2. 蚌埠医学院科研中心,安徽 蚌埠 233030
2. Scientific Research Center 2, Bengbu Medical College, Bengbu 233030, China
支气管哮喘(简称哮喘)是一种由多种细胞和炎性因子引起的慢性气道炎症。气道的高反应性、慢性炎症和气道重塑是哮喘的基本特征[1-2]。流行病学研究发现: 近年哮喘的发病率和死亡率有逐年增高的趋势,但目前其发病机制仍然不清[3]。miRNAs是一组长度约为22 个核苷酸的非编码RNA,其可通过抑制靶基因的翻译或引起靶基因mRNA 降解来调控靶基因的表达[4]。 最新的研究发现miRNAs 在哮喘的发病中起到重要作用[5-6]。本课题组前期的研究发现哮喘小鼠肺组织中miR-20b的表达明显低于正常小鼠,但miR-20b对哮喘发病的进程有何影响还不清楚[7]。本研究拟构建哮喘模型小鼠,观察鼻滴miR-20b模拟物后小鼠肺部病理变化的特点,以探讨miR-20b在哮喘发病中的可能作用。
1 材料与方法 1.1 主要试剂和仪器鸡卵清白蛋白(OVA)、氢氧化铝(Inject Alum)分别是Sigma 公司和PIERCE公司产品,VEGF ELISA试剂盒购于武汉华美公司,miR-20b mimics 和其对照是由上海吉玛公司设计合成,序列如下:miR-20b mimicssense:CAA AGU GCU CAU AGU GCA GGU AG,antisense:ACC UGC ACU AUG AGC ACU UUG UU,miR-20b mimics controlsense:UUC UCC GAA CGU GUC ACG UTT,antisense:ACG UGA CAC GUU CGG AGA ATT。YLS-8A多功能诱咳引喘仪是济南益延科技发展有限公司出品,ELISA酶标仪购于BioTek公司。
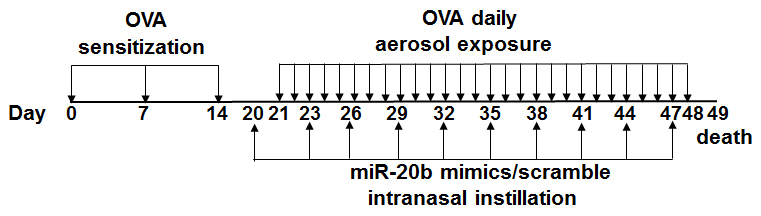
1.2 实验动物及哮喘模型的建立雌性BALB/c小鼠(2~3周龄)购于蚌埠医学院实验动物中心,随机分为4组:正常对照组(Control)、哮喘组(Asthma)、哮喘+ miR-20b 模拟物处理组(MiR-20b mimics)、哮喘+miR-20b 模拟物对照处理组(MiR-20b scramble),每组7只小鼠。除正常对照组外,其余3组于实验第0 天、7 天和14 天小鼠腹腔内注射200 μL致敏液(含OVA 50 μg,氢氧化铝2 mg),从实验第21 天起,将小鼠置于雾化吸入箱中,每天用5% OVA溶液雾化吸入激发(图 1),每次雾化30 min,连续雾化4 周。 MiR-20b mimics组小鼠于实验第20天起,经鼻滴20 μg miR-20b mimics 40 μL/次,1 次/3 d,共进行10 次。 MiR-20b scramble 组则以MiR-20b scramble 代替miR-20b mimics进行(图 2)。

|
图 1 本研究采用的雾化装置 Figure 1 Atomization device used in this experiment. |
|
图 2 本研究采用的流程图 Figure 2 Experimental model procedure in this study. |
实验第49 天,各组小鼠被拉颈处死,进行气管插管,留置12 号针头并固定,用PBS进行支气管肺泡灌洗,0.8 mL/次,连续6次。收集BALF离心,上清低温保存待用,沉淀红细胞裂解后进行细胞计数及涂片、瑞氏染色分类计数。
1.4 BALF中VEGF的检测收集各组小鼠BALF中上清,采用ELISA方法检测VEGF的含量,详细的方法见试剂盒说明书。
1.5 肺组织HE染色收集各组小鼠左肺组织,4%多聚甲醛液中固定1 周,常规酒精脱水,然后二甲苯透明及石蜡包埋,制备5 μm厚的石蜡切片,经脱蜡、浸泡等常规处理后苏木精- 伊红染色,然后二甲苯透明、中性树脂封片,光镜下观察拍照。
1.6 统计学分析数据采用均数±标准差表示,统计软件是SPSS 16.0,组间比较使用方差分析,P<0.05认为差异有统计学意义。
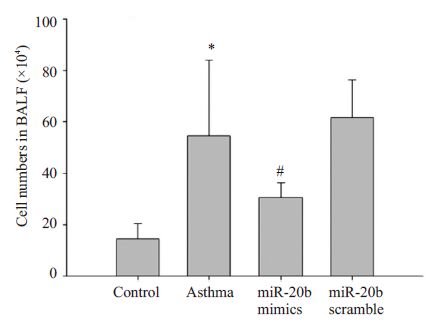
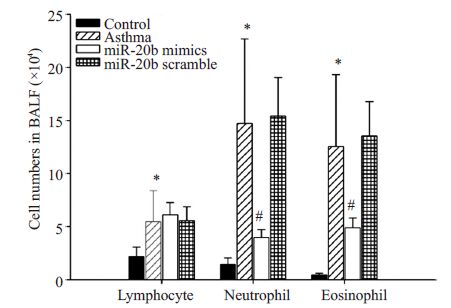
2 结果 2.1 miR-20b对BALF中细胞总数和细胞分类计数的影响哮喘组小鼠BALF中细胞总数及淋巴细胞、中性粒细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞的分类计数均较正常对照组明显升高(P<0.01),哮喘小鼠经miR-20b mimics处理后,细胞总数及中性粒细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞的分类计数均明显降低(P<0.01),但淋巴细胞的计数不受影响。哮喘+ miR-20b scramble处理组与哮喘组相比,上述细胞数无明显变化(图 3,4)。
|
