2. 丰宁县计划生育技术服务站,河北 承德 068350
2. Fengning County Family Planning Service Station, Chengde 068350, China
宫颈癌是妇科常见恶性肿瘤之一,其发病率仅次于乳腺癌位居第二位,据文献报道,我国每年新增宫颈癌病例约13.5万例,占全球宫颈癌发病数量的1/3,已成为严重威胁我国女性生命健康的主要疾病。目前认为高危型人乳头瘤病毒是引起宫颈癌的主要原因,但仍有一部分患者无病毒感染而发生宫颈癌,因此存在其他致病因素的可能。Wnt信号通路与肿瘤的发生发展密切相关,该信号通路的激活可以导致多种癌的发生。在宫颈癌的发生、发展过程中,目前该信号转导途径倍受关注。Wnt信号通路是与细胞分化、极性、转移、浸润、连接、存活密切相关的一条关键的通路[1]。研究发现Wnt信号通路受到许多不同拮抗分子的抑制调节,分泌性卷曲相关蛋白家族(SFRP1-5)及Dickkopf蛋白家族(DKK1-4)为重要的调节因子。在卵巢癌[2]和子宫内膜癌[3-4]中,SFRP1和SFRP4表达下调。相反的是,在乳腺癌、结直肠癌和前列腺癌中,SFRP4表达上调[5]。但在国内外研究中,宫颈癌中的表达比较少见。DKK1是DKK家族中研究最多的成员。DKK1是分泌性蛋白质,与胚胎发育过程中头的形成有关,与LRP5/6结合,阻断Wnt-1信号起到Wnt信号通路抑制因子的作用[6]。据报导DKK1在食管鳞癌、肝细胞癌、肺癌及多发性骨髓瘤等疾病的表达上调[7-9],但在宫颈癌的研究中较少见。由此可见DKK1和SFRP4在宫颈鳞癌中的表达情况目前仍缺乏足够的研究证据。本研究采用免疫组织化学法和RT-PCR技术,对DKK1和SFRP4在宫颈鳞癌中的表达进行检测,并分析其与临床病理特征的关系,从而进一步探讨Wnt/β-catenin信号转导途径在宫颈鳞癌发生发展中的作用机制,为临床上靶向治疗宫颈癌提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 一般资料标本采集为2011年10月~2012年10月期间,在承德医学院附属医院经手术治疗后病理证实为宫颈鳞癌标本66例,术前均未接受放化疗,患者平均年龄44岁(29~73岁),其中 < 44岁32例,≥44岁34例,病理分级:高中分化29例,低分化37例。浸润深度≤1/2的34例,>1/2的32例。其中FIGO分期Ⅰ期36例,Ⅱ期30例。淋巴结有转移者19例,无转移者47例。选取同期同年龄组因妇科良性肿瘤行全子宫切除术,术后经病理检测证实为正常宫颈组织的26例作为对照组。标本离体后快速剪取100 mg组织冻存于液氮中,随后转至-80 ℃冰箱中保存,用于提取mRNA,其余组织采取常规取材石蜡包埋,用于免疫组化染色。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 采用SP免疫组化法兔抗人SFRP4多克隆抗体购自于美国Proteintech公司,兔抗人DKK1单克隆抗体购自美国EPITOMICS公司,SP试剂盒(鼠/兔)购自北京迈新生物科技有限公司。操作步骤严格按照免疫组化试剂盒说明书进行。结果判定:DKK1及SFRP4阳性表达定位于细胞浆,并按阳性细胞比例评分:阳性细胞比例 < 25%,25%~50%,51%~75%及>75%,分别判定为0、1、2、3分;按着色强度评分:不着色为0分,浅黄色为1分,棕黄色为2分,棕褐色为3分。根据两项乘积进行综合评分:0分为阴性,1分及以上为阳性。采用双盲阅片法。
1.2.2 RT-PCR技术RNA提取试剂盒Trizol购自Gibco公司,逆转录试剂盒购自TaKaRa公司。采用Trizol试剂一步法提取总RNA,然后用AMV逆转录酶将其反转录成cDNA,扩增片段为145 bp,以β-actin作为内参照基因。DKK1基因上游引物(5'-AGCGGGGCCATTTCACAAAG-3');下游引物(5'-GATCATAGCACCTTGGATGGG-3')。SFRP4基因上游引物(5'-TGTGTTACGAGTGGCG-3');下游引物(5'-GGGGGATTACTACGACTG-3')。β-actin基因上游引物(5'-CTGGGACGACATGGAGAAAA-3');下游引物(5'-AAGGAAGGCTGGAAGAGTGC-3')。引物合成由TaKaRa公司完成。PCR反应产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳后,以每例DKK1和SFRP4分别与相应β-actin扩增产物条带累积光密度(IOD)的比值作为DKK1和SFRP4 mRNA的相对表达量。
1.3 统计学方法应用SPSS17.0统计学软件对数据进行统计分析。计量资料采用均数±标准差表示,采用两独立样本t检验。计数资料采用Fisher确切概率法或卡方检验进行比较。采用Spearman相关分析SFRP4及DKK1表达的相关性。以P < 0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
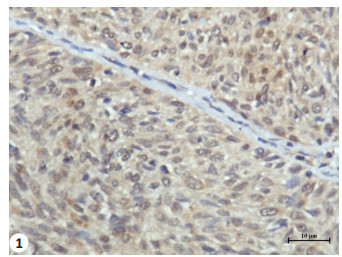
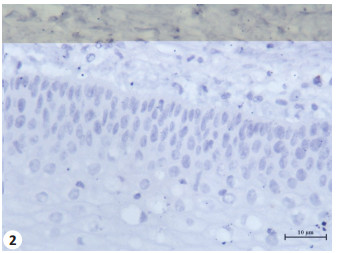
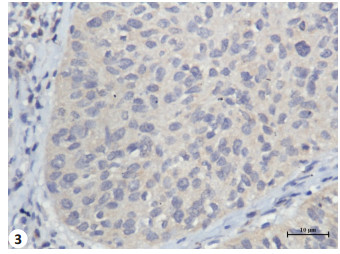
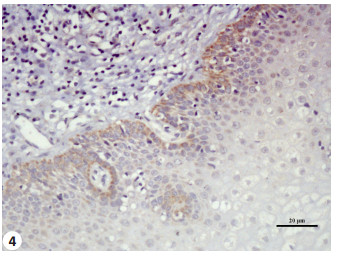
