常用的静脉麻醉药丙泊酚对宫颈癌、纤维肉瘤、骨肉瘤、黑色素瘤、结肠癌、乳腺癌等多种肿瘤细胞的侵袭力有抑制作用[1-3]。水通道蛋白家族(AQPs)是一类介导跨膜水运输的内在蛋白[4],其中AQP-3在非小细胞肺癌(NSCLC)和肺腺癌细胞中高表达[5-6]。基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)是一类以无活性酶原形式分泌的Zn2+±赖的肽链内切酶,其中MMP-9即明胶酶B被认为是肺癌细胞侵袭和转移的重要分子,在NSCLC患者的血清、肺组织中MMP-9 高表达[7-9]。研究表明,丙泊酚能抑制肺癌A549细胞AQP-1的表达,抑制其生长和迁移[10];AQP-3可参与早期肺腺癌发展过程、调节肺癌细胞生物学功能[11]。丙泊酚对A549细胞AQP-3和MMP-9表达的影响尚不清楚。本研究通过观察丙泊酚对人肺癌A549细胞侵袭力及AQP-3、MMP-9 的影响,探讨丙泊酚对A549细胞的作用及机制。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料 1.1.1 实验细胞人肺腺癌A549细胞来源于南方医科大学珠江医院肿瘤科实验室,A549细胞用10%胎牛血清DMEM/F12培养基,在37℃、5% CO2恒温培养箱培养,每2~3d换液。选择对数生长期的A549细胞用于实验。
1.1.2 主要试剂DEME/F12 培养基购于HyClone,胎牛血清购于Gibco,PCR引物由上海英潍捷基公司合成,β-actin、AQP-3 抗体购自Abcam;MMP-9 抗体购自CST,山羊抗兔IgG二抗购于Jackson,丙泊酚纯品、二甲基亚砜(DMSO)、CuSO4 分析纯级购于Sigma,Transwell小室和Matrix基质胶购于Corning。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 实验分组实验分6组:空白对照组(C组),加入等体积的PBS;DMSO溶剂组(D组),加入同体积的DMSO溶剂,总浓度不超过0.1%;丙泊酚分为25 μmol/L(P25组)、50 μmol/L(P50组)、100 μmol/L(P100组);AQP-3抑制剂CuSO4组(Cu组500μmol/L。
1.2.2 荧光定量PCR检测AQP-3 mRNA按丙泊酚作用时间和剂量分为10组:时间分组为12 h组和24 h组,剂量分组为C组、D组、P25组、P50组、P100组。细胞株传代培养3 d,加药物刺激作用后收集细胞。用RNA提取试剂盒提取细胞总RNA,取1 μg RNA进行逆转录42℃,2min。取适量cDNA产物进行荧光定量PCR,扩增条件95 ℃持续5 s,60 ℃持续60s,共40个循环。PCR引物序列从GeneBank 数据库中查找:AQP-3 上游引物${{5}^{'}}$-TCAATGGCTTCTTTGACCAGTTCA-${{3}^{'}}$,下游引物${{5}^{'}}$-CTTCACATGGGCCAGCTTCACATT-${{3}^{'}}$;β-actin上游引物${{5}^{'}}$-CATGTACGTTGCTATCCAGGC-${{3}^{'}}$,下游引物${{5}^{'}}$-CTCCTTAATGTCACGCACGAT-${{3}^{'}}$。以β-actin作为内参基因,计算AQP-3 mRNA 的相对表达量(β-actin/AQP-3),用2-ΔΔCT来评价目标mRNA的表达水平。β-actin可用来校加样误差。
