2. 广东深圳市第三人民医院 内一科,广东 深圳 518112 ;
3. 南方医科大学附属南方医院呼吸科,广东 广州 510515 ;
4. 广东深圳市第三人民医院 病理科,广东 深圳 518112 ;
5. 南方医科大学附属南方医院心内科实验室,广东 广州 510515
2. First Department of Internal Medicine, Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518112, China ;
3. Department of Respiratory Diseases, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China ;
4. Department of Pathology, Third People's Hospital of Shenzhen, Shenzhen 518112, China ;
5. Laboratory of Cardiology, Nanfang Hospital, Southern Medical University, Guangzhou 510515, China
气道重塑是支气管哮喘的基本特征之一。哮喘气道平滑肌细胞数量增加、肥大是气道重塑的重要原因[1]。miR-145是一种22-nt的高度保守的微小RNA(miRNA)。研究发现miR-145通过促进肿瘤细胞生长[2]、凋亡[3],但其是否能影响人支气管平滑肌细胞(HASMCs)增殖与凋亡,国内外未见报道。本研究拟探讨miR-145对ASMCs的增殖、凋亡的影响以初步了解其在哮喘中的作用。
1 材料和方法 1.1 材料DMEM培养基(Gibco),胎牛血清(PAA),CCK-8增殖试剂盒、Annexin V-FITC细胞凋亡检测试剂盒(北京碧云天公司),Lipofectamine 2000(Invitrogen),α-actin、骨桥蛋白单克隆抗体(武汉博士德),AntimiR-145(Applied Biosystems),流式细胞仪(美国BD)。
1.2 HASMCs原代培养传代,同文献[4]以平滑肌特异的α-actin单克隆抗体免疫荧光染色,鉴定为ASMCs。
1.3 转染将ASMCs细胞分为对照组和实验组,对照组不加Anti-miR-145,实验组加入不同浓度的Anti-miR-145(10、50、100 nmol/L)。转染在六孔板内,待细胞结合度约50%~70%时进行,加入不同浓度的AntimiR-145和10 μL的Lipofectamine 2000。转染后5 h换液。
1.4 CCK-8检测ASMC的增殖活力转染5 h后,每孔加入CCK-8 10 μL,继续37 ℃培养2 h,酶联免疫检测仪上450 nm处检测吸光度(A450值)。具体同文献[5]。
1.5 流式细胞术检测ASMCs凋亡上述细胞制成2×105/mL的悬液,取0.5 mL离心,195 μL Annexin V-FITC结合液重悬,加入5 μL Annexin V-FITC混匀避光孵育15 min。离心弃上清,再次以195 μL Annexin V-FITC结合液重悬,加10 μL氯化丙啶,流式细胞仪检测。凋亡率=阳性细胞数/细胞总数。
Western blotting检测Anti-miR-145转染对ASMCs骨桥蛋白(OPN)合成的影响。同文献[6]。
1.7 统计学处理采用SPSS 13.0统计分析,数据以均数±标准差表示。组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用LSD法。
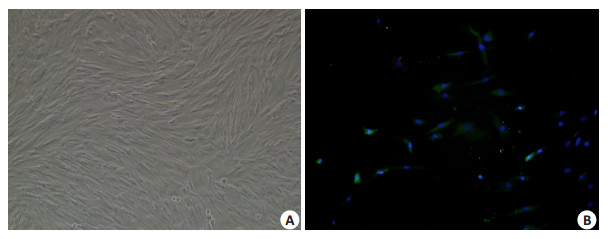
2 结果 2.1 培养的HASMCs及鉴定倒置相差显微镜下,HASMCs汇合后呈典型的“峰、谷”状。α-actin免疫荧光染色见绿色荧光。
2.2 Anti-miR-14对HASMCs增殖的影响10 nmol/L和50 nmol/L anti-miR-145转染HASMC后,平均吸光度值显著高于对照组。其中10 nmol/L组为0.986±0.103,较对照组0.834±0.128显著增高(P < 0.05);50 nmol/L组为1.101±0.089,较对照组显著增高(P < 0.01);而100 nmol/L anti-miR-145抑制剂转染ASMC后,平均吸光度0.932±0.115与对照组比较无显著差异(P > 0.05)。
|
图 1 培养的HASMCs形态及鉴定 Figure 1 Morphological and phenotypic identification of cultured HASMCs (Original magnification:×100). A: The typical peak and valley growth pattern of HASMCs; B: Immunofluorescence staining for α-SMA (green-fluorescence). |
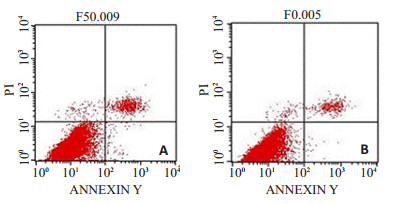
如图 2所示,50 nmol/L anti-miR-145组凋亡率(3.57±0.35)%较对照组(6.4±0.36)%显著降低(P < 0.01)。提示Anti-miR-145抑制HASMCs凋亡。
|
图 2 Anti-miR-145对HASMCs凋亡的影响 Figure 2 Effect of anti-miR-145 on HASMC apoptosis. A: Control group; B: 50 nmol/L anti-miR-145 group. |
