2. 兰州大学第二医院, 甘肃兰州 730030 ;
3. 甘肃省新药临床前研究重点实验室, 甘肃兰州 730030
2. Second Hospital of Lanzhou University, Lanzhou 730030, China ;
3. Key Lab of Preclinical Study for New Drugs of Gansu Province, Lanzhou 730030, China
类风湿关节炎(RA)是一种病因不明、以关节炎症损伤为主的慢性自身免疫性疾病,在我国RA的发病率为0.32%~0.36% [1]。其主要病变发生在滑膜,累及关节软骨、韧带、肌腱及全身组织,引起关节肿痛,继而软骨破坏、关节间隙变窄,晚期关节畸形、功能活动障碍,最终导致不同程度的残疾。
补体系统是重要的先天性固有免疫,是机体免受病原体侵害的第一道防御系统。甘露糖凝集素(MBL)是补体凝集素途径的主要蛋白质,它作为模式识别受体,通过识别病原微生物和细胞的碎片,最终激活补体系统的级联反应,补体激活产生的炎症介质参与RA的损伤过程[2]。MBL相关的丝氨酸蛋白酶-2(MASP-2)是由肝脏合成分泌的,与MBL相关的MASP有四类(MASP-1,MASP-2,MASP-3和sMAP),其中MASP-2是凝集素途径中关键蛋白酶。MBL途径激活补体过程中,MASP-2直接被激活,不需要抗原抗体的参与,被激活MASP-2能够有效的裂解C4和C2产生C3裂解酶[3-4]从而激活补体级联酶促反应[5]。MASP2基因位于1p36.3-36.2染色体,最近的研究发现RA和其它炎性自身免疫性疾病与该区域有相关性[6-7]。急性期蛋白HsCRP在体内外均能激活补体系统,血清中HsCRP的水平与RA的活动程度密切相关[8],HsCRP的水平已作为辅助诊断RA的重要参数之一。有关RA的研究目前多表现在基因多态性及基因突变方面,对于同时检测血清中MBL、MASP-2水平国内尚未见报道。本文通过检测RA患者血清中的MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3的水平,研究它们在RA疾病中的意义,为揭示RA的发生机制及其诊治提供实验依据。
1 资料和方法 1.1 临床资料RA患者50例(活动期25例和非活动期25例),为2015年2月~2015年11月来我院就诊的住院病人,其中男5例,女45例,年龄23~81岁,平均年龄50.54±14.26岁,均符合欧洲风湿病联盟和美国风湿病学会类风湿关节炎的诊断标准(2010年),并排除其他自身免疫性病、感染等疾病。健康人群40名,男18例,女22例,年龄25~66岁,平均年龄46.60±11.89岁,排除标准:(1)有严重心、肝、肾等重要脏器和血液、内分泌系统病史者;(2)孕妇、哺乳期妇女;(3)无急慢性感染性疾病;(4)恶性肿瘤患者;(5)无糖皮质激素及免疫调节药应用史;(6)无免疫疾病史和严重感染史。
1.2 主要试剂MBL、MASP-2定量分析试剂盒(ELISA)购自加拿大ELIXIR医药公司;HsCRP检测试剂盒(免疫比浊法)购自德国罗氏诊断有限公司;MBL/MASP-2检测用德国Berthold公司Multimode Microplate Reader仪。
1.3 检测方法 1.3.1 血清MBL、MASP-2含量测定方法采集检测者晨起空腹静脉血4.0 mL,分离血清,保存于-80 ℃待测。MBL和MASP-2含量的检测均采用竞争性抑制酶联免疫吸附法。所有血清标本溶解并恢复至室温,3500 r/min离心10 min,取上清液10 μL,用生理盐水加以稀释。具体操作步骤严格按试剂盒说明进行操作,酶标仪450/630 nm双波长测吸光度(A)值,根据标准浓度及测得OD值,换算出血清MBL和MASP-2的浓度。
1.3.2 血清HsCRP、C3含量测定方法两者均采用免疫比浊法,人血清HsCRP和补体C3可与比浊法试剂中特异性抗血清形成沉淀物,用COBAS8000全自动生化分析仪对血清直接进行稀释检测,自动计算出每份样本的分析物浓度。
1.3.3 统计学分析应用SPSS 19.0统计软件进行统计分析,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,组间均数比较采用t检验,检验水准设在P=0.05,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。以Pearson积距相关分析MBL与MASP-2、HsCRP、C3变量之间的相关性。
2 结果 2.1 RA患者和健康人群的一般资料所有群体均来自于兰州大学第二医院住院患者和健康体检者,常规检查(表 1)包括:血压,血糖,血脂,血沉(ESR)和抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体(Anti-CCP)。
