2. 国立癌症研究所肿瘤生物与遗传实验室,国立卫生研究院,马里兰州贝塞斯达市 美国
2. Laboratory of Cancer Biology and Genetics, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, USA
Nanog是含同源结构域的转录因子,在胚胎干细胞干性维持和自我更新中起作用,在干细胞中表达,而在分化成熟细胞中表达缺失[1];近年的研究发现,Nanog可促进肿瘤的转移。一方面,肝癌[2],结直肠癌[3]、乳腺癌[4-5]等癌组织Nanog的表达升高并与死亡率正相关;另一方面,过表达Nanog的结直肠癌细胞,迁移和侵袭能力增强[3]。有关Nanog促进肿瘤转移的机制,已有一些研究,如:Nanog可降低卵巢癌细胞中E-cadherin和FoxJ1的表达,促进卵巢癌转移[6];Nanog可促进转化生长因子家族蛋白NODAL的表达,激活上皮间质转化,从而促进肝癌细胞转移[7];Nanog促进乳腺癌转移的机制与其促进PDGFRa的表达有关[8];但Nanog促进癌细胞转移的机制目前还无定论,因此,深入研究Nanog促进癌细胞转移的机制仍很有必要。
Nanog作为转录因子,有多个靶基因。Nanog靶基因包括细胞周期蛋白D1(cyclin D1)[4, 9]、生长分化因子3(GDF3)[10]、粘着斑激酶[11]和胎肝激酶-1 [12]等激酶。激酶的活性异常与肿瘤转移的关系非常密切,如蛋白激酶C(PKC)[13-14]等,但Nanog促进乳腺癌转移是否与其对激酶的调节有关,并无相关研究。
Ezrin由Vil2基因编码,是ERM(Ezrin-Radixin-Moesin)家族的成员,其表达升高和第567位苏氨酸(ezrinT567)等位点氨基酸的磷酸化与乳腺癌转移有关[15-16]。Bruce等[17]报道,ezrin表达升高与乳腺癌的不良预后有关,敲低乳腺癌细胞ezrin可抑制乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力[18]。雌激素通过使ezrinT567磷酸化活化ezrin,促进乳腺癌细胞的迁移[19]。已经发现有几种激酶能磷酸化ezrinT567,包括蛋白激酶A [20]、Rho [21]、Akt2 [22]、PKC [23-24]包括PKC亚型PKCθ[25]、PKCα和PKCι[26],它们在不同的情形下使ezrinT567的磷酸化。在乳腺癌中,PKCɛ的表达水平可作为乳腺癌患者不良预后的指标[27],但PKCɛ是否可使ezrinT567的磷酸化没有相关报道。
我们研究了Nanog对PKCɛ表达的影响及PKCɛ对ezrinT567磷酸化的影响。我们的研究结果提示,Nanog可上调PKCɛ的表达,后者可使ezrinT567磷酸化,这可能是Nanog促进肿瘤转移的一个新机制。这一研究结果加深了对Nanog促进乳腺癌转移机制的了解。
1 材料和方法 1.1 细胞株与细胞培养人乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231、MCF-7和人胚肾上皮细胞293T购自中科院上海细胞库。MCF-7和293T细胞用DMEM(Gibco,美国)培养,MDA-MB-231细胞用L-15培养基(Hyclon,美国)培养,所有基础培养基均添加10%胎牛血清(Gibco,美国),100µg/mL青霉素和100µg/mL链霉素,细胞培养于5% CO2的37℃培养箱。
1.2 主要试剂/试剂盒L15、DMEM细胞培养液及胰酶购自美国Hyclone公司;胎牛血清购自美国Gibco公司;Transwell小室、Matrigel基质胶、PVDF膜购自美国BD公司;兔抗人Nanog单克隆抗体、兔抗人pEzrinT567单克隆抗体均购自美国Cell Signaling Technology公司;鼠抗人ezrin单克隆抗体购自美国Sigma公司;鼠抗人β-actin、山羊抗兔IgG、山羊抗鼠IgG购自武汉博士德生物工程有限公司;LipofectamineTM3000转染试剂购自美国Invitrogen公司;Protein A/G琼脂糖树脂购自美国Life公司。