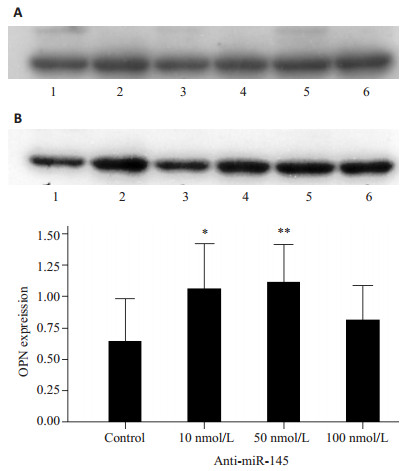
如图 3所示,10 nmol/L、50 nmol/L anti-miR-145促进HASMCs骨桥蛋白合成。100 nmol/L对HASMCs骨桥蛋白合成无明显影响。
|
图 3 不同浓度Ani-miR-145对骨桥蛋白合成的影响 Figure 3 Anti-miR-145 enhances osteopontin (OPN) synthesis in HASMCs. Upper: Western blotting results. HASMCs were stimulated with DMEM (control) and anti-miR-145 at 10, 50, and 100 nmol/L (Lanes 2, 3, and 4, respectively) for 48h. Lower: Quantitative analysis of the results (Mean±SD, n=3). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs control. |
miR-145是一种22-nt的高度保守miRNA,作用于c-Myc、CDK4进而抑制细胞增殖,使其停止在G1/S期[7],并通过Akt(P13K/Akt信号转导途径)、ERK(细胞外信号调节激酶(ERK)、EGFR(EGFR/MAPK信号通路)和NUDT1途径抑制细胞生长[8]。且miR-145可通过抑制DEF45蛋白的表达,而诱导结肠癌细胞凋亡[3]。已在肺组织中发现miR-145表达[9]。Collison等[10]发现,哮喘小鼠气道平滑肌miR-145表达上调,拮抗miR-145可减轻哮喘小鼠气道嗜酸性粒细胞炎症、气道粘液分泌、Th2细胞因子产生和气道高反应,其治疗效果可与激素媲美,提示miR-145可能在哮喘气道炎症中具有重要作用。但miR-145对哮喘气道重塑的关键细胞-ASMCs是否同样存在影响,国内外均未见相关的报道。本研究结果表明,拮抗miR-145可促进HASMCs增殖,抑制其凋亡,提示miR-145可能通过抑制平滑肌细胞增殖、促进其凋亡而参与支气管哮喘气道重塑。
Simoes等[11]和Kohan等[12-13]通过哮喘小鼠相继证实,与WT组比较,OPN-/-小鼠气道气道平滑肌增生面积减少、上皮下沉积的胶原蛋白含量降低。其研究尚发现重组OPN能促进支气管平滑肌细胞增殖分化。此外,有研究发现OPN可通过c-Myc[14]、ERK[15]通路促进细胞增殖。鉴于本研究发现Anti-miR-145可促进HASMCs增殖,我们进一步探讨了miR-145与OPN的关系。研究结果表明,Anti-miR-145促进OPN蛋白合成,提示miR-145促进HASMCs增殖可能与OPN有关。
总之,anti-miR-145可促进HASMCs增殖,抑制其凋亡,其机制可能与通过上调OPN表达有关。miR-145可能在支气管哮喘气道重塑中起重要作用。
| [1] | Johnson PR, Roth M, Tamm M, et al. Airway smooth muscle cell proliferation is increased in asthma[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2001, 164 (3) : 474-7. DOI: 10.1164/ajrccm.164.3.2010109. |
| [2] | Zhong M, Ma X, Sun CJ, et al. MicroRNAs reduce tumor growth and contribute to enhance cytotoxicity induced by gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chem Biol Interact,2010, 184 (3) : 431-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.025. |
| [3] | Zhang J, Guo H, Qian G, et al. MiR-145, a new regulator of the DNA Fragmentation Factor-45(DFF45)-mediated apoptotic network[Z], 2010: 211. |
| [4] | 高杨, 钟浩海, 罗雅玲, 等. PTEN基因表达改变对人气道平滑肌迁移的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2011, 31 (3) : 403-8. |
| [5] | 陈培芬, 罗雅玲, 赖文岩, 等. 巨噬细胞移动抑制因子促进肺成纤维细胞增殖和胶原合成[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2009, 25 (4) : 699-702. |
| [6] | 陈培芬, 罗雅玲, 赖文岩, 等. 巨噬细胞移动抑制因子经Rho途径促进人肺成纤维细胞Ⅰ型胶原合成[J]. 医学理论与实践,2011, 27 (14) : 1621-4. |