| 表 1 RA患者和健康人群的一般资料特征 Table 1 General demographic and clinical data of the patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and healthysubjects |
检测MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3 4组数据均符合正态分布,组间比较采用t检验,P < 0.05有统计学意义。与健康对照组相比较,MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP指标均有显著性差异。尤其以活动期较为显著(P < 0.001);C3组间无差异(表 2,图 1)。
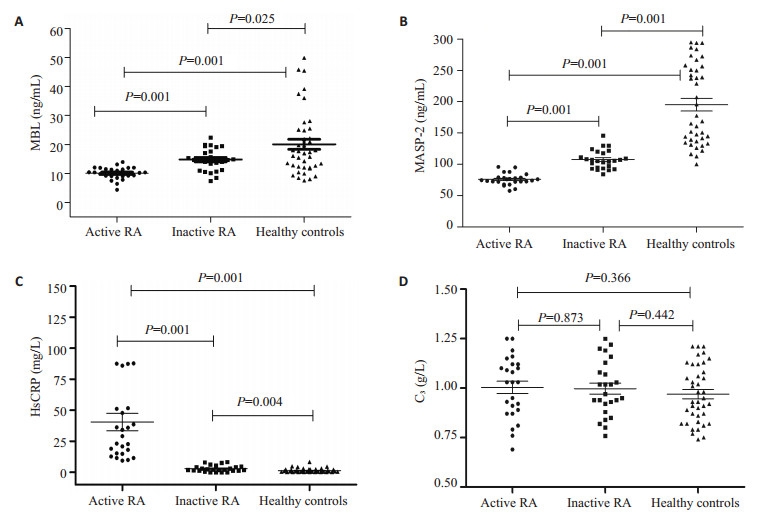
|
图 1 RA组与健康对照组血清MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3水平比较 Figure 1 Comparison of serum MBL (A), MASP-2 (B), HsCRP (C), and C3 (D) levels in RA patients and healthy control group. |
| 表 2 RA患者和健康对照组血清MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3水平比较 Table 2 Serum levels of MBL, MASP-2, HsCRP, and C3 in RA patients and healthy subjects (Mean±SD) |
RA组MBL与MASP-2、HsCRP、C3相关性分析(图 2),经双变量Pearson相关性分析得出RA组MBL与MASP-2含量呈显著正相关(r=0.550、P=0.001);与HsCRP含量呈低度负性相关(r=-0.323,P=0.022);与C3含量无相关(r=0.022,P=0.882)。RA组MASP-2与HsCRP含量呈低度负性相关(r=-0.453,P=0.001);与C3含量无相关(r=0.049,P=0.738)。
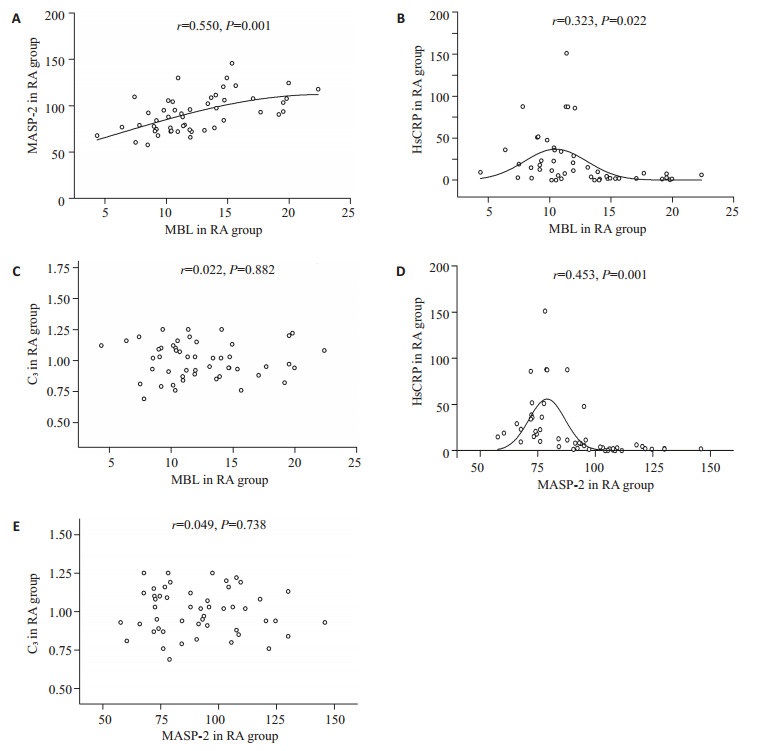
|
图 2 RA组血清MBL与MASP-2、HsCRP、C3含量的相关性分析 Figure 2 Correlation among serum levels of MBL, MASP-2, HsCRP, and C3 in RA patients. A: Correlation between MBL and MASP-2; B: Correlation between MBL and HsCRP; C: Correlation between MBL and C3; D: Correlation between MASP-2 and HsCRP; E: Correlation between MASP-2 and C3. |
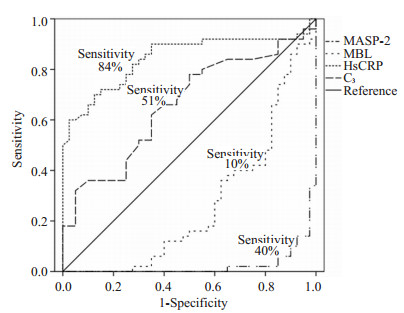
|
图 3 RA组血清MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3的ROC曲线 Figure 3 ROC curve of serum MBL, MASP-2, HsCRP and C3 in RA group. |
分别以MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3为检验变量,进行ROC曲线分析,以1-特异度为横轴,灵敏度为纵轴,SPSS软件绘制ROC曲线并计算最佳界值。MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3曲线下面积分别为0.266、0.025、0.844、0.663,其拥有诊断RA的显著性分别为P=0.001、P=0.001、P=0.001、P=0.009。公式:尤登指数=敏感性+特异性-1,求得MBL、MASP-2、HsCRP和C3的尤登指数分别为-0.8,-0.275,0.54,0.26,最佳界值(cutoff值)分别是12.96、121.74、1.57、1.05 mg/L。虽然4个指标均有统计学意义,但血清HsCRP的ROC曲线下面积大于0.5,对RA的诊断更具有意义,而血清MBL和MASP-2的ROC曲线下面均小于0.5,不能作为辅助RA诊断及其活动度评价的的独立因素。
