Journal of Southern Medical University ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (10): 2258-2269.doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.22
Wenxin JIA1,2,3( ), Shuhua HUO1,2,3, Jiaping TANG1,2,3, Yuzhen LIU1,2,3, Baosheng ZHAO1,2,3
), Shuhua HUO1,2,3, Jiaping TANG1,2,3, Yuzhen LIU1,2,3, Baosheng ZHAO1,2,3
Received:2025-03-06
Online:2025-10-20
Published:2025-10-24
Contact:
Baosheng ZHAO
E-mail:1005339926@qq.com
Wenxin JIA, Shuhua HUO, Jiaping TANG, Yuzhen LIU, Baosheng ZHAO. Inhibition of BRD4 promotes migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells with low ACC1 expression[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2258-2269.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.j-smu.com/EN/10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2025.10.22
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
ACC1-F ACC1-R | ATCCCGTACCTTCTTCTACTG |
| CCCAAACATAAGCCTTCACTG | |
BRD4-F BRD4-R | TGGATGCCGTCAAGCTGAAC |
| GTTTCTTCTGTGGGTAGCTCATT | |
GAPDH-F GAPDH-R | AATGGGCAGCCGTTAGGAAA |
| GCGCCCAATACGACCAAATC |
Tab.1 Primer sequences for RT-qPCR
| Gene | Primer sequence (5'-3') |
|---|---|
ACC1-F ACC1-R | ATCCCGTACCTTCTTCTACTG |
| CCCAAACATAAGCCTTCACTG | |
BRD4-F BRD4-R | TGGATGCCGTCAAGCTGAAC |
| GTTTCTTCTGTGGGTAGCTCATT | |
GAPDH-F GAPDH-R | AATGGGCAGCCGTTAGGAAA |
| GCGCCCAATACGACCAAATC |
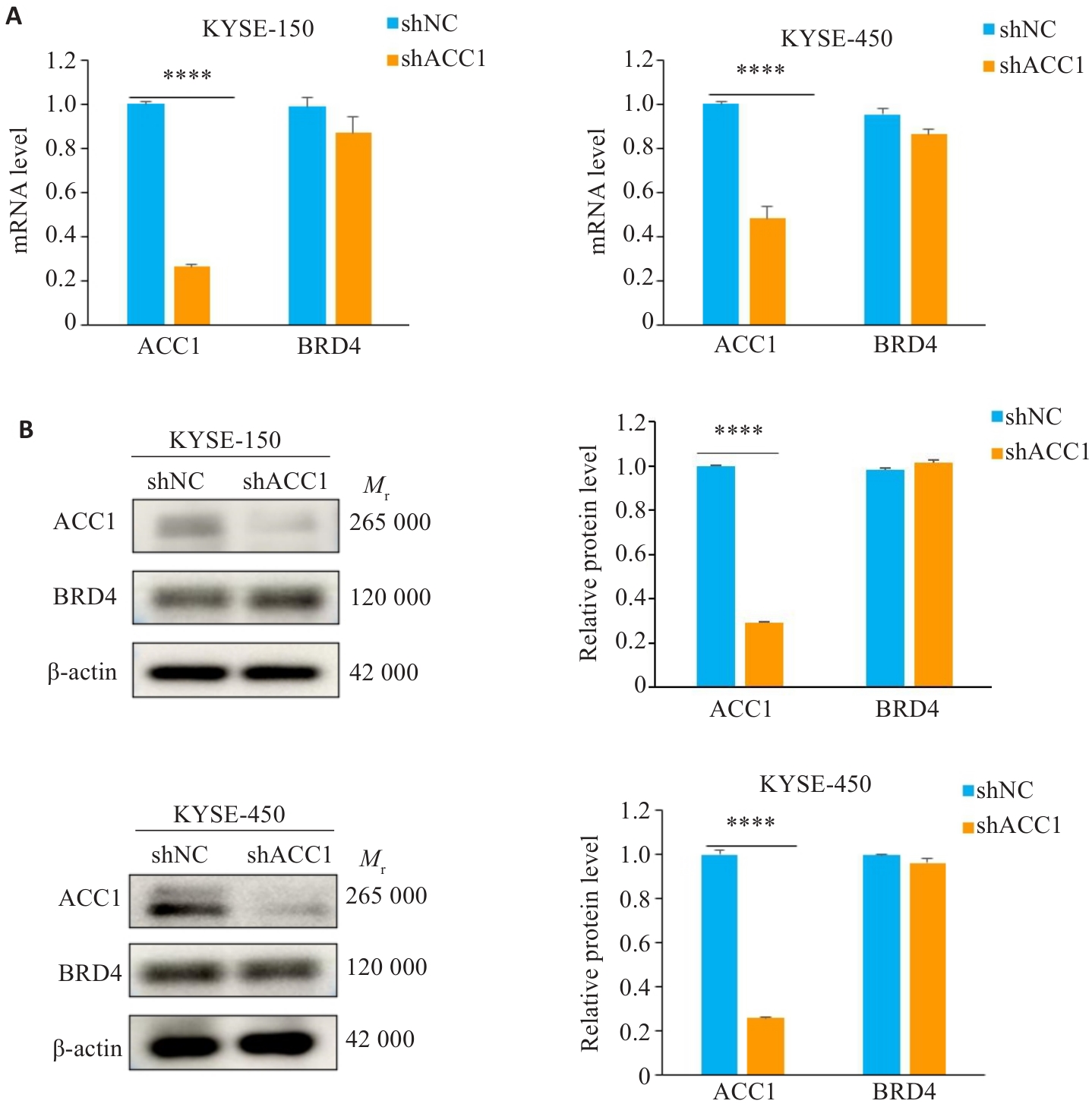
Fig.1 Expression levels of BRD4 mRNA and protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) cells with and without ACC1 knockdown. A: RT-qPCR for detecting BRD4 mRNA level. B: Western blotting for determining the protein expression level of BRD4. ****P<0.0001.
