南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (12): 2607-2615.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.12.08
• • 上一篇
丁珊珊1( ), 廖颖1, 白雪1, 黄娇阳1, 浅川哲也1,2
), 廖颖1, 白雪1, 黄娇阳1, 浅川哲也1,2
收稿日期:2025-07-22
出版日期:2025-12-20
发布日期:2025-12-22
通讯作者:
丁珊珊
E-mail:ding123shan@163.com
基金资助:
Shanshan DING1( ), Ying LIAO1, Xue BAI1, Jiaoyang HUANG1, Tetsuya ASAKAWA1,2
), Ying LIAO1, Xue BAI1, Jiaoyang HUANG1, Tetsuya ASAKAWA1,2
Received:2025-07-22
Online:2025-12-20
Published:2025-12-22
Contact:
Shanshan DING
E-mail:ding123shan@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨Cav1对小鼠肝细胞线粒体功能和mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰及表达水平的影响。 方法 采用慢病毒转染敲低小鼠肝细胞AML12中Cav1基因的表达(shCav1组),转染阴性对照病毒作为对照组。采用TMRE荧光探针检测线粒体膜电位变化,结合Seahorse能量代谢分析系统检测线粒体呼吸功能。采用甲基化RNA免疫共沉淀技术(MeRIP)联合m6A表观转录组芯片检测mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰和表达水平变化,通过富集分析筛选线粒体功能相关基因,并用qPCR验证目标基因mRNA的m6A 修饰和表达水平。 结果 与对照组相比,shCav1组线粒体膜电位(P<0.05)和线粒体呼吸能力降低(P<0.01)。m6A表观转录组芯片检测结果显示,shCav1组有7814个mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰水平发生变化(变化倍数>1.5,P<0.05),其中152个上调、7662个下调。联合表达差异分析显示,有2497个mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰和表达水平存在协同变化。协同变化的mRNA富集到氧化磷酸化通路,其中Usp15、Suclg2、Ppa2 mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰变化百分比最高。芯片和qPCR结果均显示shCav1组中Usp15、Suclg2、Ppa2 mRNA的m6A修饰和表达水平均较对照组降低(P<0.05)。 结论 Cav1敲低的小鼠肝细胞mRNA的m6A甲基化修饰变化显著,该变化与mRNA的表达有关,Cav1对线粒体功能的调节作用可能依赖于其对Usp15、Suclg2、Ppa2 mRNA的m6A修饰调控。
