南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 650-660.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.23
收稿日期:2024-12-04
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
陈超敏
E-mail:3547475276@qq.com;571611621@qq.com
作者简介:洪 永,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: 3547475276@qq.com
基金资助:
Yong HONG( ), Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN(
), Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN( )
)
Received:2024-12-04
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Chaomin CHEN
E-mail:3547475276@qq.com;571611621@qq.com
摘要:
目的 设计一个深度学习模型,实现模型复杂度和模型性能的平衡,以便于集成到可穿戴心电监护设备上,实现本地的房颤自动诊断。 方法 从公开数据集LTAFDB、AFDB和NSRDB上分别收集了84例、25例房颤患者和18例无明显心律失常受试者的数据进行实验和测试。提出了一个基于深度可分离卷积并融合通道空间信息的轻量级注意网络—DSC-AttNet,引入深度可分离卷积代替标准卷积,降低模型参数量和计算量,实现模型的高效和轻量化;并嵌入多层混合注意力机制以在不同尺度上计算通道信息和空间信息的注意权重,提高模型的特征表达能力。在LTAFDB上进行十折交叉验证,并在AFDB和NSRDB上进行外部独立测试。 结果 DSC-AttNet在测试集上的十折平均准确率达到97.33%,精确率达到97.30%,均优于其他4个对比模型以及3个经典模型。模型在外部测试集上的准确率分别达到92.78%和99.97%,优于3个经典模型。且DSC-AttNet的参数量为1.01M,计算量为27.19 G,小于3个经典模型。 结论 该房颤分类方法具有较小的复杂度,达到了更好的分类性能,并且泛化能力较好,具有良好的临床应用前景和推广能力。
洪永, 张鑫, 林铭俊, 吴秋岑, 陈超敏. 基于深度可分离卷积与注意力机制的单导联心房颤动轻量级分类网络[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 650-660.
Yong HONG, Xin ZHANG, Mingjun LIN, Qiucen WU, Chaomin CHEN. A lightweight classification network for single-lead atrial fibrillation based on depthwise separable convolution and attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 650-660.
| Method | Input | Dataset | Task | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 32 RR | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.07 | 94.95 | 97.77 | - | 93.91 |
| MT-DCNN[ | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.1 | 96.5 | 97.9 | - | 97.5 |
| LDSNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 94.57 | 99.15 | 93.03 | - | - |
| IMC-ResNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs NSR | 96.18 | 99.97 | 94.36 | 89.51 | 94.45 |
| ResNet18 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 94.82 | 94.27 | 95.29 | 95.94 | 94.60 |
| MobileNetV1 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.86 | 97.80 | 94.17 | 95.80 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.94 | 97.95 | 94.40 | 95.92 |
| DSC-AttNet,2024 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
表1 不同模型的分类性能对比
Tab.1 Comparison of classification performance among different models (%)
| Method | Input | Dataset | Task | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 32 RR | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.07 | 94.95 | 97.77 | - | 93.91 |
| MT-DCNN[ | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 97.1 | 96.5 | 97.9 | - | 97.5 |
| LDSNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs Non-AF | 94.57 | 99.15 | 93.03 | - | - |
| IMC-ResNet[ | 15 s ECG | AFDB | AF vs NSR | 96.18 | 99.97 | 94.36 | 89.51 | 94.45 |
| ResNet18 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 94.82 | 94.27 | 95.29 | 95.94 | 94.60 |
| MobileNetV1 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.86 | 97.80 | 94.17 | 95.80 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 95.64 | 97.94 | 97.95 | 94.40 | 95.92 |
| DSC-AttNet,2024 | 30 s ECG | LTAFDB | AF vs NSR | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
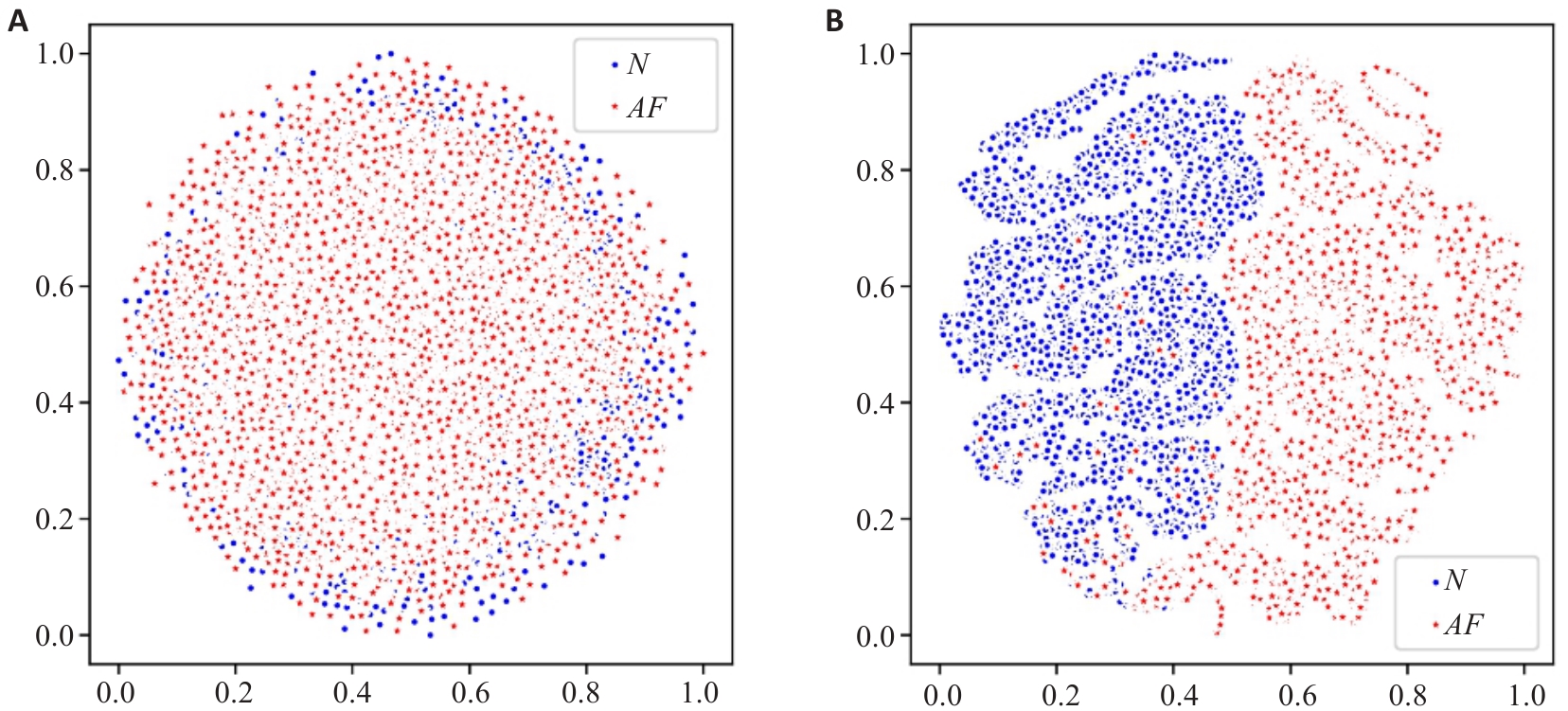
图9 NSR类特征和AF类特征的演化过程
Fig.9 Evolution process of NSR-class features and AF-class features. A: Visualization of the output features from the first standard convolution layer. B: Visualization of the output features from the global attention module.