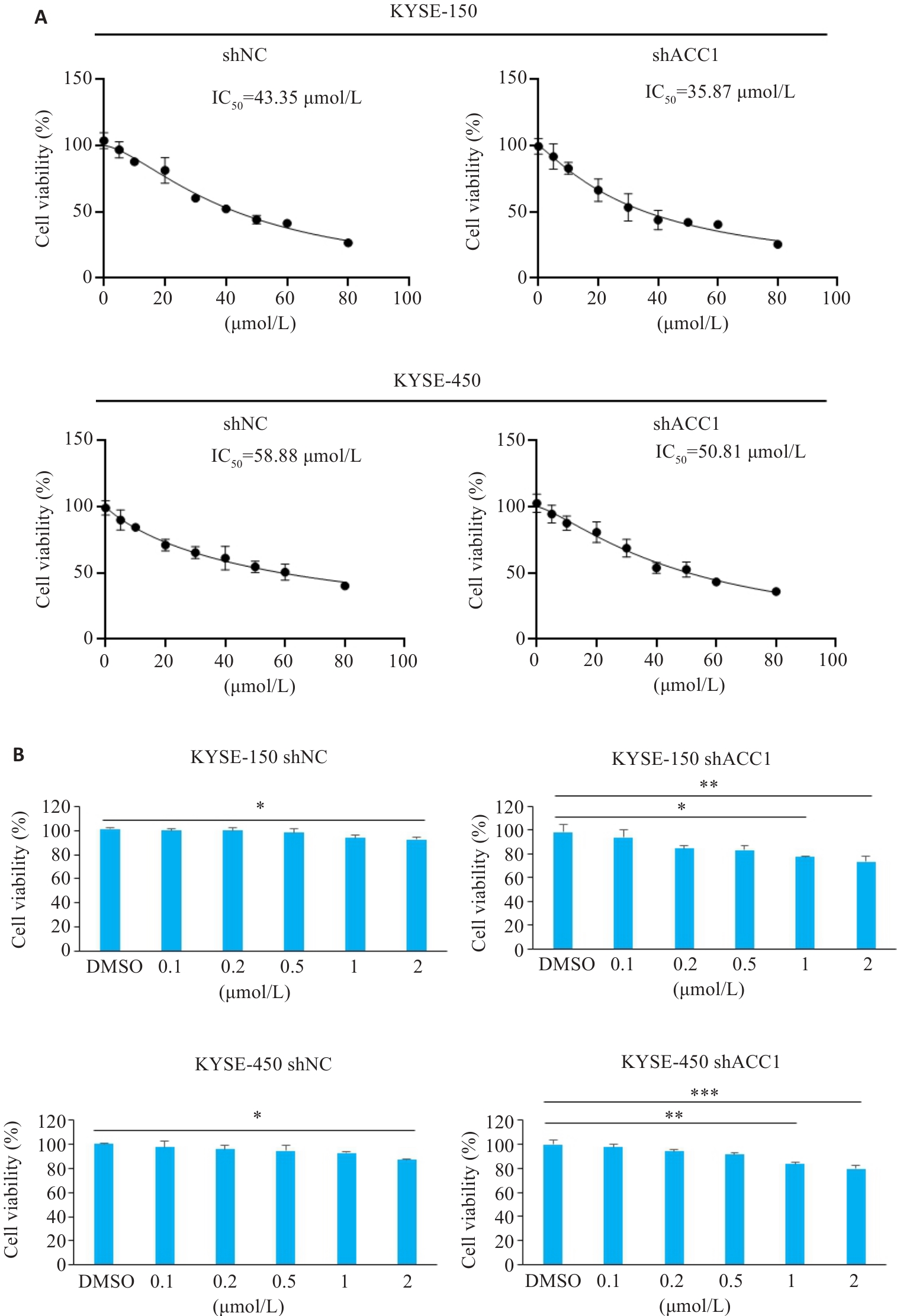
Fig.2 BRD4 inhibitors antagonize the proliferation of ESCC cells. A: Effect of JQ1 on proliferation of KYSE-150/KYSE-450 (shNC, shACC1) cells detected by CCK-8 assay. B: CCK-8 assay for assessing the effect of different concentrations of JQ1 on proliferation of ESCC cells. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.
