Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 921-928.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.04
Previous Articles Next Articles
Yanpeng PU1,2( ), Zhen WANG2, Haoran CHU3(
), Zhen WANG2, Haoran CHU3( )
)
Received:2025-01-26
Online:2025-05-20
Published:2025-05-23
Contact:
Haoran CHU
E-mail:361364304@qq.com;chuhaoran62@163.com
Supported by:Yanpeng PU, Zhen WANG, Haoran CHU. Eye acupuncture improves neural function in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by promoting angiogenesis via upregulating METTL3-mediated m6A methylation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(5): 921-928.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.05.04
| Phenotype | Score |
|---|---|
| There was no neurological impairment | 0 |
| When lifting the tail, the contralateral forelimb is adducted and flexed | 1 |
| When crawling, rotate to the opposite side | 2 |
| When standing or crawling, tip to the opposite side | 3 |
| No voluntary movement with disturbance of consciousness | 4 |
Tab.1 Longa function scoring criteria
| Phenotype | Score |
|---|---|
| There was no neurological impairment | 0 |
| When lifting the tail, the contralateral forelimb is adducted and flexed | 1 |
| When crawling, rotate to the opposite side | 2 |
| When standing or crawling, tip to the opposite side | 3 |
| No voluntary movement with disturbance of consciousness | 4 |
| Inspect | Phenotype | Score |
|---|---|---|
Gently grasp the tail and lift the rat 10 cm above the table top. Normal rats should extend their front PAWS straight. | There was no neurological impairment | 0 |
| Brain lesions flexion of the wrist, elbow and shoulder adduction | 1 | |
| The above signs+decreased resistance to push on the paralytic side | 2 | |