丁珊珊, 廖颖, 白雪, 黄娇阳, 浅川哲也. 敲低Cav1基因可抑制小鼠肝细胞线粒体功能及关键基因mRNA的m6A修饰和表达[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(12): 2607-2615.
Shanshan DING, Ying LIAO, Xue BAI, Jiaoyang HUANG, Tetsuya ASAKAWA. Knockdown of Cav1 inhibits mitochondrial function and mRNA m6A modification and expression of key genes in mouse hepatocytes[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(12): 2607-2615.
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Usp15 | CCGTGGATGAAAACCTGAGTAG | TTCTCTTAGGCAGACAGGGATAA |
| Suclg2 | CCAGCGAACTTCTTGGACCT | CACAGTTGACGATCCCACCA |
| Ppa2 | CGGTGGACAAATGCCAAGATG | TTCGGTGTGTAGCGTAGCTT |
| Gapdh | CACTGAGCAAGAGAGGCCCTAT | GCAGCGAACTTTATTGATGGTATT |
表1 MeRIP-qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequences for MeRIP-qPCR
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| Usp15 | CCGTGGATGAAAACCTGAGTAG | TTCTCTTAGGCAGACAGGGATAA |
| Suclg2 | CCAGCGAACTTCTTGGACCT | CACAGTTGACGATCCCACCA |
| Ppa2 | CGGTGGACAAATGCCAAGATG | TTCGGTGTGTAGCGTAGCTT |
| Gapdh | CACTGAGCAAGAGAGGCCCTAT | GCAGCGAACTTTATTGATGGTATT |
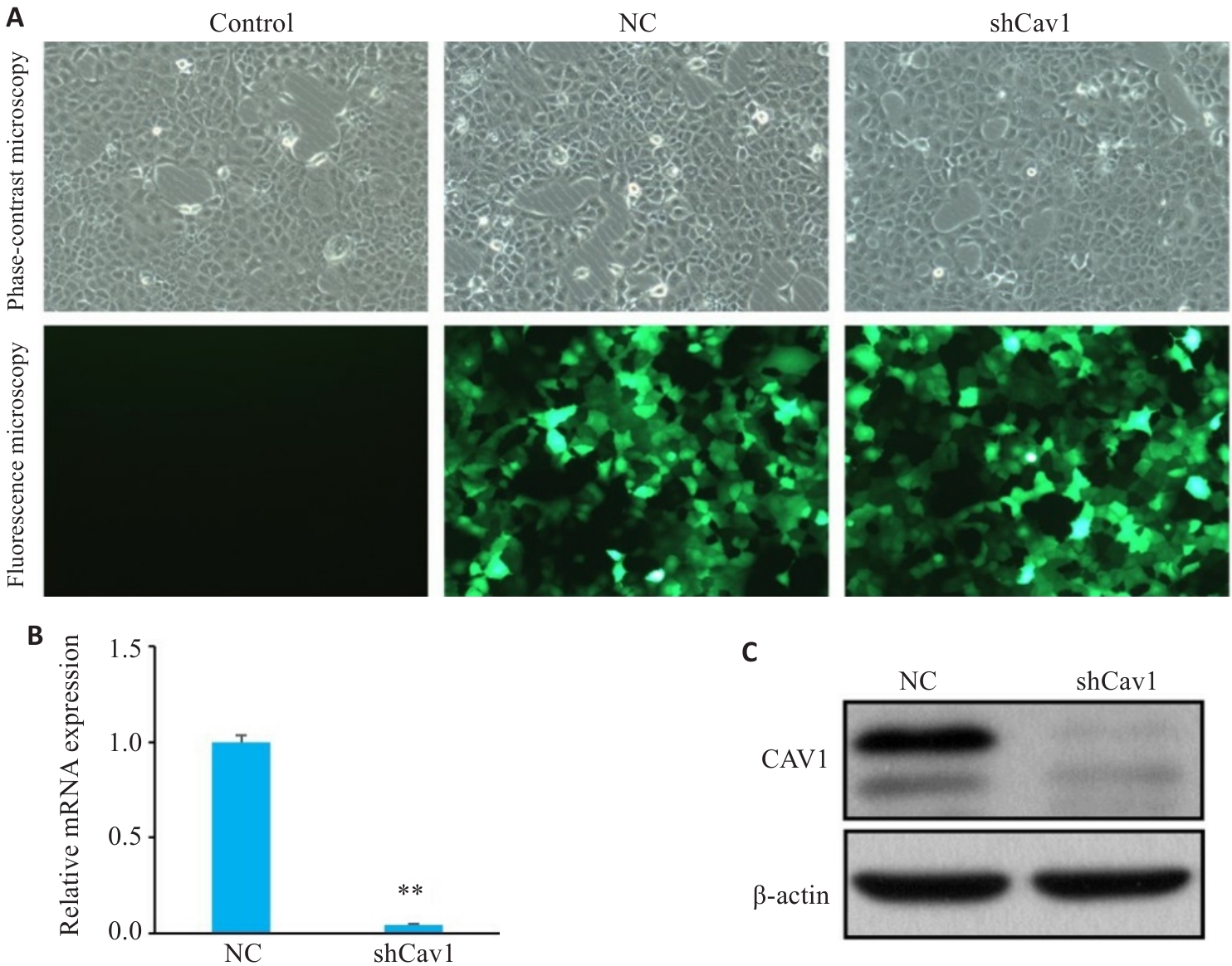
图1 shCav1慢病毒转染AML12细胞下调Cav1的表达