2 结果 2.1 通过免疫组织化学法检测SFRP4和DKK1蛋白在宫颈鳞癌及正常宫颈中的表达经χ2检验,宫颈鳞癌中SFRP4表达高于正常宫颈,差异具有统计学意义(χ2=8.49,P < 0.01)。DKK1在宫颈鳞癌中的表达低于正常宫颈,差异有高度统计学意义(χ2=5.72,P < 0.05,图 1~4和表 1)。
|
图 1 SFRP4在宫颈鳞癌组织中的表达 Figure 1 Expression level of SFRP4 in SCC (SP, original magnification, ×400). |
|
图 2 SFRP4在正常宫颈组织中的表达 Figure 2 Expression level of SFRP4 in normal cervix (SP, original magnification, ×400). |
|
图 3 DKK1在宫颈鳞癌组织中的表达 Figure 3 Expression level of DKK1 in SCC (SP, original magnification, ×400). |
|
图 4 DKK1在正常宫颈组织中的表达 Figure 4 Expression level of DKK1 in normal cervix (SP, original magnification, ×400). |
| 表 1 SFRP4和DKK1在宫颈鳞癌和正常宫颈组织中的表达 Table 1 Expression level of SFRP4 and DKK1 in SCC and normal cervix |
SFRP4蛋白在高中分化组的表达低于低分化组(χ2=6.49, P < 0.05);无淋巴结转移组低于有淋巴结转移组(χ2=7.20, P < 0.01);Ⅰ期组的表达低于Ⅱ期组(χ2=9.47, P < 0.01)。浸润深度≤1/2组低于>1/2组(χ2=8.04,P < 0.01)。SFRP4蛋白水平的表达与年龄无关(χ2=0.18,P > 0.05)。DKK1蛋白在高中分化组的表达高于低分化组(χ2=8.40,P < 0.01);Ⅰ期的表达则高于Ⅱ期组(χ2=7.83,P < 0.01);无盆腔淋巴结转移组高于有淋巴结转移组)χ2=6.41,P < 0.05)。浸润深度≤1/2组高于>1/ 2组(χ2=7.52,P < 0.01)。DKK1蛋白水平的表达与年龄无关(χ2=0.05,P > 0.05,表 2)。
| 表 2 SFRP4和DKK1蛋白的表达与宫颈鳞癌临床病理指标间的关系 Table 2 Correlations of SFRP4 and DKK1 with the clinicopathological characteristics of SCC |
正常宫颈组织中SFRP4 mRNA的表达量为0.11±0.01;高中分化宫颈鳞癌组织中SFRP4 mRNA表达量为0.39±0.04;低分化宫颈鳞癌组织中SFRP4 mRNA表达量为0.76±0.06。两两比较差异有显著性(P < 0.01,图 5)。
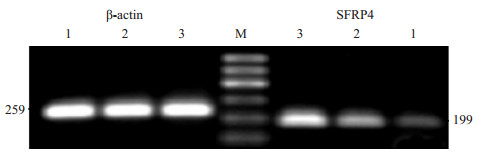
|
图 5 SFRP4在正常宫颈及宫颈鳞癌组织中RNA水平的表达 Figure 5 Expression level of SFRP4 mRNA in SCC and normal cervix. 1.Normal cervix; 2. SCC of well differentiation; 3. SCC of poor differentiation. |
正常宫颈组织中DKK1 mRNA的表达量为0.85±0.06;高中分化宫颈鳞癌组织中DKK1 mRNA表达量为0.50±0.04;低分化宫颈鳞癌组织中DKK1 mRNA表达量为0.13±0.01。两两比较差异有显著性(P < 0.01,图 6)。
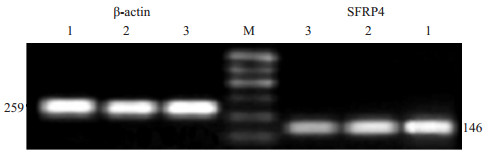
|
图 6 DKK1在正常宫颈及宫颈鳞癌组织中RNA水平的表达 Figure 6 Expression level of DKK1 mRNA in SCC and normal cervix. 1: Normal cervical tissue; 2: Well differentiated SCC; 3: Poorly differentiated SCC. |
SFRP4 mRNA水平的表达在有淋巴结转移组(0.76±0.14)高于无淋巴结转移组(0.55±0.16)。FIGO分期Ⅱ期组(0.69±0.10)高于Ⅰ期组(0.39±0.09)。浸润深度>1/2组(0.73±0.10)高于≤1/2组(0.38±0.08)。P均 < 0.05。SFRP4 mRNA表达在不同年龄分组中的表达无明显差异(P > 0.05)。
DKK1 mRNA水平的表达在有淋巴结转移组(0.15±0.09)低于无淋巴结转移组(0.35±0.19)。FIGO分期Ⅱ期组(0.13±0.05)低于Ⅰ期组(0.48±0.09)。浸润深度>1/2组(0.41±0.10)低于≤1/2组(0.70±0.12)。P均 < 0.05。DKK1 mRNA表达在不同年龄分组中的表达无明显差异(P > 0.05)。
2.5 宫颈鳞癌组织中SFRP4和DKK1表达的相关性Spearman等级相关分析结果显示,SFRP4和DKK1蛋白的表达呈明显负相关(r=-0.524, P < 0.01)。SFRP4和DKK1 mRNA的表达呈明显负相关)r=-0.861,P < 0.01)。
