2南华大学附属第一医院,湖南 衡阳421001
2First Affiliated Hospital, University of South China, Hengyang 421001, China
南方医科大学学报  2016, Vol. 36 2016, Vol. 36 Issue (6): 814-818 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.06.14 Issue (6): 814-818 DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-4254.2016.06.14
|
近年来,我国乳腺癌发病率位居女性恶性肿瘤首位,严重威胁着女性的生命和健康[1-2]。侵袭转移是恶性肿瘤重要的生物学特征,远处转移是乳腺癌致死的主要原因之一[3]。尽管对乳腺肿瘤的研究取得了一些进展,但迄今为止相关机制尚未完全阐明,尤其中晚期癌症患者发生癌症侵袭转移的机理不清楚。如能针对天然抗肿瘤活性物质进行相关的抗乳腺癌作用机制研究,将对该病防治具有重要意义。
大蒜为百合科葱属多年生宿根植物蒜的鳞茎,现代药物化学研究证明[4],其主要有效成分为有机硫化合物(organosulfur compound,OSCS),对肿瘤防治起作用的物质主要是二烯丙基二硫(diallyl disulfide,DADS)和二烯丙基三硫(diallyl trisulfide,DATS)。其中DADS对乳腺癌、宫颈癌、结肠癌和白血病等多种肿瘤均有明显的抑制作用[5-9],提示其可能是一种具有开发潜力的新型抗癌药物。最新研究初步提示[10-11],DADS可抑制三阴性乳腺癌MDA-MB-231细胞的增殖和迁移,而对雌激素受体阳性MCF-7细胞是否存在相似作用?具体机制如何?因此,本研究主要探讨DADS 对乳腺癌MCF-7细胞侵袭转移的作用及其机制。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料乳腺癌MCF-7细胞购自中科院上海生命科学研究院细胞资源中心,DADS、β-actin一抗和Transwell小室均购于Sigma公司,TGF-β1为Peprotech产品,E-cadherin和Vimentin 一抗购自万类生物,p38和p-p38一抗购自Cell Signaling Technology (CST),MMP-9 一抗为Santa Cruz公司产品,辣根过氧化物酶标记的抗鼠和抗兔二抗购于联科生物公司。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞分组DADS量效组:(0、100、200、400 μmol/L)DADS处理MCF-7 乳腺癌细胞24 h。TGF-β1 处理细胞上调p-p38表达,具体分组为:对照组和DADS组分别指0 和200 μmol/L DADS 处理MCF-7 细胞24 h,TGF-β1 组是10 ng/mL TGF-β1 单独处理细胞24 h,TGF-β1+DADS组是10 ng/mL TGF-β1预处理30 min 后和200 μmol/L DADS共同处理细胞24 h。
1.2.2 Transwell侵袭实验检测细胞侵袭能力Transwell上室均匀铺无血清培养基稀释混匀后的Matrigel,每孔加入100 μL细胞悬液(细胞密度1×106个/mL),下室加入500 μL含10%血清的DMEM,培养24 h。取出小室,擦去上室面的Matrigel和非侵袭细胞,下室用4%多聚甲醛固定,结晶紫染色、漂洗、晾干,倒置显微镜下观察。用Image ProPlus软件扫描图片,计数各组细胞,与对照组比较,计算相对比值为处理组细胞侵袭率。
1.2.3 划痕愈合实验检测细胞迁移能力在待铺板的6孔板背后均匀划5条横线,以每孔5×105个/mL的细胞密度接种细胞,培养箱中孵育12 h后,用tip头垂直横线划痕,显微镜下每组即时拍照作为0 h图片;各组加入不同浓度药物处理后继续培养24 h,再用显微镜拍照为24 h图片。结果应用Image ProPlus软件扫描图片,计算各组细胞迁移率,即各组0 h 划痕区域的面积减去24 h划痕愈合后空白区域的面积,除以0 h划痕区域的面积,再乘以100%。
1.2.4 Westernblot 检测细胞中的蛋白表达 细胞加药分组,提蛋白,BCA蛋白定量。根据总蛋白计算上样体积,依次电泳、转膜、封闭,孵适当稀释比的一抗和二抗,显影。AlphaImager2200软件扫描条带灰度。