Fig.1 Knockdown of Cav1 by lentivirus-mediated transfection with shCav1 in AML12 cells. A: Phase-contrast and fluorescence microscopy of the cells under bright-field conditions (GFP, Original magnification: ×100). B: Real-time PCR analysis of Cav1 mRNA expression levels. C: Western blotting of Cav1 protein expression. Control : Untreated control; NC: Control shRNA; shCav1: Cav1 shRNA. **P<0.01 vs NC group.
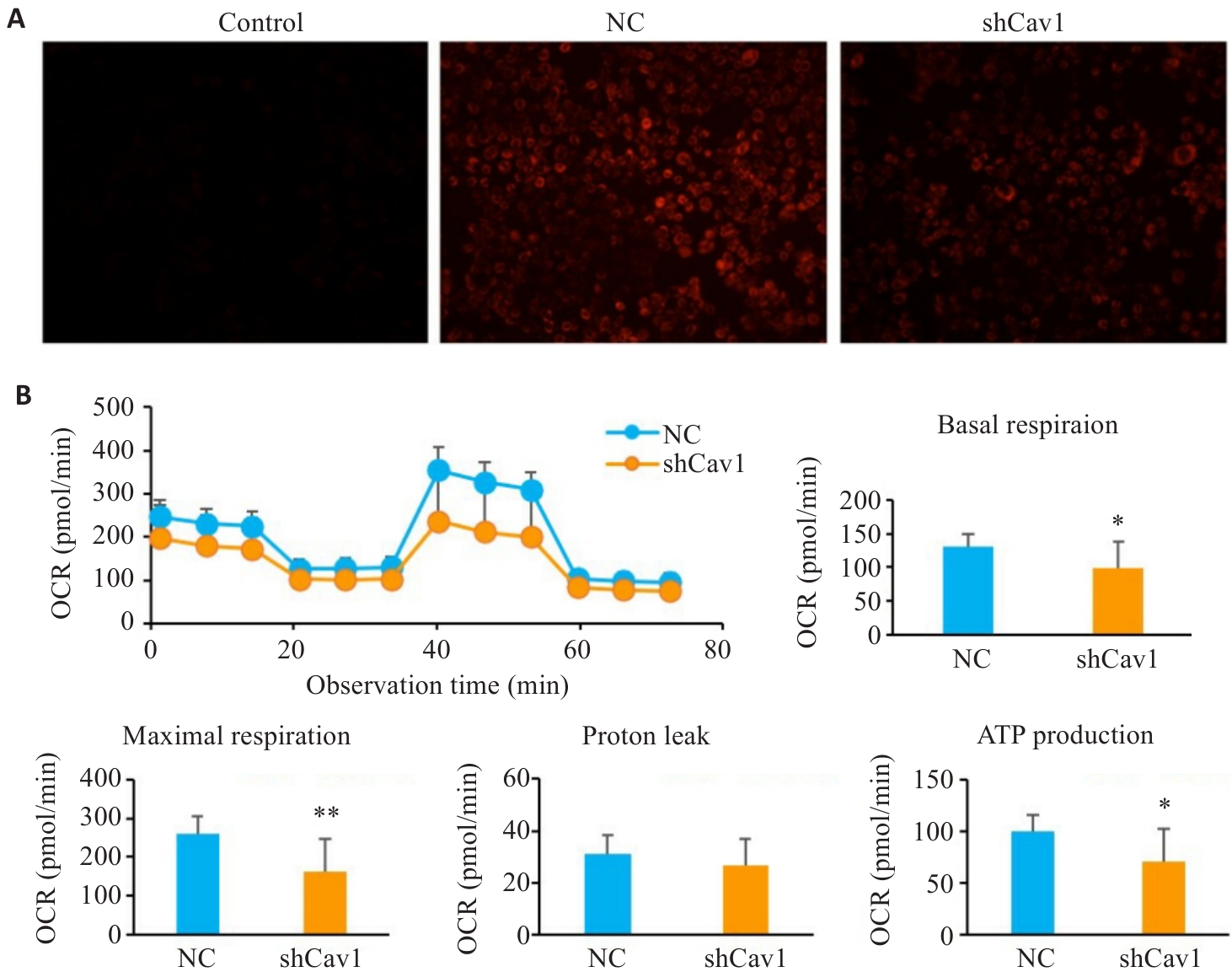
图2 Cav1敲低损伤AML12细胞线粒体膜电位和线粒体呼吸
Fig.2 Cav1 knockdown impairs mitochondrial membrane potential and respiratory function in AML12 cells. A: TMRE staining for analysis of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm) (×100). B: Seahorse XF metabolic analysis of basal respiration, maximal respiration and ATP production. CCCP: A mitochondrial uncoupler, used as a positive control to induce ΔΨm collapse (dim red fluorescence); OCR: Oxygen consumption rate. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group.
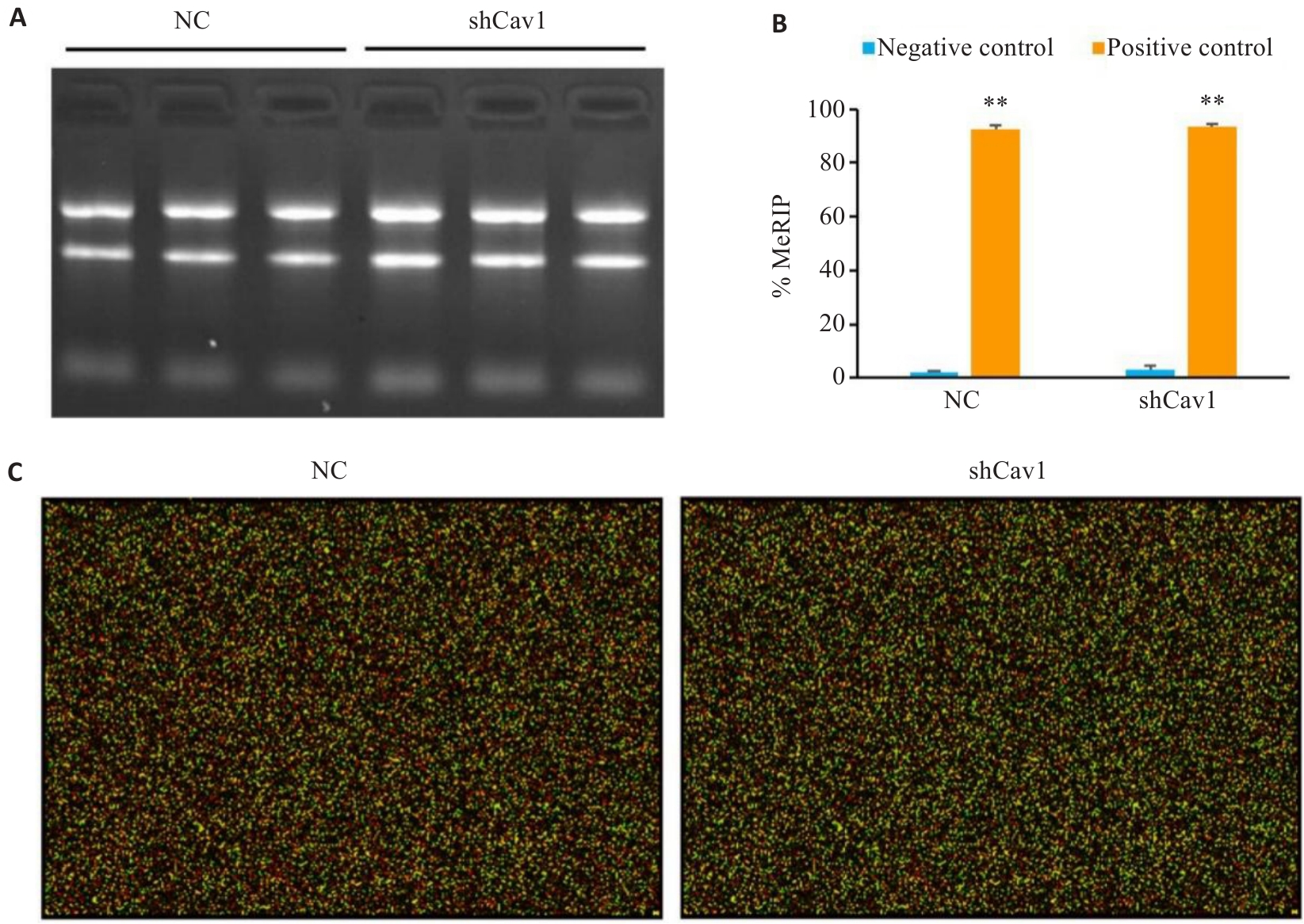
图3 MeRIP质量控制良好, 芯片数据可靠
Fig.3 Quality control of MeRIP and reliability of microarray. A: Agarose gel electrophoresis of the total RNA to confirm RNA integrity. B: MeRIP quality control demonstrating efficient m6A enrichment (%MeRIP confirming assay specificity). C: Representative RNA microarray hybridization image (Cy5 and Cy3). Positive controls: m6A-modified RNAs; Negative controls: Non-methylated RNAs. **P<0.01 vs negative control.