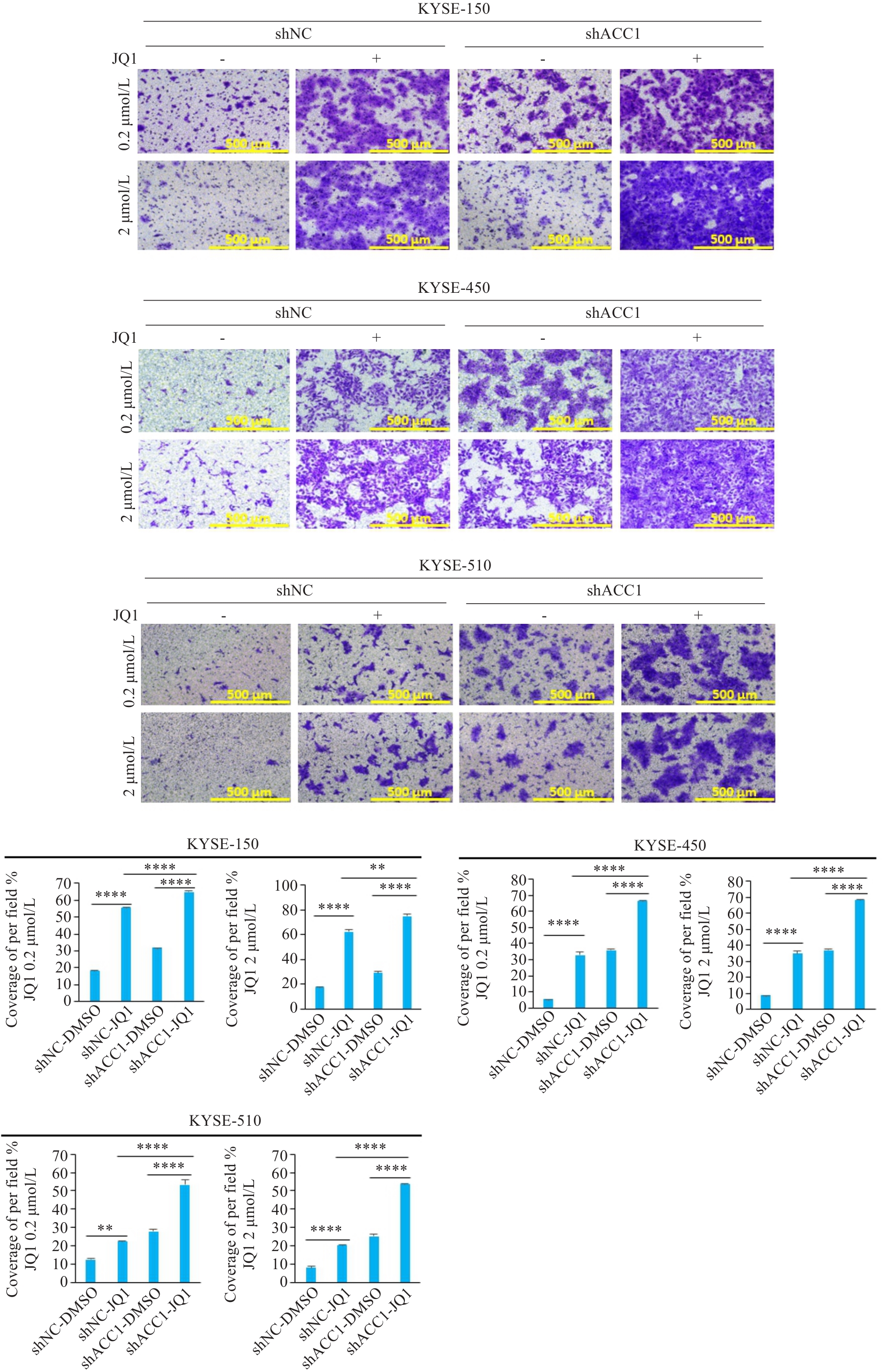
Fig.3 The promotion of ESCC cell migration by BRD4 inhibitors. Transwell migration assay for evaluating the effect of different concentrations of JQ1 on migration of ESCC cells (Original magnification: ×100). **P<0.01, ****P<0.0001.
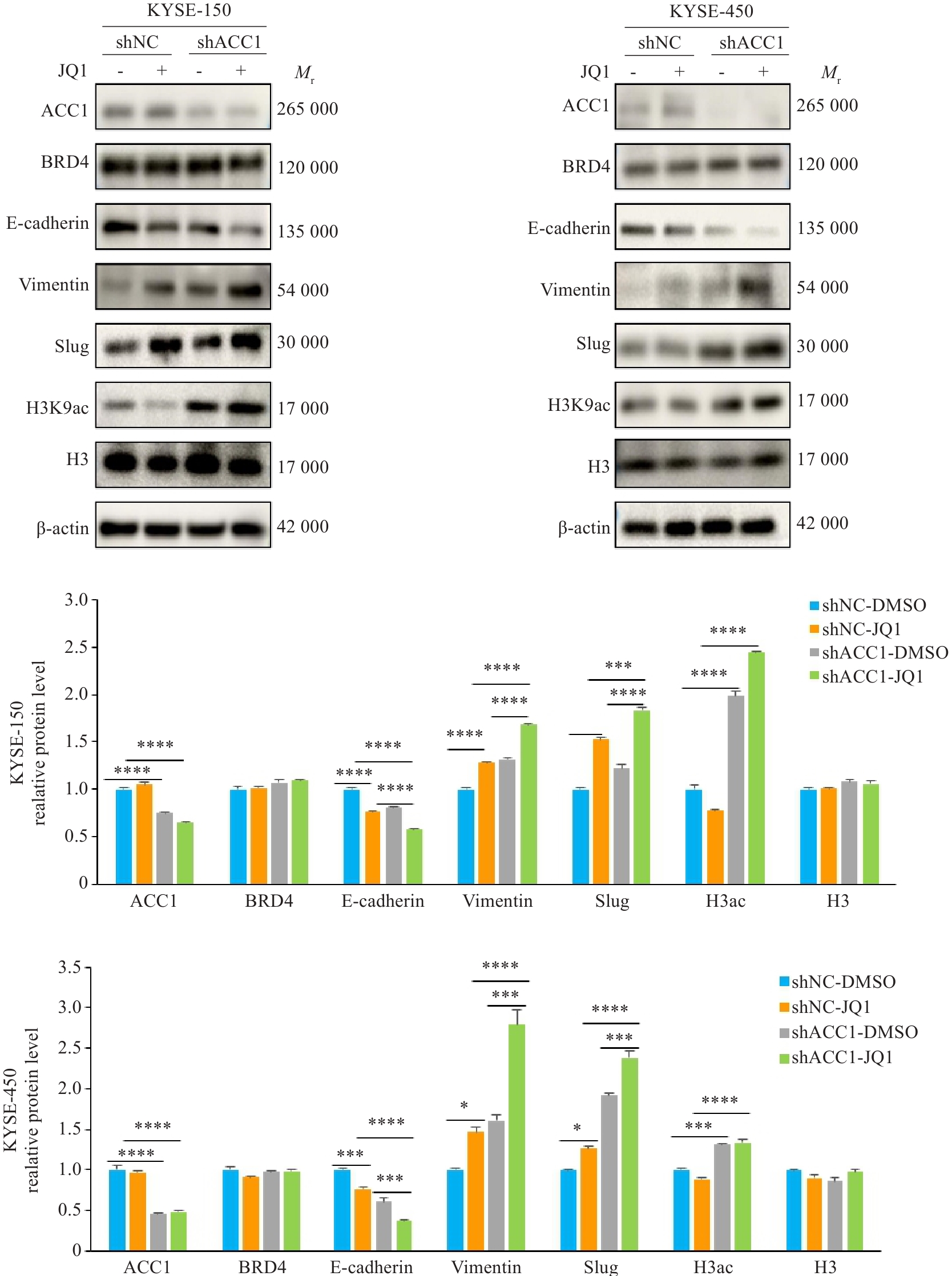
Fig.4 Inhibition of BRD4 promotes EMT in ESCC cells. The results of the Western blotting experiment showed that JQ1 inhibited the expression of E-cadherin protein and promoted the expression of vimentin and Slug. