南方医科大学学报 ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 470-478.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.03.04
张夏玮1,2( ), 杨晶晶1,2, 温亚男1,2, 刘青阳1,2, 窦立萍1(
), 杨晶晶1,2, 温亚男1,2, 刘青阳1,2, 窦立萍1( ), 高春记1(
), 高春记1( )
)
收稿日期:2024-11-28
出版日期:2025-03-20
发布日期:2025-03-28
通讯作者:
窦立萍,高春记
E-mail:phoebe_zxw@qq.com;lipingruirui@163.com;gaochunji301@163.com
作者简介:张夏玮,在读硕士研究生,E-mail: phoebe_zxw@qq.com
基金资助:
Xiawei ZHANG1,2( ), Jingjing YANG1,2, Yanan WEN1,2, Qingyang LIU1,2, Liping DOU1(
), Jingjing YANG1,2, Yanan WEN1,2, Qingyang LIU1,2, Liping DOU1( ), Chunji GAO1(
), Chunji GAO1( )
)
Received:2024-11-28
Online:2025-03-20
Published:2025-03-28
Contact:
Liping DOU, Chunji GAO
E-mail:phoebe_zxw@qq.com;lipingruirui@163.com;gaochunji301@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
目的 探讨急性髓系白血病(AML)细胞中叉头盒蛋白3(FOXO3)与甲基转移酶样蛋白3(METTL3)表达关系及FOXO3参与AML化疗耐药的机制。 方法 采用敲低或过表达METTL3和FOXO3及其对照慢病毒载体,转染AML蒽环类耐药细胞系,获取对照组、敲低组、过表达组细胞。对AML细胞采用甲基化RNA共沉淀和高通量测序技术(MeRIP-seq)和转录组测序(RNA-seq)。TCGA和GSE6891数据库对AML患者临床信息及基因表达数据进行统计分析。RT-qPCR及 Western blotting检测FOXO3 mRNA及蛋白的表达水平和FOXO3 mRNA稳定性。流式细胞术和CCK-8分别检测细胞凋亡和增殖能力的变化。MeRIP-qPCR检测m6A修饰FOXO3 mRNA的表达情况。 结果 蒽环类敏感及耐药AML细胞系和敲低METTL3前后细胞系差异基因均富集在FoxOs通路中,且耐药细胞中FOXO3 m6A修饰明显增加。公共数据库相关性分析显示FOXO3与METTL3表达呈正相关(P<0.01)。Western blotting和RT-qPCR结果提示敲低METTL3后FOXO3表达下降(P<0.05)。MeRIP-qPCR结果提示蒽环类耐药AML细胞中m6A修饰的FOXO3 mRNA表达高于蒽环类敏感AML细胞(P<0.05)。稳定性试验结果提示敲低METTL3后FOXO3 mRNA稳定性降低。公共数据库分析、Kaplan-Meier分析和RT-qPCR结果提示FOXO3与AML患者预后不良相关(P<0.05)。Western blotting和RT-qPCR结果显示,蒽环类耐药细胞中FOXO3的表达明显高于敏感细胞(P<0.05)。体外实验显示过表达FOXO3的AML细胞后细胞增殖更快,凋亡减少(P<0.05)。蒽环类敏感及耐药AML细胞系和敲低METTL3前后细胞系差异基因均富集在自噬相关通路中,抑制自噬增强阿霉素对AML细胞和过表达FOXO3细胞的抗肿瘤作用。 结论 METTL3可能通过介导的m6A修饰促进FOXO3的表达,进而调节自噬促进蒽环类药物耐药细胞的增殖和抑制凋亡。
张夏玮, 杨晶晶, 温亚男, 刘青阳, 窦立萍, 高春记. METTL3介导的m6A修饰通过调节自噬促进急性髓性白血病细胞中FOXO3表达及蒽环类药物耐药性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2025, 45(3): 470-478.
Xiawei ZHANG, Jingjing YANG, Yanan WEN, Qingyang LIU, Liping DOU, Chunji GAO. METTL3-mediated m6A modification promotes FOXO3 expression and anthracycline resistance in acute myeloid leukemia cells through autophagy regulation[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 470-478.