1.2.5 统计学分析实验结果中的数据采用均数±标准差表示,统计处理采用SPSS 20.0,组间比较应用方差分析和t检验,以P <0.05判定差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 DADS对MCF-7细胞侵袭和迁移的影响参照文献[12],预实验中用平板克隆形成实验观察0、100、200和400 μmol/L DADS对MCF-7细胞增殖的影响,结果发现,随着处理浓度的增加,DADS对MCF-7细胞增殖的抑制作用逐渐增强,并由此筛选了这4组浓度继续后续实验。
Transwell侵袭实验检测结果表明:与0 μmol/L对照组相比,100、200 和400 μmol/L DADS 组MCF-7 细胞穿过基底膜的数目均明显减少(P <0.05,图 1A)。提示DADS可呈浓度依赖性抑制MCF-7 细胞的侵袭能力。划痕愈合实验结果显示,经DADS 处理后的MCF-7细胞,与0 μmol/L DADS组相比,随着处理浓度的增加,细胞迁移能力显著降低(图 1B)。
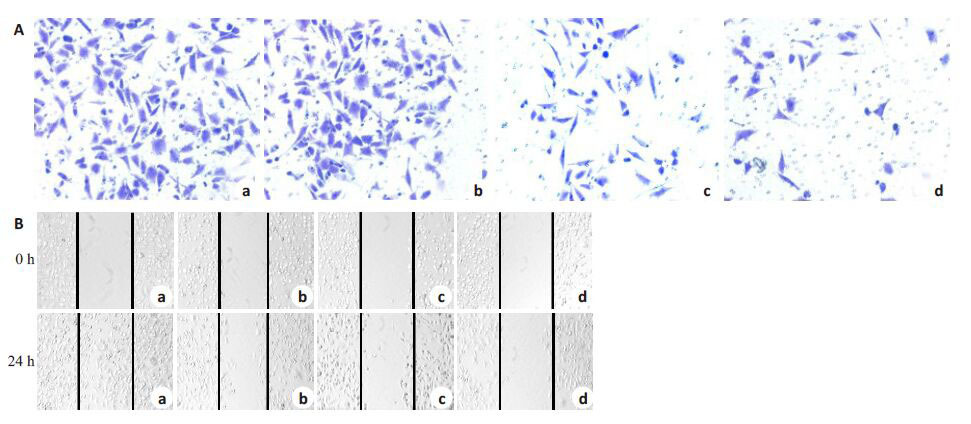
|
图1 DADS抑制MCF-7细胞侵袭迁移 Fig.1 DADS inhibits invasion and migration of MCF-7 cells. A: Transwell assay (Original magnification: × 100); B: Wound healing assay (× 40). a-d: 0,100,200,and 400 μmol/L DADS,respectively. *P <0.05 vs 0 μmol/L DADS group (n= 3). |
Western blot结果发现,随着DADS处理浓度的增加,MCF-7 细胞中EMT特征分子Vimentin 表达降低,E-cadherin表达增强,MMP-9蛋白表达减弱,p-p38表达明显降低,具有统计学意义(P <0.05,图 2),而p38表达基本无改变。提示DADS可能通过抑制p38活性,降低MMP-9的表达和调控EMT特征分子的表达,从而抑制MCF-7细胞侵袭转移。
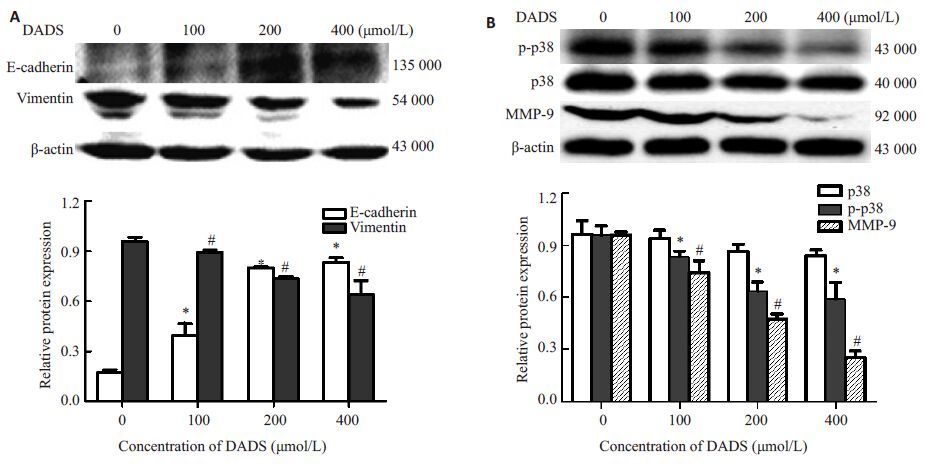
|
图2 DADS对MCF-7细胞中E-cadherin,Vimentin,p-p38和MMP-9等蛋白表达的影响 Fig.2 Effect of DADS on protein expressions of E-cadherin,vimentin,p-p38 and MMP-9 in MCF-7 cells. A: Western blotting for E-cadherin and vimentin; B: Western blotting for p-p38 and MMP-9. *P <0.05,#P <0.05 vs 0 μmol/L DADS group (n=3) |
综合上述结果,接下来的实验中取200 μmol/LDADS处理细胞24 h 作为DADS组。为进一步验证DADS 经p38 途径抑制乳腺癌细胞侵袭迁移,采用TGF-β1上调p-p38表达。参照文献[13]并结合预实验,取10 ng/mL TGF-β1 处理细胞24 h 作为TGF-β1 组,TGF-β1+DADS组是10 ng/mL TGF-β1预处理30 min 后和200 μmol/L DADS共同处理细胞24 h。
Western blotting 结果显示,DADS组MCF-7 细胞中p-p38和MMP-9蛋白表达明显减弱,TGF-β1组表达明显增强,而DADS+TGF-β1组较TGF-β1组表达明显减弱,但较DADS组表达增强(P 均<0.05,图 3),p38表达未见明显改变。提示TGF-β1 可上调p-p38 和MMP-9的表达,延缓DADS对MCF-7细胞中p-p38和MMP-9蛋白表达的抑制作用。
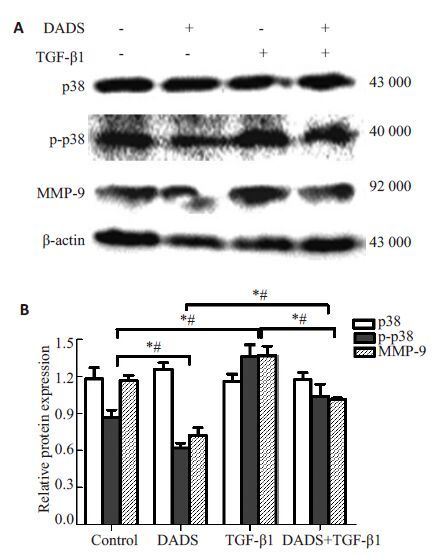
|
图3 TGF-β1 和DADS对MCF-7 细胞中p-p38 和MMP-9蛋白表达的影响 Fig.3 Effect of TGF-β1 and DADS on the protein expression of p-p38 and MMP-9 in MCF-7 cells. *P< 0.05,#P<0.05 (n=3). A: Western blotting for p-p38 and MMP-9; B: Quantitative analysis of the results ofWestern blotting. |
Transwell侵袭实验结果表明:DADS组MCF-7细胞穿过基底膜的数目较对照组明显减少,TGF-β1组细胞数目显著增多,TGF-β1与DADS共同处理组细胞数目与DADS组相比略有升高,与TGF-β1组相比明显减少(P 均<0.05,图 4A)。提示TGF-β1 可加强MCF-7 细胞的侵袭能力,部分抵消DADS对MCF-7细胞侵袭的抑制作用。
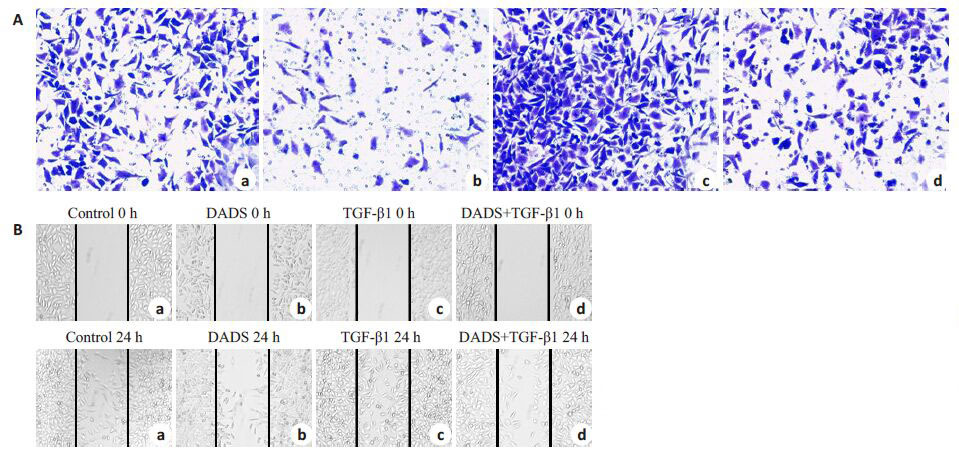