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
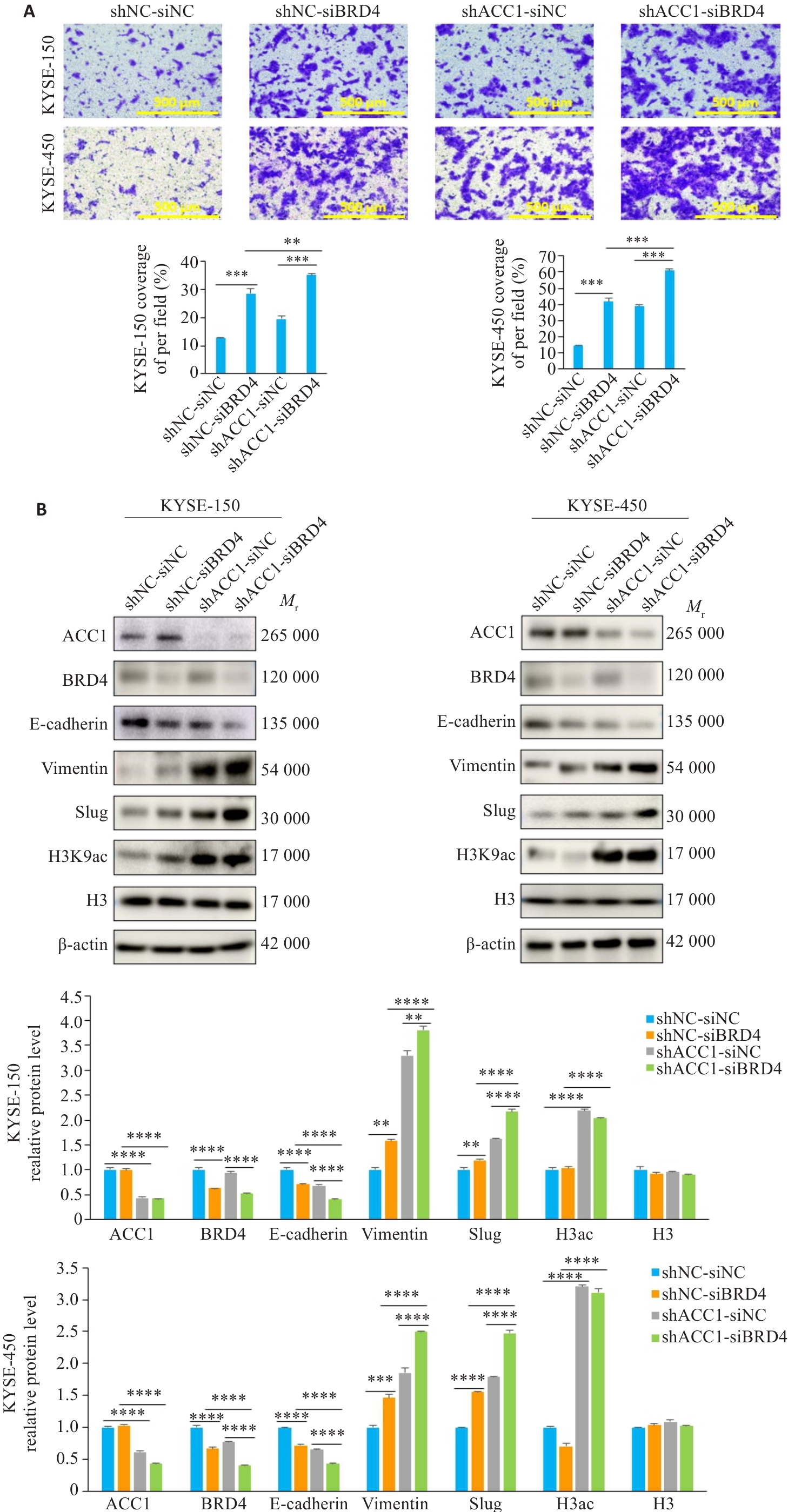
Fig.5 Knockdown of BRD4 promotes migration of ESCC cells. A: Transwell migration assay for assessing the effect of BRD4 knockdown on migration of ESCC cells (×100). B: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of BRD4 and EMT-related proteins. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
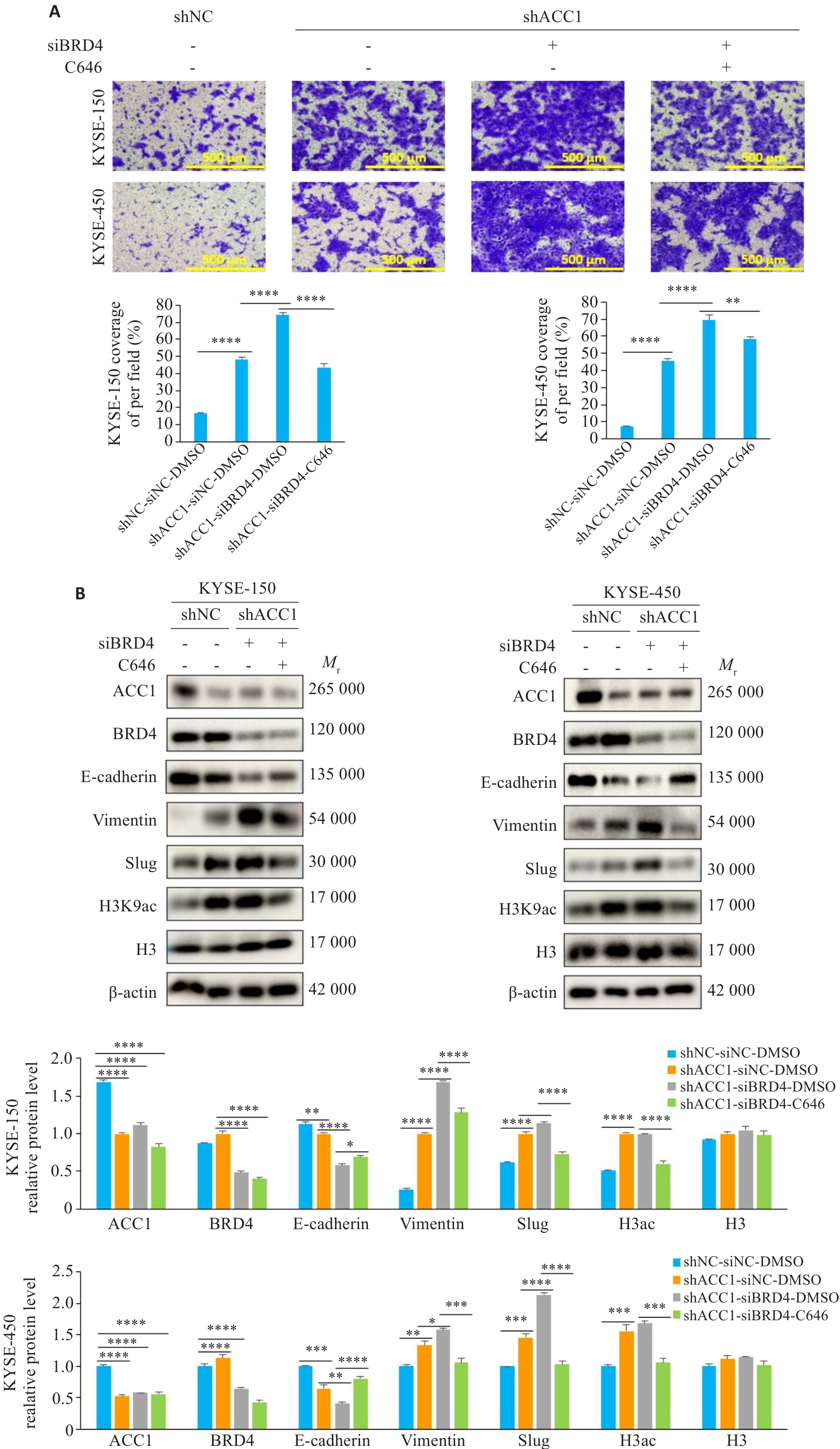
