell inflammation and barrier disruption in acute lung injury[J].
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2016, 311(2): L517-24.
DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00069.2016. |
| [3] |
Maniatis NA, Orfanos SE. The endothelium in acute lung injury/ acute respiratory distress syndrome[J].
Curr Opin Crit Care, 2008, 14(1): 22-30.
DOI: 10.1097/MCC.0b013e3282f269b9. |
| [4] |
Hida K, Wada J, Eguchi J, et al. Visceral adipose tissue-derived serine protease inhibitor: A unique insulin-sensitizing adipocytokine in obesity[J].
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2005, 102(30): 10610-5.
|
| [5] |
Liu S, Dong Y, Wang T, et al. Vaspin inhibited proinflammatory cytokine induced activation of nuclear factor-kappa B and its downstream molecules in human endothelial EA.hy926 cells[J].
Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2014, 103(3): 482-8.
|
| [6] |
Jung CH, Lee WJ, Hwang JY, et al. Vaspin protects vascular endothelial cells against free fatty acid-induced apoptosis through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway[J].
Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2011, 413(2): 264-9.
DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.08.083. |
| [7] |
Phua J, Badia JR, Adhikari NK, et al. Has mortality from acute respiratory distress syndrome decreased over time?: A systematic review[J].
Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2009, 179(3): 220-7.
|
| [8] |
Maniatis NA, Kotanidou A, Catravas JD, et al. Endothelial pathomechanisms in acute lung injury[J].
Vascul Pharmacol, 2008, 49(4/6): 119-33.
|
| [9] |
Wang C. Obesity, inflammation, and lung injury (OILI): the good[J].
Mediators Inflamm, 2014, 2014(1): 978463.
|
| [10] |
Qi D, Tang X, He J, et al. Omentin protects against LPS-induced ARDS through suppressing pulmonary inflammation and promoting endothelial barrier via an Akt/eNOS-dependent mechanism[J].
Cell Death Dis, 2016, 7(9): e2360.
DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2016.265. |
| [11] |
Zieger K, Weiner J, Krause K, et al. Vaspin suppresses cytokineinduced inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via inhibition of NFκB pathway[J].
Mol Cell Endocrinol, 2018, 460: 181-8.
DOI: 10.1016/j.mce.2017.07.022. |
| [12] |
Phalitakul S, Okada M, Hara Y, et al. Vaspin prevents methylglyoxal-induced apoptosis in human vascular endothelial cells by inhibiting reactive oxygen species generation[J].
Acta Physiol (Oxf), 2013, 209(3): 212-9.
|
| [13] |
Huang WC, Lai CL, Liang YT, et al. Phloretin attenuates LPSinduced acute lung injury in mice via modulation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways[J].
Int Immunopharmacol, 2016, 40: 98-105.
DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.08.035. |
| [14] |
Williams AE, José RJ, Mercer PF, et al. Evidence for chemokine synergy during neutrophil migration in ARDS[J].
Thorax, 2017, 72(1): 66-73.
DOI: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208597. |
| [15] |
Ma C, Zhu L, Wang J, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of water extract of Taraxacum mongolicum hand.-Mazz on lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in acute lung injury by suppressing PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway[J].
J Ethnopharmacol, 2015, 168: 349-55.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.03.068. |
| [16] |
Ley K. Molecular mechanisms of leukocyte recruitment in the inflammatory process[J].
Cardiovasc Res, 1996, 32(4): 733-42.
DOI: 10.1016/S0008-6363(96)00066-1. |
| [17] |
Huang YC, Horng CT, Chen ST, et al. Rutin improves endotoxininduced acute lung injury via inhibition of iNOS and VCAM-1 expression[J].
Environ Toxicol, 2016, 31(2): 185-91.
|
| [18] |
Galani V, Tatsaki E, Bai M, et al. The role of apoptosis in the pathophysiology of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): an up-to-date cell-specific review[J].
Pathol Res Pract, 2010, 206(3): 145-50.
DOI: 10.1016/j.prp.2009.12.002. |
| [19] |
Porter AG, Janicke RU. Emerging roles of caspase-3 in apoptosis[J].
Cell Death Differ, 1999, 6(2): 99-104.
|
| [20] |
Fan TJ, Han LH, Cong RS, et al. Caspase family proteases and apoptosis[J].
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai), 2005, 37(11): 719-27.
DOI: 10.1111/abbs.2005.37.issue-11. |
| [21] |
Osaki M, Oshimura M, Ito H. PI3K-Akt pathway: its functions and alterations in human cancer[J].
Apoptosis, 2004, 9(6): 667-76.
DOI: 10.1023/B:APPT.0000045801.15585.dd. |
| [22] |
Zhang Y, Li P, Gao Q, et al. 2-Methoxyestradiol prevents monocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cells via downregulation of VCAM-1 expression[J].
Gynecol Endocrinol, 2016, 32(7): 571-6.
DOI: 10.3109/09513590.2016.1141880. |
| [23] |
Schabbauer G, Tencati M, Pedersen B, et al. PI3K-Akt pathway suppresses coagulation and inflammation in endotoxemic mice[J].
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2004, 24(10): 1963-9.
|
| [24] |
Qi D, He J, Wang D, et al. 17β-estradiol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through PI3K/Akt/SGK1 mediated up-regulation of epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in vivo and in vitro[J].
Respir Res, 2014, 15(1): 159.
|
| [25] |
Sun N, Wang H, Wang L. Vaspin alleviates dysfunction of endothelial progenitor cells induced by high glucose via PI3K/Akt/ eNOS pathway[J].
Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(1): 482-9.
|
 2018, Vol. 38
2018, Vol. 38