1.2.3 Western Blot检测AQP-3和MMP-9蛋白按上述丙泊酚作用时间和剂量分为10组,加500 μmol/LCuSO4 2 h处理组(Cu组)。收集处理过的细胞,提取总蛋白,BCA 法测蛋白浓度,计算上样量。制备12%SDS-PAGE凝胶,每孔加50 μg蛋白样品,进行电泳。转膜后,5%脱脂奶粉封闭1 h,1%TBST洗膜3次,加入一抗AQP-3(1∶200)、MMP-9(1∶500)、β-actin(1∶1000),共同孵育4 ℃恒温过夜。洗膜后于左右摇床上室温孵育二抗(山羊抗兔抗体:1∶3000),2 h。采用ECL发光试剂盒发光、显影,使用凝胶图像分析系统采集图像,图像采集后使用Image J软件处理系统分析目标条带的光密度值。
1.2.4 Transwell小室检测细胞侵袭力饥饿A549细胞24 h后,按上述实验分组处理细胞,消化收集,调整细胞悬液浓度为5×105/mL。每个上室加入200 μL细胞悬液,下室加入含10%胎牛血清的培养基,放入37 ℃,5%CO2的细胞培养箱中孵育24 h。用棉签擦去上室内面的细胞和基质胶,无水甲醇固定20 min,PBS洗涤,风干后0.1%结晶紫染色细胞20 min,PBS洗涤3~4次。棉签擦净残留在小室内壁的细胞和液体,静置待小室风干。将Transwell 小室膜朝上,在200倍镜的正置显微镜下观察,随机选5个视野,计数细胞数。
1.2.5 统计学方法用SPSS 20.0统计软件分析,计量资料以均数±标准差表示。实验结果数据采用单因素方差分析。组间两两比较:方差齐采用LSD分析,方差不齐用Dunnet${{\text{t}}^{'}}$sT3分析。P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 丙泊酚对A549细胞AQP-3 mRNA和蛋白表达的影响AQP-3 mRNA变化与C组的比值分别为:D12h组0.91±0.015,D24h组0.78±0.020,P25~12h组0.65±0.027,P25~24h组0.41±0.031,P50~12h组0.52±0.047,P50~24h组0.25±0.071,P100~12h组0.19±0.027,P100~24h组0.13±0.035。除D12h组,其余组与空白组比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 1A)。AQP-3蛋白表达变化与空白组的比值分别为:D24 h组0.78±0.025,P25~24 h组0.91±0.009,P50~24 h组0.60±0.020,P100~24 h组0.57±0.006,Cu组0.51±0.074。与空白组比较各组差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 1B,图 C)。P50~24 h组、P100~24 h组和Cu组AQP-3蛋白表达明显下降,3者间无显著性差异。