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| METTL3 | ATCCCCAAGGCTTCAACCAG | GCGAGTGCCAGGAGATAGTC |
| FOXO3 | CGGACAAACGGCTCACTCT | GGACCCGCATGAATCGACTAT |
| GAPDH | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |
表1 RT-qPCR引物序列
Tab.1 Primer sequence of RT-qPCR
| Gene | Forward primers sequences | Reverse primers sequences |
|---|---|---|
| METTL3 | ATCCCCAAGGCTTCAACCAG | GCGAGTGCCAGGAGATAGTC |
| FOXO3 | CGGACAAACGGCTCACTCT | GGACCCGCATGAATCGACTAT |
| GAPDH | GGAGCGAGATCCCTCCAAAAT | GGCTGTTGTCATACTTCTCATGG |

图1 AML细胞系测序分析
Fig.1 Sequencing analysis of AML cells. A: KEGG enrichment analysis of differential genes in HL60 cells and HL60/ADR cells. B: KEGG enrichment analysis of differential genes in K562/ADR sh-METTL3 cells and K562/ADR sh-con cells. C: MeRIP-seq methylation modification peak analysis in HL60 cells and HL60/ADR cells.
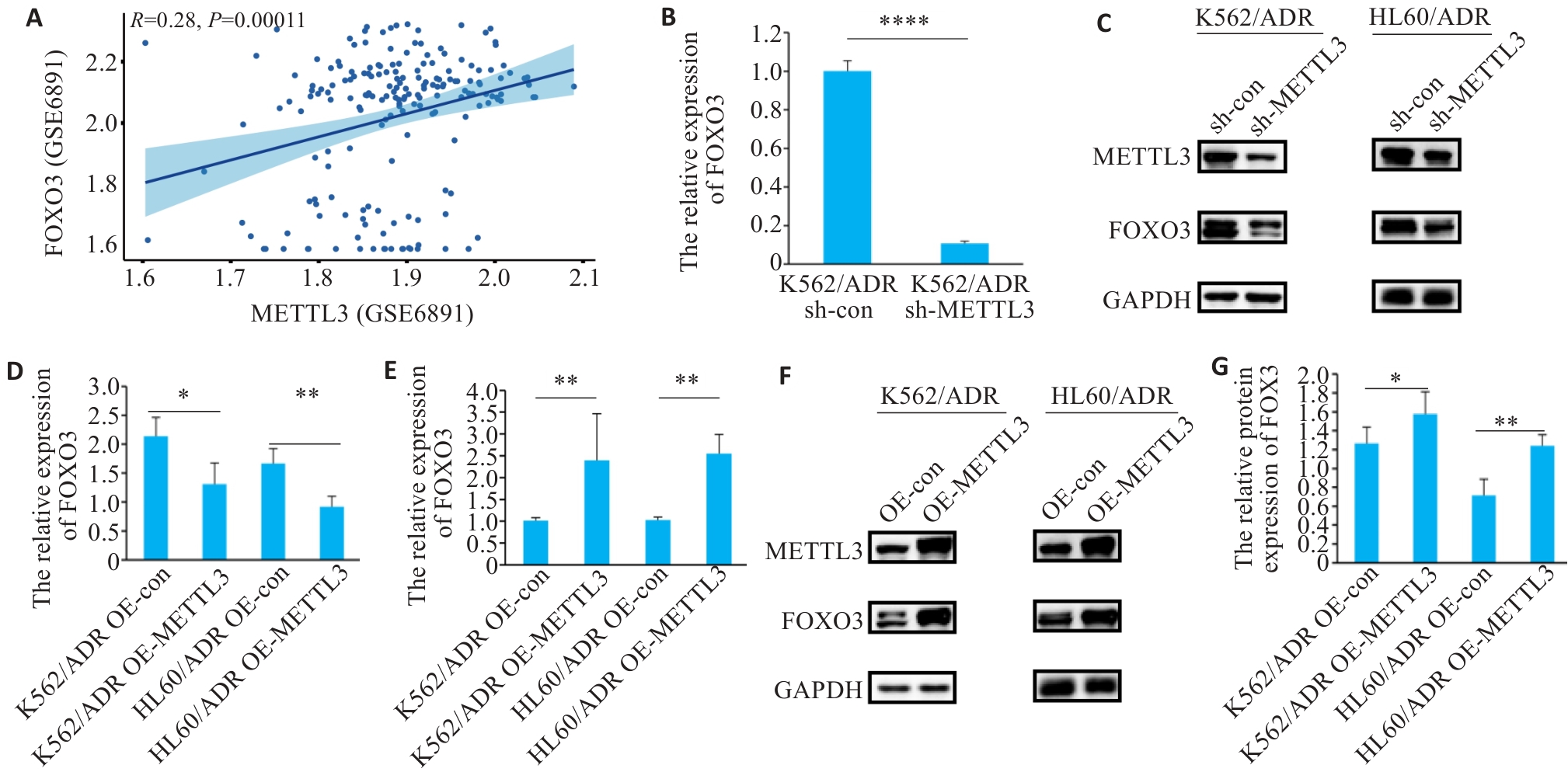
图2 METTL3与FOXO3表达相关性
Fig.2 Correlation of METTL3 with FOXO3 expression. A: Correlation analysis of METTL3 and FOXO3 expression in 163 AML patients from TCGA. B: RT-qPCR analysis of FOXO3 expression in sh-METTL3 cells and sh-con cells. C, D: Western blotting of FOXO3 levels in sh-con cells and sh-METTL3 cells. E: RT-qPCR analysis of FOXO3 expression in OE-METTL3 cells and OE-con cells. F, G: Western blotting of FOXO3 levels in OE-con cells and OE-METTL3. ADR: Adriamycin; sh-con: control shRNA; sh-METTL3: METTL3 shRNA; OE-con: overexpressed control RNA; OE-METTL3: METTL3 overexpression. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