|
图4 TGF-β1 和DADS对MCF-7 细胞侵袭迁移的影响 Fig.4 Effect of TGF-β1 and DADS on the invasion and migration of MCF-7 cells. A: Transwell invasion assay (Original magnification: × 100). a: Control; b: DADS; c: TGF-β1; d: DADS +TGF-β1; B: Wound healing assay (Original magnification: × 40). *P<0.05 (n=3) |
划痕愈合实验结果显示,与对照组相比,DADS组细胞迁移能力显著降低,划痕后的细胞经TGF-β1处理后,划痕区域明显愈合,而TGF-β1+DADS组的划痕区域愈合情况不如TGF-β1明显,但比DADS组增强(P 均<0.05,图 4B)。提示TGF-β1可促进MCF-7细胞迁移,部分抵消DADS对MCF-7细胞迁移的抑制作用。
3 讨论DADS能明显抑制MDA-MB-231 乳腺癌细胞增殖和转移[10-11],而对MCF-7细胞的侵袭转移作用如何?至今未见报道。我们首先应用Transwell侵袭实验和划痕愈合实验系统观察,结果发现,DADS随处理浓度的增加,可明显抑制MCF-7细胞的侵袭迁移能力(图 1)。
上皮细胞间质化(epithelial-mesenchymal transition,EMT)是上皮细胞通过特定程序从黏附细胞形态向具有间质表型游离细胞形态转化,并获得侵入细胞外基质能力的一系列转化过程,可分为3 种类型。其中Ⅲ型EMT与肿瘤形成及转移相关:癌细胞向间质细胞表现转化而具有侵袭性并向肿瘤发展[14],进而形成局部扩散发生转移。在EMT 过程中,上皮标志物E-cadherin表达降低,间质标志物Vimentin 表达升高,细胞侵袭转移能力增强[15]。乳腺癌95%为上皮来源的恶性类型,EMT在乳腺癌的发生和发展中起到重要作用,且与导管原位癌发展成为浸润性乳腺癌和乳腺癌淋巴结转移密切相关[16]。基质金属蛋白酶(matrix metalloproteinases,MMPs)与肿瘤的侵袭转移密切相关,其中基质金属蛋白酶-9(matrix metalloproteinase-9,MMP-9)与肿瘤的转移潜能关系最密切,它能降解细胞外基质和基底膜,使基底膜完整性的破坏引起肿瘤细胞发生局部侵袭和远处转移[17-18]。通过Western blot 检测,我们进一步发现,DADS 可显著下调MCF-7 细胞中MMP-9 和Vimentin的表达,上调E-cadherin的表达(图 2)。进一步证实DADS对乳腺癌细胞侵袭转移的抑制作用。肿瘤侵袭转移相关基因的调节涉及复杂的机制及多条信号转导途径,其中MAPK通路是研究最多的激酶通路[19]。在哺乳动物细胞中,MAPK信号转导通路主要有3条,即细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)通路、JNK通路和p38通路。当中p38 MAPK是真核细胞介导细胞外信号到细胞内反应的重要蛋白激酶:内源性p38 MAPK的活性与乳癌细胞的侵袭转移密切相关[20]。上述过程提示p38 MAPK通路在肿瘤浸润转移过程中起着重要作用。我们的检测结果发现,DADS在抑制乳腺癌细胞侵袭转移的同时,下调p38活性(图 2)。转化生长因子β1(transforming growth factor β1,TGF-β1)是一种分布广泛,在细胞外基质形成、免疫和炎症的调控以及肿瘤发生发展中起重要作用的细胞生长因子。作为p38MAPK 信号途径中重要的上游介质,TGF-β1通过MKK 介导激活p38MAPK,MAPK 底物绝大部分是核转录因子,通过对下游多种靶基因的转录调控,参与细胞凋亡、转分化、炎症等过程[21-22]。TGF-β1可上调p-p38和MMP-9的表达,明显抵消DADS对MCF-7细胞侵袭迁移的抑制效果(图 3,4)。说明DADS确可通过p38途径抑制MCF-7细胞的侵袭转移。
接下来我们将进一步通过动物实验验证其在体内是否具有一致作用并探讨可能机制,以期为乳腺癌提供新的治疗靶点并深入开发DADS的抗肿瘤作用。
| [1] | Katie Lee SY, Knobf MT. Primary breast cancer decision-making among Chinese American women: satisfaction, regret[J]. Nurs Res, 2015, 64(5): 391-401.( 1) 1) |