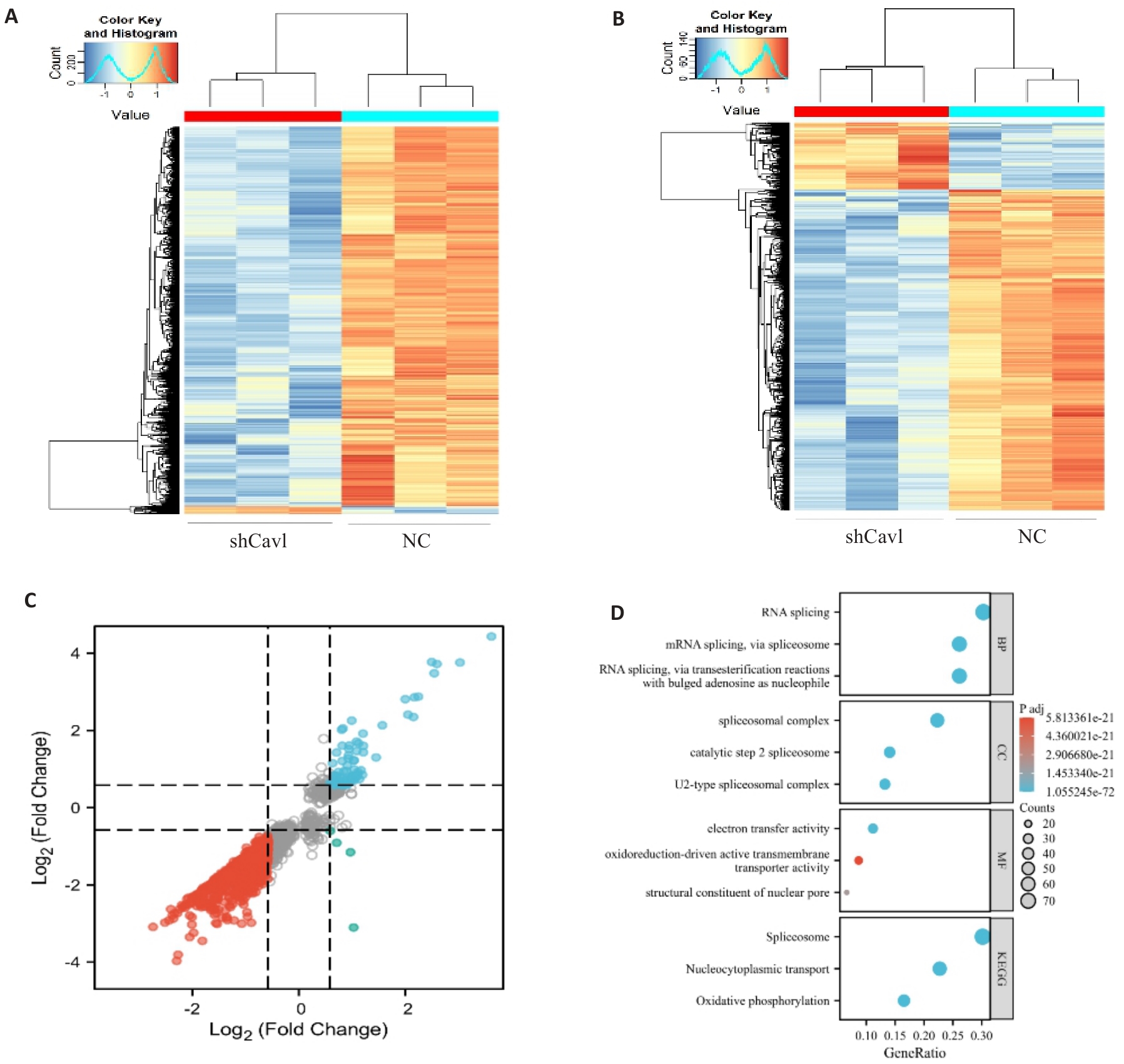
图4 Cav1敲低改变AML12细胞mRNA的m6A修饰和表达
Fig.4 Cav1 knockdown alters mRNA m6A modification and expression profiles in AML12 cells. A: Heatmap of differentially methylated mRNAs. B: Heatmap of differentially expressed mRNAs. C: Nine-quadrant analysis of coordinated m6A methylation and mRNA expression changes. D: Gene Ontology and KEGG pathway enrichment analysis of genes with concurrent m6A and expression changes. |log2 fold change|>0.58, P<0.05.