3 讨论MBL是由肝脏合成的C型凝集素样急性时相期蛋白,它通过结合病原微生物表面的甘露糖、N-乙酰氨基葡萄糖等糖基配体而直接介导调理吞噬作用,或通过凝集素途径激活补体系统,从而在机体的天然免疫防御中发挥重要作用[9, 18]。本研究选取的实验对象包括RA活动期、非活动期和健康对照人群的年龄大致相似,健康人群性别比按男女约1:1匹配。RA活动期及非活动期判断依据为中华医学会编著临床诊疗指南(风湿病分册)[10],主要指征有晨僵、关节压痛、肿胀,炎性指标有ESR、CRP等。血清MBL缺乏,增加了细菌、病毒感染和RA的风险,它与免疫调节和炎症复发的敏感性有关。Yang等[11]研究发现RA患者血清及滑膜液中补体C3、C4及免疫复合物增加,表明补体系统参与RA发生过程。近年来研究表明[8, 12],补体系统和HsCRP在RA发病机制中起重要作用,检测血清中的补体和HsCRP对RA的疗效及预后的判断有一定的临床意义。Ip WK等研究表明[13]:香港南部地区人群中MBL基因表型和等位基因的变异中发现,低水平的MBL可诱发RA的发展,是导致该疾病严重的独立的危险因素之一。研究显示[13-14],RA患者血清MBL水平与健康对照组比较显著性降低,差异有显著性,血清MBL缺乏可能是发生RA危险因素之一。有研究表明巴西人群MBL2多态性与MBL血清水平与RA的易感性具有显著相关性, 对RA患者进行治疗时必需考虑MBL水平[15]。侯玲等[16]研究了宁夏回族MBL基因突变与RA相关性,MBL52C/T位的等位基因可能参与RA的发生。我们研究的目的是通过检测兰州地区RA患者血清中MBL、MASP-2水平,来推测MBL途径是否参与了RA病情的发展。结果表明MBL含量显著降低(P=0.001),可能与RA患者体内MBL参与凝集素途径的激活,导致其大量消耗使血清水平降低,表明MBL参与RA发生发展的损伤过程。Goeldner等[17]研究中发现血清MASP-2水平活性下降是受基因突变的影响,MASP-2基因单倍体2A1和2B1-i发生变异者,RA易感性明显增加。MASP-2的基因突变(GAC120GGC)导致编码产物由Asp变为Gly,该突变使得MBL及纤维蛋白胶凝素与MASP-2蛋白的结合能力下降,阻碍了MBL途径的激活[18],引起病原体的反复感染。我们的研究显示,与健康对照组比较MASP-2水平在RA活动期和非活动期均显著性下降(P < 0.01),以活动期下降更为显著。表明MASP-2水平的下降可能与RA患者病情进展相关,MASP-2水平的下降并非合成降低,而是消耗增加。
在一般资料中,RA患者和健康人群中血沉(ESR)和抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体(Anti-CCP)均升高,与健康组比较有显著性差异(P=0.001),表明在炎症状态下血浆中的球蛋白和纤维蛋白原的变化,使得血沉加速。Anti-CCP是RA早期诊断指标,Kim等[19]研究发现Anti-CCP阳性患者出现严重的关节损坏明显多于阴性患者,表明抗CCP抗体与疾病的活动度相关。HsCRP是组织损伤时血浆中急剧上升的急性蛋白,在机体的天然免疫过程中发挥着重要的保护作用,是组织损伤和感染后监测炎症和感染的常规参数。我们的结果显示:RA患者血清中C3水平升高,但无统计学差异(P> 0.05)。表明在严重RA患者中,补体合成减少与消耗增加,RA患者可表现补体水平的减低。
RA患者对关节的损伤程度越重,MBL与MASP-2水平和活性越低,表明MBL、MASP-2参与MBL途径活化补体。MBL途径在RA的早期诊断中具有参考意义,MBL、MASP-2水平的检测不能作为疾病活动程度的评价指标,可作为预测疾病病情发展的依据之一。HsCRP是炎症和组织损伤的灵敏性指标,在RA活动期急剧增高。ESR、Anti-CCP是RA早期诊断及预后的重要指标。相关性分析表明RA患者血清MBL水平与MASP-2呈显著正相关;检测血清中MBL、MASP-2水平对RA的早期诊断有一定的参考意义。经ROC曲线分析,血清HsCRP的ROC曲线下面积最大,对RA的诊断更具有意义,而血清MBL、MASP-2水平ROC曲线下面积较小,对RA的诊断仅有一定的参考意义。
| [1] | 葛均波, 徐永健. 内科学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2013 : 808 -14. |
| [2] | Boschmann SE, Goeldner I, Tuon FF, et al. Mannose-binding lectin polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis:A short review and meta-analysis[J]. Mol Immunol,2016, 69 (6) : 77-85. |