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 87.24 | 83.97 | 91.90 | 78.62 | 81.21 |
| MobileNetV1 | 91.27 | 96.74 | 98.24 | 80.56 | 87.91 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 90.15 | 83.88 | 92.21 | 85.81 | 84.84 |
| DSC-AttNet | 92.78 | 89.98 | 95.05 | 88.26 | 89.11 |
表2 不同模型在外部测试集AFDB上的分类性能对比
Tab.2 Comparison of classification performance among different models on external test set AFDB (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 87.24 | 83.97 | 91.90 | 78.62 | 81.21 |
| MobileNetV1 | 91.27 | 96.74 | 98.24 | 80.56 | 87.91 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 90.15 | 83.88 | 92.21 | 85.81 | 84.84 |
| DSC-AttNet | 92.78 | 89.98 | 95.05 | 88.26 | 89.11 |
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 99.80 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| MobileNetV1 | 99.94 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| EfficientNetB0 | 99.77 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| DSC-AttNet | 99.97 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
表3 不同模型在外部测试集NSRDB上的分类性能对比
Tab.3 Comparison of classification performance among different models on external test set NSRDB (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 99.80 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| MobileNetV1 | 99.94 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| EfficientNetB0 | 99.77 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| DSC-AttNet | 99.97 | - | 1.0 | - | - |
| Method | Input size | MACs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 1*32 | 0.02 | 1.49 |
| LDSNet[ | 1*3000 | 0.33 | 0.2 |
| ResNet18 | 1*3840 | 183.65 | 4.20 |
| MobileNetV1 | 1*3840 | 39.46 | 3.19 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 1*3840 | 31.68 | 7.00 |
| DSC-AttNet, 2024 | 1*3840 | 27.19 | 1.01 |
表4 不同模型的复杂度比较
Tab.4 Comparison of complexity among different models
| Method | Input size | MACs (G) | Params (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MGNN[ | 1*32 | 0.02 | 1.49 |
| LDSNet[ | 1*3000 | 0.33 | 0.2 |
| ResNet18 | 1*3840 | 183.65 | 4.20 |
| MobileNetV1 | 1*3840 | 39.46 | 3.19 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 1*3840 | 31.68 | 7.00 |
| DSC-AttNet, 2024 | 1*3840 | 27.19 | 1.01 |
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 97.13 | 97.70 | 97.80 | 96.89 | 97.15 |
| +CBAM | 97.21 | 96.30 | 96.77 | 98.07 | 97.04 |
| +Global Attention | 95.90 | 96.19 | 96.64 | 96.08 | 95.87 |
| DSC-AttNet | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
表5 消融实验结果
Tab.5 Results of ablation study (%)
| Method | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | 97.13 | 97.70 | 97.80 | 96.89 | 97.15 |
| +CBAM | 97.21 | 96.30 | 96.77 | 98.07 | 97.04 |
| +Global Attention | 95.90 | 96.19 | 96.64 | 96.08 | 95.87 |
| DSC-AttNet | 97.33 | 97.50 | 97.63 | 97.30 | 97.31 |
| Method | Data input | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 10s ECG | 61.97 | 55.29 | 90.41 | 60.30 | 54.23 |
| MobileNetV1 | 10s ECG | 75.65 | 65.57 | 93.69 | 66.80 | 64.18 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 10s ECG | 81.38 | 70.25 | 95.19 | 69.09 | 68.62 |
| DSC-AttNet | 10s ECG | 71.20 | 60.98 | 92.44 | 77.13 | 59.19 |
表 6 不同模型在LTAFDB上的五分类性能对比
Tab.6 Comparison of the performance of different models for 5 classification tasks on LTAFDB (%)
| Method | Data input | Acc | Sen | Spe | Pre | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet18 | 10s ECG | 61.97 | 55.29 | 90.41 | 60.30 | 54.23 |
| MobileNetV1 | 10s ECG | 75.65 | 65.57 | 93.69 | 66.80 | 64.18 |
| EfficientNetB0 | 10s ECG | 81.38 | 70.25 | 95.19 | 69.09 | 68.62 |
| DSC-AttNet | 10s ECG | 71.20 | 60.98 | 92.44 | 77.13 | 59.19 |
| 1 | Shi SB, Tang YH, Zhao QY, et al. Prevalence and risk of atrial fibrillation in China: a national cross-sectional epidemiological study[J]. Lancet Reg Health West Pac, 2022, 23: 100439. |
| 2 | 苏 晞, 张劲林, 韩宏伟, 等. 单导联心电图记录系统进行心房颤动机会性筛查的首个国内经验[J]. 中华心律失常学杂志, 2017, 21(6): 485-8. |
| 3 | Halcox JPJ, Wareham K, Cardew A, et al. Assessment of remote heart rhythm sampling using the AliveCor heart monitor to screen for atrial fibrillation: the REHEARSE-AF study[J]. Circulation, 2017, 136(19): 1784-94. |