Fig.6 Histone acetyltransferase inhibitors antagonize migration of shACC1 cells after BRD4 knockdown. A: Transwell migration assay for assessing the effect of C646 on migration of ESCC cells with both ACC1 and BRD4 knockdown (×100). B: Western blotting for detecting expression levels of BRD4 and EMT-related proteins in the cells after treatment with C646. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
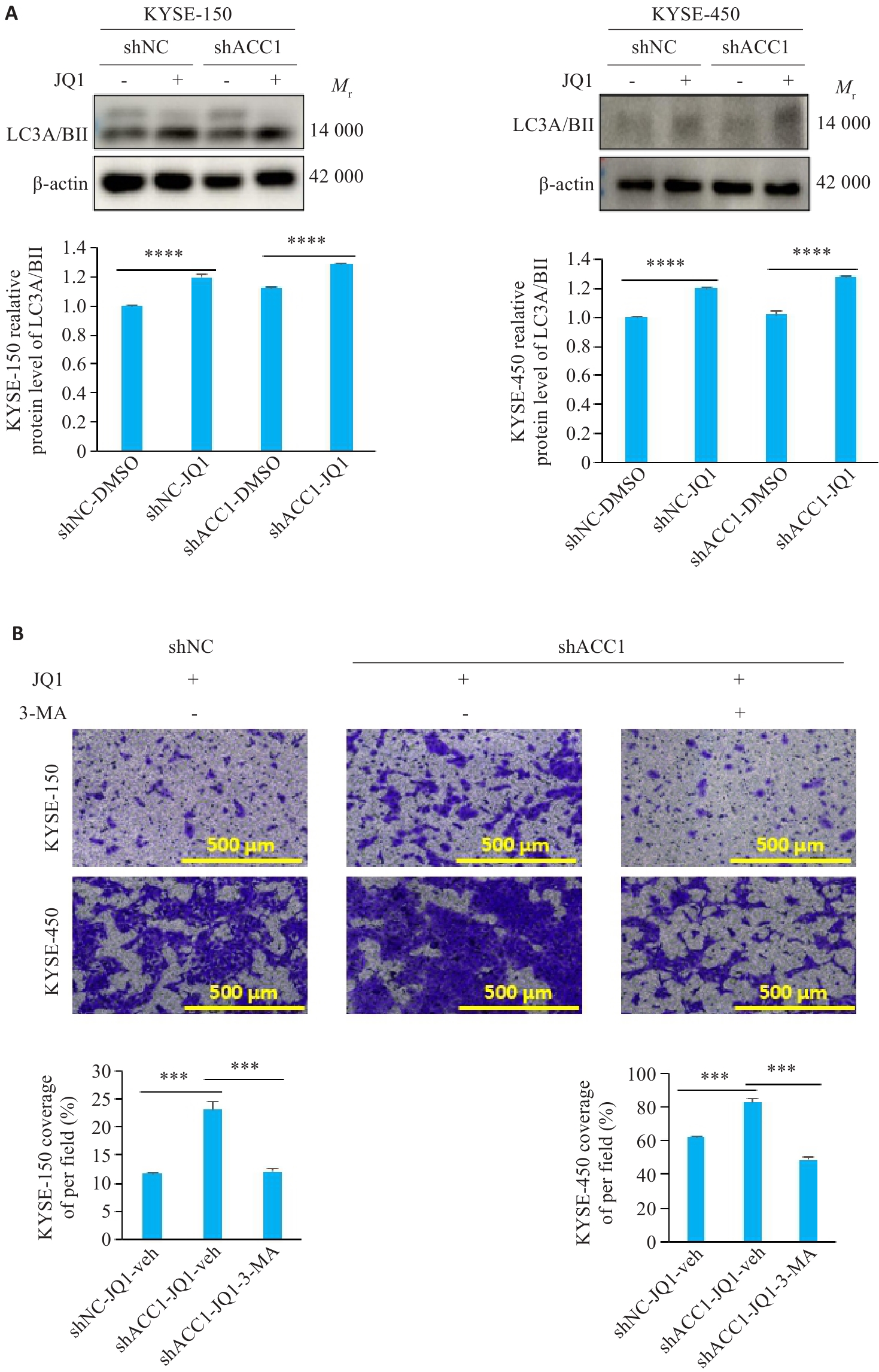
Fig.7 Inhibition of BRD4 promotes migration of ESCC cells with low ACC1 expression through