1.3 免疫印迹实验免疫印迹实验用于检测蛋白表达。将细胞消化后接种到12孔板,1×104个细胞每孔。用预冷的PBS洗涤细胞2次,吸净液体。将细胞放置在冰上,加入1 mL预冷的PBS,细胞刮刀刮下细胞,离心收集。向每管细胞中加入100μL RIPA裂解液,冰上裂解30 min,12 000 g,4℃离心10 min,取上清,BCA法测定总蛋白浓度。蛋白样品上样前加入上样缓冲液,100℃金属浴加热5 min,12 000 g离心3 min,直接用于蛋白免疫印迹。SDSPAGE分离蛋白,转膜至PVDF膜,5%脱脂牛奶摇床上室温封闭1 h,加入相关蛋白的一抗(Nanog抗体,1: 500;ezrin抗体,1:4000;pEzrinT567抗体,1:1000;β-actin抗体,1:3000),4℃孵育过夜;二抗羊抗兔/鼠(1:3000)室温孵育1 h,ECL显影。
1.4 siRNA转染MCF-7细胞和MDA-MB-231细胞按1.2×105/mL密度接种于6孔板中,过夜后分别用Lip3000将siRNA转染入MCF-7和MDA-MB-231细胞,37℃孵箱中培养60 h,收集细胞裂解液,进行Western blotting。转染过程按Lipofectamine3000说明书进行。
小分子干扰RNAsi-Nanog、si-Ezrin和si-PKCε由上海吉玛公司合成,其序列分别是:siRNA-Nanog,Negative control:5'-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUT T-3',si-Nanog1:5'-CCAGACCUGGAACAAUUCAT T-3',si-Nanog2:5'-CCAUGGAUUUAUUCCUAAAT T-3',si-Nanog3:5'-GGGUUAAGCUGUAACAUACT T-3'。si-PKCɛnegative control:5'-UUCUCCGAACG UGUCACGUTT-3',si-PKCɛ:5'-UCAAUGACAAGG CCUUCCgg-3'。具体转染方法按Lipofectamine3000的说明书进行。
1.5 Transwell实验Transwell实验用于检测细胞的迁移和侵袭能力。取5µL Matrigel基质胶溶于95μL DMEM基础培养基,加入到Transwell小室中,在37℃孵箱静置1 h,小心吸除小室中未凝液体(迁移实验不需要经过此步),24孔板内加入750µL基培/孔,将小室放在孔内(确保无气泡),向小室内加入500µL基培,放入37℃孵箱30 min;用于Transwell实验的癌细胞为对数生长期细胞,消化离心,用无血清培养基稀释细胞至3×105/mL,每个小室中加入500µL细胞悬液,下室每孔加入含10%胎牛血清的培养基750µL,MDAMB-231培养12 h,MCF-7细胞培养48 h,用棉签擦去小室上层未侵袭的细胞,4%多聚甲醛固定15 min,0.1%结晶紫染色30 min。显微镜下拍摄,在400×视野下取上、下、左、右、中5个固定的视野拍照,计算这5个视野内的细胞总数。
1.6 免疫荧光染色制备细胞爬片,将传代消化下来的细胞计数,稀释成密度为1×104个细胞/mL的细胞悬液,混匀后取400μL/孔细胞悬液于8孔载玻片中,放入37℃孵箱中培养;24 h待细胞长开后,用1×PBS洗细胞3次,加入4%多聚甲醛,室温固定30 min;去除多聚甲醛并用30 mmoL甘氨酸终止固定;用0.5%的Triton-X透化细胞5 min;用1×PBS洗2次,每次5 min;用5%牛奶和2%BSA(用PBS稀释)室温封闭1 h;加一抗(用封闭液稀释一抗),按照相应比例加入Nanog抗体(1:100),Ezrin抗体(1:200),pEzrin T567抗体(1:100),4℃过夜;洗脱一抗(用0.05% Triton-X在摇床上洗3次,每次5 min);加二抗(将二抗羊抗兔/鼠,1:100,用封闭液稀释),常温孵育1 h。洗脱二抗(用0.05% Triton-X在摇床上洗3次,每次5 min);用DAPI染核5 min;用1×PBS洗掉多余的DAPI;滴加抗免疫荧光衰减剂,盖盖玻片,用透明无色指甲油封片;激光共聚焦显微镜下观察拍照。