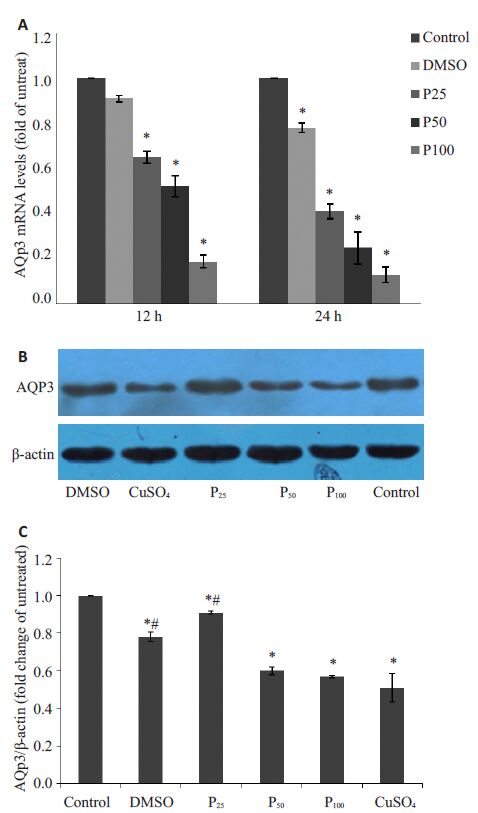
|
图 1 丙泊酚对A549细胞AQP-3 mRNA和蛋白表达的影响 Figure 1 Effect of propofol on AQP-3 expressionin A549 cells.A: AQP-3 mRNA expression in A549 cells; B, C: AQP-3protein expression in A549 cells treated with propofol for24 h. *P<0.05 vs control cells; #P<0.05 vs CuSO4 group. |
与空白组比较,D组(1.28±0.011)和P25~24 h组(1.12±0.014)MMP-9 蛋白表达有所增加。P50~24 h组(0.65 ±0.006)、P100~24 h组(0.46±0.021)MMP-9蛋白水平较对照组相比表达量有显著下降(P<0.05),两处理组间差异有统计学意义。并且与Cu组(0.94±0.023)比较,P50~24 h组、P100~24 h组对A549 细胞MMP-9蛋白表达抑制作用明显增加,且差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 2)。
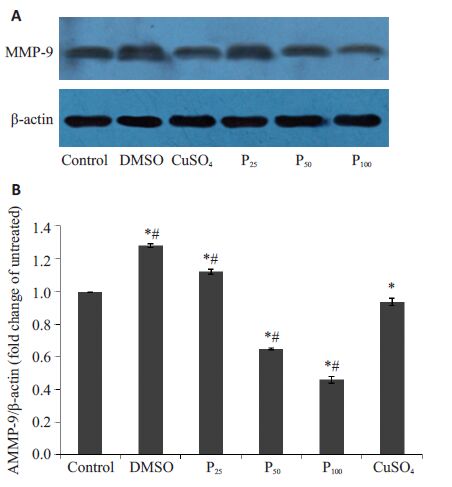
|
图 2 丙泊酚对A549细胞MMP-9蛋白表达的影响 Figure 2 Effect of propofol on MMP-9 protein expression in A549 cells. A: Protein expression of MMP-9 in A549 cells treated with propofol for 24 h measured by Western blotting; B: Quantitative analysis of MMP-9 protein level in A549 cells treated with propofol for 24 h. *P<0.05 vs control group; #P<0.05 vs CuSO4 group |
不同浓度丙泊酚处理24 h对A549细胞的侵袭力均有抑制作用。随丙泊酚作用浓度增加,其对侵袭力的抑制增强。A549 细胞各实验组穿膜数分别为C 组199.33±23.88,D组146.22±14.82,P25组122.55±17.20,P50组96.33±5.82,P100组74.33±2.85。细胞侵袭抑制比值分别为:D组73.36%、P25组61.48%、P50组48.33%、P100组37.29%。各处理组和对照组比较差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 3)。
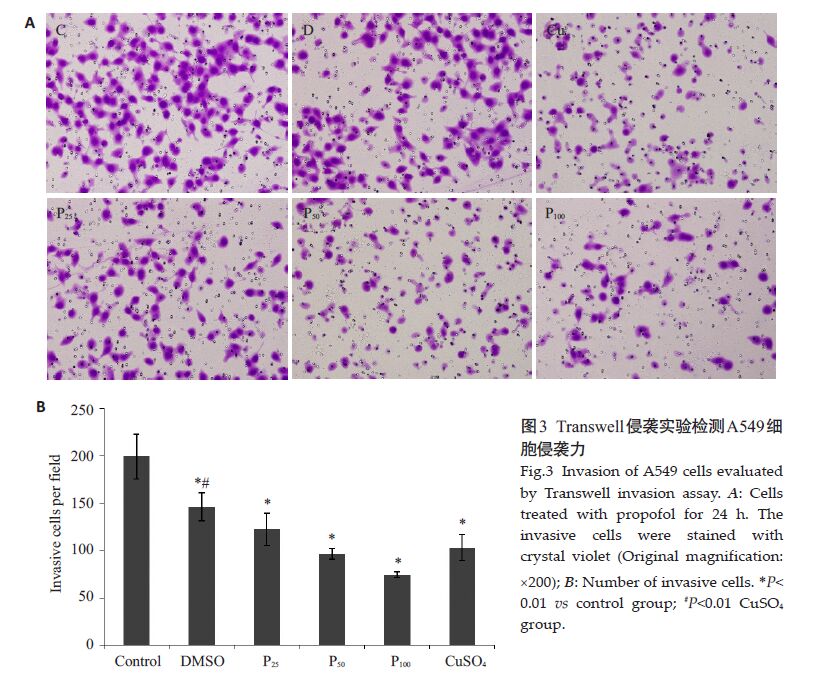
|