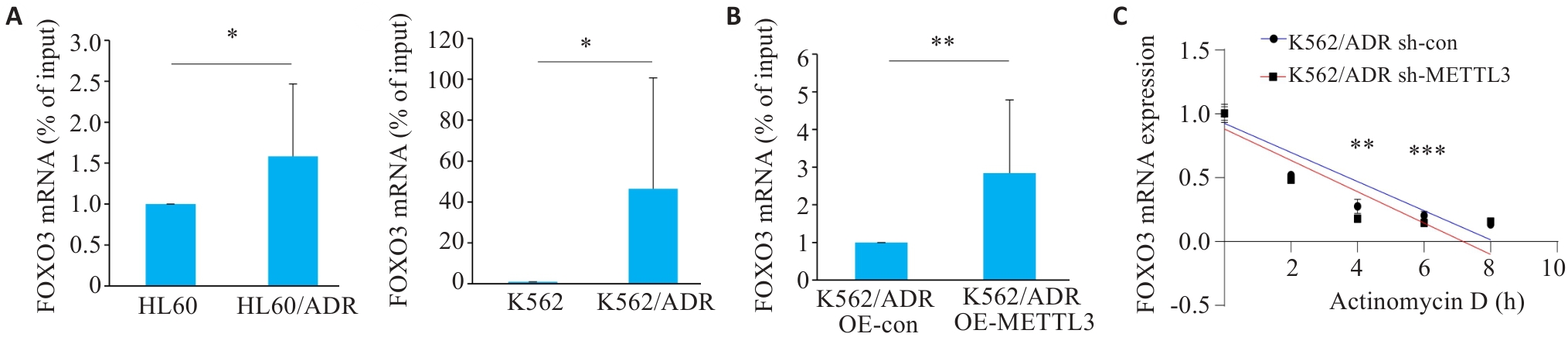
图3 METTL3通过m6A修饰调控FOXO3 mRNA稳定性
Fig.3 METTL3-mediated m6A modification enhances stability of FOXO3 mRNA. A: MeRIP-qPCR for detecting expression levels of m6A-modified FOXO3 mRNA in anthracycline-resistant cells and anthracycline-sensitive cells. B: MeRIP-qPCR for detecting expression levels of m6A-modified FOXO3 mRNA in OE-con and OE-METTL3 K562/ADR cells. C: RNA stability assay of FOXO3 mRNA in sh-con vs sh-METTL3 groups. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| Characteristics | TCGA | GSE6891 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Age [year, median (range)] | 58 (18-88) | - | 49 (15-60) | - |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 76 | 46.6 | 213 | 49.0 |
| Male | 87 | 53.4 | 222 | 51.0 |
| FAB classification | ||||
| M0 | 16 | 9.8 | 16 | 3.7 |
| M1 | 44 | 27.0 | 94 | 21.6 |
| M2 | 40 | 24.5 | 105 | 24.1 |
| M3 | - | - | 1 | 0.2 |
| M4 | 35 | 21.5 | 84 | 19.3 |
| M5 | 21 | 12.9 | 103 | 23.7 |
| M6 | 2 | 1.2 | 6 | 1.4 |
| M7 | 3 | 1.8 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Unkown | 2 | 1.2 | 25 | 5.7 |
| Cytogenetic risk classification | ||||
| Favorable | 18 | 11.0 | 75 | 17.2 |
| Intermediate | 92 | 56.4 | 258 | 59.3 |
| Poor | 50 | 30.7 | 92 | 21.1 |
| Unknown | 3 | 1.8 | 10 | 2.3 |
表2 TCGA 和 GSE6891 数据库中患者临床特征.