| [2] | Niu HY, Niu CY, Wang JH, et al. Health-related quality of Life in women with breast cancer: a literature-based review of psychometric properties of breast cancer-specific measures[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(8): 3533-6.( 1) 1) |
| [3] | Almendro V, Kim HJ, Cheng YK, et al. Genetic and phenotypic diversity in breast tumor metastases[J]. Cancer Res, 2014, 74(5): 1338-48.( 1) 1) |
| [4] | Yi L, Su Q. Molecular mechanisms for the anti-cancer effects of diallyl disulfide[J]. Food Chem Toxicol, 2013, 57: 362-70.( 1) 1) |
| [5] | Altonsy MO, Habib TN, Andrews SC. Diallyl disulfide-induced apoptosis in a breast-cancer cell line (MCF-7) May be caused by inhibition of histone deacetylation[J]. Nutr Cancer, 2012, 64(8): 1251-60.( 1) 1) |
| [6] | Lai KC, Kuo CL, Ho HC, et al. Diallyl sulfide, diallyl disulfide and diallyl trisulfide affect drug resistant gene expression in colo 205 human colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Phytomedicine, 2012, 19(7): 625-30. |
| [7] | Ling H, Lu LF, He J, et al. Diallyl disulfide selectively causes checkpoint kinase-1 mediated G2/M arrest in human MGC803 gastric cancer cell line[J]. Oncol Rep, 2014, 32(5): 2274-82. |
| [8] | Di C, Sun C, Li H, et al. Diallyl disulfide enhances Carbon ion beams-induced apoptotic cell death in cervical cancer cells through regulating Tap73/ΔNp73[J]. Cell Cycle, 2015, 14(23): 3725-33. |
| [9] | Luo N, Zhao LC, Shi QQ, et al. Induction of apoptosis in human leukemic cell lines by diallyl disulfide via modulation of EGFR/ ERK/PKM2 signaling pathways[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2015, 16(8): 3509-15.( 1) 1) |
| [10] | Huang J, Yang B, Xiang T, et al. Diallyl disulfide inhibits growth and metastatic potential of human triple-negative breast cancer cells through inactivation of the β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Mol Nutr Food Res, 2015, 59(6): 1063-75.( 2) 2) |
| [11] | Xiao X, Chen B, Liu X, et al. Diallyl disulfide suppresses SRC/Ras/ ERK signaling-mediated proliferation and metastasis in human breast cancer by up-regulating miR-34a[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(11): e112720.( 2) 2) |