3 讨论女性生殖系统肿瘤中,宫颈癌是发病率最高的恶性肿瘤之一,而且发病年龄趋于年轻化。目前Wnt信号转导途径备受关注,宫颈癌的发生与癌基因的激活,抑癌基因的失活密切相关。Wnt信号转导途径受到分泌型蛋白的调节,如Dikkopf (Dkk),分泌型卷曲蛋白(sFRP)和Cerberus1(Cer1)[10-11]。据研究文献表明,我们推测宫颈癌是通过Wnt抑制因子SFRP进行经典通路的活化,特别是SFRP4和DKK的失活完成的[12-13]。
大量的研究表明DKKl在多种病理和生理过程中起到重要作用,如破骨细胞[14]和成人海马细胞[15]的形成,以及肿瘤的增生、存活、转移和侵袭[16-17]。然而,DKKl在肿瘤中的作用尚存在争议。一方面,DKKl作为肿瘤的抑制剂发挥作用。例如:Qi等[19-20]研究发现DKKl在结肠癌中的低表达,表明DKKl在肿瘤形成中可能扮演着抑癌基因的作用[18],确实,上调DKKl能够降低结肠癌细胞的增殖、克隆、转移和侵裂。另一方面,一项研究显示DKKl在小细胞肺癌、非小细胞肺癌和鳞状食道癌存在过表达[21];并且,DKKl在肾癌和乳腺癌也是高表达[22]。然而DKK1在宫颈鳞癌中的表达国内尚缺乏足够的研究证据。本研究通过免疫组织化学法和PT-PCR技术检测DKK1在宫颈鳞癌中的表达,结果显示:无论是在蛋白水平还是mRNA水平,DKK1在宫颈鳞癌中的表达均下调,并且与临床病理分期、组织分化程度、有无淋巴转移及浸润深度密切相关。由此我们可以推论:DKK1是宫颈鳞癌中Wnt信号通路的拮抗剂,由于DKK1表达减少或缺失,可引起Wnt信号通路的激活,从而导致宫颈鳞癌的发生,DKK1表达与宫颈鳞癌的侵袭和转移也密切相关。
SFRPs是直接与Wnt结合的分泌型蛋白家族[23],SFRPs蛋白结构中富含半胱氨酸区域(cysteine-rich domain, CRD),此半胱氨酸富含区域与卷曲型蛋白受体家族中的CRD具有30%~50%的同源性。SFRPs蛋白可以竞争性抑制Frizzled受体与Wnt的结合从而阻断Wnt的信号传导[24]。在多种肿瘤中SFRPs表达下调,包括间皮瘤和胃癌等。相反,在结直肠癌、乳腺癌和前列腺癌中,SFRP4则表达上调[5]。本研究采用免疫组织化学法和PT-PCR技术对宫颈鳞癌中SFRP4表达进行检测,结果显示:宫颈鳞癌中SFRP4表达上调,并且SFRP4与临床病理分期、组织分化程度、有无淋巴转移及浸润深度密切相关。因此,SFRP4可能作为宫颈鳞癌的监测指标,进一步评估宫颈鳞癌的侵袭转移等生物学特性等方面发挥重要的临床意义。
综上所述,在宫颈鳞癌组织中DKK1低表达,而SFRP4高表达,在宫颈鳞癌组织中两者呈负相关,并且均与宫颈鳞癌的临床病理分期、组织分化程度、有无淋巴转移及浸润深度密切相关。因此可推论,SFRP4表达上调与DKK1的表达下调协同作用,促使宫颈鳞癌的发生。DKK1作为Wnt信号通路的拮抗剂,为宫颈鳞癌的诊断和治疗提供一个新的分子靶点。而SFRP4的高表达,可能作为宫颈鳞癌的监测指标发挥作用。
| [1] | Chien AJ, Conrad WH, Moon RT. A Wnt survival guide: from flies to human disease[J]. J Invest Dermatol,2009, 129 : 1614-27. DOI: 10.1038/jid.2008.445. |
| [2] | Heinzelmann-Schwarz VA, Gardiner-Garden M, Henshall SM, et al. Overexpression of the cell adhesion molecules DDR1, Claudin 3, and Ep-CAM in metaplastic ovarian epithelium and ovarian cancer[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2004, 10 : 4427-36. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0073. |
| [3] | Carmon KS, Loose DS. Secreted frizzled-related protein 4 regulates two Wnt7a signaling pathways and inhibits proliferation in endometrial cancer cells[J]. Mol Cancer Res,2008, 6 : 1017-28. DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-08-0039. |
| [4] | Risinger JI, Maxwell GL, Chandramouli GV, et al. Gene expression profiling of microsatellite unstable and microsatellite stable endometrial cancers indicates distinct pathways of aberrant signaling[J]. Cancer Res,2005, 65 : 5031-7. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0850. |