Tab.2 Clinical characteristics of patients in TCGA and GSE6891 databases
| Characteristics | TCGA | GSE6891 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | % | n | % | |
| Age [year, median (range)] | 58 (18-88) | - | 49 (15-60) | - |
| Gender | ||||
| Female | 76 | 46.6 | 213 | 49.0 |
| Male | 87 | 53.4 | 222 | 51.0 |
| FAB classification | ||||
| M0 | 16 | 9.8 | 16 | 3.7 |
| M1 | 44 | 27.0 | 94 | 21.6 |
| M2 | 40 | 24.5 | 105 | 24.1 |
| M3 | - | - | 1 | 0.2 |
| M4 | 35 | 21.5 | 84 | 19.3 |
| M5 | 21 | 12.9 | 103 | 23.7 |
| M6 | 2 | 1.2 | 6 | 1.4 |
| M7 | 3 | 1.8 | 1 | 0.2 |
| Unkown | 2 | 1.2 | 25 | 5.7 |
| Cytogenetic risk classification | ||||
| Favorable | 18 | 11.0 | 75 | 17.2 |
| Intermediate | 92 | 56.4 | 258 | 59.3 |
| Poor | 50 | 30.7 | 92 | 21.1 |
| Unknown | 3 | 1.8 | 10 | 2.3 |
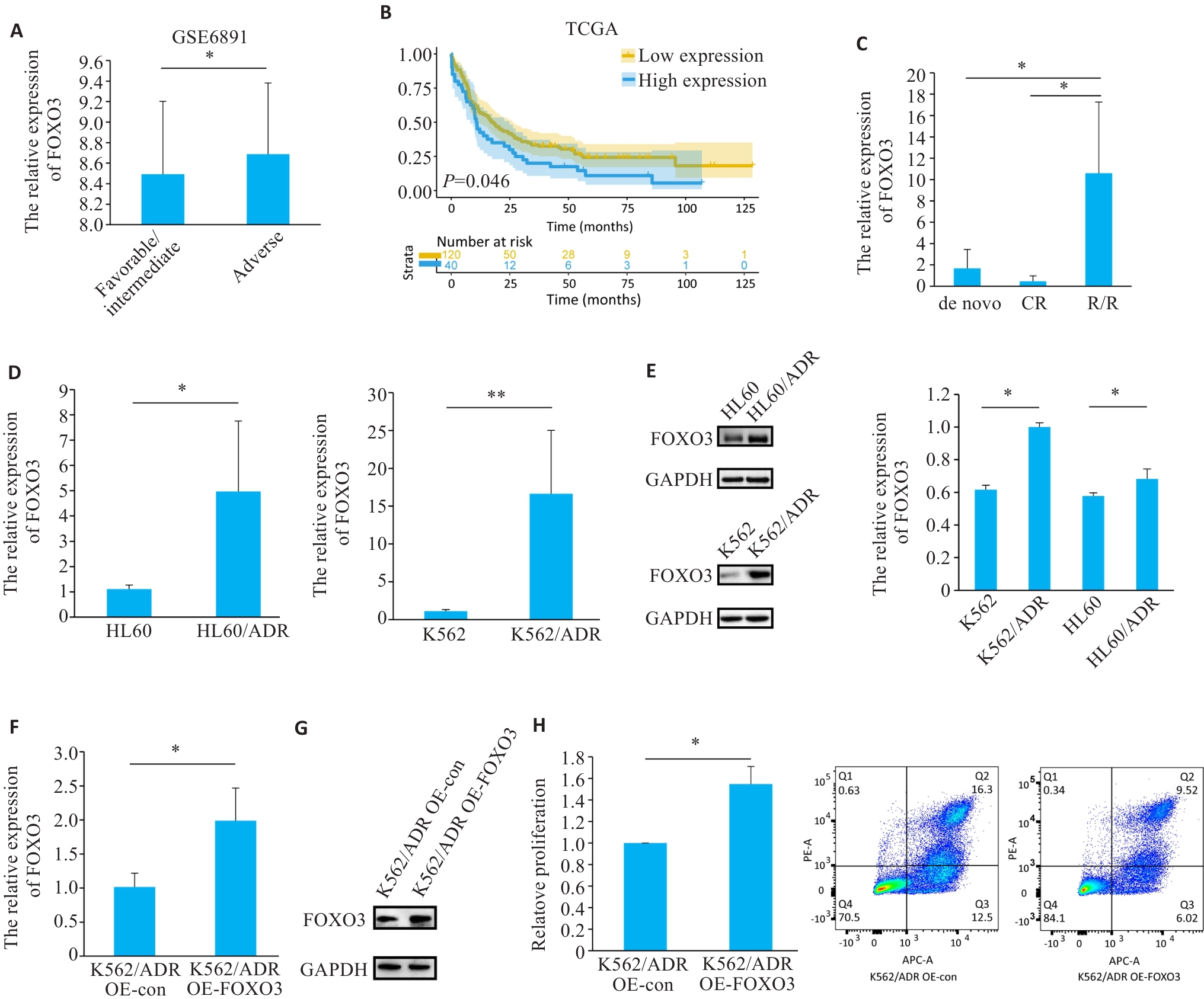
图4 FOXO3高表达提示患者不良预后
Fig.4 High FOXO3 expression suggests poor prognosis for patients. A: Analysis of FOXO3 expression levels stratified by cytogenetic prognosis in GSE6891 datasets. B: Survival analysis of 160 AML patients in TCGA. C: RT-qPCR analysis of FOXO3 expression in AML patients. D, E: RT-qPCR (D) and Western blotting (E) of FOXO3 expression in anthracycline-sensitive cells and anthracycline-resistant cells. F, G: RT-qPCR (F) and Western blotting (G) of FOXO3 expression in OE-con and OE-FOXO3 K562/ADR cells. H: Cell proliferation and apoptosis analysis of FOXO3-overexpressing cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01.

图5 FOXO3通过自噬影响AML蒽环类耐药
Fig.5 FOXO3 affects anthracycline resistance of AML cells by regulating autophagy. A: GO enrichment analysis in HL60 and HL60/ADR cells. B: GO enrichment analysis in sh-con cells and sh-METTL3 cells. C: Western blotting of autophagy flow in K562 cells and K562/ADR cells. D: Western blotting of autophagy flow in OE-con cells and OE-FOXO3 cells. E: Proliferation analysis of K562/ADR cells treated with Baf.A1 (100 nmol/L) for 72 h. F: Proliferation analysis of OE-FOXO3 cells treated with ADR and Baf.A1 (10 nmol/L) for 72 h. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
| 1 | Bhansali RS, Pratz KW, Lai C. Recent advances in targeted therapies in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. J Hematol Oncol, 2023, 16(1): 29. |
| 2 | Pollyea DA, Altman JK, Assi R, et al. Acute myeloid leukemia, version 3.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology[J]. J Natl Compr Canc Netw, 2023, 21(5): 503-13. |