1.7 免疫共沉淀将细胞接种到10 cm培养皿中,待细胞长满后弃培养基,用预冷的1×PBS洗3次,用预冷的PBS洗涤细胞2次,吸净液体。将细胞放置在冰上,加入600 mL预冷的RIPA裂解液,细胞刮刀刮下细胞,收集到1.5 mL离心管中,冰上裂解30 min,12 000 g 4℃离心10 min,取上清,BCA法测定总蛋白浓度,蛋白量约400µg。取10%上清作为Input,将剩下的蛋白裂解液分成两部分,一部分加入5µL兔IgG抗体,另一部分加入5µL PKCε抗体,4℃旋转过夜。次日,取60µL Protein A/G琼脂糖树脂,用ddH2O洗3次,将树脂均分成两管,分别将孵育了兔IgG抗体和PKCε抗体的蛋白裂解液加入含树脂的管内,4℃旋转2 h,离心,弃上清,用裂解液清洗沉淀3次,离心弃上清,将上清吸净,加入2×Loading buffer,100℃金属浴加热5 min,12 000 g 4℃离心3 min,进行Western blotting。
1.8 统计学分析不同实验组的数据以均数±标准差表示,统计分析和柱状图制作均用Gaphpad prism5.0,不同组之间分析用非配对t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
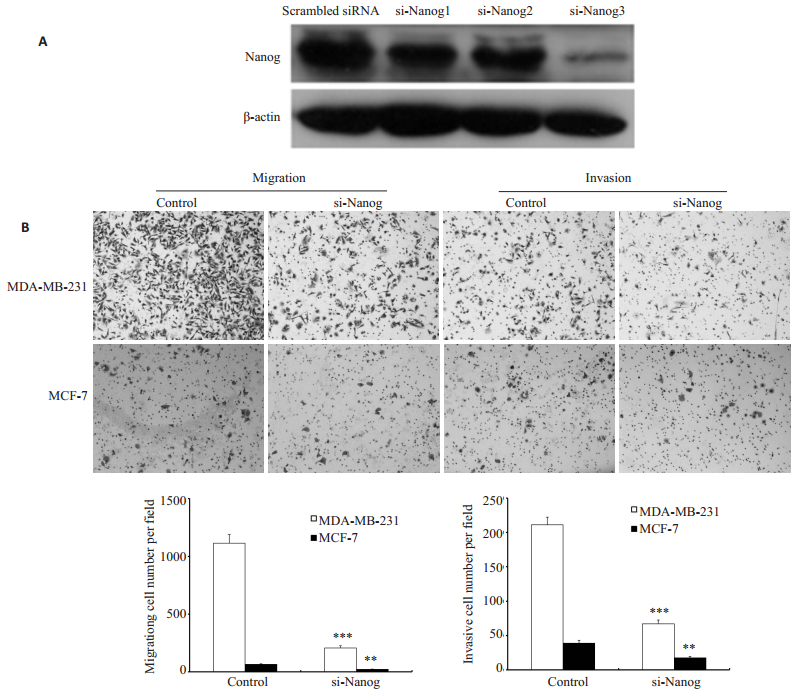
2 结果 2.1 敲低Nanog降低乳腺癌细胞迁移与侵袭能力我们先用免疫印迹检测了3条Nanog特异的siRNA敲低乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7 Nanog表达的效果,发现第3条si-Nanog3的敲除效果最明显。我们选取Nanog siRNA3用于后续实验。用Nanog siRNA3敲低乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231和MCF-7中的Nanog,癌细胞的迁移与侵袭能力减弱(图 1)。
|
图 1 敲低Nanog降低MDA-MB-231和MCF-7细胞的迁移和侵袭 Figure 1 Nanog knockdown decreased the migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. A: Nanog protein expression in MCF-7 transfected with each of the 3 different siRNAsequences targeting Nanog; B: Nanog knockdown decreased the migration and invasion ability of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells (Original magnification:×400). ***P < 0.05 MDA-MB-231 vs control group; **P < 0.05 MCF-7 vs control group. |
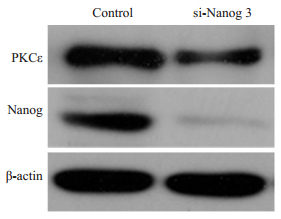
由于PKCɛ的表达水平可作为乳腺癌患者不良预后的指标[27],且又有研究报道[9-12]Nanog可促进多个激酶的表达促进肿瘤转移,因此我们观察了敲低Nanog对PKCɛ的表达的影响。结果表明,用Nanog siRNA3敲低乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7中的Nanog,PKCε的蛋白表达量也相应下降(图 2)。