| [5] | Horvath LG, Henshall SM, Kench JG, et al. Membranous expression of secreted frizzled-related protein 4 predicts for good prognosis in localized prostate cancer and inhibits PC3 cellular proliferation in vitro[J]. Clin Cancer Res,2004, 10 : 615-25. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-0707-03. |
| [6] | Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signalling[J]. Nature,2002, 417 : 664-7. DOI: 10.1038/nature756. |
| [7] | Wirths O, Waha A, Weggen S, et al. Overexpression of human Dickkopf-1, an antagonist of wingless/WNT signaling, in human hepatoblastomas and Wilms' tumors[J]. Lab Invest,2003, 83 : 429-34. DOI: 10.1097/01.LAB.0000059926.66359.BD. |
| [8] | Yu B, Yang X, Xu Y, et al. Elevated expression of DKK1 is associated with cytoplasmic/nuclear beta-catenin accumulation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinomas[J]. J Hepatol,2009, 50 : 948-57. |
| [9] | Yamabuki T, Takano A, Hayama S, et al. Dikkopf-1 as a novel serologic and prognostic biomarker for lung and esophageal carcinomas[J]. Cancer Res,2007, 67 : 2517-25. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3369. |
| [10] | Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, et al. Kremen proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin signaling[J]. Nature,2002, 417 : 664-7. DOI: 10.1038/nature756. |
| [11] | Pinson KI, Brennan J, Monkley S, et al. An LDLreceptor-related protein mediates Wnt signalling in mice[J]. Nature,2000, 407 : 535-8. DOI: 10.1038/35035124. |
| [12] | Perez-Plasencia C, Vazquez-Ortiz G, Lopez-Romero R, et al. Genome wide expression analysis in HPV16 Cervical Cancer: identification of altered metabolic pathways[J]. Infectious Agents and Cancer,2007, 2 : 16. DOI: 10.1186/1750-9378-2-16. |
| [13] | Duenas-Gonzalez A, Candelaria M, Perez-Plascencia C, de la CruzHernandez E. Herrera LA: Valproic acid as epigenetic cancer drug: Preclinical, clinical and transcriptional effects on solid tumors[J]. Cancer Treat Rev,2008, 34 : 206-22. DOI: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2007.11.003. |
| [14] | Pozzi S, Fulciniti M, Yan H, et al. In vivo and in vitro effects of a novel anti-Dkkl neutralizing antibody in multiple myeloma[J]. Bone,2013, 53 (2) : 487-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.bone.2013.01.012. |
| [15] | Seib DR, Corsini NS, Ellwanger K, et al. Loss of Dickkopf-1 restores neurogenesis in old age and counteracts cognitive decline[J]. Cell Stem Cell,2013, 12 (2) : 204-14. DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2012.11.010. |