| [3] | Thiel S, Vorup-Jensen T, Stover CM, et al. A second serine protease associated with mannan-binding lectin that activates complement[J]. Nature,1997, 386 (6624) : 506-10. DOI: 10.1038/386506a0. |
| [4] | Moller-Kristensen M, Thiel S, Sjoholm AA, et al. Cooperation between MASP-1 and MASP-2 in the Generation of C3 convertase through the MBL pathway[J]. Int Immunol,2007, 19 (2) : 141-9. |
| [5] | Ricklin D, Hajishengallis G, Yang K, et al. Complement:a key system for immune surveillance and homeostasis[J]. Nat Immunol,2010, 11 (9) : 785-97. DOI: 10.1038/ni.1923. |
| [6] | Lopez Herraez D, Martinez-Bueno M, Riba LA, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis in Latin americans enriched for amerindian ancestry is associated with loci in chromosomes 1, 12, and 13, and the HLA class II region[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2013, 65 (6) : 1457-67. DOI: 10.1002/art.37923. |
| [7] | Jostins L, Ripke S, Weersma RK, et al. Host-microbe interactions have shaped the genetic architecture of inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Nature,2012, 491 (7422) : 119-24. DOI: 10.1038/nature11582. |
| [8] | Hiura K, Iwaki-Egawa S, Kawashima TA, et al. The diagnostic utility of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein for predicting rheumatoid arthritis in anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody-negative patients with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis[J]. Rheumatol Int,2013, 33 (9) : 2309-14. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-013-2716-1. |
| [9] | Taylor ME, Brickell PM, Craig RK, et al. Structure and evolutionary origin of the gene encoding a human serum mannose-binding protein[J]. Biochem J,1989, 262 (3) : 763-71. DOI: 10.1042/bj2620763. |
| [10] | 中华医学会. 临床诊疗指南-风湿病分册[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005 : 6 -8. |