| Move in a circle towards the paralyzed side (rear-end) | 3 |
Tab.2 Bederson scoring criteria
| Inspect | Phenotype | Score |
|---|---|---|
Gently grasp the tail and lift the rat 10 cm above the table top. Normal rats should extend their front PAWS straight. | There was no neurological impairment | 0 |
| Brain lesions flexion of the wrist, elbow and shoulder adduction | 1 | |
| The above signs+decreased resistance to push on the paralytic side | 2 | |
| Move in a circle towards the paralyzed side (rear-end) | 3 |
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'→3') | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| METTL3 | F:TGGGGGTATGAACGGGTAGA R:TCCTTTGACACCAACCAAGC | 129 |
| HIF-1α | F:TTACAGGATTCCAGCAGACCCA R:GCTGATGCCTTAGCAGTGGTC | 145 |
| VEGF-A | F:TAAATCCTGGAGCGTTCACTGTG R:TTCGTTTAACTCAAGCTGCCTC | 145 |
| GAPDH | F:GGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG R:CGCCAGTAGACTCCACGACAT | 150 |
Tab.3 Primer sequences used for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'→3') | Product length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| METTL3 | F:TGGGGGTATGAACGGGTAGA R:TCCTTTGACACCAACCAAGC | 129 |
| HIF-1α | F:TTACAGGATTCCAGCAGACCCA R:GCTGATGCCTTAGCAGTGGTC | 145 |
| VEGF-A | F:TAAATCCTGGAGCGTTCACTGTG R:TTCGTTTAACTCAAGCTGCCTC | 145 |
| GAPDH | F:GGCAAGTTCAACGGCACAG R:CGCCAGTAGACTCCACGACAT | 150 |
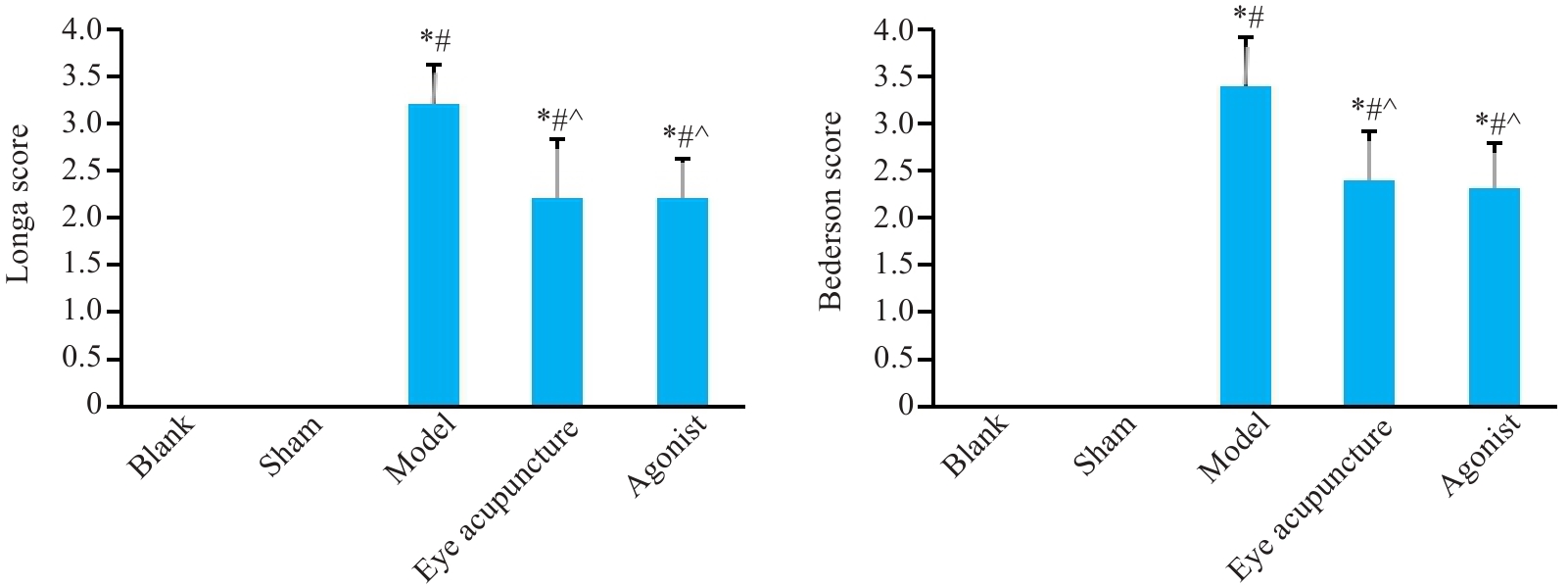
Fig.1 Neurological function scores of the rats in different groups (Mean±SD, n=10). *P<0.05 vs Blank group; #P<0.05 vs Sham group; ^P<0.05 vs model group.
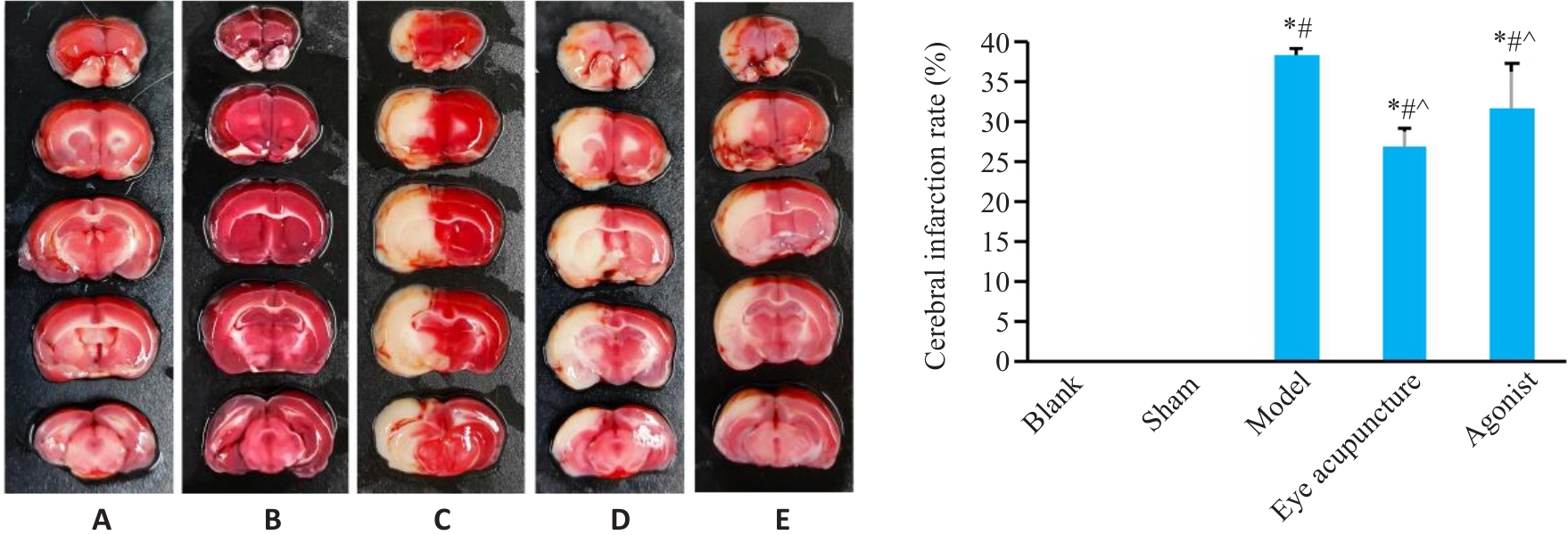
Fig.2 Brain TTC staining showing cerebral infarct sizes in different groups (Mean±SD, n=3). A: Blank group; B: Sham operation group; C: Model group; D: Eye acupunctrue group; E: HIF-1α agonist group. *P<0.05 vs Blank group; #P<0.05 vs Sham group; ^P<0.05 vs model group.
