2. 惠州市中心人民医院超声医学科,广东 惠州 516001
2. Department of Ultrasound, Huizhou Municipal Central Hospital, Huizhou 516001, China
近年来,肌肉骨骼超声广泛应用于类风湿关节炎(RA)、运动损伤、慢性劳损等运动系统疾病。RA发病早期以手腕部滑膜增厚为主要表现,部分病人滑膜增厚甚至早于实验室指标改变[1],早期发现手腕部滑膜增厚对RA一类关节炎的早期诊断及治疗意义重大。高频超声因其对软组织具有分辨率高、便捷、重复性好,目前广泛用于RA的诊断、治疗监控、疗效评估,欧洲抗风湿病联盟和美国风湿病学会均有关于其地位重要意义的阐述[2]。国内外多位学者运用高频超声进行手腕部滑膜的研究[3-4],研究者普遍采用常规高频探头,对于手腕小关节而言,体积偏大,所测量数值受影响因素多,而且早期超声探头分辨率不高,而正常关节滑膜菲薄,普通高频探头显示滑膜较为困难。部分学者运用间接测量法测量滑膜厚度并计算获得正常参考值[5-6],间接测量法测值准确,但测量内容包含滑膜、关节囊及纤维膜等结构,且所得正常参考值范围较大,对临床诊疗意义有待进一步提高。随着超高频超声探头的研发应用,其图像分辨率更高,能清晰的显示手腕小关节滑膜、关节软骨、肌腱等结构。本研究拟采用18 M超高频术中探头观察健康中青年人群双侧手腕关节,直接测量滑膜厚度,以获得手腕小关节滑膜厚度的特点及正常参考值范围,为RA等疾病的早期诊断、疗效监控提供更准确的依据。
1 资料和方法 1.1 研究对象100例健康中青年志愿者,男性50例(18~54岁,平均年龄36.2±5.0岁)、女性50例(20~56岁,平均年龄38.8±5.5岁)。所选志愿者均无手部不适症状,除外手腕部外伤、手术史,占位性病变、系统性疾病如类风湿关节炎等疾病。
1.2 仪器与方法选用GE Logiq S8型超声诊断仪,18 M马球棍形线阵术中探头。被检者坐于操作者对面,舒适体位,手掌平放在检查床上,局部适当增加耦合剂,探头直接接触扫查,纵断面扫查双侧腕关节(Wrist,W)的尺侧(W1)、伸面尺侧(W2)、伸面桡侧(W3)(图 1A)、桡侧(W4),第1~5掌指关节(MCP)(图 1B)和第1~5近端指间关节(PIP)(图 1C)的屈面(F)及伸面(E),观察关节软骨、滑膜、周围韧带及肌腱等结构,探头扫查过程中,保持探头压力适中,避免软组织受压变形,测量滑膜厚度时局部放大图像,避开关节软骨,光标放置于滑膜边缘,垂直骨面,测量滑膜双层厚度。每个部位重复测量3次,取均值并计算滑膜单层厚度。
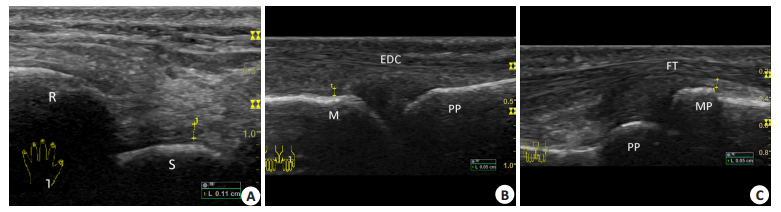
|
图 1 正常手腕小关节声像图 Figure 1 Ultrasonography of normal wrist and small joints of the hand. A: Longitudinal section of extended radialis of the left wrist. +···+ indicates the thickness of the synovial membranes of the wrist. R: Radius. S: Scaphoid bone; B: Longitudinal section of extended fourth MCP joints of the left hand. +···+ indicates the thickness of the synovial membranes of the MCP joints. M: Metacarpal bone. PP: Proximal phalanx. EDC: Extensor digitorum communis muscle; C: Longitudinal section of bent fourth PIP joint of the left hand. +···+ indicates the thickness of the synovial membranes of the PIP joint. PP: Proximal phalanx; MP: Middle phalanx; FT: Flexor tendon. |
本研究运用SPSS 19.0软件进行统计,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,两组间比较采用t检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节结构及正常声像图腕关节由尺、桡骨远端及手舟骨、月骨、三角骨等构成;掌指关节由掌骨头与近节指骨底构成;近端指间关节由近节指骨头与中节指骨底构成。关节面被覆无回声关节软骨,掌指关节及近节指间关节屈面内可见掌板,关节由低回声滑膜及关节囊包绕,关节囊外有韧带、肌腱等结构(图 1)。
2.2 腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度特点双手间比较,腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);屈面与伸面间比较,腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);不同年龄组(< 40岁组vs≥40岁组)比较,腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05);男性与女性间比较,腕关节0.79±0.07 mm vs 0.65±0.08 mm、掌指关节0.59±0.06 mm vs 0.52±0.07 mm及近端指间关节0.51±0.05 mm vs 0.46±0.06 mm,滑膜厚度差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