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ifrd1 | 0.07 | 0.002 | Down | -55% | Olfr175-ps1 | 19.55 | 0.001 | Up | 54% | |
| Zfp934 | 0.08 | 0.000 | Down | -54% | Crhr2 | 13.70 | 0.000 | Up | 52% | |
| Kif18a | 0.06 | 0.001 | Down | -54% | Glis1 | 13.21 | 0.008 | Up | 49% | |
| Kif20b | 0.07 | 0.000 | Down | -51% | Olfr175-ps1 | 21.62 | 0.000 | Up | 47% | |
| Tcaf1 | 0.12 | 0.001 | Down | -51% | Fam19a2 | 2.14 | 0.045 | Up | 40% | |
| Zufsp | 0.08 | 0.004 | Down | -50% | Gss | 11.18 | 0.001 | Up | 37% | |
| Zfp932 | 0.09 | 0.000 | Down | -50% | Slc13a4 | 7.35 | 0.000 | Up | 36% | |
| Klhl32 | 0.13 | 0.000 | Down | -49% | Elavl2 | 4.16 | 0.003 | Up | 33% | |
| Slc35d1 | 0.15 | 0.003 | Down | -49% | Crlf1 | 4.78 | 0.032 | Up | 33% | |
| Mis18bp1 | 0.12 | 0.028 | Down | -47% | Mdc1 | 2.62 | 0.042 | Up | 32% | |
| Samd9l | 0.14 | 0.002 | Down | -46% | Grm2 | 7.02 | 0.004 | Up | 32% | |
| Smek1 | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Tulp2 | 4.39 | 0.001 | Up | 31% | |
| Fastkd2 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | -45% | Dynap | 2.69 | 0.020 | Up | 28% | |
| Zfp280d | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Adamtsl1 | 3.05 | 0.008 | Up | 26% | |
| Sema6d | 0.10 | 0.002 | Down | -44% | Txnip | 2.68 | 0.005 | Up | 26% | |
| Pole4 | 0.15 | 0.006 | Down | -44% | Dpp4 | 13.55 | 0.000 | Up | 26% | |
| Kif20b | 0.10 | 0.000 | Down | -43% | Il5ra | 7.25 | 0.000 | Up | 25% | |
| Pcdhb18 | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | -42% | Klrc1 | 3.28 | 0.001 | Up | 24% | |
| Wac | 0.14 | 0.005 | Down | -42% | Txnip | 3.17 | 0.004 | Up | 24% | |
| Cdadc1 | 0.15 | 0.015 | Down | -42% | Kcne3 | 2.70 | 0.048 | Up | 23% |
表2 Cav1敲低导致AML12细胞m6A修饰上调前20位和下调前20位的mRNA
Tab.2 Top 20 upregulated and downregulated m6A-modified mRNAs in AML12 cells with Cav1 knockdown
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | Gene | FC | P | Reg | %m6A | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ifrd1 | 0.07 | 0.002 | Down | -55% | Olfr175-ps1 | 19.55 | 0.001 | Up | 54% | |
| Zfp934 | 0.08 | 0.000 | Down | -54% | Crhr2 | 13.70 | 0.000 | Up | 52% | |
| Kif18a | 0.06 | 0.001 | Down | -54% | Glis1 | 13.21 | 0.008 | Up | 49% | |
| Kif20b | 0.07 | 0.000 | Down | -51% | Olfr175-ps1 | 21.62 | 0.000 | Up | 47% | |
| Tcaf1 | 0.12 | 0.001 | Down | -51% | Fam19a2 | 2.14 | 0.045 | Up | 40% | |
| Zufsp | 0.08 | 0.004 | Down | -50% | Gss | 11.18 | 0.001 | Up | 37% | |
| Zfp932 | 0.09 | 0.000 | Down | -50% | Slc13a4 | 7.35 | 0.000 | Up | 36% | |
| Klhl32 | 0.13 | 0.000 | Down | -49% | Elavl2 | 4.16 | 0.003 | Up | 33% | |
| Slc35d1 | 0.15 | 0.003 | Down | -49% | Crlf1 | 4.78 | 0.032 | Up | 33% | |
| Mis18bp1 | 0.12 | 0.028 | Down | -47% | Mdc1 | 2.62 | 0.042 | Up | 32% | |
| Samd9l | 0.14 | 0.002 | Down | -46% | Grm2 | 7.02 | 0.004 | Up | 32% | |
| Smek1 | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Tulp2 | 4.39 | 0.001 | Up | 31% | |
| Fastkd2 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | -45% | Dynap | 2.69 | 0.020 | Up | 28% | |
| Zfp280d | 0.13 | 0.001 | Down | -45% | Adamtsl1 | 3.05 | 0.008 | Up | 26% | |
| Sema6d | 0.10 | 0.002 | Down | -44% | Txnip | 2.68 | 0.005 | Up | 26% | |
| Pole4 | 0.15 | 0.006 | Down | -44% | Dpp4 | 13.55 | 0.000 | Up | 26% | |
| Kif20b | 0.10 | 0.000 | Down | -43% | Il5ra | 7.25 | 0.000 | Up | 25% | |
| Pcdhb18 | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | -42% | Klrc1 | 3.28 | 0.001 | Up | 24% | |
| Wac | 0.14 | 0.005 | Down | -42% | Txnip | 3.17 | 0.004 | Up | 24% | |
| Cdadc1 | 0.15 | 0.015 | Down | -42% | Kcne3 | 2.70 | 0.048 | Up | 23% |