图 3 miR-20b对BALF中细胞总数的影响 Figure 3 Effect of miR-20b on the total numbers of cells in BALF. |
|
图 4 miR-20b对BALF中白细胞分类计数的影响 Figure 4 Effect of miR-20b on the leukocyte classification counts in BALF. |
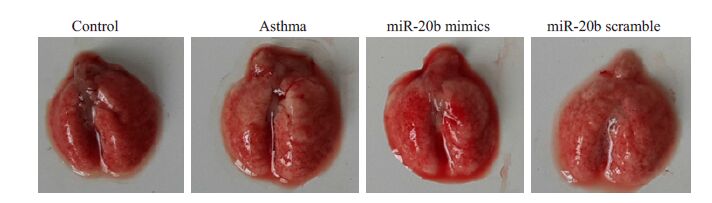
肉眼观察:正常小鼠肺组织均匀红润,而哮喘小鼠肺体积明显增大,肺表面多个区域肿胀泛白,呈地图状。哮喘+miR-20b mimics处理组小鼠肺体积较哮喘组有所减少,部分泛白区域趋于红润。哮喘+miR-20b scramble组小鼠肺大体与哮喘组类似(图 5)。
|
图 5 miR-20b对肺大体形态的影响 Figure 5 Effect of miR-20b on the morphology of the lung. |
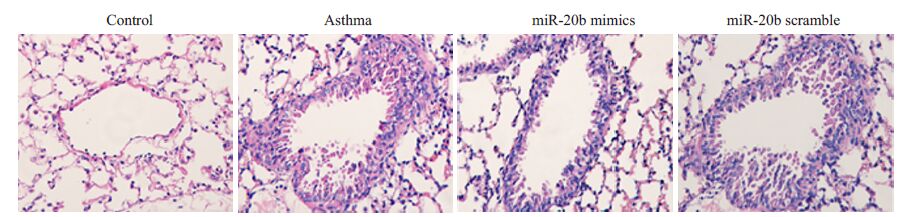
肺组织HE染色后镜下观察:正常对照组小鼠支气管及肺泡壁结构完整、规则,无明显增生、增厚,支气管管腔光滑,官腔中未见明显渗出物。哮喘组小鼠气道粘膜水肿增厚,褶皱增加,平滑肌增生,管腔狭窄,管腔中有大量粘液分泌,支气管周围有明显的炎性细胞浸润。 哮喘小鼠经miR-20b mimics处理后,黏膜增厚减轻,管腔规则,无明显平滑肌增生,仅有少量的粘液分泌,支气管周围炎性细胞的浸润也有所减轻。但哮喘小鼠经miR-20b scramble处理后肺组织形态改变不明显(图 6)。
|
图 6 miR-20b对肺组织病理学变化的影响 Figure 6 Effectof miR-20b on pathological changes of lung tissue. Control: normal control group; Asthma: asthma group; MiR-20b mimics: asthma+miR-20b analogues treatment group; MiR-20b scramble: asthma+miR-20b scramble treatment group. |
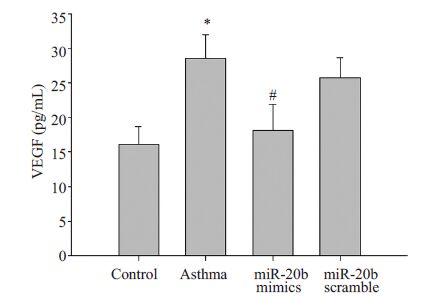
VEGF在慢性哮喘的发病中起到重要作用,因此我们对miR-20b 是否影响BALF中VEGF的表达进行了观察。结果如图 7:哮喘组小鼠BALF 中VEGF 浓度28.55±3.42 pg/mL较正常组16.13±2.61 pg/mL明显升高(P<0.01);哮喘小鼠经miR-20b mimics 处理后, BALF 中VEGF 含量降为18.19 ± 3.67 pg/mL,但MiR-20b scramble的处理对其无明显影响(图 7)。
|
图 7 miR-20b对BALF中VEGF浓度的影响 Figure 7 Effectof miR-20b on the concentration of VEGF in BALF. Control: normal control group; Asthma: asthma group; MiR-20b mimics: asthma + miR-20b analogues treatment group;MiR-20b scramble: asthma + miR-20b scramble treatment group. *P<0.01 υs control group; #P<0.01υs asthma group. |
哮喘是呼吸系统最常见的疾病之一,流行病学调查研究表明,目前全球约有3 亿哮喘患者,平均每年因哮喘死亡的病例多达250 000 人,并且哮喘的发病率、死亡率有逐年增高的趋势,哮喘已成为世界性的社会公共卫生问题[8]。
哮喘的实质是气道的一种慢性炎症,多种因素牵涉其中,目前确切的发病机制仍然不清[9]。miRNAs是一种约22个核苷酸长度的非编码RNA,其主要通过阻止翻译或mRNA的转录从而控制细胞的生长发育、增殖、 凋亡等生物学过程[10]。近期有多个课题组报道miRNAs对哮喘的发病产生了重要影响。Simpson等[11] 的研究表明:哮喘病人气道浸润T细胞miR-19的表达升高,miR-19促进Th2型细胞因子的产生并增加了气道炎症反应,miR-17~92基因簇缺陷的T细胞,Th2极化反应明显降低,该研究指出哮喘中miR-19的上调可能是气道Th2 型细胞因子产生增加的标志和原因。 Haj-Salem[12]则证明重度哮喘病人支气管上皮细胞miR-19a 的表达上调,miR-19a 通过靶向TGF-β受体2 而增加支气管上皮细胞的增殖,从而在气道重塑中起到重要作用。Martinez-Nunez课题组[13]发现,哮喘病人支气管上皮细胞miR-18a、miR-27a、miR-128、miR-155的表达下调,并且有趣的是只有当所有这些成分的功能同时被抑制时,才能控制IL-6、IL-8等炎性因子的表达上调,而单个miRNA的调节并无此效应。