2.3 手腕各关节正常滑膜厚度范围在本研究中,我们发现所测得的腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度进行统计分析并计算,发现各部位测值波动在0.1 mm左右,临床意义较小,为了使临床工作更便捷、高效,本研究对相应部位的滑膜厚度进行合并计算求均值(表 1)。研究对象腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节间比较,滑膜厚度差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
| 表 1 腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度范围 Table 1 Ranges of thickness of the synovial membranes of the wrist joints, MCP joints and PIP joints (mm) |
近年来,肌肉骨骼超声的应用日渐广泛。随着超高频超声探头的研发应用,其图像分辨率更高,能清晰的显示手腕小关节的滑膜、关节软骨及肌腱等结构,特别在手腕小关节的检查中具有较大优势。
手腕关节滑膜病变在临床中较常见,RA、痛风、劳损及炎症等多种因素均可导致滑膜病变。RA是一种以侵犯关节滑膜为主要表现的自身免疫性疾病,以中青年高发,首先累及腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节[7],早期RA以滑膜增厚发生率最高[8-9],滑膜增厚以滑膜与关节软骨相连处明显,可表现为均匀增厚或不规则增厚,严重者呈结节状向滑膜腔内突起。ACR/EULAR 2010年新的RA分类标准中就提到可以把MRI或超声发现的滑膜炎做为临床滑膜炎的辅助证据[10]。研究表明高频超声在检测关节滑膜炎方面比临床化验上具有更高的敏感性[11]。高频超声检测滑膜厚度能为RA疾病的早期诊断,疗效评估,据此调整治疗方案和用药剂量,甚至治疗终点的选择提供重要的指导意义[12-13]。
既往学者运用高频超声进行手腕部滑膜的研究多采用常规高频探头[4, 14],如Schmidt等[6]的研究采用意大利百胜公司探头LA 523(频率10~5 MHz;探头长度45 mm;质量100 g,轴向空间分辨率和横向空间分辨率分别为0.154 mm和0.260 mm),而本研究采用美国GE公司L8-18i马球棍形术中探头,最高频率可达18 MHz,其纵向分辨力理论最大值约为0.04 mm,且探头长度仅为2 cm,体积小巧,质量轻,检查中可避免压力导致的软组织形变,显示手腕部滑膜等结构更清晰,适于手腕部小关节检查。
本研究主要以中青年健康人群为研究对象,采用了滑膜直接法测量关节滑膜厚度,增加临床实用性,分别测量被检者双手第1~5掌指关节(MCP1-5)与第1~5指近端指间关节(PIP1-5)的屈面及伸面和腕部(W1、W2、W3、W4)。对腕关节的扫查,Vlad等[15]人的研究表明,因腕关节屈面特殊的解剖结构,只从伸面测量,尚未有屈面测量滑膜的研究。
本研究结果表明,双手间比较:研究对象腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜测值差异无统计学意义,双侧对比是肌肉骨骼超声的检查要点之一,检查中发现滑膜增厚与否有疑问时,可以采用患侧与健侧自身对比判断滑膜是否增厚。若患者双手均受累,则可依照滑膜正常参考值进行诊断分析,所以手腕部滑膜正常参考值的制定尤为重要。
屈面与伸面间滑膜厚度的比较:掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度差异无统计学意义。据文献报道,RA侵犯掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜在伸面多见或者屈面多见存在一定的争议[16-18],故对RA病人,掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜伸面及屈面均需做检查,以获得更多的影像学信息。
不同年龄组间(< 40岁vs≥40岁)比较:被检者腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜测值差异无统计学意义,表明腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度随年龄增长变化不显著。
男性与女性间比较:腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节滑膜厚度差异有统计学意义,男性与女性由于身高和体格等均有所不同,滑膜厚度存在一定的差异。研究对象腕关节、掌指关节及近端指间关节间比较:滑膜厚度差异有统计学意义。不同节段的关节滑膜厚度不同,这在RA关节滑膜测量中要多加注意。
检查过程中动作轻巧,避免软组织受压形变,必要时局部充分耦合,清晰显示关节结构,通过调整探头使声束方向与所需观察结构垂直,避免各向异性伪像。注意识别关节软骨、滑膜、关节积液及肌腱。关节软骨为关节面均匀无回声,滑膜为位于肌腱与骨面之间的一层低回声区[19],关节积液呈无回声,肌腱长轴切面呈多个平行强回声线间隔纤细低回声区。当滑膜与关节积液鉴别困难时,可局部加压,关节积液可消失,滑膜不消失,可通过运动手指辨别肌腱与滑膜。测量时,应局部放大图像,减少测量误差,测量光标位于滑膜低回声带边缘。
本次研究获得了正常手腕部小关节滑膜厚度特点及正常参考值范围,对类风湿性关节炎等以滑膜增厚为首发病变的疾病早期诊断及治疗有重要的指导意义,但也存在一定的局限性。本组没有进行不同身高、不同体质量方面滑膜厚度的比较,亦无脑力劳动者与体力劳动者间差异的比较,无法断定滑膜厚度正常值在不同身高间、不同体质量间、脑力劳动者与体力劳动者间的差异,这些都待日后的进一步研究补充完善。
| [1] |
岳涛, 程鹏, 范晓蕾, 等. 抗环瓜氨酸肽抗体和关节磁共振成像对早期类风湿关节炎的意义[J].