|
图 2 敲低Nanog降低MCF-7细胞中的PKCε蛋白表达 Figure 2 Nanog knockdown decreased the expression of PKCεprotein in MCF-7 cells. |
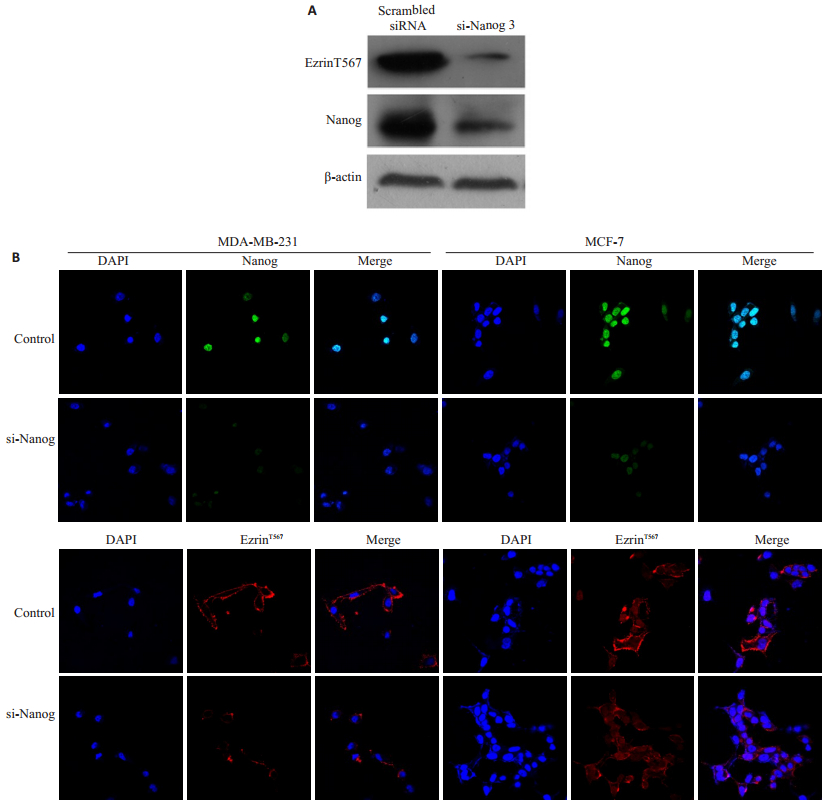
由于PKCε是否是ezrinT567磷酸化的上游激酶并无相关研究,我们研究了PKCε是否是使ezrinT567磷酸化的另一个PKC亚型。研究结果显示,用Nanog siRNA3敲低乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7中的Nanog,免疫印迹实验结果表明,ezrinT567磷酸化水平相应降低(图 3A)。敲低MCF-7和MDA-MB231细胞Nanog,免疫荧光染色实验检测发现,ezrinT567磷酸化水平相应降低(图 3B)。
|
图 3 敲低乳腺癌细胞中的Nanog降低ezrinT567磷酸化水平 Figure 3 Nanog knockdown in breast cancer cells decreased the phosphorylation level of ezrinT567. A: Western blotting for detecting the phosphorylation level of ezrinT567 in MCF-7 cells with Nanog knockdown; B: Immunofluorescent images showing decreased phosphorylation level of ezrinT567 in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells with Nanog knockdown (Original magnification:×200). |
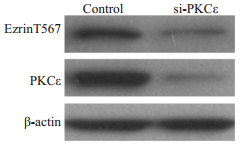
为进一步研究PKCε是否可磷酸化ezrinT567,用PKCε特异的siRNA敲低乳腺癌细胞系MDA-MB-231中的PKCε,然后免疫印迹检测ezrinT567酸化水平,结果表明,敲低PKCε,MDA-MB-231细胞中ezrinT567的磷酸化水平也同时下降(图 4)。
|
图 4 敲低PKCε降低MDA-MB-231细胞中的ezrinT567的磷酸化水平 Figure 4 PKCεknockdown decreased the phosphorylation level of ezrinT567 in MDA-MB-231 cells. |
为研究PKCε使ezrinT567磷酸化是否需要PKCε和ezrin的相互作用,我们用MCF-7和MDA-MB-231细胞的细胞裂解液和抗PKCε抗体作免疫共沉淀实验,抗PKCε抗体的免疫沉淀复合物中,可检出ezrin(图 5)。
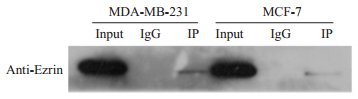
|
图 5 ezrin与PKCε免疫共沉淀 Figure 5 Co-immunocipitation of ezrin and PKCεwith anti-PKCε. |
我们的研究发现,敲低Nanog,在乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力下降的同时,PKCɛ蛋白表达和ezrinT567磷酸化水平相应下降,敲低PKCε降低ezrinT567磷酸化水平,PKCε与ezrin可免疫共沉淀。