| 3 | Thol F, Ganser A. Treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Curr Treat Options Oncol, 2020, 21(8): 66. |
| 4 | DiNardo CD, Erba HP, Freeman SD, et al. Acute myeloid leukaemia[J]. Lancet, 2023, 401(10393): 2073-86. |
| 5 | Stelmach P, Trumpp A. Leukemic stem cells and therapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Haematologica, 2023, 108(2): 353-66. |
| 6 | An YY, Duan H. The role of m6A RNA methylation in cancer metabolism[J]. Mol Cancer, 2022, 21(1): 14. |
| 7 | Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng YM, et al. The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells[J]. Nat Med, 2017, 23(11): 1369-76. |
| 8 | Hornsveld M, Dansen TB, Derksen PW, et al. Re-evaluating the role of FOXOs in cancer[J]. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018, 50: 90-100. |
| 9 | Farhan M, Silva M, Li S, et al. The role of FOXOs and autophagy in cancer and metastasis-Implications in therapeutic development[J]. Med Res Rev, 2020, 40(6): 2089-113. |
| 10 | Naka K, Hoshii T, Muraguchi T, et al. TGF-beta-FOXO signalling maintains leukaemia-initiating cells in chronic myeloid leukaemia[J]. Nature, 2010, 463(7281): 676-80. |
| 11 | Chakrabarty A, Bhola NE, Sutton C, et al. Trastuzumab-resistant cells rely on a HER2-PI3K-FoxO-survivin axis and are sensitive to PI3K inhibitors[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(3): 1190-200. |
| 12 | Yu C, Chen DQ, Liu HX, et al. Rosmarinic acid reduces the resistance of gastric carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil by downregul-ating FOXO4-targeting miR-6785-5p[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2019, 109: 2327-34. |
| 13 | Niu JF, Yan TQ, Guo W, et al. The COPS3-FOXO3 positive feedback loop regulates autophagy to promote cisplatin resistance in osteosarcoma[J]. Autophagy, 2023, 19(6): 1693-710. |
| 14 | Lin ZY, Niu Y, Wan A, et al. RNA m6 A methylation regulates sorafenib resistance in liver cancer through FOXO3‑mediated autophagy[J]. EMBO J, 2020, 39(12): e103181. |
| 15 | Santamaría CM, Chillón MC, García-Sanz R, et al. High FOXO3a expression is associated with a poorer prognosis in AML with normal cytogenetics[J]. Leuk Res, 2009, 33(12): 1706-9. |
| 16 | Chen Z, Guo Q, Huang SC, et al. Overcoming adaptive resistance in AML by synergistically targeting FOXO3A-GNG7-mTOR axis with FOXO3A inhibitor Gardenoside and rapamycin[J]. Genes Dis, 2023, 11(1): 397-412. |