| 4 | Daqrouq K, Alkhateeb A, Ajour MN, et al. Neural network and wavelet average framing percentage energy for atrial fibrillation classification[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2014, 113(3): 919-26. |
| 5 | Fuadah YN, Lim KM. Optimal classification of atrial fibrillation and congestive heart failure using machine learning[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 12: 761013. |
| 6 | Bashar SK, Hossain MB, Ding E, et al. Atrial fibrillation detection during sepsis: study on mimic iii icu data[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2020, 24(11): 3124-35. |
| 7 | Bashar SK, Han D, Zieneddin F, et al. Novel density poincaré plot based machine learning method to detect atrial fibrillation from premature atrial/ventricular contractions[J]. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 2021, 68(2): 448-60. |
| 8 | García-Isla G, Mainardi L, Corino VDA. A detector for premature atrial and ventricular complexes[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 678558. |
| 9 | Gupta K, Bajaj V, Ahmad Ansari I. Atrial fibrillation detection using electrocardiogram signal input to LMD and ensemble classifier[J]. IEEE Sens Lett, 2023, 7(6): 7002904. |
| 10 | Asgari S, Mehrnia A, Moussavi M. Automatic detection of atrial fibrillation using stationary wavelet transform and support vector machine[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2015, 60: 132-42. |
| 11 | Abdul-Kadir NA, Mat Safri N, Othman MA. Dynamic ECG features for atrial fibrillation recognition[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2016, 136: 143-50. |
| 12 | Luongo G, Rees F, Nairn D, et al. Machine learning using a single-lead ECG to identify patients with atrial fibrillation-induced heart failure[J]. Front Cardiovasc Med, 2022, 9: 812719. |
| 13 | Kalidas V, Tamil LS. Detection of atrial fibrillation using discrete-state Markov models and Random Forests[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2019, 113: 103386. |
| 14 | Li XY, Shi XL, Handa BS, et al. Classification of fibrillation organisation using electrocardiograms to guide mechanism-directed treatments[J]. Front Physiol, 2021, 12: 712454. |
| 15 | Mateo J, Joaquín Rieta J. Radial basis function neural networks applied to efficient QRST cancellation in atrial fibrillation[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2013, 43(2): 154-63. |
| 16 | Chen B, Maslove DM, Curran JD, et al. A deep learning model for the classification of atrial fibrillation in critically ill patients[J]. Intensive Care Med Exp, 2023, 11(1): 2. |
| 17 | Pourbabaee B, Roshtkhari MJ, Khorasani K. Deep convolutional neural networks and learning ECG features for screening paroxysmal atrial fibrillation patients[J]. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst, 2017, 48(12): 2095-104. |
| 18 | Faust O, Shenfield A, Kareem M, et al. Automated detection of atrial fibrillation using long short-term memory network with RR interval signals[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2018, 102: 327-35. |
| 19 | Kumar D, Peimankar A, Sharma K, et al. Deepaware: a hybrid deep learning and context-aware heuristics-based model for atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2022, 221: 106899. |
| 20 | Laghari AA, Sun YQ, Alhussein M, et al. Deep residual-dense network based on bidirectional recurrent neural network for atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Sci Rep, 2023, 13(1): 15109. |
| 21 | Iandola FN, Han S, Moskewicz MW, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5MB model size[EB/OL]. 2016: 1602.07360. . |
| 22 | Howard AG, Zhu ML, Chen B, et al. MobileNets: efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL]. 2017: 1704.04861. . |
| 23 | Li YJ, Chen M, Wang Y, et al. Diagnosis of atrial fibrillation based on lightweight detail-semantic network[J]. Biomed Signal Process Contr, 2023, 85: 105025. |
| 24 | Petrutiu S, Sahakian AV, Swiryn S. Abrupt changes in fibrillatory wave characteristics at the termination of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation in humans[J]. Europace, 2007, 9(7): 466-70. |