autophagy. A: Western blotting showing that 2 μmol/L JQ1 promotes expressions of LC3A/BII in KYSE-150 and KYSE-450 cells. B: 4 mmol/L 3-MA inhibits migration of the cells with ACC1 knockdown and JQ1 treatment (×100). ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
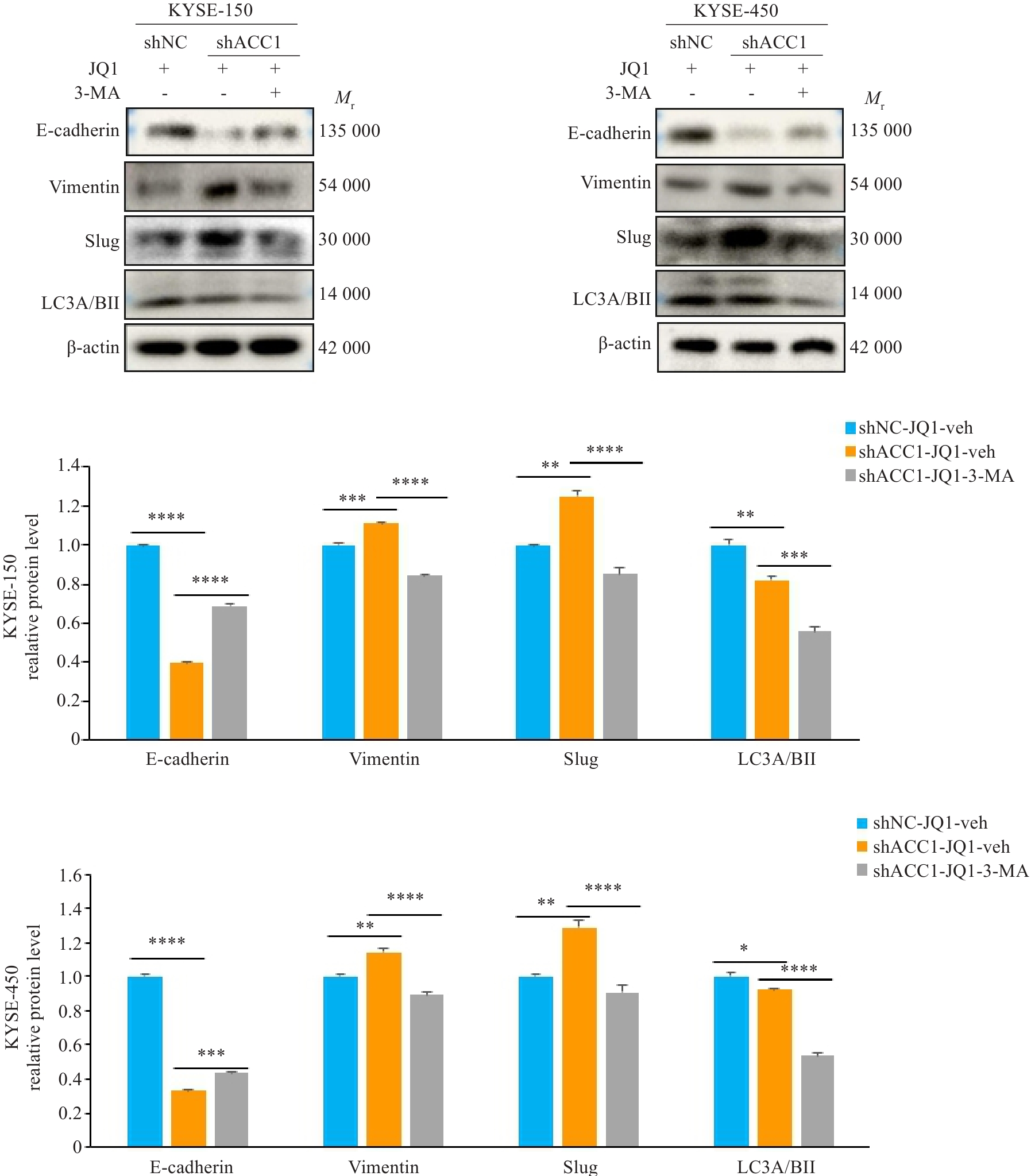
Fig.8 Inhibition of autophagy counteracts the effect of BRD4 inhibition on EMT of ESCC cells with low expression of ACC1. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001, ****P<0.0001.