| 17 | 中华医学会血液学分会白血病淋巴瘤学组. 中国成人急性髓系白血病(非急性早幼粒细胞白血病)诊疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2021, 42(8): 617-23. |
| 18 | Zhuang HZ, Yu B, Tao D, et al. The role of m6A methylation in therapy resistance in cancer[J]. Mol Cancer, 2023, 22(1): 91. |
| 19 | Boulias K, Greer EL. Biological roles of adenine methylation in RNA[J]. Nat Rev Genet, 2023, 24(3): 143-60. |
| 20 | Zheng X, Gong YP. Functions of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Biomark Res, 2021, 9(1): 36. |
| 21 | Hong YG, Yang ZG, Chen Y, et al. The RNA m6A reader YTHDF1 is required for acute myeloid leukemia progression[J]. Cancer Res, 2023, 83(6): 845-60. |
| 22 | Cheng Y, Gao ZY, Zhang TT, et al. Decoding m6A RNA methylome identifies PRMT6-regulated lipid transport promoting AML stem cell maintenance[J]. Cell Stem Cell, 2023, 30(1): 69-85. e7. |
| 23 | Li MY, Ye JJ, Xia Y, et al. METTL3 mediates chemoresistance by enhancing AML homing and engraftment via ITGA4[J]. Leukemia, 2022, 36(11): 2586-95. |
| 24 | Fang S, Peng B, Wen YN, et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification in adriamycin-resistant acute myeloid leukemia cells[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 833694. |
| 25 | Xu YQ, Song M, Hong ZY, et al. The N6-methyladenosine METTL3 regulates tumorigenesis and glycolysis by mediating m6A methylation of the tumor suppressor LATS1 in breast cancer[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2023, 42(1): 10. |
| 26 | Yin H, Chen L, Piao SQ, et al. M6A RNA methylation-mediated RMRP stability renders proliferation and progression of non-small cell lung cancer through regulating TGFBR1/SMAD2/SMAD3 pathway[J]. Cell Death Differ, 2023, 30(3): 605-17. |
| 27 | Orea-Soufi A, Paik J, Bragança J, et al. FOXO transcription factors as therapeutic targets in human diseases[J]. Trends Pharmacol Sci, 2022, 43(12): 1070-84. |
| 28 | Rodriguez-Colman MJ, Dansen TB, Burgering BMT. FOXO transcription factors as mediators of stress adaptation[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2024, 25(1): 46-64. |
| 29 | Eijkelenboom A, Burgering BMT. FOXOs: signalling integrators for homeostasis maintenance[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2013, 14(2): 83-97. |
| 30 | van der Horst A, Burgering BMT. Stressing the role of FoxO proteins in lifespan and disease[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2007, 8(6): 440-50. |
| 31 | Long J, Jia MY, Fang WY, et al. FLT3 inhibition upregulates HDAC8 via FOXO to inactivate p53 and promote maintenance of FLT3-ITD+ acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Blood, 2020, 135(17): 1472-83. |