我们前期的研究发现:与正常小鼠相比,哮喘小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞miR-20b 的表达明显下调[7]。本研究则进一步证明miR-20b 可以抑制哮喘小鼠气道的炎症。miR-20b 属于miR-106a-363 基因簇成员,位于X染色体[14]。目前关于miR-20b的研究相对较少,Lei等[15]人的研究表明, 低氧状态下,miR-20b 的升高降低了H22 肝癌细胞VEGF与HIF-1α蛋白的表达,miR-20b可以负性调节这种细胞VEGF 的表达。此后,Cascio 等[16]又证明在MCF-7 乳腺癌细胞中miR-20b 可通过靶向HIF-1α与STAT-3降低VEGF的表达。VEGF是最重要的血管生成诱导因子,涉及多种生理性(胚胎发育、骨骼生长、生殖功能)和病理性(肿瘤、缺血、炎症)的血管发生过程[17-18]。 VEGF一方面可引起血管通透性增加,导致炎性细胞和介质渗出到气道血管外间隙内,产生气道炎症;另一方面它能刺激血管内皮细胞增殖,促进气道新生血管生成,在气道重塑中起到重要作用,因此VEGF对于哮喘的发病具有重要的病理生理学意义[19]。我们前期的研究证明哮喘小鼠肺泡巨噬细胞VEGF的表达上调,与miR-20b的表达正好相反,本研究进一步证明miR-20b 的作用使BALF中VEGF的含量降低。miRNAs的作用主要是通过其5’端7-8个碱基的“种子区”(seed region) 与靶基因3’-UTR互补结合来抑制靶基因的表达。根据miRanda 算法(http://www.microrna.org/microrna/), VEGF的3’-UTR区含有miR-20b 的作用靶点。因此miR-20b可能是通过直接靶向VEGF而抑制哮喘小鼠气道炎症,当然,要明确此问题,仍有待进一步研究。
| [1] | Pelaia G, Vatrella A, Busceti MT, et al. Cellular mechanisms underlying eosinophilic and neutrophilic airway inflammation in asthma[J]. Mediators Inflamm,2015, 2015 (8) : 879783. |
| [2] | Fahy JV. Type 2 inflammation in asthma--present in most, absent in many[J]. Nat Rev Immunol,2015, 15 (1) : 57-65. |
| [3] | Olin JT, Wechsler ME. Asthma: pathogenesis and novel drugs for treatment[J]. BMJ,2014, 349 : g5517. DOI: 10.1136/bmj.g5517. |
| [4] | Su Z, Yang Z, Xu Y, et al. MicroRNAs in apoptosis, autophagy and necroptosis[J]. Oncotarget,2015, 6 (11) : 8474-90. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget. |
| [5] | Perry MM, Adcock IM, Chung KF. Role of microRNAs in allergic asthma: present and future[J]. CurrOpin Allergy ClinImmunol,2015, 15 (2) : 156-62. |
| [6] | Kai W, Qian XU, Qun WU. MicroRNAs and Asthma Regulation[J]. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol,2015, 14 (2) : 120-5. |
| [7] | Song C, Ma H, Yao C, et al. Alveolar macrophage-derived vascular endothelial growth factor contributes to allergic airway inflammation in a mouse asthma model[J]. Scand J Immunol,2012, 75 (6) : 599-605. DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2012.02693.x. |
| [8] | Wang HY, Wong GW, Chen YZ, et al. Prevalence of asthma among Chinese adolescents living in Canada and in China[J]. CMAJ,2008, 179 (11) : 1133-42. DOI: 10.1503/cmaj.071797. |