| [1] | Mao YS, Gao SG, Wang Q, et al. Analysis of a registry database for esophageal cancer from high-volume centers in China[J]. Dis Esophagus, 2020, 33(8): doz091. doi:10.1093/dote/doz091 |
| [2] | Zhang JL, Dong YX, Di SY, et al. Tumor associated macrophages in esophageal squamous carcinoma: Promising therapeutic implications[J]. Biomed Pharmacother, 2023, 167: 115610. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115610 |
| [3] | 钱 河, 谷城威, 刘玉珍, 等. 敲低乙酰辅酶A羧化酶1通过上调热休克蛋白27促进食管鳞状细胞癌迁移[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志,2023,45(06): 482-9. |
| [4] | Guo JW, Zheng QQ, Peng Y. BET proteins: Biological functions and therapeutic interventions[J]. Pharmacol Ther, 2023, 243: 108354. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2023.108354 |
| [5] | Liu L, Lin BC, Yin SS, et al. Arginine methylation of BRD4 by PRMT2/4 governs transcription and DNA repair[J]. Sci Adv, 2022, 8(49): eadd8928. doi:10.1126/sciadv.add8928 |
| [6] | Kotekar A, Singh AK, Devaiah BN. BRD4 and MYC: power couple in transcription and disease[J]. FEBS J, 2023, 290(20): 4820-42. doi:10.1111/febs.16580 |
| [7] | Jin WK, Tan HD, Wu JH, et al. Dual-target inhibitors of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) in cancer therapy: Current situation and future directions[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2022, 27(1): 246-56. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2021.08.007 |
| [8] | Yang WQ, Liang R, Gao MQ, et al. Inhibition of bromodomain-containing protein 4 enhances the migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells by inducing cell autophagy[J]. World J Gastrointest Oncol, 2022, 14(12): 2340-52. doi:10.4251/wjgo.v14.i12.2340 |
| [9] | Zhu HH, Wei T, Cai Y, et al. Small molecules targeting the specific domains of histone-mark readers in cancer therapy[J]. Molecules, 2020, 25(3): 578. doi:10.3390/molecules25030578 |
| [10] | Le K, Matar H, Gupta M. Bromodomain epigenetic protein promotes metastatic potential in melanoma cells through increased invasiveness and decreased macrophage-mediated phagocytosis[J]. J Invest Dermatol, 2021, 141(2): 454-8.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jid.2020.06.016 |
| [11] | Li LY, Meng Y, Wu XL, et al. Bromodomain-containing protein 4 inhibitor JQ1 promotes melanoma cell apoptosis by regulating mitochondrial dynamics[J]. Cancer Sci, 2021, 112(10): 4013-25. doi:10.1111/cas.15061 |
| [12] | Hu Y, Zhou JQ, Ye F, et al. BRD4 inhibitor inhibits colorectal cancer growth and metastasis[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2015, 16(1): 1928-48. doi:10.3390/ijms16011928 |
| [13] | Karagiannis D, Wu W, Li A, et al. Metabolic reprogramming by histone deacetylase inhibition preferentially targets NRF2-activated tumors[J]. Cell Rep, 2024, 43(1): 113629. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113629 |
| [14] | Gibbons HR, Mi DJ, Farley VM, et al. Bromodomain inhibitor JQ1 reversibly blocks IFN-γ production[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 10280. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-46516-x |
| [15] | 吕倩倩, 梁嘉杰, 季 红. 基于PROTACs技术的表观遗传抗肿瘤药物研究进展[J]. 化学试剂, 2024, 46(5): 1-9. |
| [16] | Wu XC, Liu D, Gao XM, et al. Inhibition of BRD4 suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in renal cell carcinoma[J]. Cell Physiol Biochem, 2017, 41(5): 1947-56. doi:10.1159/000472407 |
| [17] | Kanno T, Kanno Y, LeRoy G, et al. BRD4 assists elongation of both coding and enhancer RNAs by interacting with acetylated histones[J]. Nat Struct Mol Biol, 2014, 21(12): 1047-57. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2912 |
| [18] | Rhyasen GW, Yao Y, Zhang JW, et al. BRD4 amplification facilitates an oncogenic gene expression program in high-grade serous ovarian cancer and confers sensitivity to BET inhibitors[J]. PLoS One, 2018, 13(7): e0200826. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0200826 |
| [19] | Hu JF, Pan D, Li G, et al. Regulation of programmed cell death by Brd4[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2022, 13(12): 1059. doi:10.1038/s41419-022-05505-1 |
| [20] | Zhang JC, Fan XK, Zhou YF, et al. The PRMT5-LSD1 axis confers Slug dual transcriptional activities and promotes breast cancer progression[J]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 41(1): 191. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02400-7 |
| [21] | Sterneck E, Poria DK, Balamurugan K. Slug and E-cadherin: stealth accomplices[J]? Front Mol Biosci, 2020, 7: 138. doi:10.3389/fmolb.2020.00138 |
| [22] | Shrimp JH, Sorum AW, Garlick JM, et al. Characterizing the covalent targets of a small molecule inhibitor of the lysine acetyltransferase P300[J]. ACS Med Chem Lett, 2015, 7(2): 151-5. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.5b00385 |