| 25 | Moody GB, Mark RR. New method for detecting atrial fibrillation using r-r intervals[J]. Comput Cardiol, 1983: 227-30. |
| 26 | Goldberger AL, Amaral LA, Glass L, et al. PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: components of a new research resource for complex physiologic signals[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(23): E215-20. |
| 27 | 谭 琛. 《2020 ECS/EACTS心房颤动诊断和管理指南》解读[J]. 中国循证心血管医学杂志, 2021, 13(2): 129-32. |
| 28 | Hamilton P. Open source ECG analysis[C]//Computers in Cardiology. September 22-25, 2002, Memphis, TN, USA. IEEE, 2002: 101-4. |
| 29 | Christov II. Real time electrocardiogram QRS detection using combined adaptive threshold[J]. Biomed Eng Online, 2004, 3(1): 28. |
| 30 | Woo S, Park J, Lee JY, et al. CBAM: convolutional block attention module[C]//Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 3-19. |
| 31 | Liu S, Wang AG, Deng XT, et al. MGNN: a multiscale grouped convolutional neural network for efficient atrial fibrillation detection[J]. Comput Biol Med, 2022, 148: 105863. |
| 32 | Prabhakararao E, Dandapat S. Atrial fibrillation burden estimation using multi-task deep convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2022, 26(12): 5992-6002. |
| 33 | Sun YH, Li YJ, Chen M, et al. IMC-ResNet: Atrial fibrillation detection method based on interlayer multiscale coupling[J]. Biomed Signal Process Contr, 2024, 97: 106683. |
| 34 | Mousavi SS, Afghah F, Razi A, et al. ECGNET: Learning where to attend for detection of atrial fibrillation with deep visual attention[J]. IEEE EMBS Int Conf Biomed Health Inform, 2019: 10.1109/BHI.2019.8834637. |
| 35 | Chollet F. Xception: deep learning with depthwise separable convolutions[C]//2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). July 21-26, 2017, Honolulu, HI, USA. IEEE, 2017: 1800-7. |
| 36 | Chen LC, Zhu YK, Papandreou G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]// Computer Vision-ECCV 2018. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2018: 833-51. |
| [1] | 朱晓庆, 石亚君, 沈娟, 王清松, 宋婷婷, 修建成, 陈韬, 郭军. 早期心房颤动预测模型构建:基于中国人群窦性心律期间心电定量特征[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(2): 223-228. |
| [2] | 王泓森, 米利杰, 张越, 葛兰, 赖杰伟, 陈韬, 李健, 时向民, 修建成, 唐闵, 阳维, 郭军. 室上性心动过速机制的智能分类模型:基于十二导联穿戴式心电设备[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(5): 851-858. |
| [3] | 高 琦, 耿嘉逸, 丁洋洋, 姚卓亚, 孟金金, 王 聪, 张 恒, 康品方, 唐 碧. 内皮素-1和结缔组织生长因子在心房颤动患者中高表达并与射频消融术后的复发相关[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1689-1696. |
| [4] | 曹 石, 巩 高, 肖 慧, 方威扬, 阙与清, 陈超敏. 胎儿心电信号的无创提取:基于时间卷积编解码网络[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1672-1680. |
| [5] | 周萌萌, 陈金东, 王 昊, 席斯祺, 甘 田, 赵 亮. 低CHA2DS2-VASc评分的非瓣膜性心房颤动患者的心房血栓形成的独立危险因素[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2021, 41(8): 1243-1249. |
| [6] | 钟世茂,覃羽华,黎作茶,韦叶生. 血清可溶性CD163在心房颤动患者中的水平及临床意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(10): 1406-. |
| [7] | 顾俊,贾锋鹏,封盼攀. CHADS2与CHA2DS2-VASc评分对非瓣膜病房颤患者左房血栓的风险评估[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(11): 1601-. |
| [8] | 张飞飞,赵冬华,彭新辉,杨浩,朱庭延,黄福美,彭健. 心房颤动导管射频消融术桥接使用磺达肝癸钠或低分子肝素的临床[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(04): 448-. |
| [9] | 张璐,唐红,陈良龙,吴晓霞,程流泉,王湛博,王叶,黄鹤,李金国,汪晶晶,冯斌,智光. 心脏淀粉样变性的临床及影像特征:多中心病例分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2014, 34(03): 295-. |
| [10] | 彭健; 阮发晖; 杨溶海; 易绍东; 崔英凯; 黄晓波; 贾满盈; 孟素荣;. 不同类型特发性室性心动过速的临床特点及射频消融治疗[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(08): 1152-. |
| [11] | 熊鹰;. 1587例胎儿心电图检测分析及临床意义[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2006, 26(02): 245-246. |
| [12] | 王得坤, 姜海明, 郑俊猛, 梁毅, 凌飞海, 王旭广. 6例同种异体原位心脏移植的经验[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2005, 25(07): 917-918. |
| [13] | 孙中波1, 张琴1, 杨霞芳2. 沙门氏菌食物中毒心肌酶谱和心电图的改变[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2004, 24(11): 1311-1312,1315. |
| [14] | 黄邹琴1, 李活霞1, 王嘉丽1, 万颂国2. 泰索帝联合阿霉素治疗乳腺癌对心电图的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2004, 24(05): 582-583. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||