| [16] | Shi RY, Yang XR, Shen QJ, et al. High expression of Dickkopfrelated protein l is related to lymphatic metastasis and indicates poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients after surgery[J]. Cancer,2013, 119 (5) : 994-1003. |
| [17] | Wang B, Liu J, Ma LN, et al. Chimeric 5/35 adenovirus-mediated Dickkopf-l overexpression suppressed tumorigenicity of CD44(+) gastric cancer cells via attenuating Wnt signaling[J]. J Gastroenterol,2013, 48 (7) : 798-808. DOI: 10.1007/s00535-012-0711-z. |
| [18] | Gonzalez-Sancho JM, Aguilera O, Garcia JM, et al. The Wnt antagonist DICKKOPF-l gene is a downstream target of betacatenin/TCF and is downregulated in human colon cancer[J]. Oncogene,2005, 24 (6) : 1098-103. DOI: 10.1038/sj.onc.1208303. |
| [19] | Qi L, Sun B, Liu Z, et al. Dickkopf-l inhibits epithelialmesenchymal transition of colon cancer cells and contributes to colon cancer suppression[J]. Cancer Sci,2012, 103 (4) : 828-35. DOI: 10.1111/cas.2012.103.issue-4. |
| [20] | Sikandar S, Dizon D, Shen X, et al. The class l HDAC inhibitor MGCD0103 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer initiating cells by upregulating Dickkopf-1 and non-canonical Wnt signaling[J]. Oncotarget,2010, 1 (7) : 596-605. DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget. |
| [21] | Yamabuki T, Takano A, Hayama S, et al. Dikkopf-1 as a novel serologic and prognostic biomarker for lung and esophageal carcinomas[J]. Cancer Res,2007, 67 (6) : 2517-25. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3369. |
| [22] | Forget MA, Turcotte S, Beauseigle D, et al. The Wnt pathway regulator DKK 1 is preferentially expressed in hormone-resistant breast tumours and in some common cancer types[J]. Br J Cancer,2007, 96 (4) : 646-53. DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603579. |
| [23] | Jana R, Maximilian M, Martin N, et al. Transcriptional downregulation of the Wnt antagonist SFRP1 in haematopoietic cells of patients with different risk types of MDS[J]. Leukemia Research,2010, 34 : 1610-6. DOI: 10.1016/j.leukres.2010.04.013. |
| [24] | Tang D, Wang DR, Li HB. Combination analysis of hypermethylated SFRP1 and SFRP2 gene in fecal as a novel epige-netic biomarker panel for colorectal cancer screening[J]. J Nanjing Medical University,2008, 22 (2) : 96-101. DOI: 10.1016/S1007-4376(08)60020-9. |
 2015, Vol. 35
2015, Vol. 35