中华医学杂志,2011, 91 (23) : 1633-6.
( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
Nam JL, Hensor EM, Hunt L, et al. Ultrasound findings predict progression to inflammatory arthritis in anti-CCP antibody-positive patients without clinical synovitis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2016. pii: annrheumdis-2015-208235.[Epub ahead of print]
( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
Grassi W, Lamanna G, Farina A, et al. Synovitis of small joints: sonographic guided diagnostic and therapeutic approach[J].
Ann Rheum Dis,1999, 58 (10) : 595-7.
DOI: 10.1136/ard.58.10.595. ( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
Hau M, Schultz H, Tony HP, et al. Evaluation of pannus and vascularization of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis by high-resolution ultrasound (multidimensional linear array)[J].
Arthritis Rheum,1999, 42 (11) : 2303-8.
DOI: 10.1002/(ISSN)1529-0131. ( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
钱亚君, 沈伟伟, 贾建文, 等. 高频术中探头测量正常青年手腕部小关节结构正常值的应用研究[J].
中国超声医学杂志,2013, 29 (5) : 402-5.
( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
Schmidt WA, Schmidt H, Schicke B, et al. Standard reference values for musculoskeletal ultrasonography[J].
Ann Rheum Dis,2004, 63 (8) : 988-94.
DOI: 10.1136/ard.2003.015081. ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
Weidekamm C, Koller M, Weber A, et al. Diagnostic value of high-resolution B-mode and doppler sonography for imaging of hand and finger joints in rheumatoid arthritis[J].
Arthritis Rheum,2003, 48 (2) : 325-33.
DOI: 10.1002/art.10784. ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Mottonen T, et al. Early suppression of disease activity is essential for maintenance of work capacity in patients with recent-onset rheumatoid arthritis:five-year experience from the FIN-RACo trial[J].
Arthritis Rheum,2005, 52 (1) : 36-41.
DOI: 10.1002/art.20716. ( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
张新, 吴荣秀. 超声在早期类风湿性关节炎的临床研究[J].
中国超声医学杂志,2009, 25 (12) : 1158-61.
( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/ European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative[J].
Arthritis Rheum Dis,2010, 69 (9) : 1580-8.
DOI: 10.1136/ard.2010.138461. ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
Szkudlarek M, Klarlund M, Narvestad EA, et al. Ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography and clinical examination[J].
Arthritis Res Ther,2006, 8 (2) : 52.
DOI: 10.1186/ar1904. ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
Ikeda K. Roles of musculoskeletal ultrasonography in the management of rheumatic diseases[J].
Rinsho Byori,2015, 63 (5) : 580-9.
( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
Vlad V, Micu M, Porta F, et al. Ultrasound of the hand and wrist in rheumatology[J].
Med Ultrason,2012, 14 (1) : 42-8.
( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
李翠芳, 李华, 伍镝, 等. 高频超声对类风湿关节炎指关节滑膜病变的研究[J].
中华超声影像学杂志,2011, 20 (4) : 338-40.
( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
Vlad V, Berghea F, Libianu S, et al. Ultrasound in rheumatoid arthritis: volar versus dorsal synovitis evaluation and scoring[J].
BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2011, 12 (3) : 124.
( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
王丽萍, 刘艳芳, 李应强, 等. 类风湿性关节炎手部小关节病变的声像图表现[J].
中华医学超声杂志:电子版,2010, 7 (3) : 450-5.
( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
Scheel AK, Hermann KG, Kahler E, et al. A novel ultrasonographic synovitis scoring system suitable for analyzing finger joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis[J].
Arthritis Rheum,2005, 52 (3) : 733-43.
DOI: 10.1002/art.20939. ( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
Scheel AK, Backhaus M. Ultrasonographic assessment of finger and toe joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis: comment on the article by Szkudlarek et al[J].
Arthritis Rheum,2004, 50 (3) : 1008.
( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
Terslev L, Torp-Pedersen S, Savnik A, et al. Doppler ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of synovial inflammation of the hand in rheumatoid arthritis: a comparative study[J].
Arthritis Rheum,2003, 48 (9) : 2434-41.
DOI: 10.1002/art.v48:9. ( 0) 0)
|
 2016, Vol. 36
2016, Vol. 36