我们用siRNA敲低乳腺癌细胞系MCF-7和DA-MB-231中的Nanog,发现乳腺癌细胞的迁移和侵袭能力减弱,我们的研究结果和Lu等[8]报告的结果一致,Lu等在MCF-7细胞过表达Nanog,可以促进乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和迁移;这一研究结果也与Nanog促进其它癌细胞迁移的研究结果一致,如肝癌[7],卵巢癌[6]等。
促进肿瘤转移的因素如雌激素[19]和内皮细胞生长因子[28]等促进癌细胞的侵袭与ezrinT567磷酸化水平升高有关,因此,我们假设Nanog促进乳腺癌转移的机制与Nanog调节ezrinT567磷酸化水平有关。为验证这一假设,我们用siRNA敲低乳腺癌细胞中Nanog后,检测了ezrinT567的磷酸化水平,结果发现Nanog降低后,ezrinT567的磷酸化水平确实相应的降低了(图 3)。这一结果验证了我们的假设。除了ezrinT567磷酸化与癌细胞转移有关外,第477位酪氨酸(ezrinY477)磷酸化[29]也与肿瘤转移有关。本研究没有检测ezrinY477磷酸化水平变化的情况,今后可进一步研究。
可使ezrinT567的磷酸化的激酶有多种,包括蛋白激酶A [21]、Rho [21]、Akt2 [22]、PKC [23-24]包括PKC亚型PKCθ[25]、PKCα和PKCι[26],它们在不同的情形下使ezrinT567的磷酸化。这自然使我们推测Nanog调节ezrinT567的磷酸化是由于Nanog调节这些激酶表达所致,而且,以前的研究也表明,Nanog的确可调节一些激酶的表达,如粘着斑激酶[11]和胎肝激酶-1[12]等。我们注意到,在乳腺癌中,PKCɛ的表达水平可作为乳腺癌患者不良预后的指标[27],因此我们选PKCɛ作为观察对象,看Nanog是否可调节PKCɛ的表达。我们发现,用siRNA敲低MCF-7细胞中的Nanog,细胞中的PKCε蛋白表达量也降低,这是一个新的发现,提示Nanog可调节PKCε表达。我们的研究没有观察敲低Nanog对其它激酶,尤其PKC家族的其它相关亚型表达的影响,因此不能排除Nanog也可能通过影响其它激酶的表达,影响ezrinT567磷酸化。
对于PKCɛ是否可以使ezrinT567磷酸化,以前并无研究。我们的研究表明,敲低Nanog,可降低MCF-7和MDA-MB-231细胞ezrinT567磷酸化,提示ezrinT567是PKCɛ的底物;用siRNA敲低乳腺癌细胞系MDAMB-231中的PKCε,ezrinT567的磷酸化水平下降,这些结果进一步证明,PKCε可使ezrinT567磷酸化;我们用免疫共沉淀实验检测到PKCε能与ezrin直接相互作用,这可能是PKCε使ezrinT567的磷酸化的分子基础。
我们的这一研究还存在一些不足,如我们没有通过过表达Nanog观察Nanog对PKCε表达的影响;由于敲除Nanog后PKCε蛋白的表达水平降低,我们只能推测Nanog是通过影响PKCε的转录所致,这一推测主要是基于Nanog是转录因子。但这一推测还需更多实验证明,因为也不能排除Nanog通过影响PKCε蛋白的稳定性调节PKCε的表达水平。此外,敲低Nanog降低ezrinT567的磷酸化也可能还存在其他机制,还有待进一步研究。
综上所述,我们的研究发现,敲低Nanog,乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力下降的同时,PKCɛ蛋白表达和ezrinT567磷酸化水平相应降低,提示Nanog通过促进PKCε表达使ezrinT567磷酸化,后者促进乳腺癌细胞的侵袭能力。Nanog-PKCε-ezrinT567轴可能是Nanog促进乳腺癌转移的一个新途径。
| [1] |
Chambers I, Colby D, Robertson M, et al. Functional expression cloning of Nanog, a pluripotency sustaining factor in embryonic stem cells[J].