| [11] | Yang X, Gao F, Liu Y. Association of homocysteine with immunological inflammatory and metabolic laboratory markers and factors in relation to hyperhomocysteinaemia in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol,2015, 33 (6) : 900-3. |
| [12] | Sumiya M, Super M, Tabona P, et al. Molecular basis of opsonic defect in immunodeficient children[J]. Lancet,1991, 337 (8757) : 1569-70. DOI: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)93263-9. |
| [13] | Ip WK, Lau YL, Chan SY, et al. Mannose-binding lectin and rheumatoid arthritis in southern Chinese[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2000, 43 (8) : 1679-87. DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131. |
| [14] | Saevarsdottir S, Ding B, Steinsson K, et al. Mannan binding lectin (MBL) genotypes coding for high MBL serum levels are associated with rheumatoid factor negative rheumatoid arthritis in never smokers[J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2011, 13 (2) : R65. |
| [15] | Goeldner I, Skare TL, Utiyama SR, et al. Mannose binding lectin and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in Brazilian patients and their relatives[J]. PLoS One,2014, 9 (4) : e95519. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095519. |
| [16] | 侯玲, 杨冬华, 徐金瑞. MBL基因突变与宁夏地区类风湿性关节炎的相关性研究[J]. 现代预防医学,2013, 40 (14) : 2710-3. |
| [17] | Goeldner I, Skare T, Boldt AB, et al. Association of MASP-2 levels and MASP2 gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in patients and their relatives[J]. PLoS One,2014, 9 (3) : e90979. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090979. |
| [18] | Stengaard-Pedersen K, Thiel S, Gadjeva M, et al. Inherited deficiency of mannan-binding lectin-associated serine protease 2[J]. N Engl J Med,2003, 349 (6) : 554-60. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa022836. |
| [19] | Kim HH, Kim J, Park SH, et al. Correlation of anti-cyclic citrullinated antibody with hand joint erosion score in rheumatoid arthritis patients[J]. Korean J Intern Med,2010, 25 (2) : 201-6. DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2010.25.2.201. |
 2016, Vol. 36
2016, Vol. 36