| 32 | Kornblau SM, Singh N, Qiu YH, et al. Highly phosphorylated FOXO3A is an adverse prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2010, 16(6): 1865-74. |
| 33 | Debnath J, Gammoh N, Ryan KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2023, 24(8): 560-75. |
| 34 | Luo YH, Zheng ST, Wu QY, et al. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) EIF3J-DT induces chemoresistance of gastric cancer via autophagy activation[J]. Autophagy, 2021, 17(12): 4083-101. |
| 35 | Warr MR, Binnewies M, Flach J, et al. FOXO3A directs a protective autophagy program in haematopoietic stem cells[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7437): 323-7. |
| [1] | 杜越, 张秀森, 周克旭, 金星, 原翔, 高社干. RgpB通过抑制自噬小体与溶酶体融合避免Cx43降解参与食管癌化疗耐药[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2024, 44(9): 1670-1676. |
| [2] | 陈 兴, 王开万, 储德海, 朱 羽, 张文兵, 曹慧萍, 谢文宇, 鲁传豪, 李 侠. 连翘酯苷B抑制小鼠脑缺血/再灌注引起的氧化应激损伤:基于激活AMPK/DAF-16/FOXO3通路[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2023, 43(2): 199-205. |
| [3] | 温亚男, 方 姝, 杨晶晶, 王 昊, 焦一帆, 王 楠, 魏 岩, 王莉莉, 窦立萍. t(8;21)急性髓系白血病中RNA N6-甲基腺嘌呤(m6A)的修饰特征[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(5): 690-697. |
| [4] | 张晓宁, 张晓瑜, 刘 鹏, 刘 阔, 李文文, 陈倩倩, 马万山. 白三烯B4受体在急性髓系白血病中的预后价值和功能富集分析[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(3): 309-320. |
| [5] | 郝艳梅, 纪俊莉, 刘纯艺, 张 楠, 宫雅娟. 苦参碱联合LY294002对人髓系白血病K562细胞增殖、凋亡和细胞周期的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2022, 42(11): 1739-1746. |
| [6] | 杨艳丽, 李甜甜, 耿英华, 李 骏. RUNX1基因突变对成人急性髓细胞白血病的预后有不良影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(11): 1601-1606. |
| [7] | 吴明彩, 蒋 明, 薛梦雅, 李 青, 程 彬, 黄梦珠, 徐 蕾, 章 尧. 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯促进急性髓系白血病细胞凋亡的机制[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2020, 40(09): 1230-1238. |
| [8] | 徐亚文,郑少波,陈玢屾,温勇,朱善文. 苯丁酸钠对多烯紫杉醇耐药前列腺癌细胞株的增值抑制和凋亡诱导作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2017, 37(01): 130-. |
| [9] | 杨玥,房丽红,王雪峰. Foxo3a基因调控大鼠卵巢颗粒细胞体外发育及预防顺铂对卵巢的毒性作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2016, 36(06): 796-. |
| [10] | 王巍,孟灿,刘佳,杨志刚. 急性髓系白血病CDX2和β-catenin基因表达的相关性[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2015, 35(05): 728-. |
| [11] | 许露露,刘晓力,杜庆锋,宋兰林,曹睿,许娜,张进芳,黄彬涛,骆许静. 八探针荧光原位杂交技术在急性髓系白血病诊断中的应用[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(07): 1204-. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||