Cell,2003, 113 (5) : 643-55.
DOI: 10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00392-1. ( 0) 0)
|
| [2] |
Shan J, Shen J, Liu L, et al. Nanog regulates self-renewal of cancer stem cells through the insulin-like growth factor pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma[J].
Hepatology,2012, 56 (3) : 1004-14.
DOI: 10.1002/hep.25745. ( 0) 0)
|
| [3] |
Meng HM, Zheng P, Wang XY, et al. Over-expression of Nanog predicts tumor progression and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer[J].
Cancer Biol Ther,2010, 9 (4) : 295-302.
DOI: 10.4161/cbt.9.4.10666. ( 0) 0)
|
| [4] |
Nagata T, Shimada Y, Sekine S, et al. Prognostic significance of NANOG and KLF4 for breast cancer[J].
Breast Cancer,2014, 21 (1) : 96-101.
DOI: 10.1007/s12282-012-0357-y. ( 0) 0)
|
| [5] |
Wang D, Lu P, Zhang H, et al. Oct-4 and Nanog promote the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells and are associated with poor prognosis in breast cancer patients[J].
Oncotarget,2014, 5 (21) : 10803-15.
DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget. ( 0) 0)
|
| [6] |
Siu MK, Wong ES, Kong DS, et al. Stem cell transcription factor NANOG controls cell migration and invasion via dysregulation of E-cadherin and FoxJ1 and contributes to adverse clinical outcome in ovarian cancers[J].
Oncogene,2013, 32 (30) : 3500-9.
DOI: 10.1038/onc.2012.363. ( 0) 0)
|
| [7] |
Sun C, Sun L, Jiang K, et al. NANOG promotes liver cancer cell invasion by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition through NODAL/SMAD3 signaling pathway[J].
Int J Biochem Cell Biol,2013, 45 (6) : 1099-108.
DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.02.017. ( 0) 0)
|
| [8] |
Lu X, Mazur SJ, Lin T, et al. The pluripotency factor nanog promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis and metastasis[J].
Oncogene,2014, 33 (20) : 2655-64.
DOI: 10.1038/onc.2013.209. ( 0) 0)
|
| [9] |
Han J, Zhang F, Yu M, et al. RNA interference-mediated silencing of NANOG reduces cell proliferation and induces G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in breast cancer cells[J].
Cancer Lett,2012, 321 (1) : 80-8.
DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.02.021. ( 0) 0)
|
| [10] |
Park SW, Lim HY, Do HJ, et al. Regulation of human growth and differentiation factor 3 gene expression by NANOG in human embryonic carcinoma NCCIT cells[J].
FEBS Lett,2012, 586 (19) : 3529-35.
DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2012.08.013. ( 0) 0)
|
| [11] |
Ho B, Olson G, Figel S, Gelman I, Cance WG. Golubovskaya VM: Nanog increases focal adhesion kinase(FAK)promoter activity and expression and directly binds to FAK protein to be phosphorylated[J].
J Biol Chem,2012, 287 (22) : 18656-73.
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M111.322883. ( 0) 0)
|
| [12] |
Kohler EE, Cowan CE, Chatterjee I, et al. NANOG induction of fetal liver kinase-1(FLK1)transcription regulates endothelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis[J].
Blood,2011, 117 (5) : 1761-9.
DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-295261. ( 0) 0)
|
| [13] |
Fujii T, Yokoyama G, Takahashi H, et al. Preclinical and clinical studies of novel breast cancer drugs targeting molecules involved in protein kinase C signaling, the putative metastasis-suppressor gene Cap43 and the Y-box binding protein-1[J].
Curr Med Chem,2008, 15 (6) : 528-37.
DOI: 10.2174/092986708783769759. ( 0) 0)
|
| [14] |
Sledge GW, J R. Gokmen-Polar Y: Protein kinase C-beta as a therapeutic target in breast cancer[J].
Semin Oncol,2006, 33 (3 Suppl 9) : S15-8.
( 0) 0)
|
| [15] |
Ren L, Hong SH, Chen QR, et al. Dysregulation of ezrin phosphorylation prevents metastasis and alters cellular metabolism in osteosarcoma[J].