| [9] | Woo Y, Jeong D, Chung DH, et al. The roles of innate lymphoid cells in the development of asthma[J]. Immune Netw,2014, 14 (4) : 171-81. DOI: 10.4110/in.2014.14.4.171. |
| [10] | Takasaki S. Roles of microRNAs in cancers and development[J]. Methods MolBiol,2015, 1218 : 375-413. |
| [11] | Simpson LJ, Patel S, Bhakta NR, et al. A microRNA upregulated in asthma airway T cells promotes TH2 cytokine production[J]. Nat Immunol,2014, 15 (12) : 1162-70. DOI: 10.1038/ni.3026. |
| [12] | Haj-Salem I, Fakhfakh R, Bérubé JC, et al. MicroRNA-19a enhances proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells by targeting TGFβR2 gene in severe asthma[J]. Allergy,2015, 70 (2) : 212-9. DOI: 10.1111/all.2015.70.issue-2. |
| [13] | Martinez-Nunez RT, Bondanese VP, Louafi F, et al. A microRNA network dysregulated in asthma controls IL-6 production in bronchial epithelial cells[J]. PLoS One,2014, 9 (10) : e111659. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0111659. |
| [14] | Landais S, Landry S, Legault P, et al. Oncogenic potential of the miR-106-363 cluster and its implication in human T-cell leukemia[J]. Cancer Res,2007, 67 (12) : 5699-707. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-4478. |
| [15] | Lei Z, Li B, Yang Z, et al. Regulation of HIF-1alpha and VEGF by miR-20b tunes tumor cells to adapt to the alteration of oxygen concentration[J]. PLoS One,2009, 4 (10) : e7629. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007629. |
| [16] | Cascio S, D'Andrea A, Ferla R, et al. miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells[J]. J Cell Physiol,2010, 224 (1) : 242-9. |
| [17] | Goel HL, Mercurio AM. VEGF targets the tumour cell[J]. Nat Rev Cancer,2013, 13 (12) : 871-82. DOI: 10.1038/nrc3627. |
| [18] | Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors[J]. Nat Med,2003, 9 (6) : 669-76. DOI: 10.1038/nm0603-669. |
| [19] | Meyer N, Akdis CA. Vascular endothelial growth factor as a key inducer of angiogenesis in the asthmatic airways[J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep,2013, 13 (1) : 1-9. DOI: 10.1007/s11882-012-0317-9. |
 2015, Vol. 35
2015, Vol. 35