| [23] | Zhang GZ, Chen HW, Deng YJ, et al. BRD4 inhibition suppresses senescence and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells by inducing autophagy during intervertebral disc degeneration: an in vitro and in vivo study[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev, 2022, 2022: 9181412. doi:10.1155/2022/9181412 |
| [24] | Strippoli R, Niayesh-Mehr R, Adelipour M, et al. Contribution of autophagy to epithelial mesenchymal transition induction during cancer progression[J]. Cancers (Basel), 2024, 16(4): 807. doi:10.3390/cancers16040807 |
| [1] | Xiuying GONG, Shunfu HOU, Miaomiao ZHAO, Xiaona WANG, Zhihan ZHANG, Qinghua LIU, Chonggao YIN, Hongli LI. LncRNA SNHG15 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of lung adenocarcinoma cells by regulating COX6B1 through sponge adsorption of miR-30b-3p [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(7): 1498-1505. |
| [2] | Shunjie QING, Zhiyong SHEN. High expression of hexokinase 2 promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells by activating the JAK/STAT pathway and regulating tumor immune microenvironment [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 542-553. |
| [3] | Lu TAO, Zhuoli WEI, Yueyue WANG, Ping XIANG. CEACAM6 inhibits proliferation and migration of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells by suppressing epithelial-mesenchymal transition [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(3): 566-576. |
| [4] | Zhoufang CAO, Yuan WANG, Mengna WANG, Yue SUN, Feifei LIU. LINC00837/miR-671-5p/SERPINE2 functional axis promotes pathological processes of fibroblast-like synovial cells in rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(2): 371-378. |
| [5] | Yuan MI, Xuzhe LI, Zhanpeng WANG, Yanjie LIU, Chuntao SONG, Lantao WANG, Lei WANG. LINC00261 suppresses esophageal squamous cell carcinoma proliferation, invasion, and metastasis by targeting the miR-23a-3p/ZNF292 axis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2025, 45(10): 2118-2125. |
| [6] | Xiaohua CHEN, Hui LU, Ziliang WANG, Lian WANG, Yongsheng XIA, Zhijun GENG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Xue SONG, Yueyue WANG, Jing LI, Jianguo HU, Lugen ZUO. Role of Abelson interactor 2 in progression and prognosis of gastric cancer and its regulatory mechanisms [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1653-1661. |
| [7] | Yue DU, Xiusen ZHANG, Kexu ZHOU, Xing JIN, Xiang YUAN, Shegan GAO. RgpB contributes to chemoresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by preventing Cx43 degradation via inhibiting autophagosome-lysosome fusion [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(9): 1670-1676. |
| [8] | Yuanguo WANG, Peng ZHANG. Ferroptosis suppressor genes are highly expressed in esophageal cancer to inhibit tumor cell ferroptosis [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(7): 1389-1396. |
| [9] | Ze YANG, Xiusen ZHANG, Xudong ZHANG, Ying LIU, Jiacheng ZHANG, Xiang YUAN. Porphyromonas gingivalis infection facilitates immune escape of esophageal cancer by enhancing YTHDF2-mediated Fas degradation [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1159-1165. |
| [10] | Chang SUN, Shiyao ZHENG, Mei LI, Ming YANG, Mengyuan QIN, Yuan XU, Weihua LIANG, Jianmin HU, Lianghai WANG, Feng LI, Hong ZHOU, Lan YANG. High expression of the stemness-associated molecule Nanog in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma tissues promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by activating the TGF‑β signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(6): 1209-1216. |
| [11] | Zhi CUI, Cuijiao MA, Qianru WANG, Jinhao CHEN, Ziyang YAN, Jianlin YANG, Yafeng LÜ, Chunyu CAO. A recombinant adeno-associated virus expressing secretory TGF‑β type II receptor inhibits triple-negative murine breast cancer 4T1 cell proliferation and lung metastasis in mice [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(5): 818-826. |
| [12] | HUANG Qiuhu, ZHOU Jian, WANG Zizhen, YANG Kun, CHEN Zhenggang. MiR-26-3p regulates proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting CREB1 [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 578-584. |
| [13] | ZHU Jin, OUYANG Xin, LIU Yu, QIAN Yemei, XIA Bin, SHI Yanan, YU Lifu. MiR-132-3p negatively regulates CAMTA1 to promote Schwann cell proliferation and migration and alleviates I-125 seeds-induced exacerbation of facial nerve injury in rats [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(3): 571-577. |
| [14] | Huahua ZHANG, Qingyin TA, Yun FENG, Jiming HAN. Holliday junction-recognizing protein is a potential predictive and prognostic biomarker for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(12): 2347-2358. |
| [15] | Qianlong LING, Kai JI, Jinye CHEN, Jiajia GUAN, Ruipeng WANG, Wenjiang MAN, Bing ZHU. Sphingosine kinase-1 regulates migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via targeting the nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway [J]. Journal of Southern Medical University, 2024, 44(11): 2163-2171. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||