Cancer Res,2012, 72 (4) : 1001-12.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-0210. ( 0) 0)
|
| [16] |
Chen Y, Wang D, Guo Z, et al. Rho kinase phosphorylation promotes ezrin-mediated metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma[J].
Cancer Res,2011, 71 (5) : 1721-9.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4683. ( 0) 0)
|
| [17] |
Bruce B, Khanna G, Ren L, et al. Expression of the cytoskeleton linker protein ezrin in human cancers[J].
Clin Exp Metastasis,2007, 24 (2) : 69-78.
DOI: 10.1007/s10585-006-9050-x. ( 0) 0)
|
| [18] |
Li Q, Wu M, Wang H, et al. Ezrin silencing by small hairpin RNA reverses metastatic behaviors of human breast cancer cells[J].
Cancer Lett,2008, 261 (1) : 55-63.
DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2007.11.018. ( 0) 0)
|
| [19] |
Zheng S, Huang J, Zhou K, et al. 17beta-Estradiol enhances breast cancer cell motility and invasion via extra-nuclear activation of actin-binding protein ezrin[J].
PLoS One,2011, 6 (7) : e22439.
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022439. ( 0) 0)
|
| [20] |
Sun F, Hug MJ, Bradbury NA, et al. Protein kinase A associates with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator via an interaction with ezrin[J].
J Biol Chem,2000, 275 (19) : 14360-6.
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.275.19.14360. ( 0) 0)
|
| [21] |
Matsui T, Maeda M, Doi Y, et al. Rho-kinase phosphorylates COOH-terminal threonines of ezrin/radixin/moesin(ERM)proteins and regulates their head-to-tail association[J].
J Cell Biol,1998, 140 (3) : 647-57.
DOI: 10.1083/jcb.140.3.647. ( 0) 0)
|
| [22] |
Shiue H, Musch MW, Wang Y, et al. Akt2 phosphorylates ezrin to trigger NHE3 translocation and activation[J].
J Biol Chem,2005, 280 (2) : 1688-95.
DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M409471200. ( 0) 0)
|
| [23] |
Ren L, Hong SH, Cassavaugh J, et al. The actin-cytoskeleton linker protein ezrin is regulated during osteosarcoma metastasis by PKC[J].
Oncogene,2009, 28 (6) : 792-802.
DOI: 10.1038/onc.2008.437. ( 0) 0)
|
| [24] |
Ng T, Parsons M, Hughes WE, et al. Ezrin is a downstream effector of trafficking PKC-integrin complexes involved in the control of cell motility[J].
EMBO J,2001, 20 (11) : 2723-41.
DOI: 10.1093/emboj/20.11.2723. ( 0) 0)
|
| [25] |
Simons PC, Pietromonaco SF, Reczek D, et al. C-terminal threonine phosphorylation activates ERM proteins to link the cell's cortical lipid bilayer to the cytoskeleton[J].
Biochem Biophys Res Commun,1998, 253 (3) : 561-5.
DOI: 10.1006/bbrc.1998.9823. ( 0) 0)
|
| [26] |
Wald FA, Oriolo AS, Mashukova A, et al. Atypical protein kinase C(iota)activates ezrin in the apical domain of intestinal epithelial cells[J].
J Cell Sci,2008, 121 (Pt 5) : 644-54.
( 0) 0)
|
| [27] |
Pan Q, Bao LW, Kleer CG, et al. Protein kinase C epsilon is a predictive biomarker of aggressive breast cancer and a validated target for RNA interference anticancer therapy[J].
Cancer Res,2005, 65 (18) : 8366-71.
DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-0553. ( 0) 0)
|
| [28] |
Adada MM, Canals D, Jeong N, et al. Intracellular sphingosine kinase 2-derived sphingosine-1-phosphate mediates epidermal growth factor-induced ezrin-radixin-moesin phosphorylation and cancer cell invasion[J].
FASEB J,2015, 29 (11) : 4654-69.
DOI: 10.1096/fj.15-274340. ( 0) 0)
|
| [29] |
Mak H, Naba A, Varma S, et al. Ezrin phosphorylation on tyrosine 477 regulates invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells[J].
BMC Cancer,2012, 12 : 82.
DOI: 10.1186/1471-2407-12-82. ( 0) 0)
|
 2016, Vol. 36
2016, Vol. 36