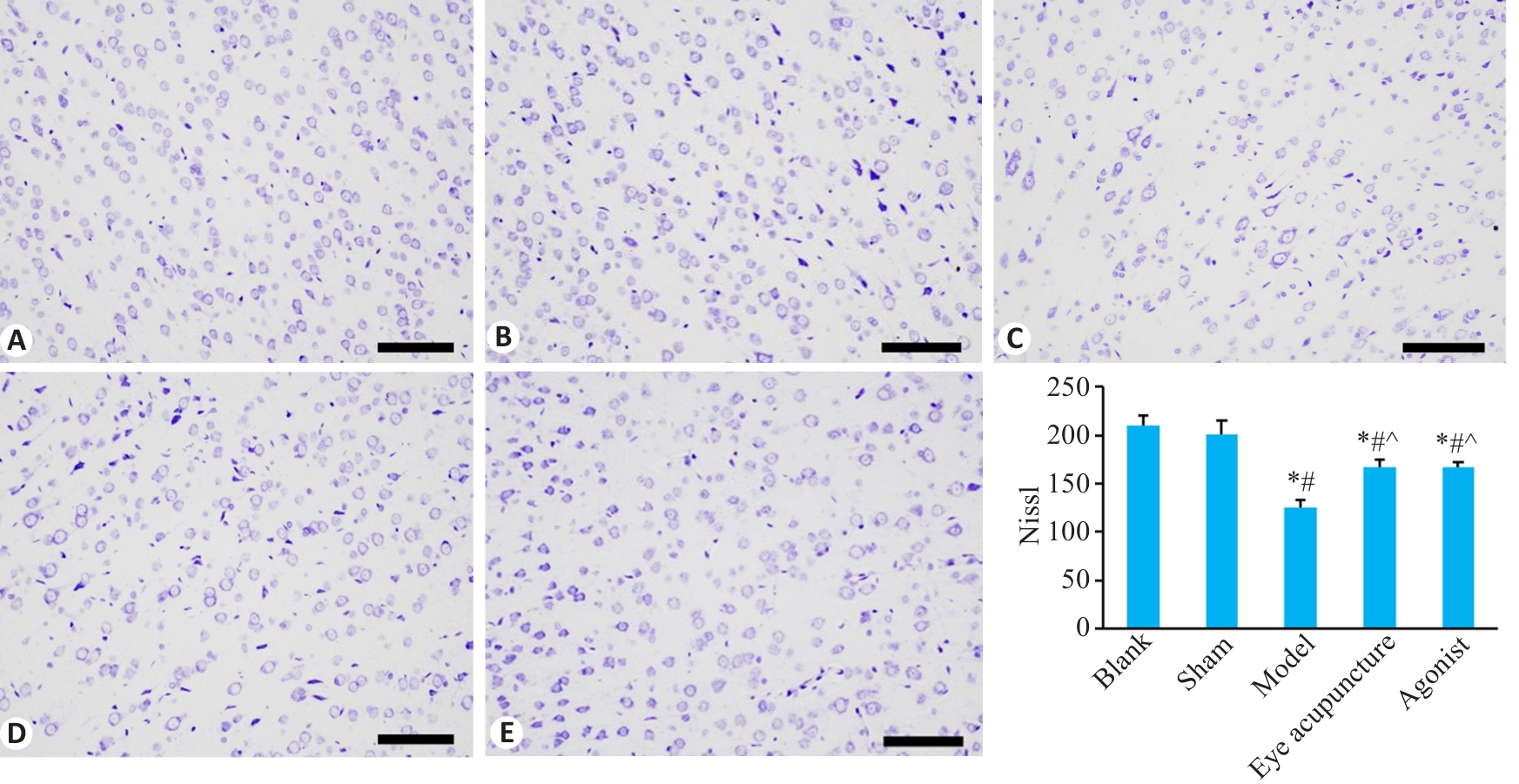
Fig.3 Nissl staining of the cortical tissue in different groups (Scale bar=100 μm; Mean±SD, n=3). A: Blank group; B: Sham operation group; C: Model group; D: Eye acupunctrue group; E: HIF-1α agonist group. *P<0.05 vs Blank group; #P<0.05 vs Sham group; ^P<0.05 vs model group.
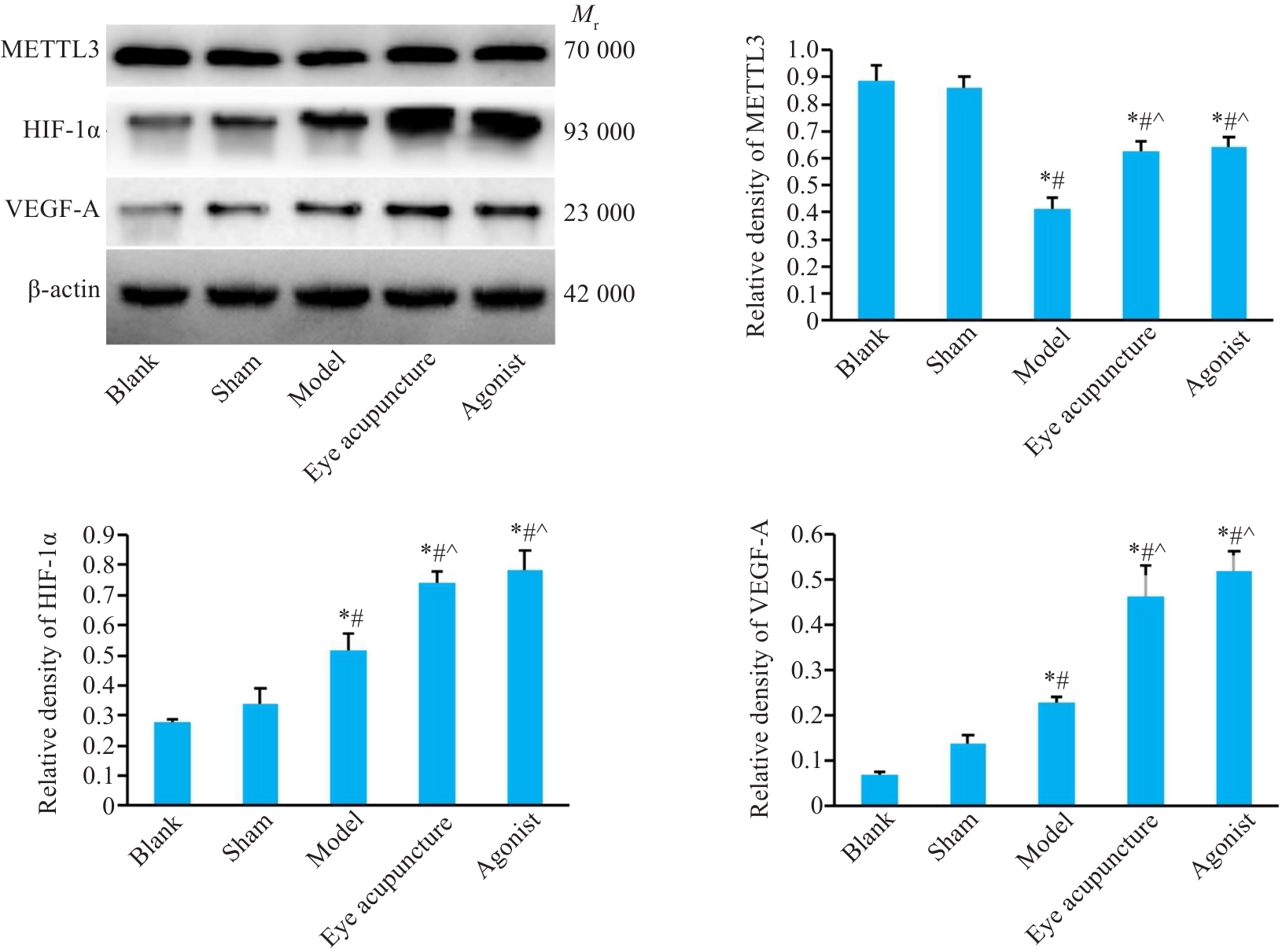
Fig.6 Expression of METTL3 and HIF-1α/VEGF-A in rat cerebral cortex detected by Western blotting (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05 vs Blank group; #P<0.05 vs Sham group; ^P<0.05 vs model group.
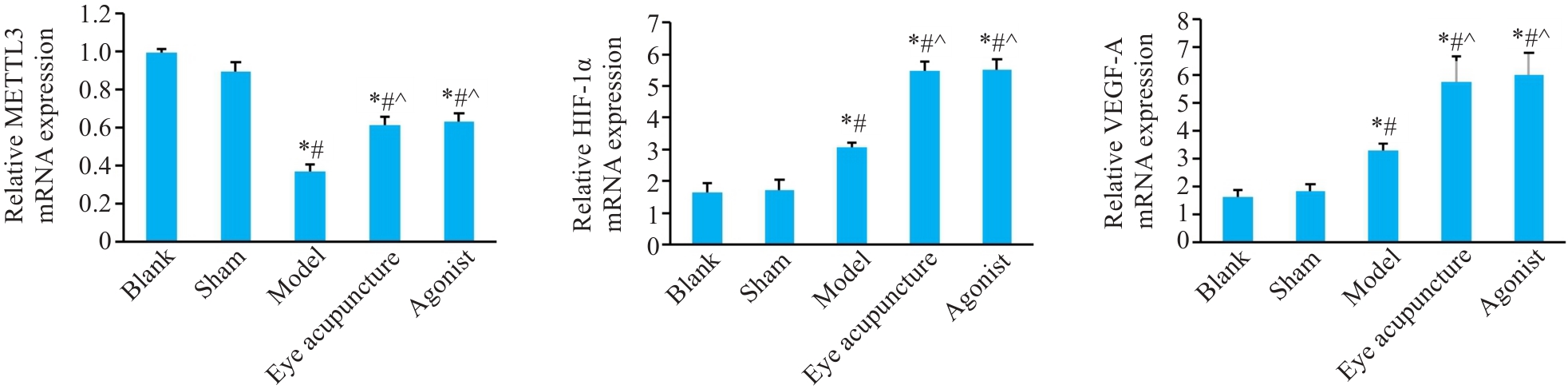
Fig.7 mRNA expression of METTL3 and HIF-1α/VEGF-A in rat cerebral cortex detected by RT-qPCR (Mean±SD, n=3). *P<0.05 vs Blank group; #P<0.05 vs Sham group; ^P<0.05 vs model group.