图 3 Transwell侵袭实验检测A549细胞侵袭力 Figure 3 Invasion of A549 cells evaluated by Transwell invasion assay. A: Cells treated with propofol for 24 h. The invasive cells were stained with crystal violet (Original magnification: ×200); B: Number of invasive cells. *P<0.01 vs control group; #P<0.01 CuSO4 group. |
Cu组使用500 μmol/L CuSO4,处理2 h,Transwell实验C组和Cu组穿膜细胞数分别为199.33±19.75 和103.11±13.68,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 3)。
2.5 CuSO4对A549 细胞AQP-3和MMP-9蛋白表达的影响Cu组AQP-3 和MMP-9 蛋白表达与空白组比较,分别为0.51±0.074 和0.94±0.023,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05,图 4)。
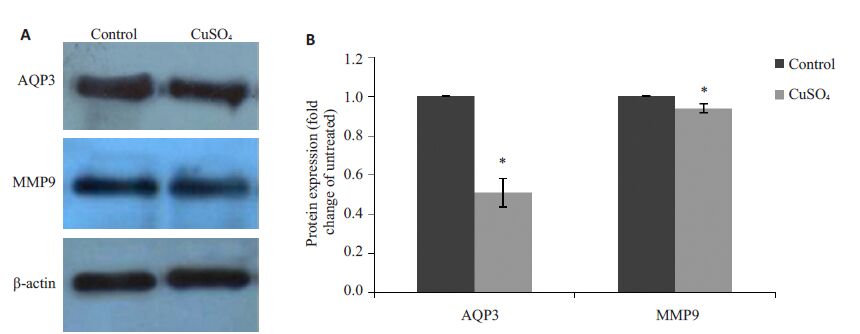
|
图 4 CuSO4对A549细胞AQP-3、MMP-9蛋白表达的影响 Figure 4 Effect of CuSO4 on protein expression of AQP-3 and MMP-9 in A549 cells. A: Results of Western blotting; B: Quantitative analysis of AQP-3 and MMP-9 protein level in A549 cells. *P<0.05 vs control group. |
AQPs是一类跨膜转运通道蛋白,根据其通透性不同分为水通道和水-甘油通道两类,AQP-3 属于后者。AQPs与肿瘤细胞的增殖、侵袭迁移力和血管生成有密切关系[12]。在NSCLC中尤其是肺腺癌和高分化乳头状支气管肺泡癌中,AQP-3高表达[5, 11-12]。研究表明,丙泊酚通过降低AQPs的表达,发挥其器官保护作用:丙泊酚可减少AQP-4、MMP-9及pJNK的表达,减缓脑缺血再灌注损伤[13];可以减少神经胶质瘤术后脑水肿患者AQP-4 的表达[14];还可下调LPS引起的AQP-2、TNF-α和ICAM-1的表达,对内毒素引起的肺损伤和肾损伤有保护作用[15]。另有研究发现,丙泊酚能抑制A549肿瘤细胞AQP-1的表达,对A549细胞的生长、迁移有明显抑制作用,并诱导肿瘤细胞的凋亡[10];AQP-3可能参与早期肺腺癌发展过程、调节肺癌细胞生物学功能[11]。迄今,丙泊酚对A549肿瘤细胞(非小细胞肺癌)AQP-3作用的影响,尚未明确。本研究,采用体外培养人肺腺癌A549 细胞株,测定不同浓度和作用时间的丙泊酚对A549细胞AQP-3 mRNA和蛋白表达的影响。结果发现,12 h和24 h丙泊酚低、中、高剂量组AQP-3 mRNA表达均明显减少,24 h丙泊酚低、中、高剂量组AQP-3蛋白表达均明显减少,表明丙泊酚对人肺癌A549 细胞AQP-3的表达有抑制作用,且呈时间-剂量依赖性。