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | Gene | FC | P | Reg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cav1 | 0.05 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 12.25 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 8.42 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.15 | 0.000 | Down | Dpp4 | 8.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Upf3b | 0.16 | 0.000 | Down | Glis1 | 6.03 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Tpr | 0.18 | 0.000 | Down | Gss | 5.82 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Arid4b | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Crhr2 | 5.64 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dtnbp1 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Slc13a4 | 4.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Hells | 0.20 | 0.010 | Down | Il5ra | 4.49 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Slc45a4 | 4.44 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif18a | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Pdzd2 | 4.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccl2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Grm2 | 3.99 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Cdh26 | 3.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif20b | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Ube2i | 3.13 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Thoc2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Tulp2 | 2.96 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr70 | 2.81 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Chpf2 | 2.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| mt-Nd1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Slc6a20b | 2.66 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Zfp950 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Msantd3 | 2.61 | 0.020 | Up | |
| Zfp960 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Atp2c1 | 2.59 | 0.010 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.23 | 0.010 | Down | Fam32a | 2.58 | 0.050 | Up |
表3 Cav1敲低导致AML12细胞表达上调前20位和下调前20位的mRNA
Tab.3 Top 20 upregulated and downregulated mRNAs in AML12 cells with Cav1 knockdown
| Gene | FC | P | Reg | Gene | FC | P | Reg | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cav1 | 0.05 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 12.25 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr175-ps1 | 8.42 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.15 | 0.000 | Down | Dpp4 | 8.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Upf3b | 0.16 | 0.000 | Down | Glis1 | 6.03 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Tpr | 0.18 | 0.000 | Down | Gss | 5.82 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Arid4b | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Crhr2 | 5.64 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dtnbp1 | 0.19 | 0.000 | Down | Slc13a4 | 4.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Hells | 0.20 | 0.010 | Down | Il5ra | 4.49 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Slc45a4 | 4.44 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif18a | 0.20 | 0.000 | Down | Pdzd2 | 4.14 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccl2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Grm2 | 3.99 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Dek | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Cdh26 | 3.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Kif20b | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Ube2i | 3.13 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Thoc2 | 0.21 | 0.000 | Down | Tulp2 | 2.96 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Olfr70 | 2.81 | 0.000 | Up | |
| Zfml | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Chpf2 | 2.73 | 0.000 | Up | |
| mt-Nd1 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Slc6a20b | 2.66 | 0.040 | Up | |
| Zfp950 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Msantd3 | 2.61 | 0.020 | Up | |
| Zfp960 | 0.22 | 0.000 | Down | Atp2c1 | 2.59 | 0.010 | Up | |
| Ccar1 | 0.23 | 0.010 | Down | Fam32a | 2.58 | 0.050 | Up |
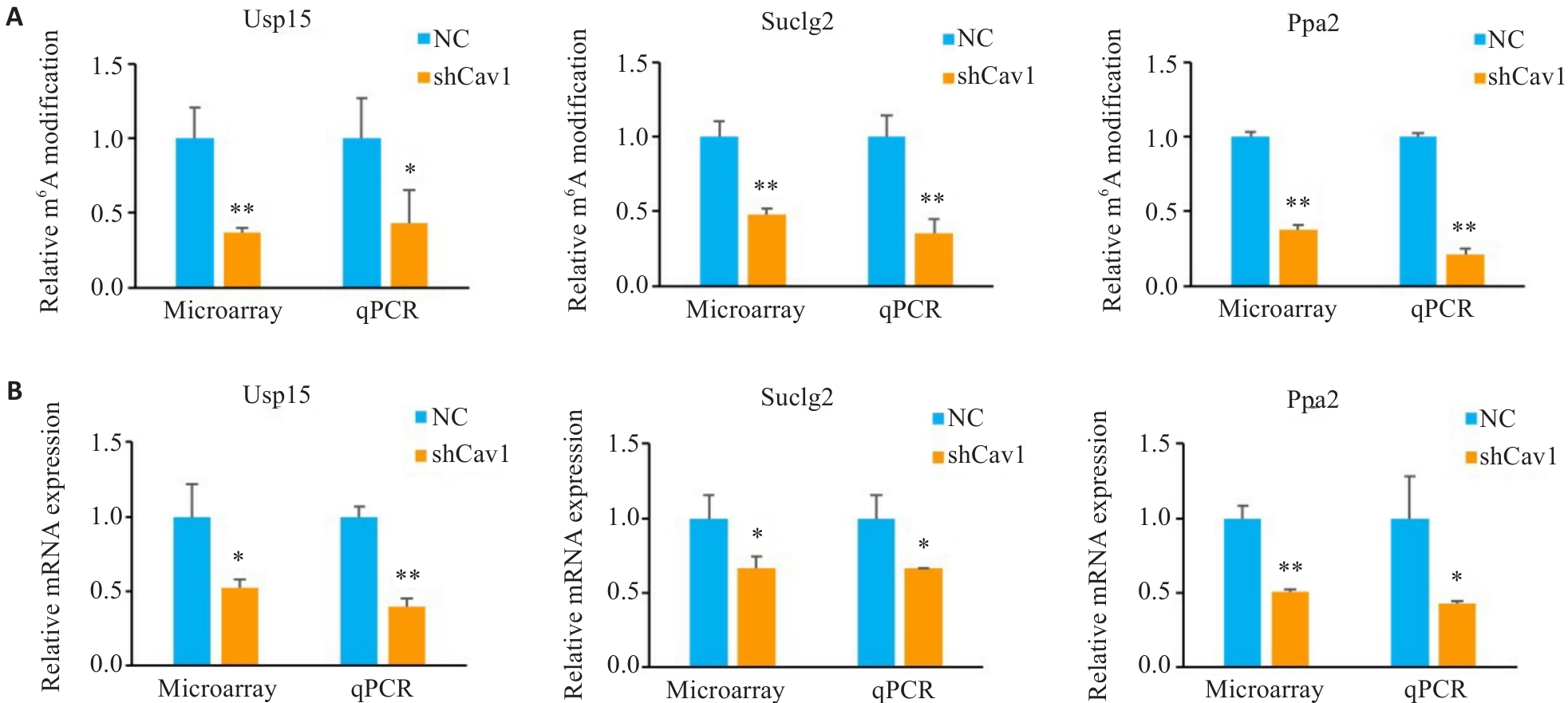
图5 Cav1敲低调节AML12细胞线粒体功能相关mRNA的m6A修饰和表达
Fig.5 m6A modification and relative expression levels of mitochondrial function-associated mRNAs in AML12 cells. A: Microarray and qPCR analysis of relative m6A modification of Usp15, Suclg2 and Ppa2 mRNA. B: Microarray and qPCR analysis of relative mRNA expression of Usp15, Suclg2 and Ppa2. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs NC group.