| 1 | Collaborators G 2 S. Global, regional, and national burden of stroke and its risk factors, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019[J]. Lancet Neurol, 2021, 20(10): 795-820. |
| 2 | 浦延鹏, 王鹏琴, 程景艳, 等. 基于数据挖掘探析眼针的优势病种及治疗方法[J]. 辽宁中医杂志, 2023, 50(4): 11-6. DOI: 10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2023.04.003 |
| 3 | 楚 宝, 张继杰, 董立朋, 等. 脑血管侧支循环评价的研究进展[J]. 中国全科医学, 2020, 23(5): 516-24. DOI: 10.12114/j.issn.1007-9572.2019.00.305 |
| 4 | 武家竹, 陈林玲, 邸嘉玮, 等. 针灸改善缺血性脑卒中侧支循环的血管作用机制[J]. 针灸临床杂志, 2023, 39(6): 105-9. |
| 5 | 付彩红, 吴 爽, 张 虎, 等. 针刺促进缺血性脑卒中血管新生研究进展[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报, 2021, 23(12): 87-93. DOI: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2021.12.018 |
| 6 | Vatte S, Ugale R. HIF-1, an important regulator in potential new therapeutic approaches to ischemic stroke[J]. Neurochem Int, 2023, 170: 105605. |
| 7 | 谭佳佳, 唐丽亚, 孙晓莹, 等. 电针预处理对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经功能及缺血半暗带区VEGF、CD31表达的影响[J]. 湖南中医药大学学报, 2023, 43(9): 1679-84. |
| 8 | Xu SY, Ni SM, Zeng CL, et al. Electro-acupuncture promotes angiogenesis via exosomal miR-210 in the hypoxia-induced HUVECs mediated HIF-1α/VEGF/Notch 1 signal pathway[J]. Curr Neurovasc Res, 2022, 19(4): 406-17. |
| 9 | Zhang HS, Zhou JW, Li JX, et al. N6-methyladenosine promotes translation of VEGFA to accelerate angiogenesis in lung cancer[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(13): 2208-25. |
| 10 | Yao MD, Jiang Q, Ma Y, et al. Role of METTL3-dependent N6-methyladenosine mRNA modification in the promotion of angiogenesis[J]. Mol Ther, 2020, 28(10): 2191-202. |
| 11 | Chen K, Li WD, Li XQ. The role of m6A in angiogenesis and vascular diseases[J]. iScience, 2024, 27(7): 110082. |
| 12 | 马贤德, 孙宏伟, 柴纪严, 等. 线栓法制备大鼠脑缺血再灌注模型的方法研究[J]. 中华中医药学刊, 2009, 27(6): 1200-1. |
| 13 | Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, et al. Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats[J]. Stroke, 1989, 20(1): 84-91. |
| 14 | 彭静山原著,彭筱山, 王鹏琴整理. 眼针疗法[M]. 2版. 沈阳: 辽宁科学技术出版社, 2018. |
| 15 | Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, et al. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination[J]. Stroke, 1986, 17(3): 472-6. |
| 16 | Zhang W, Han L, Wen Y, et al. Electroacupuncture reverses endothelial cell death and promotes angiogenesis through the VEGF/Notch signaling pathway after focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. Brain Behav, 2023, 13(3): e2912. |
| 17 | Wang L, Sheng G, Cui J, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates ischemic injury after stroke and promotes angiogenesis via activation of EPO mediated Src and VEGF signaling pathways[J]. PLoS One, 2022, 17(9): e0274620. |
| 18 | Geiseler SJ, Morland C. The Janus face of VEGF in stroke[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2018, 19(5): 1362. |