MMPs可以降解、破坏基底膜和细胞外基质(ECM),促进血管表面生长因子的释放参与肿瘤血管形成和肿瘤生长[16],其中MMP-2和MMP-9与多种肿瘤的侵袭转移关系最为密切[17]。MMP-9以酶原形式分泌至胞外,主要存在于单核-巨噬细胞内,在恶性细胞株中的表达增加与肿瘤细胞的转移能力相关[18]。MMP-9被认为是肺癌细胞侵袭和转移的重要分子,NSCLC患者的血清、肺组织中MMP-9水平显著增高[7-8]。抑制肺癌细胞MMP-9的表达,能够减少肺癌早期转移并且可破坏肿瘤的脉管系统,达到抗肿瘤的作用[19]。Meta分析表明,非小细胞肺癌MMP-9免疫组化染色结果阳性的患者5年生存率低于结果阴性者[9],提示MMP-9在NSCLC患者预后中的重要作用。本研究,中、高剂量丙泊酚组(50、100 μmol/L)MMP-9蛋白表达明显减少,表明丙泊酚可以抑制人肺癌A549细胞MMP-9蛋白表达,然低剂量丙泊酚组(25 μmol/L)的MMP-9蛋白表达较C组增加。有研究报道,丙泊酚34 μmol/L可以促进人乳腺癌MDA-MB-468 细胞迁移[20];丙泊酚0~40 μmol/L呈剂量-时间±赖性促进胆囊癌GBC-SD细胞增殖、侵袭,并抑制细胞凋亡[21];低剂量(15、20、25 μg/mL)丙泊酚处理24 h对A549细胞MMP-9蛋白表达为促进作用,而处理48 h为抑制作用[22]。可见,中、高剂量的丙泊酚对肿瘤细胞侵袭力的抑制作用更确切,低剂量的丙泊酚对肿瘤细胞侵袭转移能力的影响有待进一步验证。除剂量因素外,丙泊酚对不同肿瘤细胞侵袭转移能力的影响是否不同,值得探讨。
对其作用机制的研究发现,敲除人非小细胞肺癌A549细胞的AQP-3基因,可以通过AKT/MMPs途径降低肺癌细胞的侵袭力,并且AQP-3表达下调能抑制肿瘤细胞甘油摄取和线粒体ATP生成[23];可以延迟肿瘤细胞的生长,可能与阻止HIF-1α/VEGF和Raf/MEK/ERK信号通路有关[24]。本研究表明,丙泊酚50、100 μmol/L处理24 h,可下调人肺癌A549 细胞AQP-3 mRNA、AQP-3 蛋白和MMP-9 蛋白的表达,抑制A549 细胞的侵袭力。但是,丙泊酚是否通过下调AQP-3表达影响AKT和ERK信号通路,从而抑制人肺癌A549 细胞的MMPs表达和细胞侵袭力,其作用机制还有待深入研究。CuSO4 是AQP-3 特异性抑制剂[25],500 μmol/LCuSO4作用2 h可明显抑制肿瘤细胞的侵袭力和AQP-3的蛋白表达[26-30]。本实验CuSO4组明显减少肺腺癌A549细胞AQP-3和MMP-9蛋白的表达,对A549细胞的侵袭力有明显的抑制作用,进一步说明通过减少肺癌A549细胞的AQP-3表达可以抑制MMP-9表达和肿瘤细胞的侵袭力。
本研究表明,50、100 μmol/L丙泊酚可下调人肺腺癌A549细胞AQP-3和MMP-9的表达,抑制A549细胞的侵袭,为肿瘤手术患者麻醉方式和药物的选择提供实验±据。关于丙泊酚下调A549细胞AQP-3和MMP-9表达的具体机制、通路,以及丙泊酚对肿瘤转移机制的动物实验、临床观察,均值得进一步探讨。
| [1] |
Song J, Shen Y, Zhang J, et al. Mini profile of potential anticancer properties of propofol[J].