| [12] | Lei XY, Yao SQ, Zu XY, et al. Apoptosis induced by diallyl disulfide in human breast cancer cell line MCF-7[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2008, 29(10): 1233-9.( 1) 1) |
| [13] | Mo N, Li ZQ, Li J, et al. Curcumin inhibits TGF-β1-induced MMP-9 and invasion through ERK and Smad signaling in breast cancer MDA- MB-231 cells[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2012, 13 (11): 5709-14.( 1) 1) |
| [14] | 龚晓萌, 陶仪声, 周蕾, 等. 宫颈癌中Snail、Slug和KAI1的表达及临 床意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(12): 1733-8.( 1) 1) |
| [15] | 胡萍, 杨佳佳, 黄翼, 等. 转录因子Twist基因慢病毒质粒构建及其促 进乳腺肿瘤上皮细胞MCF-7上皮间质转化[J]. 重庆医科大学学报, 2014, 39(3): 328-31.( 1) 1) |
| [16] | 吴斯敏, 刘志明, 贺文兴, 等. 缺氧微环境下HIF-1α对乳腺癌上皮间质 转化及侵袭迁移的影响[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2015, 32(3): 410-3.( 1) 1) |
| [17] | Fan SH, Wang YY, Lu J, et al. CERS2 suppresses tumor cell invasion and is associated with decreased V-ATPase and MMP-2/ MMP-9 activities in breast cancer[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2015, 116(4): 502-13.( 1) 1) |
| [18] | 姚广裕, 陈路嘉, 胡晓磊, 等. MT1-MMP在乳腺癌中的独特表达模式 [J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(1): 94-7.( 1) 1) |
| [19] | Pereira L, Igea A, Canovas B, et al. Inhibition of p38 MAPK sensitizes tumour cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis mediated by reactive Oxygen species and JNK[J]. EMBO Mol Med, 2013, 5 (11): 1759-74.( 1) 1) |
| [20] | Wang XF, Zhou QM, Du J, et al. Baicalin suppresses migration, invasion and metastasis of breast cancer via p38MAPK signaling pathway[J]. Anticancer Agents Med Chem, 2013, 13(6): 923-31.( 1) 1) |
| [21] | Zhang S, Liu Q, Xiao J, et al. Molecular validation of the precisioncut kidney slice (PCKS) model of renal fibrosis through assessment of TGF-β1-induced Smad and p38/ERK signaling [J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2016, 34: 32-6.( 1) 1) |
| [22] | 王巍巍, 张金元. 丹酚酸B对马兜铃酸诱导的HK-2细胞TGF-β1与 p38MAPK表达的影响[J]. 中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2010, 11(8): 673-6.( 1) 1) |