| 19 | Yang L, Yang BC, Zhang CX, et al. Protective effects of acupuncture and LGNHFD on expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, and cluster of differentiation 34 in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury[J]. J Tradit Chin Med, 2021, 41(3): 463-70. |
| 20 | 邵 妍, 王鹏琴, 王树东, 等. 眼针运动疗法对脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑缺血半暗带区VEGF蛋白及VEGFmRNA表达的影响[J]. 中国中医基础医学杂志, 2015, 21(4): 445-8. |
| 21 | Chen HX, Ma D, Yue FX, et al. The potential role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 in the progression and therapy of central nervous system diseases[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2022, 20(9): 1651-66. |
| 22 | Hu QM, Liu L, Zhou L, et al. Effect of fluoxetine on HIF-1α- Netrin/VEGF cascade, angiogenesis and neuroprotection in a rat model of transient middle cerebral artery occlusion[J]. Exp Neurol, 2020, 329: 113312. |
| 23 | Wang L, Li JC, Wang Y, et al. Dan-Deng-Tong-Nao softgel capsule promotes angiogenesis of cerebral microvasculature to protect cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via activating HIF-1α-VEGFA-Notch1 signaling pathway[J]. Phytomedicine, 2023, 118: 154966. |
| 24 | Ni HZ, Li JX, Zheng JY, et al. Cardamonin attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the HIF-1α/VEGFA pathway[J]. Phytother Res, 2022, 36(4): 1736-47. |
| 25 | Han F. N6 -methyladenosine modification in ischemic stroke: Functions, regulation, and therapeutic potential[J]. Heliyon, 2024, 10(3): e25192. |
| 26 | Wang LJ, Xue YM, Huo R, et al. N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase METTL3 affects the phenotype of cerebral arteriovenous malformation via modulating Notch signaling pathway[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2020, 27(1): 62. |
| 27 | Huang HL, Weng HY, Chen JJ. m6A modification in coding and non-coding RNAs: roles and therapeutic implications in cancer[J]. Cancer Cell, 2020, 37(3): 270-88. |
| 28 | Tian S, Li YL, Wang J, et al. Chinese Ecliptae herba (Eclipta prostrata (L.) L.) extract and its component wedelolactone enhances osteoblastogenesis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via targeting METTL3-mediated m6A RNA methylation[J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2023, 312: 116433. |
| 29 | 庞立健, 王鹏琴, 吕晓东, 等. 彭氏眼针疗法理论阐释及应用[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2023, 38(1): 90-5. |
| 30 | 浦延鹏. 基于Wnt3a/β-catenin/LEF1信号通路探讨眼针促MCAO/R大鼠血管新生的作用机制[D]. 沈阳: 辽宁中医药大学, 2021. |
| 31 | Sen T, Sen N. Treatment with an activator of hypoxia-inducible factor 1, DMOG provides neuroprotection after traumatic brain injury[J]. Neuropharmacology, 2016, 107: 79-88. |
| 32 | 牛雨晴, 秦合伟, 李彦杰, 等. 眼针干预脑缺血模型大鼠调节血管新生因子表达促进血管新生[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(23): 3674-81. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||