| [7] | Chen Z, Zeng HZ, Guo Y, et al. miRNA-145 inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation by targeting c-Myc[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res,2010, 29 (8) : 151. |
| [8] | Zhong M, Ma X, Sun C, et al. MicroRNAs reduce tumor growth and contribute to enhance cytotoxicity induced by gefitinib in non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Chem Biol Interact,2010, 184 (3) : 431-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2010.01.025. |
| [9] | Boettger T, Beetz N, Kostin S, et al. Acquisition of the contractile phenotype by murine arterial smooth muscle cells depends on the Mir143/145 gene cluster[J]. J Clin Invest,2009, 119 (9) : 2634-47. DOI: 10.1172/JCI38864. |
| [10] | Collison A, Mattes J, Plank M, et al. Inhibition of house dust miteinduced allergic airways disease by antagonism of mircoRNA-145 is comparable to glucocorticoid treatment[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol,2011, 128 (1) : 160-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.04.005. |
| [11] | Simoes DC, Xanthou G, Petrochilou KA, et al. Osteopontin deficiency protects against airway remodeling and hyperresponsiveness in chronic asthma[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2009, 179 (10) : 894-902. DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200807-1081OC. |
| [12] | Kohan M, Breuer R, Berkman N, et al. Osteopontin induces airway remodeling and lung fibroblast activation in a murine model of asthma[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,2009, 41 (3) : 290-6. DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2008-0307OC. |
| [13] | Kohan M, Bader R, Puxeddu I, et al. Enhanced osteopontin expression in a murine model of allergen-induced airway remodelling[J]. Clin Exp Allergy,2007, 37 (10) : 1444-54. |
| [14] | Martinez C, Churchman M, Freeman T, et al. Osteopontin provides early proliferative drive and May be dependent upon aberrant c-myc signalling in murine intestinal tumours[J]. Exp Mol Pathol,2010, 88 (2) : 272-7. DOI: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2009.12.008. |
| [15] | Yu HW, Liu QF, Liu GN. Positive regulation of the Egr-1/ osteopontin positive feedback loop in rat vascular smooth muscle cells by TGF-beta, ERK, JNK, and p38 MAPK signaling[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun,2010, 396 (2) : 451-6. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.04.115. |
 2015, Vol. 35
2015, Vol. 35