PLoS One,2014, 9 (12) : e114440.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0114440. ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
Mammoto T, Mukai M, Mammoto A, et al. Intravenous anesthetic, propofol inhibits invasion of cancer cells[J].
Cancer Lett,2002, 184 (2) : 165-70.
DOI: 10.1016/S0304-3835(02)00210-0. ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
Garib V, Niggemann B, Z?nker KS, et al. Influence of non-volatile anesthetics on the migration behavior of the human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-468[J].
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand,2002, 46 (7) : 836-44.
DOI: 10.1034/j.1399-6576.2002.460714.x. ( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
Denker BM, Smith BL, Kuhajda FP, et al. Identification, purification, and partial characterization of a novel Mr 28 000 integral membrane protein from erythrocytes and renal tubules[J].
J Biol Chem,1988, 263 (30) : 15634-42.
( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
Warth A, Muley T, Meister M, et al. Loss of aquaporin-4 expression and putative function in non-small cell lung cancer[J].
BMC Cancer,2011, 11 (3) : 161.
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
Machida Y, Ueda Y, Shimasaki M, et al. Relationship of aquaporin 1, 3, and 5 expression in lung cancer cells to cellular differentiation, invasive growth, and metastasis potential[J].
Hum Pathol,2011, 42 (5) : 669-78.
DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2010.07.022. ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
Iniesta P, Morán A, De Juan C, et al. Biological and clinical significance of MMP-2, MMP-9, TIMP-1 and TIMP-2 in non-small cell lung cancer[J].
Oncol Rep,2007, 17 (1) : 217-23.
( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
Leinonen T, Pirinen R, B?hm J, et al. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases 7 and 9 in non-small cell lung cancer. Relation to clinicopathological factors, beta-catenin and prognosis[J].
Lung Cancer,2006, 51 (3) : 313-21.
DOI: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2005.11.002. ( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
Peng WJ, Zhang JQ, Wang BX, et al. Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in patients with non-small cell lung cancer[J].
Clin Chim Acta,2012, 413 (13/14) : 1121-6.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
赵佳, 刘东雷, 杨洋, 等. 丙泊酚对肺癌A549细胞凋亡的影响及其机 制[J].
中华实验外科杂志,2015, 32 (4) : 792-4.
( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
Liu YL, Matsuzaki T, Nakazawa T, et al. Expression of aquaporin 3 (AQP3) in normal and neoplastic lung tissues[J].
Hum Pathol,2007, 38 (1) : 171-8.
DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2006.07.015. ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
Wang J, Feng L, Zhu Z, et al. Aquaporins as diagnostic and therapeutic targets in cancer: how far we are[J].
? J Transl Med,2015, 13 (4) : 96.
( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
Ji FT, Liang JJ, Miao LP, et al. Propofol postconditioning protects the blood brain barrier by decreasing matrix metalloproteinase9 and aquaporin4 expression and improves the neurobehavioral outcome in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemiareperfusion injury[J].
Mol Med Rep,2015, 12 (2) : 2049-55.
( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
Yang WC, Zhou LJ, Zhang R, et al. Effects of propofol and sevoflurane on aquaporin-4 and aquaporin-9 expression in patients performed gliomas resection[J].
Brain Res,2015, 1622 (8) : 1-6.
( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
Cui WY, Tian AY, Bai T. Protective effects of propofol on endotoxemia-induced acute kidney injury in rats[J].
Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol,2011, 38 (11) : 747-54.
DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2011.05584.x. ( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
Jodele S, Chantrain CF, Blavier L, et al. The contribution of bone marrow-derived cells to the tumor vasculature in neuroblastoma is matrix metalloproteinase-9 dependent[J].
Cancer Res,2005, 65 (8) : 3200-8.
( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
方伟岗, 李红梅, 孔灵玲, 等. 肿瘤侵袭转移过程中基质金属蛋白酶作 用机制系列研究[J].
北京大学学报: 医学版,2003, 35 (4) : 441-3.
( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
Baruch RR, Melinscak H, Lo J, et al. Altered matrix metalloproteinase expression associated with oncogene-mediated cellular transformation and metastasis formation[J].
Cell Biol Int,2001, 25 (5) : 411-20.
DOI: 10.1006/cbir.2000.0647. ( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
Rao JS, Gondi C, Chetty C, et al. Inhibition of invasion, angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis by adenovirusmediated transfer of antisense uPAR and MMP-9 in non-small cell lung cancer cells[J].
Mol Cancer Ther,2005, 4 (9) : 1399-408.
DOI: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0082. ( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
Garib V, Lang K, Niggemann B, et al. Propofol-induced Calcium signalling and actin reorganization within breast carcinoma cells[J].
Eur J Anaesthesiol,2005, 22 (8) : 609-15.
DOI: 10.1017/S026502150500102X. ( 0) 0)
|
| [21] |
Zhang L, Wang N, Zhou S, et al. Propofol induces proliferation and invasion of gallbladder cancer cells through activation of Nrf2[J].
J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2012, 31 (8) : 66.
( 0) 0)
|
| [22] |
Wu KC, Yang ST, Hsia TC, et al. Suppression of cell invasion and migration by propofol are involved in down-regulating matrix metalloproteinase-2 and p38 MAPK signaling in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma epithelial cells[J].
Anticancer Res,2012, 32 (11) : 4833-42.
( 0) 0)
|
| [23] |
Xia H, Ma YF, Yu CH, et al. Aquaporin 3 knockdown suppresses tumour growth and angiogenesis in experimental non-small cell lung cancer[J].
Exp Physiol,2014, 99 (7) : 974-84.
DOI: 10.1113/eph.2014.99.issue-7. ( 0) 0)
|
| [24] |
Hou SY, Li YP, Wang JH, et al. Aquaporin-3 inhibition reduces the growth of NSCLC cells induced by hypoxia[J].
Cell Physiol Biochem,2016, 38 (1) : 129-40.
DOI: 10.1159/000438615. ( 0) 0)
|
| [25] |
Zelenina M, Tritto S, Bondar AA, et al. Copper inhibits the water and glycerol permeability of aquaporin-3[J].
J Biol Chem,2004, 279 (50) : 51939-43.
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M407645200. ( 0) 0)
|
| [26] |
Li A, Lu D, Zhang Y, et al. Critical role of aquaporin-3 in epidermal growth factor-induced migration of colorectal carcinoma cells and its clinical significance[J].
Oncol Rep,2013, 29 (2) : 535-40.
( 0) 0)
|
| [27] |
Ji C, Cao C, Lu S, et al. Curcumin attenuates EGF-induced AQP3 up-regulation and cell migration in human ovarian cancer cells[J].
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol,2008, 62 (5) : 857-65.
DOI: 10.1007/s00280-007-0674-6. ( 0) 0)
|
| [28] |
Cao XC, Zhang WR, Cao WF, et al. Aquaporin3 is required for FGF-2-induced migration of human breast cancers[J].
PLoS One,2013, 8 (2) : e56735.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056735. ( 0) 0)
|
| [29] |
李昂, 方育, 李嘉, 等. 表皮生长因子调节水通道蛋白3表达对结肠 癌细胞迁移能力的影响[J].
现代肿瘤医学,2012, 20 (8) : 1557-60.
( 0) 0)
|
| [30] |
杨泉涌, 张颖, 张伟然, 等. 水通道蛋白3在表皮生长因子诱导的乳腺 癌细胞迁移中的作用机制研究[J].
中华乳腺病杂志: 电子版,2012, 6 (6) : 640-8.
( 0) 0)
|
 2016, Vol. 36
2016, Vol. 36