| [1] | 范建高, 徐小元, 南月敏, 等. 代谢相关(非酒精性)脂肪性肝病防治指南(2024年版)[J]. 实用肝脏病杂志, 2024, 27(4): 494-510. |
| [2] | Eslam M, Sarin SK, Wong VW, et al. The Asian Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver clinical practice guidelines for the diagnosis and management of metabolic associated fatty liver disease[J]. Hepatol Int, 2020, 14(6): 889-919. doi:10.1007/s12072-020-10094-2 |
| [3] | Radosavljevic T, Brankovic M, Samardzic J, et al. Altered mitochondrial function in MASLD: key features and promising therapeutic approaches[J]. Antioxidants (Basel), 2024, 13(8): 906. doi:10.3390/antiox13080906 |
| [4] | Shin S, Kim J, Lee JY, et al. Mitochondrial quality control: its role in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD)[J]. J Obes Metab Syndr, 2023, 32(4): 289-302. doi:10.7570/jomes23054 |
| [5] | Bhowmick S, Biswas T, Ahmed M, et al. Caveolin-1 and lipids: association and their dualism in oncogenic regulation[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer, 2023, 1878(6): 189002. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.189002 |
| [6] | Jiang Y, Krantz S, Qin X, et al. Caveolin-1 controls mitochondrial damage and ROS production by regulating fission - fusion dynamics and mitophagy[J]. Redox Biol, 2022, 52: 102304. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2022.102304 |
| [7] | Fu DD, Wu S, Jiang XF, et al. Caveolin-1 alleviates acetaminophen-induced vascular oxidative stress and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Free Radic Biol Med, 2023, 195: 245-57. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.12.095 |
| [8] | Tang WX, Li YS, Li Y, et al. Caveolin-1, a novel player in cognitive decline[J]. Neurosci Biobehav Rev, 2021, 129: 95-106. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.06.044 |
| [9] | Timmins LR, Ortiz-Silva M, Joshi B, et al. Caveolin-1 promotes mitochondrial health and limits mitochondrial ROS through ROCK/AMPK regulation of basal mitophagic flux[J]. FASEB J, 2024, 38: e23343. doi:10.1096/fj.202201872rr |
| [10] | You TY, Li Y, Li BW, et al. Caveolin-1 protects against liver damage exacerbated by acetaminophen in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting the ERK/HIF-1α pathway[J]. Mol Immunol, 2023, 163: 104-15. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2023.09.003 |
| [11] | Deng GH, Wu CF, Li YJ, et al. Caveolin-1 is critical for hepatic iron storage capacity in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease[J]. Mil Med Res, 2023, 10(1): 53. doi:10.1186/s40779-023-00487-3 |
| [12] | Ćorović M, Hoch-Kraft P, Zhou Y, et al. m6A in the coding sequence: linking deposition, translation, and decay[J]. Trends Genet, 2025: S0168-9525(25)00132-5. doi:10.1016/j.tig.2025.06.002 |
| [13] | Xie XZ, Fang Z, Zhang HY, et al. The role of N(6)-methyladenosine (m6a) modification in cancer: recent advances and future directions[J]. EXCLI J, 2025, 24: 113-50. |
| [14] | Ming XY, Chen SR, Li HJ, et al. m6A RNA methylation and implications for hepatic lipid metabolism[J]. DNA Cell Biol, 2024, 43(6): 271-8. doi:10.1089/dna.2023.0410 |
| [15] | Yan W, Saqirile, Li K, et al. The role of N6-methyladenosine in mitochondrial dysfunction and pathology[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2025, 26(8): 3624. doi:10.3390/ijms26083624 |
| [16] | Fan JH, You JB, Liu ZY, et al. Novel landscapes of N6-methyladenosine modification of mitochondrial oxidative stress in organ fibrosis[J]. Eur J Pharmacol, 2025, 1003: 177888. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2025.177888 |
| [17] | Fromenty B, Roden M. Mitochondrial alterations in fatty liver diseases[J]. J Hepatol, 2023, 78(2): 415-29. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2022.09.020 |
| [18] | 丁珊珊, 庄 妍, 廖 颖, 等. 二陈汤通过抑制mTORC1/SREBP1/CAV1通路改善高脂饮食小鼠肝脏线粒体功能的作用研究[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2024, 49(3): 763-9. |
| [19] | Xu HL, Li Y, Guo N, et al. Caveolin-1 mitigates the advancement of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease by reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress and pyroptosis through the restoration of cholesterol homeostasis[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2025, 21(2): 490-506. doi:10.7150/ijbs.100794 |
| [20] | Razani B, Combs TP, Wang XB, et al. Caveolin-1-deficient mice are lean, resistant to diet-induced obesity, and show hypertriglyc-eridemia with adipocyte abnormalities[J]. J Biol Chem, 2002, 277(10): 8635-47. doi:10.1074/jbc.m110970200 |
| [21] | Xu YQ, Chen BW, Yi J, et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction alleviates cerebral ischemic injury through modulating caveolin-1-mediated mitochondrial quality control[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2023, 14: 1137609. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1137609 |
| [22] | Wu S, Guo N, Xu HL, et al. Caveolin-1 ameliorates hepatic injury in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting ferroptosis via the NOX4/ROS/GPX4 pathway[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2024, 230(Pt 2): 116594. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2024.116594 |
| [23] | Kahl M, Xu ZF, Arumugam S, et al. m6A RNA methylation regulates mitochondrial function[J]. Hum Mol Genet, 2024, 33(11): 969-80. doi:10.1093/hmg/ddae029 |
| [24] | Wang SW, Zhang WY, Wang ZJ, et al. Mettl3-m6A-YTHDF1 axis promotion of mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease[J]. Cell Signal, 2024, 121: 111303. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2024.111303 |
| [25] | Huangfu LT, Zhu HB, Wang GJ, et al. The deubiquitinase USP15 drives malignant progression of gastric cancer through glucose metabolism remodeling[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2024, 43(1): 235. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03152-2 |
| [26] | Fang RH, Jia ZG, Xin YH, et al. N6-methyladenosine-modification of USP15 regulates chemotherapy resistance by inhibiting LGALS3 ubiquitin-mediated degradation via AKT/mTOR signaling activation pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Cell Death Discov, 2025, 11(1): 3. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-02282-y |
| [27] | Wu BW, Qiu JT, Zhao TV, et al. Succinyl-CoA ligase deficiency in pro-inflammatory and tissue-invasive T cells[J]. Cell Metab, 2020, 32(6): 967-80.e5. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2020.10.025 |
| [28] | Zhang XM, Liu J, Cheng YJ, et al. Metabolic enzyme Suclg2 maintains tolerogenicity of regulatory dendritic cells diffDCs by suppressing Lactb succinylation[J]. J Autoimmun, 2023, 138: 103048. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103048 |
| [29] | Hu QF, Xu J, Wang L, et al. SUCLG2 regulates mitochondrial dysfunction through succinylation in lung adenocarcinoma[J]. Adv Sci (Weinh), 2023, 10(35): e2303535. doi:10.1002/advs.202303535 |
| [30] | Yu HF, Zeng QR, Xiao PY, et al. Hippo-YAP signaling alleviates copper-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage via the ATOX1-PPA2 pathway[J]. Int J Biol Macromol, 2025, 290: 138908. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.138908 |
| [31] | Zhang X, Di YQ, Wang YP, et al. SIRT5-mediated desuccinylation of PPA2 enhances HIF-1alpha-dependent adaptation to hypoxic stress and colorectal cancer metastasis[J]. EMBO J, 2025, 44(9): 2514-40. doi:10.1038/s44318-025-00416-1 |
| [32] | Zhou Y, Wang Q, Deng HF, et al. N6-methyladenosine demethylase FTO promotes growth and metastasis of gastric cancer via m6A modification of caveolin-1 and metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(1): 72. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04503-7 |
| [33] | Golubeva VA, Das AS, Rabolli CP, et al. YTHDF1 is pivotal for maintenance of cardiac homeostasis[J]. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2024, 193: 25-35. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2024.05.008 |
| [1] | 梁 猛, 周今朝, 孙训英, 贺超凡, 张克甲, 胡 柯. 双酚A对小鼠卵巢腔前卵泡颗粒细胞凋亡和卵巢发育的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(1): 93-99. |
| [2] | 周亮,林敏仕,尹恝. 线粒体呼吸链复合物Ⅰ缺陷与海洛因海绵状白质脑病的关系[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2013, 33(09): 1357-. |
| [3] | 马晓冬; 晏芳; 马安德; 王慧君;. 白藜芦醇通过影响线粒体膜电位诱导HepG2细胞凋亡[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(04): 406-. |
| [4] | 余志坚1, 陈俊2, 袁亚维2, 肖明星2, 陈春2. P糖蛋白功能抑制对耐药肿瘤细胞MCF-7/Adr放射敏感性的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2004, 24(08): 885-887. |
| [5] | 季锡清, 李朝龙, 杨进城, 刘兴国, 王孟龙, 林智琪, 林建华. 血流阻断的缺血预处理技术在肝癌切除术中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2004, 24(01): 66-68,71. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||